金屬頂刊雙語導讀丨Acta Mater. Vol.195
2020-06-09 來源:Goal Science
《Acta Materialia》本期(Volume 195, 15 August 2020)刊出9篇科研論文,涵蓋高熵合金、鋁銅合金、鎂合金以及不銹鋼等多個金屬材料領域。
Vol. 195 目錄
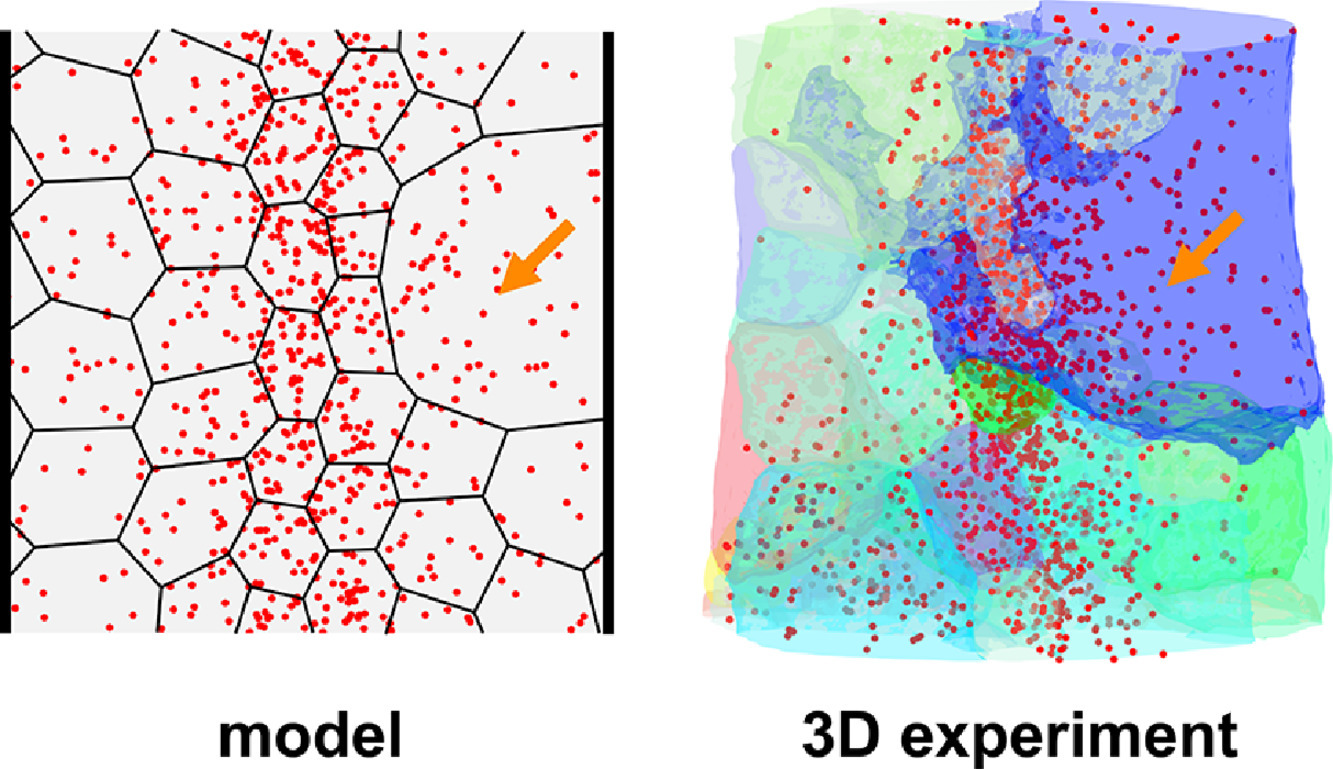
1. Dynamics of particle-assisted abnormal grain growth revealed through integrated three-dimensional microanalysis
集成三維微觀尺度分析揭示第二相粒子對晶粒異常長大影響的動力學特征
2.
鎂{10-12}孿晶中形成
3. Kink Formation Process in Long-Period Stacking Ordered Mg-Zn-Y Alloy
長周期有序堆垛Mg-Zn-Y合金中的扭折形成過程
4. Diffusion, defects and understanding the growth of a multicomponent interdiffusion zone between Pt-modified B2 NiAl bond coat and single crystal superalloy
擴散、缺陷以及含鉑B2 NiAl涂層與單晶高溫合金間多組分互擴散區的長大
5. Twisting of pre-twinned α-Fe nanowires from mild to wild avalanche dynamics
孿晶 α-Fe 納米線在扭轉過程中從溫和到劇烈的動力學“雪崩”
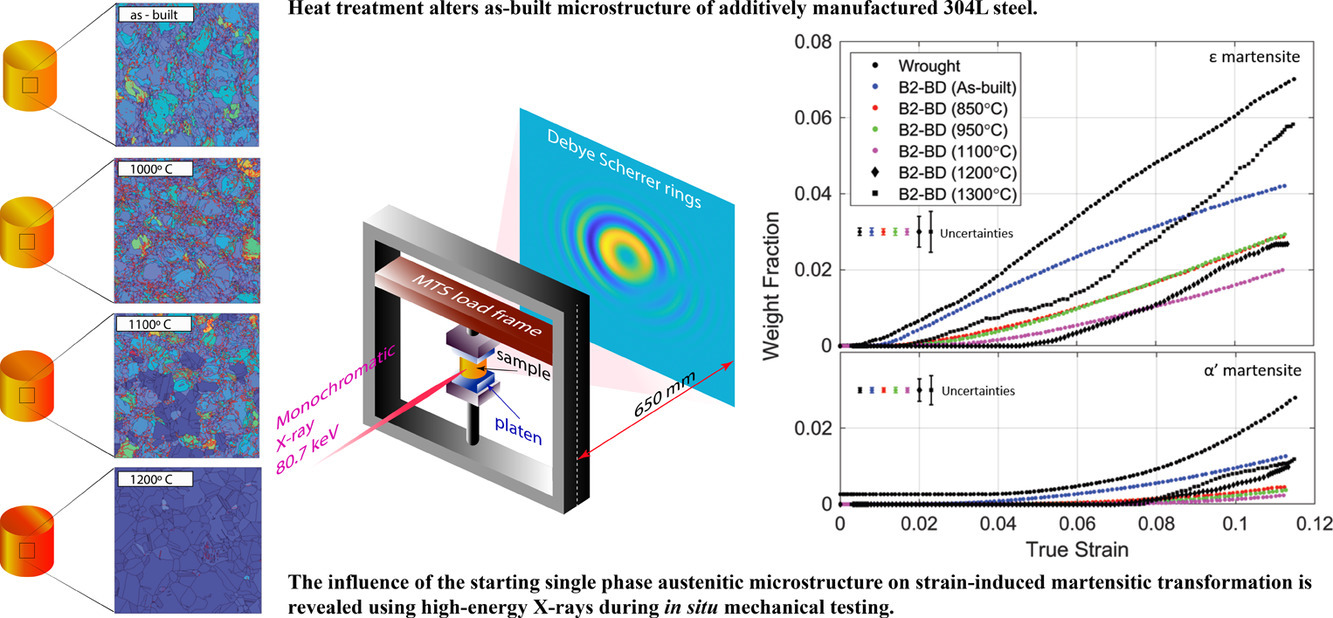
6. Effects of heat treatment and build orientation on the evolution of ? and α′ martensite and strength during compressive loading of additively manufactured 304L stainless steel
增材制造304L不銹鋼熱處理及打印方向對?和α′組織演變和壓縮性能的影響
7. Consideration of kinetics on intermetallics formation in solid-solution high entropy alloys
固溶態高熵合金中的金屬間化合物形成動力學
8. Composition dependence of metallic glass plasticity and its prediction from anelastic relaxation – A shear transformation zone analysis
金屬玻璃塑性的成分依賴以及基于非彈性弛豫的塑性預測——切變區分析
9. Radius-dependent homogeneous strain in uncoalesced GaN nanowires
非聚合GaN納米線的徑向相關均勻應變
ACTA Vol. 195, 15 Aug. 2020, P1-12
Dynamics of particle-assisted abnormal grain growth revealed through integrated three-dimensional microanalysis
集成三維微觀尺度分析揭示第二相粒子對晶粒異常長大影響的動力學特征
Ning Lua, Jiwoong Kang, Nancy Senabulya, Ron Keinana, Nicolas Gueninchault, Ashwin J. Shahania
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.04.049
摘要
通常彌散分布在金屬、陶瓷等多晶體材料中的第二相粒子會阻礙晶粒長大,使晶粒細化,提升材料的力學性能。然而,在較高溫度下經常會觀測到部分晶粒的優先長大或異常長大,使得材料的使用壽命大大降低。第二相粒子促進晶粒異常長大的成因和機理一直是學界爭論的焦點。在本研究中,作者通過3D-XRD成像技術,揭示了Al-Cu模型合金中晶界和第二相粒子之間的復雜交互作用。在具有高度非隨機分布粒子的體系中,觀測到了晶粒的異常長大現象。初始晶粒尺寸受控于第二相粒子的集中分布情況,大晶粒往往產生在第二相粒子較少的區域,而某些特定尺寸的晶粒可能會“逃離”晶粒尺寸分布,與考慮了表面張力和粒子釘扎的理論模型預測結果一致。
英文摘要
Secondary-phase particles are routinely dispersed in metals and ceramics to prevent grain growth and take full advantage of the small grain size in the mechanical properties of polycrystals. Somewhat surprisingly, the preferential or abnormal growth of a few grains is observed in particle-containing systems at relatively high temperature, which will limit the lifetime of the material. The origins and mechanisms of particle-assisted abnormal grain growth are widely contested. Here, we employ integrated three-dimensional X-ray imaging to throw new light on the complex interactions between grain boundaries and particles in an Al–Cu alloy as a model system. We observe abnormal grain growth in the presence of a highly non-random distribution of particles. The incipient grain size is set by the local distribution of particles such that the larger grains come from particle-poor regions. Subsequently, grains with a size advantage may “run away” from the grain size distribution, in agreement with predictions from an analytical model that takes into account the competing capillary and particle pinning pressures.
ACTA Vol. 195, 15 Aug. 2020, P13-24
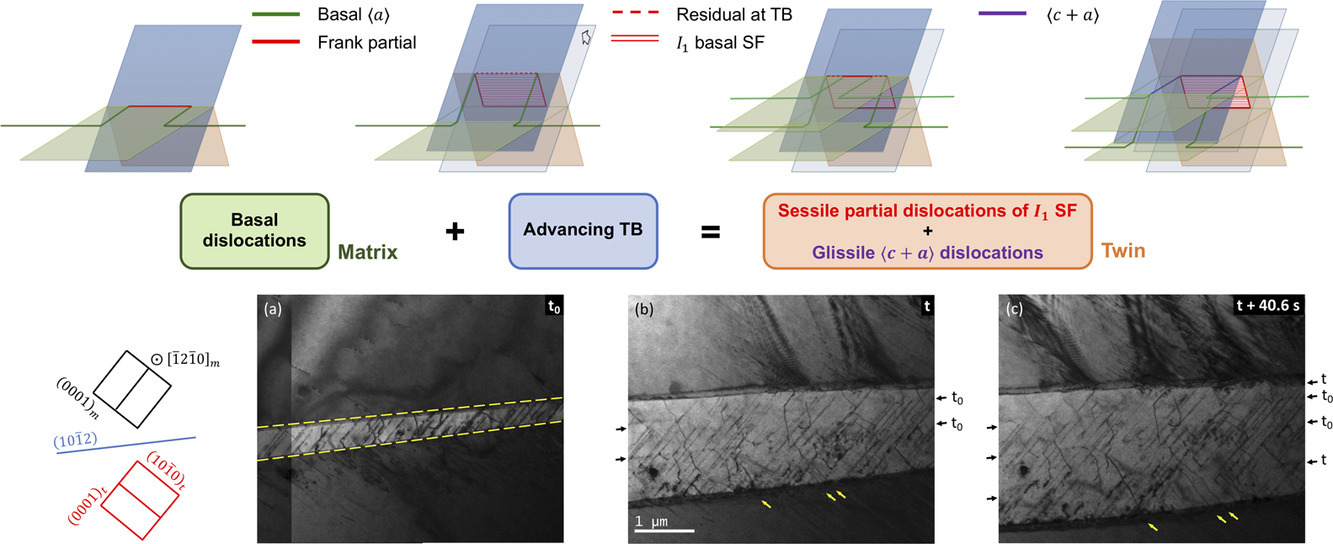
鎂{10-12}孿晶中形成
Fulin Wang, Yejun Gu, Rodney J. McCabe, Laurent Capolungo, Jaafar A. El-Awady, Sean R.Agnew
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.04.033
摘要
根據已發表文獻中關于密排六方金屬中基體位錯和{10-12}孿晶界相互作用的TEM和分子動力學研究結果,啟發學界作出了如下猜想,即在孿晶中可以形成
Consideration of published TEM and molecular dynamics studies of interactions between matrix dislocations and {10-12} twin boundaries (TB) in hexagonal close packed metals inspires a hypothesis regarding the formation of dislocations with
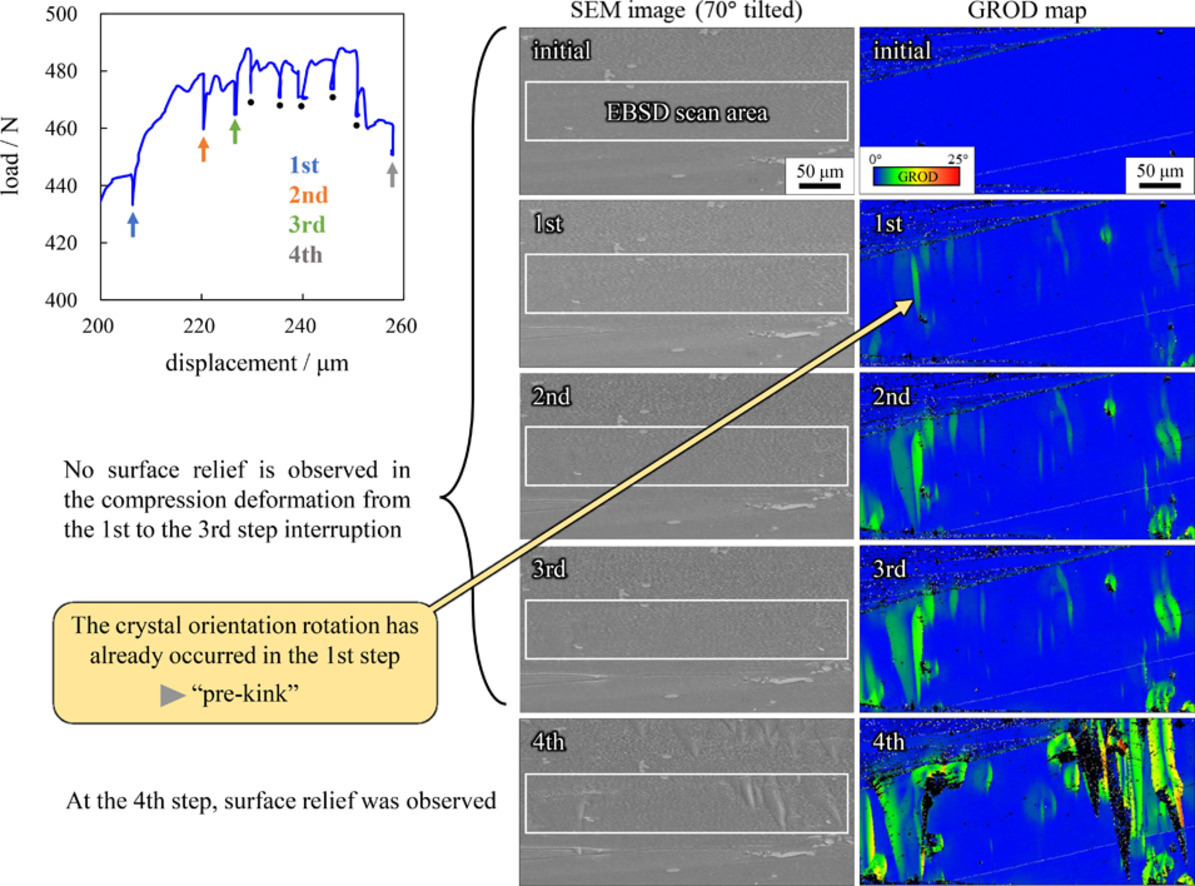
Kink Formation Process in Long-Period Stacking Ordered Mg-Zn-Y Alloy
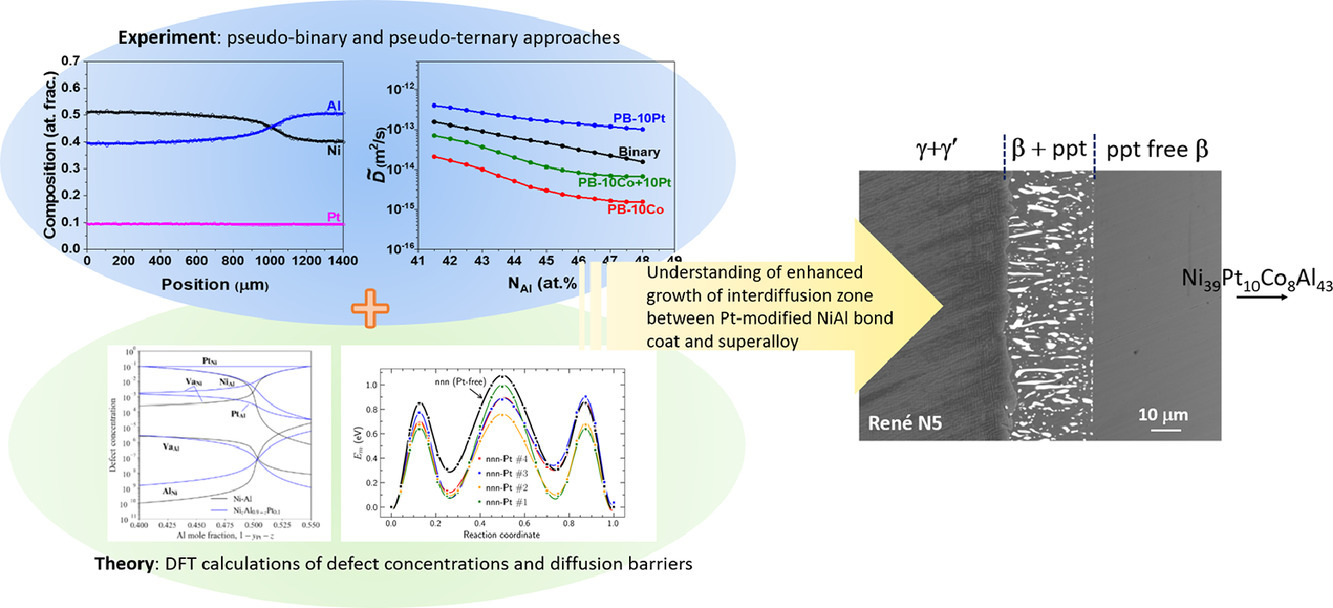
擴散、缺陷以及含鉑B2 NiAl涂層與單晶高溫合金間多組分互擴散區的長大
Neelamegan Esakkiraja, Ankit Gupta, Vikram Jayaram, Tilmann Hickel, Sergiy V.Divinsk, Aloke Paul
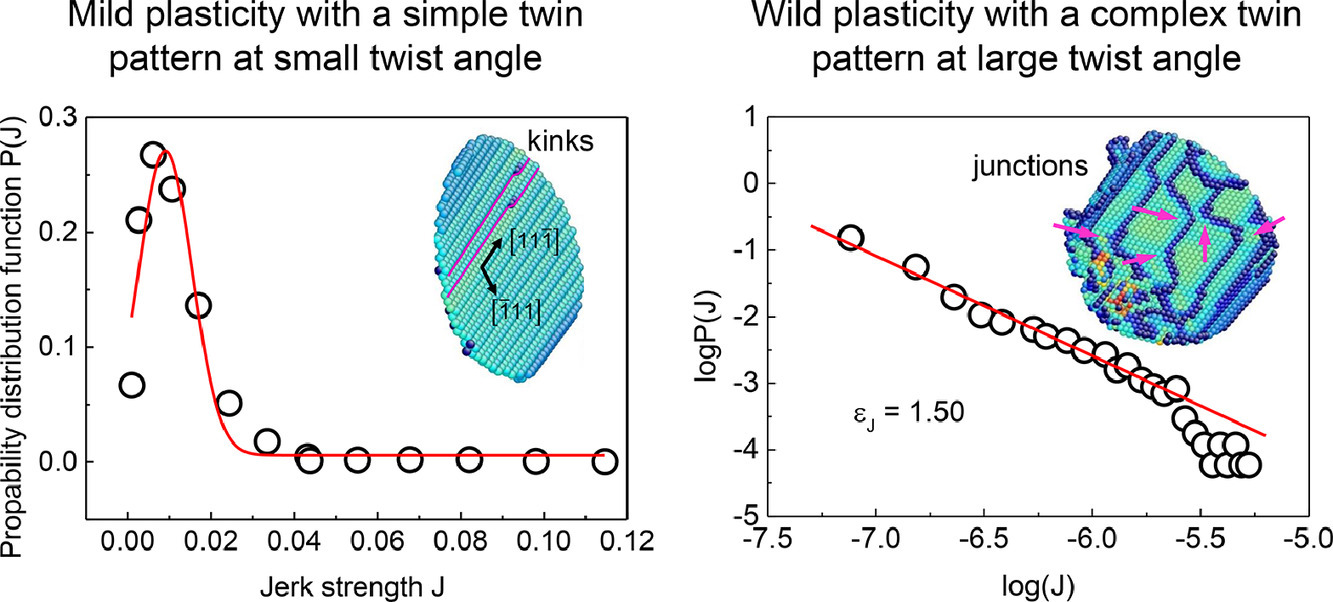
Twisting of pre-twinned α-Fe nanowires from mild to wild avalanche dynamics
孿晶 α-Fe 納米線在扭轉過程中從溫和到劇烈的動力學“雪崩”
Yang Yang, Suzhi Li, Xiangdong Ding, Jun Sun, Jerome Weiss, Ekhard K.H. Salje
增材制造304L不銹鋼熱處理及打印方向對?和α′組織演變和壓縮性能的影響
Consideration of kinetics on intermetallics formation in solid-solution high entropy alloys
金屬玻璃塑性的成分依賴以及基于非彈性弛豫的塑性預測——切變區分析
T.J.Lei, L. Rangel DaCosta, M.Liu, J.Shen, Y.H.Sun, W.H.Wang, M.Atzmon
Radius-dependent homogeneous strain in uncoalesced GaN nanowires