金屬頂刊雙語導讀丨Acta Mater. Vol.196, 1 Sept. 2020(下)
2020-08-12 來源: Goal Science
本期包含金屬材料領域論文27篇,涵蓋了孿晶金屬納米線、純鋯、鈷基合金、鈦合金、雙相不銹鋼、3D打印、高溫合金、高熵合金、鋁合金等,國內科研單位包括西安交通大學、復旦大學、山東大學等(通訊作者單位)。
Vol. 196 目錄
ACTA Vol. 196, 1 Sept. 2020, P295-303
15. Accelerated prediction of Vickers hardness of Co- and Ni-based superalloys from microstructure and composition using advanced image processing techniques and machine learning
采用先進圖像處理技術和機器學習基于組織和成分預測Co基和Ni基高溫合金的維氏硬度
Nikhil Khatavkar, Sucheta Swetlana, Abhishek Kumar Singh?
A.K. Singh:abhishek@iisc.ac.in
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.06.042
摘要
高溫合金是一種在飛機發動機和發電廠渦輪中大量使用的重要材料而維氏硬度則是篩選材料時的一項重要力學性能。在這項工作中,我們開發了一種方法,基于顯微組織估計,利用先進的圖像處理技術和數據驅動的機器學習(ML)算法預測鈷基和鎳基高溫合金的維氏硬度。我們采用從圖像中導出的復雜性質(如兩點相關性)和高溫合金成分作為特征輸入構建機器學習模型。基于微觀結構和成分特征的高斯過程回歸(GPR)模型表現出了極高的精度,均方根誤差(RMSE)和R2分別達到了0.14和0.98。我們通過對模型進行的進一步分析,建立了維氏硬度與顯微組織和合金成分之間的關系。鐵和鈦等元素的加入一般會增加維氏硬度,而鋁、鉭和鉿等元素的加入則會降低維氏硬度。本研究中至關重要的一點在于,我們開發的機器學習模型是在實驗數據上進行訓練的,而非基于模擬數據,這使得我們的方法可以直接用于維氏硬度的準確預測。
英文摘要
Superalloys constitute an important class of materials that are heavily employed in turbines of aircraft engines and power plants. Vickers hardness is an important mechanical property for selection of a material. In this work, we develop an alternate approach, which uses the microstructures to estimate the hardness of a Co- and Ni- based superalloys. Advanced image processing techniques coupled with data-driven machine learning (ML) are used to predict the Vickers hardness of these superalloys. Complex image derived properties such as 2-point correlations and compositions of superalloys are utilized as a feature to develop highly accurate ML model. The ML model trained through Gaussian process regression (GPR) using microstructure and compositional features show unprecedented accuracy with root mean square error (RMSE) of 0.14 and R2 of 0.98. Further analysis of the model is done to establish a relationship between the Vickers hardness with microstructural and compositional parameters. Addition of certain compounds such as iron and titanium can in general lead to increase in Vickers hardness, while addition of elements such as aluminium, tantalum and hafnium negatively affect the Vickers hardness. Most importantly, the developed ML model is trained on experimental data, as opposed to simulated data, making our approach directly applicable for accurate prediction of Vickers hardness.
ACTA Vol. 196, 1 Sept. 2020, P304-312
16. In-situ TEM study of dislocation interaction with twin boundary and retraction in twinned metallic nanowires
孿晶金屬納米線收縮以及位錯與孿晶界相互作用的原位TEM研究
Guangming Cheng?, Sheng Yin, Chengjun Li, Tzu-Hsuan Chang, Gunther Richter , Huajian Gao?, Yong Zhu?
G. Cheng:gcheng@ncsu.edu
H. Gao:huajian.gao@ntu.edu.sg
Y. Zhu:yong_zhu@ncsu.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.06.055
摘要
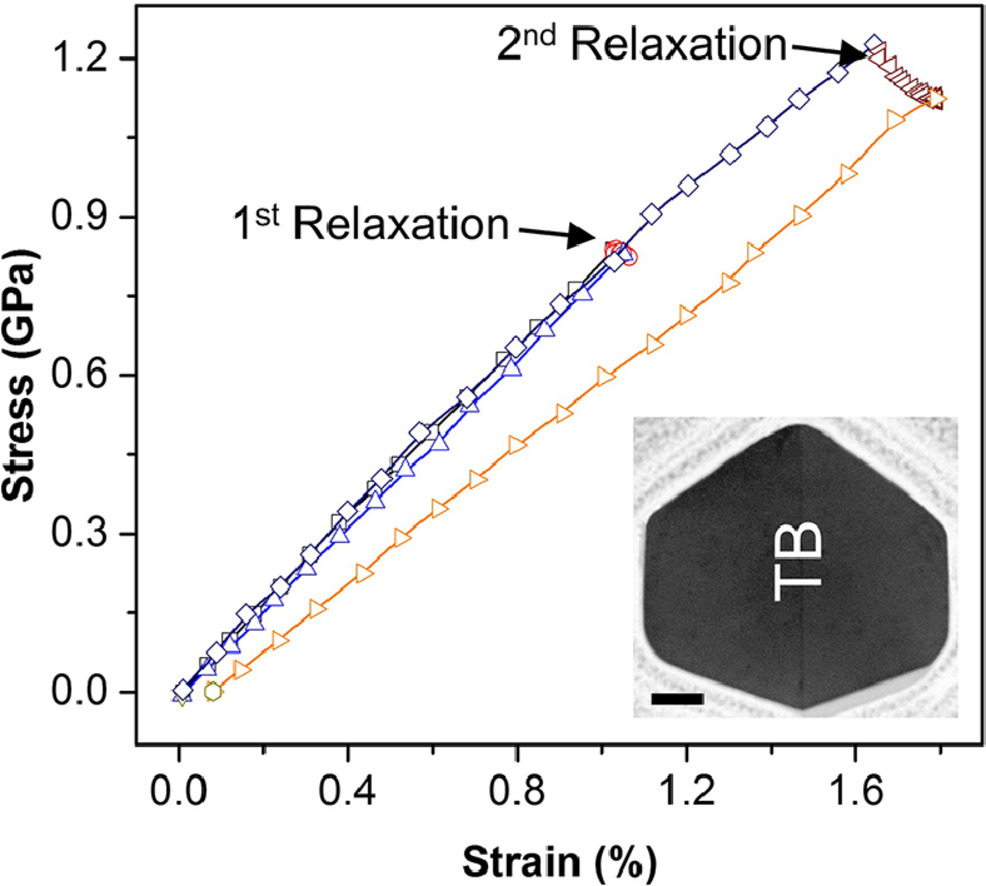
由于位錯與孿晶界的相互作用,使得具有平行于納米線長度方向的孿晶界的金屬納米線能夠表現出不同尋常的塑性應變回復。我們通過原位透射電子顯微鏡下的納米力學測試和分子動力學模擬,對位錯的形核、位錯和孿晶界的相互作用以及具有單一孿晶界的Ag納米線沿長度方向的收縮進行了觀測和定量研究。結果表明,在自由表面核形的先導分位錯可能會受到孿晶界的阻礙作用。而在卸載時,由于孿晶界的排斥作用,全部或部分的先導分位錯可能會發生收縮,從而導致完全或部分的塑性應變恢復(即包辛格效應)。即使在低于屈服強度的條件下,雙重孿晶銀納米線會發生應力松弛。我們將其應力松弛和回復行為與五重孿晶Ag 納米線進行了比較,結果進一步表明納米線內部的孿晶界與在表面形核的位錯之間相互作用導致了具有時間依賴性的塑性應變恢復和包辛格效應。
英文摘要
Metallic nanowires (NWs) with twin boundaries (TBs) running parallel to the NW length direction exhibit unusual plastic strain recovery owing to the interaction of dislocations with TBs. Here, based on in-situ transmission electron microscopy nanomechanical testing and molecular dynamics simulations, we report observation and quantification of dislocation nucleation, interaction with TBs, and retraction in bi-twinned Ag NWs with a single TB along the NW length direction. Our results show that leading partial dislocations nucleated from the free surface can be hindered by the TB, and upon unloading all or part of the leading partials can retract due to the repulsive force from the TB, leading to full or partial plastic strain recovery (Bauschinger effect), respectively. The bi-twinned Ag NWs can undergo stress relaxation, even at a stress below the yield strength, where the plastic strain also recovers upon unloading. The relaxation and recovery behaviors are compared to those of penta-twinned Ag NWs. Our results illustrate that the internal TBs in NWs can interact with surface-nucleated dislocations, leading to time-dependent plastic strain recovery and Bauschinger effect.
ACTA Vol. 196, 1 Sept. 2020, P338-346
17. In situ quantitative study of plastic strain-induced phase transformations under high pressure: Example for ultra-pure Zr
以純Zr為例原位定量研究高壓下的塑性形變誘導相變
K.K. Pandey? Valery I. Levitas?
K.K. Pandey:kkpandey@iastate.edu
V.I. Levitas:vlevitas@iastate.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.06.015
摘要
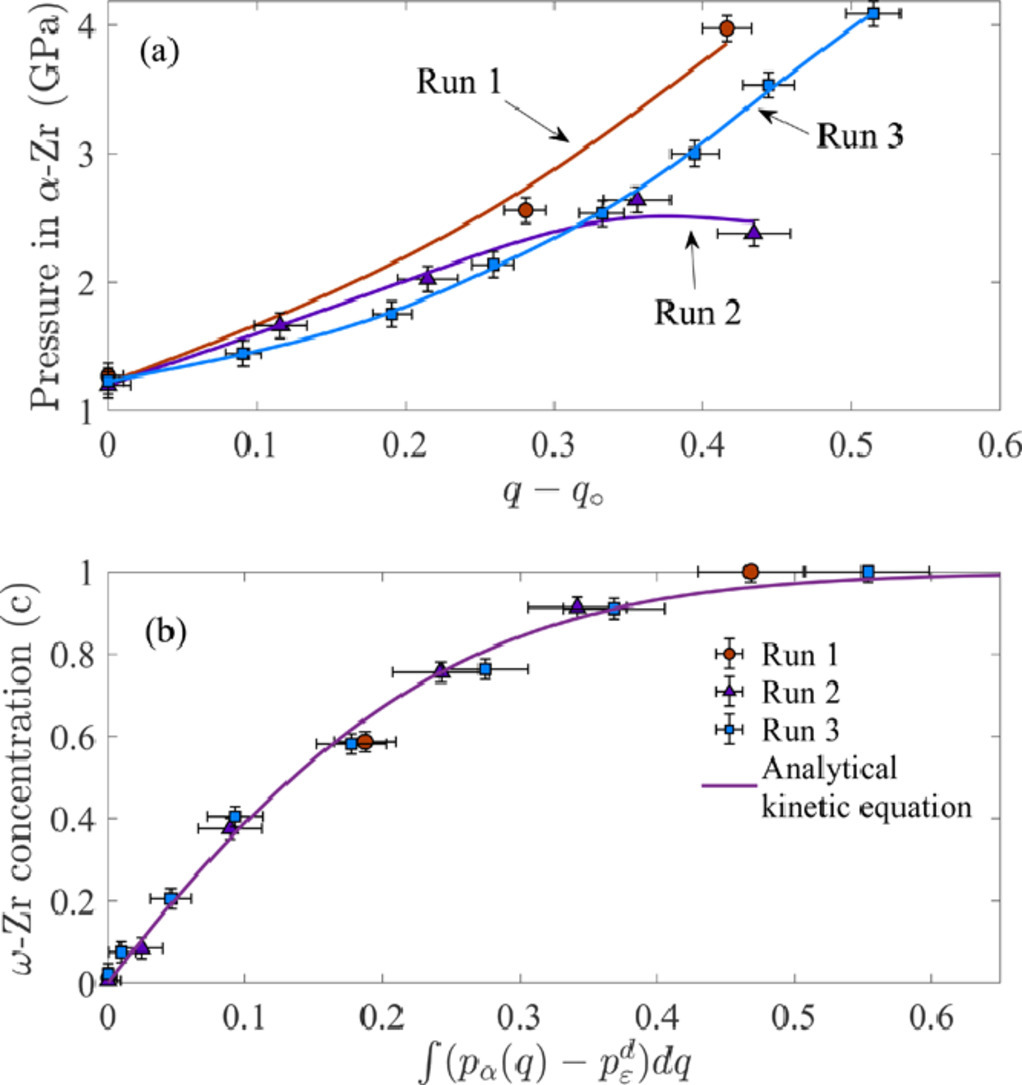
在本工作中,我們首次使用了原位的定量同步輻射X射線衍射技術,以經過強烈預塑性變形的純Zr中 的α−ω相變為例,研究了轉動金剛石晶胞中不同的壓縮-切變路徑。我們測量了每一相中的壓力分布和平均ω相含量隨樣品深度的變化。形變誘導α−ω相變的最小壓強為1.2GPa, 比靜載荷下小4.5倍,比平衡壓強小3倍,并且與壓縮-切變路徑無關。我們對理論預測的塑性應變控制動力學方程進行了量化分析和驗證:它與應變加載路徑和pεd以下發生的塑性變形無關。因此,壓縮和扭轉條件下在金剛石晶胞應變誘導相變沒有根本性的區別。我們通過硬度和X射線峰展寬估算了兩相的屈服強度;剪切屈服強度不能通過接觸摩擦達到,因此無法使用壓力梯度進行評估。這些實驗結果對于定量研究應變誘導相變及其在材料合成加工和機械化學等領域的應用具有重要意義。
英文摘要
The first in situ quantitative synchrotron X-ray diffraction (XRD) study of plastic strain-induced phase transformation (PT) has been performed on α−ω PT in ultra-pure, strongly plastically predeformed Zr as an example, under different compression-shear pathways in rotational diamond anvil cell (RDAC). Radial distributions of pressure in each phase and in the mixture, and concentration of ω-Zr, all averaged over the sample thickness, as well as thickness profile were measured. The minimum pressure for the strain-induced α−ω PT, =1.2?GPa, is smaller than under hydrostatic loading by a factor of 4.5 and smaller than the phase equilibrium pressure by a factor of 3; it is independent of the compression-shear straining path. The theoretically predicted plastic strain-controlled kinetic equation was verified and quantified; it is independent of the pressure-plastic strain loading path and plastic deformation at pressures below pεd. Thus, strain-induced PTs under compression in DAC and torsion in RDAC do not fundamentally differ. The yield strength of both phases is estimated using hardness and x-ray peak broadening; the yield strength in shear is not reached by the contact friction stress and cannot be evaluated using the pressure gradient. Obtained results open a new opportunity for quantitative study of strain-induced PTs and reactions with applications to material synthesis and processing, mechanochemistry, and geophysics.
ACTA Vol. 196, 1 Sept. 2020, P355-369
18. A novel operando approach to analyze the structural evolution of metallic materials during friction with application of synchrotron radiation
一種利用同步輻射分析金屬材料摩擦過程中組織演化的新方法
I.A. Bataev?, D.V. Lazurenko, A.A. Bataev, V.G. Burov, I.V. Ivanov, K.I. Emurlaev, A.I. Smirnov, M. Rosenthal, M. Burghammer, D.A. Ivanov, K. Georgarakis, A.A. Ruktuev, T.S. Ogneva, A.M.J. Jorge
I.A. Bataev:ivanbataev@ngs.ru
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.06.049
摘要
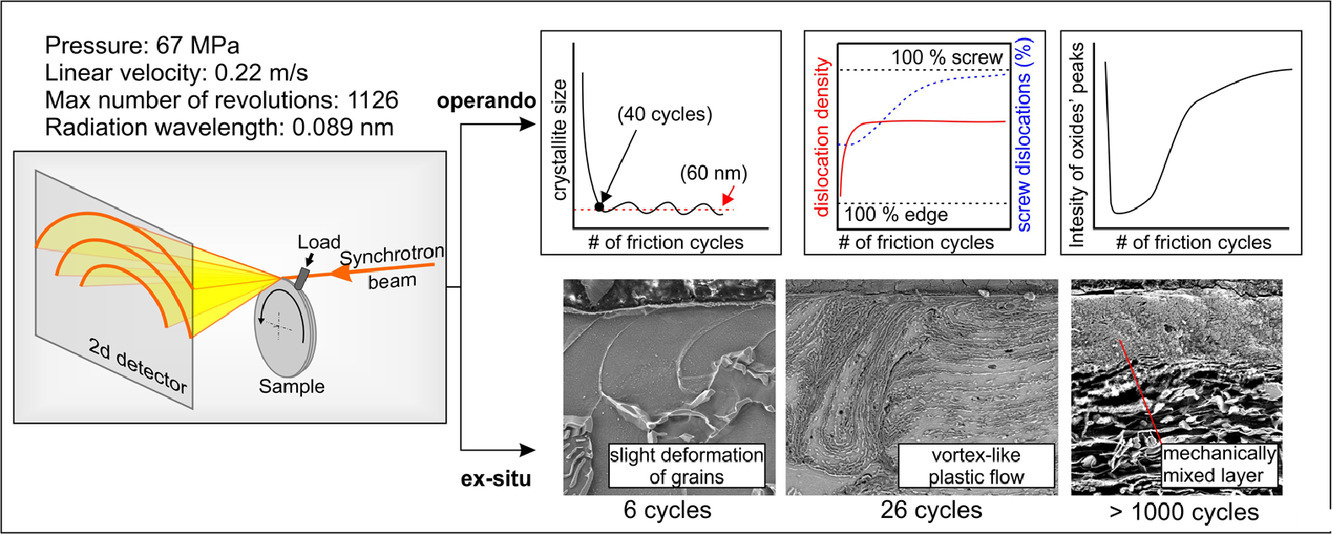
在本研究中,我們提出了一種新的實驗裝置和方法來研究材料在摩擦磨損過程中的結構演變。該裝置適用于各種摩擦副的測試,包括兩個金屬摩擦體之間的摩擦。該裝置可以規避金屬X射線散射較為嚴重引起的問題,使得樣品在同步輻射的反射模式下更接近其真實狀態。為了說明該裝置的性能和新方法的實用性,我們使用了一個硬質合金銷對一個鐵基大塊樣本進行了數千次的摩擦循環,在離開摩擦區后幾毫秒內對材料進行同步X射線輻照檢測。基于微觀組織結構和各種數學模型的分析結果, 使得我們能夠對材料的大量特征進行評估,包括缺陷的逐步積累,結構的細化,位錯密度的變化,表層氧化,以及由滑動摩擦引起的一些其他現象。磨損過程主要可以歸結為氧化和塑性變形的協同作用,它們從摩擦的第一個周期就開始發生,并導致位錯密度和類型在在測試過程中的不斷改變。材料中的缺陷密度很快到達臨界值,隨后由于材料磨損過程中周期性的缺陷積累和應力釋放而在臨界值上下不斷浮動。我們同時還觀測到,摩擦導致機械混合層快速形成,這種混合層由樣品本身的材料和兩種鐵的氧化物構成。該層的剝離可能是磨損的主要機制。
英文摘要
In this study, we describe an experimental setup and a new approach for operando investigation of structural evolution of materials during wear and friction. The setup is particularly suited for testing various friction pairs, including those in which both rubbing bodies are made of metals. The developed device allows circumventing the problems related to significant scattering of X-rays produced by metals and makes it possible using “real samples” in synchrotron beamlines operating in reflection mode. To demonstrate the capabilities of the device and the proposed new approach, an iron-based massive sample was subjected to thousands of friction cycles using a cemented carbide pin. The material was probed with synchrotron X-ray radiation within a few milliseconds after leaving the friction zone. The results of the microstructural and structural analysis, as well as results obtained from diverse mathematical models, allowed us to evaluate several features, including gradual accumulation of defects, microstructural refinement, dislocation density changes, surface layer oxidation, as well as several other phenomena caused by the dry sliding friction process. Mainly, it was possible to conclude that the process of wear occurred due to the cooperative action of oxidation and plastic deformation, which began during the first cycle of frictional interaction and was manifested in increasing the dislocation density, whose type was changed gradually during testing. The number of defects quickly reached a threshold value and subsequently fluctuated around it due to periodically repeated processes of defect accumulation and stress relaxation resulting from material wear. It was also observed that friction led to the quick formation of a mechanically mixed layer, consisting of the sample material and a mixture of two types of iron oxide – hematite and magnetite. The delamination of this layer was probably the primary wear mechanism.
ACTA Vol. 196, 1 Sept. 2020, P370-383
19. Effects of Cu addition on resistance to hydrogen embrittlement in 1 GPa-grade duplex lightweight steels
添加銅對1GPa強度等級雙相輕質鋼氫脆性能的影響
Jisung Yoo, Min Chul Jo, Dae Woong Kim, Hyejin Song, Minseo Koo, Seok Su Sohn?, Sunghak Lee?
S.S. Sohn:sssohn@korea.ac.kr
S. Lee:shlee@postech.ac.kr
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.06.051
摘要
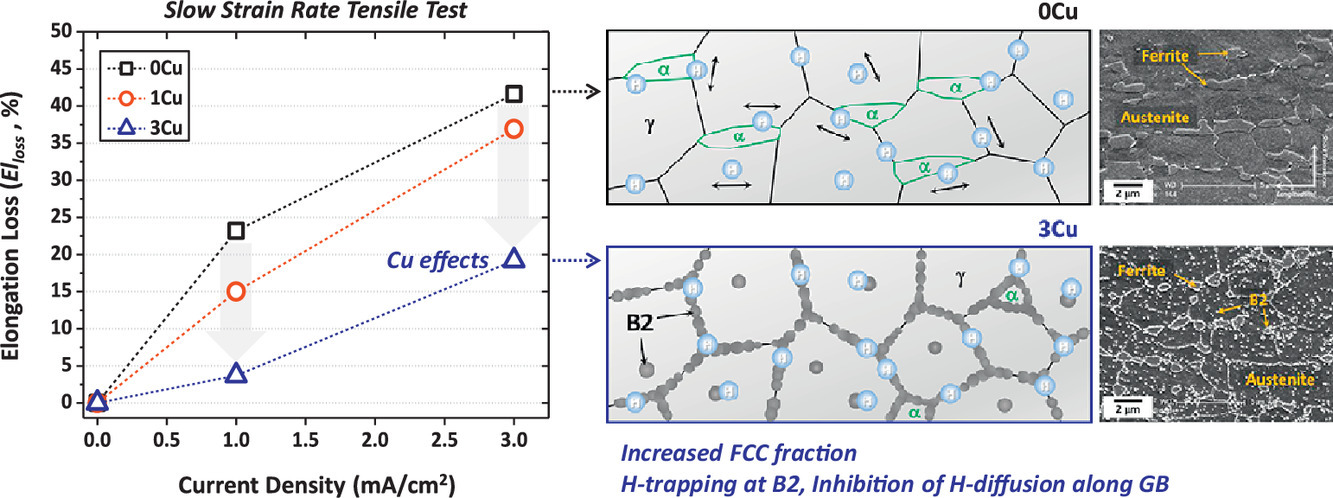
氫脆問題已成為高強度輕量鋼面臨的主要問題之一。由于小尺度的析出相可以提供穩定的H俘獲位點,因此成為了幫助克服高強度鋼氫脆問題的首選。然而,具有B2相析出的高強度輕量鋼中的氫脆目前還少有研究。本研究中,我們制備了3種Fe-0.8C-15Mn-7Al - (0,1,3)Cu雙相輕量鋼,并對其氫脆性能進行了評價。我們基于低應變速率拉伸試驗測得的延伸率損失和電化學滲透試驗測得的氫濃度和擴散率,研究了Cu的作用。結果表明,添加銅元素降低了延伸率損失,降低H的濃度和擴散,提高了氫脆性能。其具體機制是:銅的添加導致了奧氏體體積分數增加,而奧氏體中H的擴散速率遠低于鐵素體。同時,它也減小了鐵素體晶粒附近的應變集中,從而減少了變形過程中H的內部擴散。此外,銅的添加促進了復雜的半共格富銅 B2粒子的形成,在界面上提供了失配位錯作為穩定且不可逆的H捕獲位點。B2相粒子優先在晶界和相界等位置形核,從而促進了H可逆位點向不可逆位點的轉變,這也進一步降低了H的擴散系數。因此,基于本研究中的發現,我們建議在高強度輕量鋼的設計中加入銅以同時提高其抗拉強度和氫脆性能。
英文摘要
Hydrogen embrittlement (HE) has arisen as one of main issues for developing high-strength lightweight steels. The precipitation of fine particles providing as stable H-trapping sites is preferred to overcome the intrinsic HE of high-strength steels. However, studies on HE in high-strength lightweight steels along with roles of B2 particles have not been reported yet. In this study, three Fe–0.8C–15Mn–7Al–(0,1,3)Cu duplex lightweight steels were fabricated, and their resistance to HE was evaluated. Roles of Cu addition were investigated by the loss of elongation measured from slow-strain-rate tensile tests and by the concentration and diffusivity of H measured from electrochemical H permeation tests. The Cu addition results in the decreased elongation loss and the lower concentration and effective diffusivity of reversible H, indicating the higher resistance to HE. The unraveled mechanism is that the Cu addition increases the fraction of austenite, where the diffusivity of H is much lower than ferrite, and decreases the strain localization along ferrite grains to reduce the internal diffusion of H during deformation. In addition, it promotes the formation of complex semi-coherent Cu-rich B2 particles, which provides misfit dislocations at interfaces as stable and irreversible H-trapping sites. The B2 particles preferentially nucleated at reversible sites such as grain boundaries and phase interfaces promote a transition from reversible to irreversible sites, which further reduces the diffusivity of H. The present work, thus, would suggest the Cu addition to enhance both tensile properties and resistance to HE for designing high-strength lightweight steels.
ACTA Vol. 196, 1 Sept. 2020, P384-395
20. An improved description of creep in dispersion-strengthened metals
一種對于彌散強化金屬中蠕變的改進性描述方法
M. Zhang, S.E. Broyles, J.C. Gibeling?
J.C. Gibeling:jcgibeling@ucdavis.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.06.036
摘要
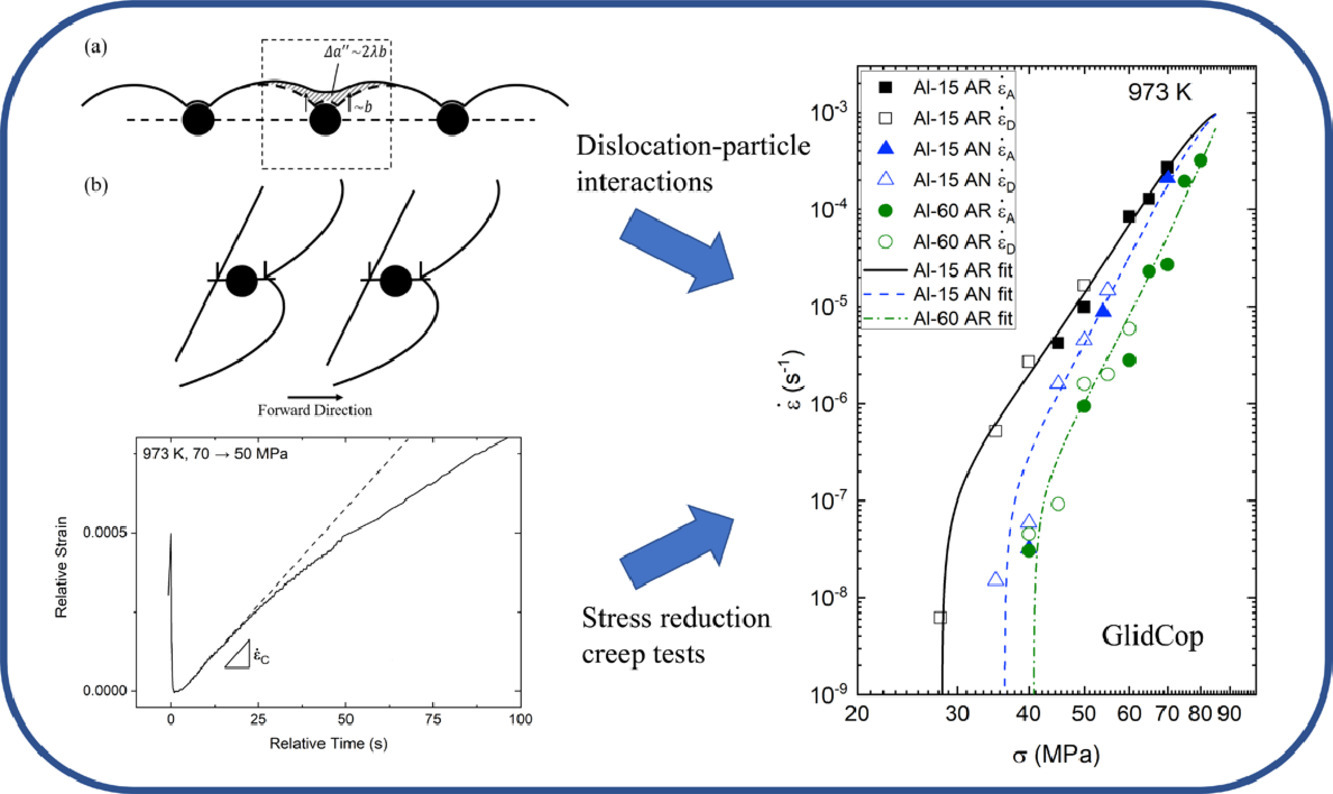
我們提出了一種基于熱激活位錯滑移的模型,描述擠壓退火的GlidCop Al-15和GlidCop Al-60合金在973 K下由位錯掙脫控制的蠕變過程,以及低應力下觀察到的臨界行為。與傳統的Rösler-Arzt方法分析不同,我們進行了穩態條件下和瞬態應變-應力降低條件下的蠕變試驗,以獲得蠕變的激活能和阻礙強度。與純銅不同的是,在所有測試中,GlidCop合金的恒定結構階段蠕變速率都大于之后的的穩態蠕變速率。這一結果表明位錯脫離粒子,而非位錯之間的相互作用,是控制蠕變速率的主要因素。此外,在降低相同應力的條件下,初始應力高,則恒定結構階段的蠕變速率更大。這一結果表明,粒子附近的位錯相互作用導致的內應力,對位錯脫釘所需的初始應力有影響。我們將這種應力以及這種應力與可動位錯密度的關系引入了我們的模型。此外,我們確定了恒定溫度和結構條件下的位錯滑移啟動面積,其值與粒子間距與伯氏矢量的乘積一致。這進一步支持了對于脫釘控制滑移過程的理論解釋。最后,我們基于脫釘位錯會由于熱力學上粒子/基體界面的吸引而發生回遷這一假設,對蠕變臨界應力進行了模擬。
英文摘要
An improved model based on thermally activated dislocation glide is proposed to describe the dislocation detachment-controlled creep of extruded and annealed GlidCop Al-15 and extruded GlidCop Al-60 at 973 K as well as the threshold behavior observed at lower stresses. Unlike the customary analysis using the Rösler-Arzt approach, both steady-state and strain-transient stress reduction creep tests were performed to obtain the activation energies and the obstacle strengths for creep. In contrast to pure copper, the constant-structure creep rates of GlidCop were greater than the subsequent steady-state creep rates in all tests. This result supports the concept that dislocation detachment from particles, rather than dislocation-dislocation interactions, is rate-controlling.In addition, the constant-structure creep rates at the same reduced stresses were found to be greater at higher initial stresses. This observation is interpreted as evidence that a forward internal stress arising from inter-dislocation interactions near the particles acts on the ready-to-detach dislocations and scales with the initial stress. This forward stress and an explicit treatment of the stress dependence of mobile dislocation density were incorporated in the improved model. Furthermore, the operational activation area for dislocation glide was determined at constant temperature and structure, and the values are consistent with the interparticle distances multiplied by the Burgers vector, which further supports the interpretation of detachment controlled glide. Finally, the true threshold stress for creep is modeled as originating from thermodynamic back jumps of just-detached dislocations due to the attractive nature of the particle/matrix interface.
ACTA Vol. 196, 1 Sept. 2020, P396-408
21. Microstructure and creep performance of a multicomponent co-based L12–ordered intermetallic alloy
一種多元素組成L12有序Co基合金的組織和蠕變性能
F.R. Long, S.I. Baik, D.W. Chung, F. Xue?, E.A. Lass , D.N. Seidman, D.C. Dunand
F. Xue:fei.xue@northwestern.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.06.050
摘要
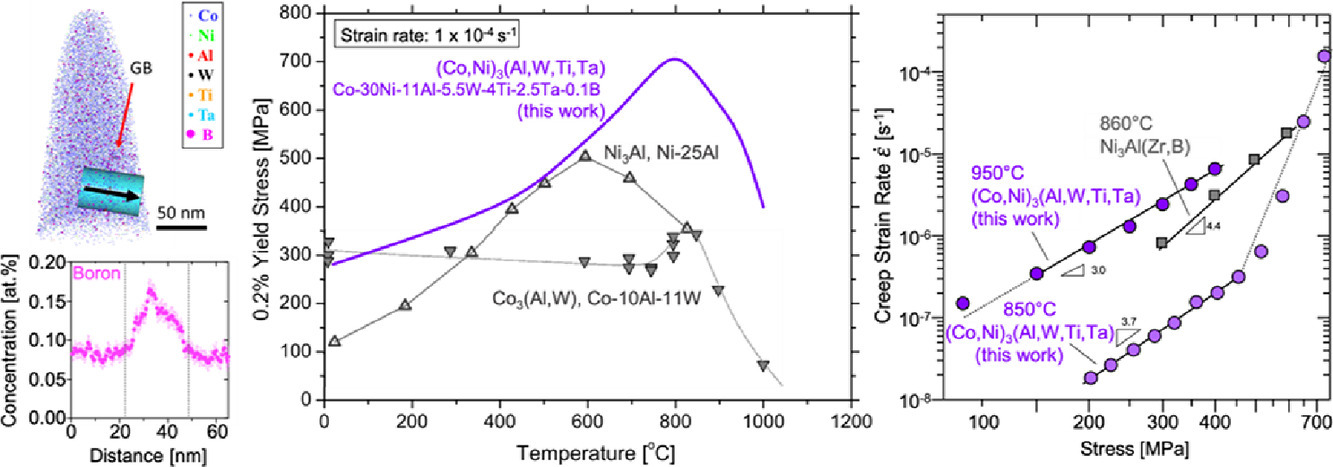
了解L12有序的Co3(Al,W)γ’相的化學、熱力學和機械性能對于我們深入理解γ(f.c.c.)/γ’(L12)鈷基高溫合金至關重要。最近,研究人員通過相圖方法發現了一種單相γ’(L12)合金,其成分為Co-30Ni-11Al-5.5W-4Ti-2.5Ta-0.10B (at.%),γ’相溶解溫度為1268 °C。掃描和透射電子顯微鏡實驗表明合金的單相組織在900°C 和1000 °C 1000小時,以及1100 °C 168 h小時下保持穩定,沒有觀測到其他相的產生,這使得所有退火溫度下的顯微硬度值大體相當。原子探針實驗進一步證實了γ’(L12)單相結構,其成分為(Co,Ni)3(Al,W,Ti,Ta)。晶界處貧Ni、 W 、Ta,富Co、Al、B。實驗觀測到材料的屈服強度反常提高,從室溫下的約300MPa提高到了800 °C下的約700MPa,這一強度超過了Co3(Al,W)(L12)和Ni3Al(L12)。材料在850 和950 °C的蠕變實驗中表現出冪律行為,應力指數n約為3,(Co,Ni)3(Al,W,Ti,Ta)的應變激活能約為497 kJ•mol-1。這一激活能與單相Ni3Al(L12)的406–421 kJ•mol-1接近。
英文摘要
The chemistry,thermodynamics and mechanical properties of the L12-ordered Co3(Al,W)γ’-phase are crucial for the understanding of γ(f.c.c.)/γ’(L12)cobalt-based superalloys. A single-phase γ’(L12) alloy with thecomposition Co-30Ni-11Al-5.5W-4Ti-2.5Ta-0.10B (at.%) and a γ’(L12)-solvustemperature of 1268 °C was recently identified using the Calphad-methodology.Scanning and transmission electron microscopy reveals that the single-phase microstructureis stable at 900 and 1000 °C for 1000 h and at 1100 °C for 168 h, without otherphases being observed, resulting in similar levels of microhardness for allannealing temperatures. Atom-probe tomography confirms the presence of asingle-phase γ’(L12)-microstructure with a composition of (Co,Ni)3(Al,W,Ti,Ta).Grain boundaries exhibit depletion of Ni, W and Ta and enrichment of Co, Al andB. A remarkable yield stress anomaly is observed, with the yield strengthincreasing from ~ 300 to ~ 700 MPa from room temperature to 800 °C, which isstronger than Co3(Al,W)(L12) and Ni3Al(L12).The creep tests at 850 and 950 °C display power-law behavior with a stressexponent of n = ~ 3 and an activation energy of Qn = 497 kJ•mol-1for (Co,Ni)3(Al,W,Ti,Ta), similar to that of single-phase Ni3Al(L12)compound (Qn = 406–421 kJ•mol-1) .
ACTA Vol. 196, 1 Sept. 2020, P409-417
22. Novel transformation pathway and heterogeneous precipitate microstructure in Ti-alloys
鈦合金中的新型相變路徑和非均勻析出組織研究
Tianlong Zhang, Dong Wang?, Yunzhi Wang?
D. Wang:wang_dong1223@mail.xjtu.edu.cn,西安交通大學
Y. Wang:wang.363@osu.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.06.048
摘要
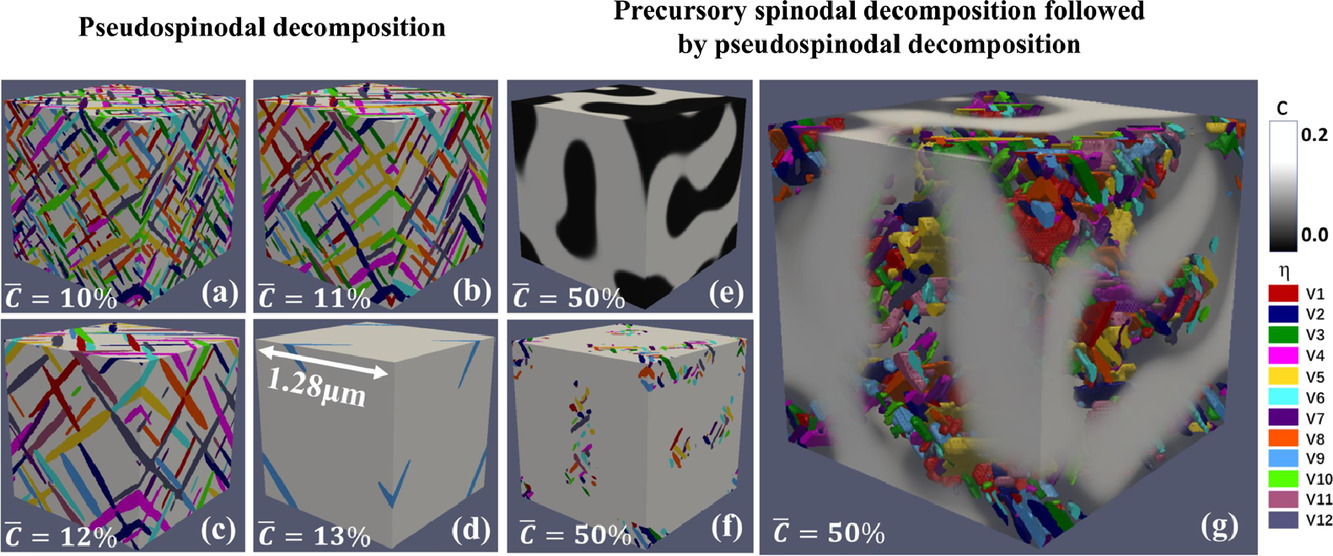
研究表明,具有一定非均勻微觀結構的材料已被證明具有強度和延展性的協同結合。在這項研究中,我們通過將熱力學數據庫與相場模擬相結合,證明了在鈦合金中創造這種非均勻微觀結構的新轉變途徑。結果表明,濃度調節不同長度尺度(a)所產生的前兆旋節線分解在父階段和(b)相互擴散在多層不同合金成分可以有效地生成層次和梯度α+β兩相微觀結構,混合好α沉淀區和αprecipitate-free-zones或粗α沉淀區域。所產生的新型微結構包括“倒球狀微觀結構”雙模態微結構和在顆粒尺寸和顆粒數密度上具有控制空間梯度的梯度微結構。這項研究可能有助于設計新穎的分層和梯度兩相微結構,使其具有可調的尺寸和密度,以及其空間異質性的長度尺度來達到預期的性能。
英文摘要
Materials with certain heterogeneous microstructures have been shown to hold a synergistic combination of strength and ductility. In this study, we demonstrate novel transformation pathways for creating such heterogeneous microstructure in Ti-alloys by integrating thermodynamic databases with phase field simulations. The results show that the concentration modulations at different length scales produced by (a) precursory spinodal decomposition in the parent phase and (b) interdiffusion in multi-layers having different alloy compositions can generate effectively hierarchical and gradient α + β two-phase microstructures, with a mixture of fine α precipitate regions and α precipitate-free-zones or coarse α precipitate regions. The novel microstructures produced include “inverted globular α” bi-modal microstructures and gradient microstructures with controlled spatial gradients in particle size and number density of α precipitates. This study may shed light on how to design novel hierarchical and gradient two-phase microstructures with tunable size and density of precipitates as well as the length scale of their spatial heterogeneity for desired properties.
ACTA Vol. 196, 1 Sept. 2020, P430-443
23. Strain-induced multivariant martensitic transformations: A scale-independent simulation of interaction between localized shear bands and microstructure
應變誘導多變體馬氏體相變過程中局部切變帶與組織相互作用的非尺寸依賴模擬
S. Ehsan Esfahani, Iman Ghamarian, Valery I. Levitas?
V.I. Levitas:vlevitas@iastate.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.06.059
摘要
我們對一種描述多邊體相變和不連續剪切帶相互作用,且與尺度無關的模型進行了改進,并以此模擬了高壓力下的塑性形變誘導相變。這一模型包含一種尺度無關的馬氏體相變的相場理論,通過接觸問題公式引入局部剪切帶。也就是說,通過模擬沿滑移表面滑移位移的連續分布,再現高壓相形核所需的塑性應變誘發的應力集中。我們研究了壓縮和切變條件下單晶/雙晶樣品中的應變誘導相變。模擬結果表明,與靜力條下件相比,塑性剪切使相變壓力顯著降低,甚至低于相平衡壓力,這與已有實驗中的觀測結果一致。模擬確定了每一種馬氏體變體對應的相變動力學隨切變應變的變化,以及單一晶粒和整個體系中高壓相的體積分數。在13個晶粒和38個晶粒的兩種體系中,高壓相的穩態體積分數相同,進一步切變不會繼續導致相變。幾乎所有靜態相界面處的局部相平衡都滿足相變功判據。從平均應力的角度來看,整個多晶或高壓力相也到達了類似的相平衡狀態。這些結果對于建立微觀動力學方程,以模擬高壓扭轉、球磨、摩擦和其他變形過程具有重要意義。
英文摘要
A scale-independent model for the interaction between multivariant phase transformations (PTs) and discrete shear bands is advanced and utilized to simulate plastic strain-induced PTs at high pressure. The model includes a scale-free phase-field theory for martensitic PTs. The localized shear bands are introduced via a contact problem formulation. That is, the continuous distribution of sliding displacements along the prescribed slip surfaces is modeled to reproduce the plastic-strain-induced stress concentrators necessary for nucleation of a high-pressure phase (HPP). The strain-induced PTs in the bi/polycrystalline samples subjected to compression and shear are studied. The simulations show a severe reduction in the PT pressure by the plastic shear in comparison to a hydrostatic condition, even below the phase equilibrium pressure, like in known experiments. Transformation kinetics versus shear strain for each martensitic variant and the volume fraction of the HPP in individual grains and the entire aggregate are determined. The stationary volume fraction of the HPP is the same for polycrystals consisting of 13 and 38 grains, and a further shearing does not cause PT. The local phase equilibrium condition based on the transformation-work criterion is satisfied at almost all stationary phase interfaces. A similar phase equilibrium condition in terms of stresses averaged over the entire polycrystal or HPP is fulfilled. These results are important for the development of the microscale kinetic equations and modeling the sample behavior in traditional and rotational diamond anvils during the high-pressure torsion, ball milling, friction, and other deformation-transformation processes.
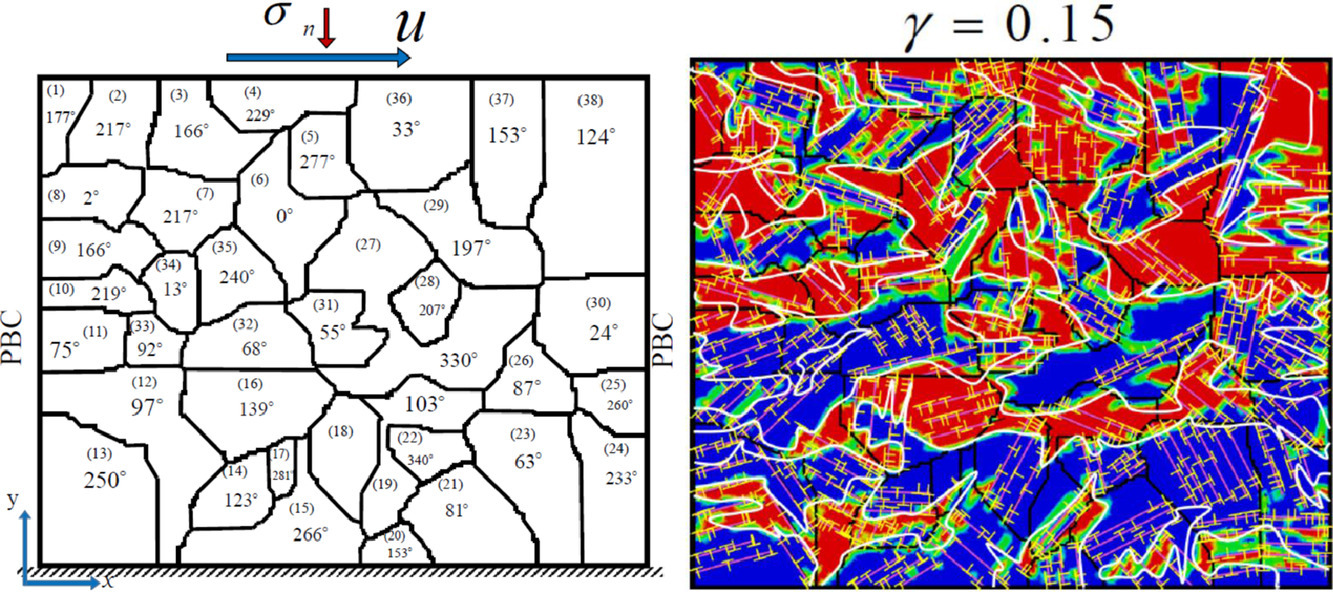
ACTA Vol. 196, 1 Sept. 2020, P456-469
24. Precipitation-site competition in duplex stainless steels: Cu clusters vs spinodal decomposition interfaces as nucleation sites during thermal aging
雙相不銹鋼時效過程中析出位置的競爭:銅原子團簇 vs. 調幅分解界面
Timothy G. Lach?, William E. Frazier, Jing Wang, Arun Devaraj, Thak Sang Byun
T.G. Lach:lachtg@ornl.gov
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.05.017
摘要
雙相不銹鋼在高溫環境幾十年的服役過程中,可能同時存在多種微觀結構演化機制的競爭。這種不同微觀組織演化途徑之間的競爭很難用簡單的模型合金進行確定,因此需要對復雜合金的相變機制進行詳細的微觀組織分析。因此,我們采用具有復雜但已被充分了解的化學成分的雙相不銹鋼,來研究不同非均勻形核位點,特別是調幅分解和Cu團簇,在時效過程中對Ni-Si-Mn析出的相對重要程度。時效和輻照過程中鐵素體軸承鋼中的Ni-Si-Mn析出能極大地影響機械性能。通過對成分優化后的雙向不銹鋼進行細致的組織表征和蒙特卡羅動力學模擬,我們發現盡管調幅分解過程中形成的Fe、Cr界面可以作為溶質擴散的通道,但它卻非Ni-Si-Mn的優先形核位點。相對地,高濃度的Cu導致了Cu原子團簇的形成,這些團簇具有高能界面,非常有利于Ni-Si-Mn的形核。這些結果能夠為建立高溫服役條件下析出強化合金的預測模型提供很大的幫助。
英文摘要
Competing microstructural evolution mechanisms can exist simultaneously when duplex stainless steels are operating for several decades in a high temperature service environment. Such competition between different microstructural evolution pathways can be difficult to ascertain using simple model alloy systems necessitating detailed microstructural analysis of phase transformation mechanisms in complex alloys. Thus, duplex stainless steels with complex but well understood chemistries were used to investigate the relative importance of different heterogeneous nucleation sites – specifically, spinodal decomposition and Cu clustering – on Ni-Si-Mn precipitation during thermal aging. Precipitation of Ni-Si-Mn particles in ferrite-bearing steels during thermal aging and irradiation can greatly change mechanical properties. Using duplex stainless steels with custom-modified compositions along with advanced microstructural characterization and first-passage kinetic Monte Carlo simulations, it is revealed that while the interface between Cr and Fe formed during spinodal decomposition can be a pathway for solute diffusion, it is not a preferred site for Ni-Si-Mn precipitation. Instead, the presence of a higher concentration of Cu leads to the formation of small Cu-rich clusters with high energy interfaces that act as nucleation sites for Ni-Si-Mn particles. These results will inform predictive models for the use of precipitation-hardened alloys for extended operation at high temperatures.
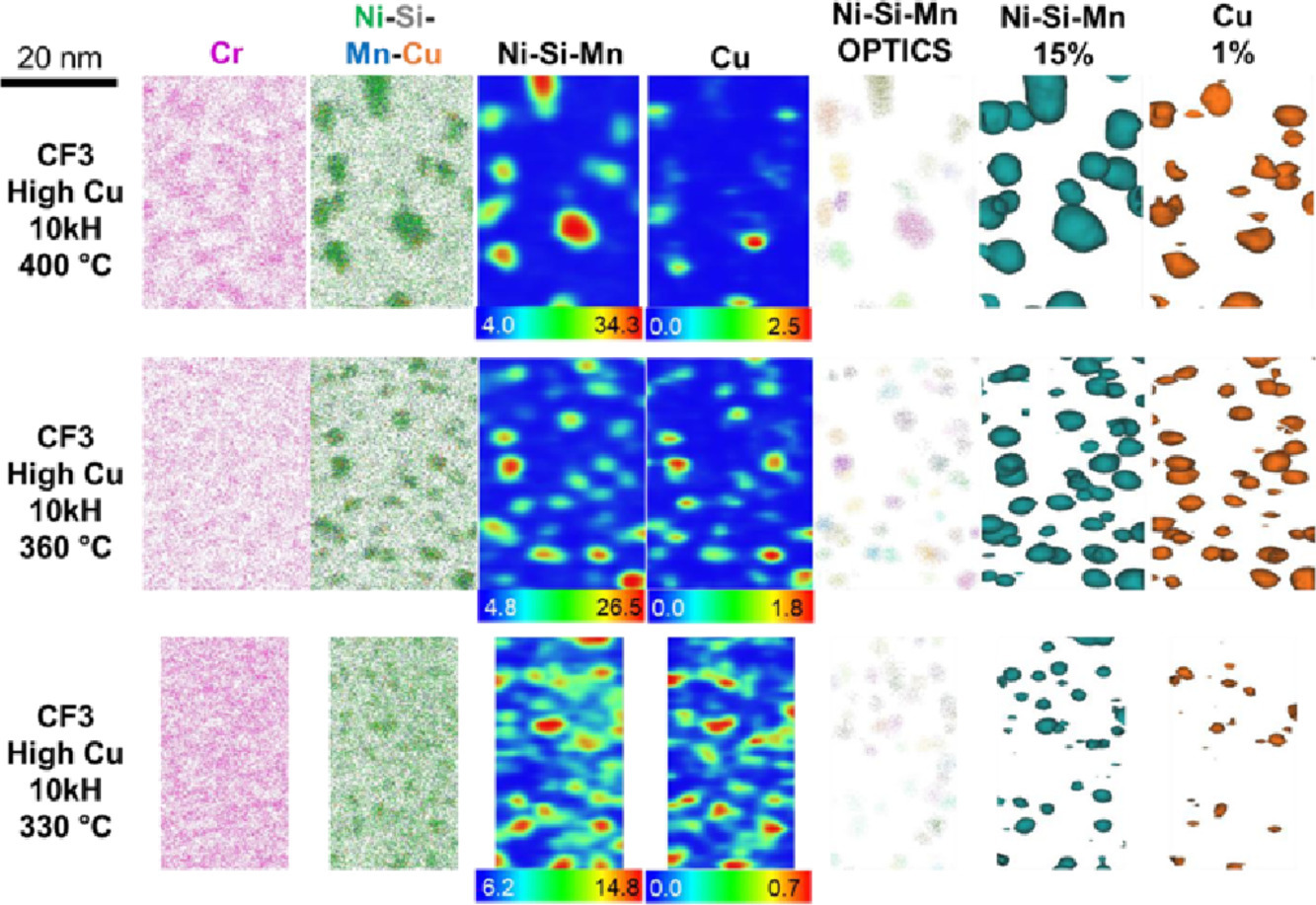
ACTA Vol. 196, 1 Sept. 2020, P470-487
25. Austenite formation kinetics from multicomponent cementite-ferrite aggregates
多組分滲碳體-鐵素體的奧氏體相變動力學
Y.X. Wu, L.Y. Wang, W.W. Sun, M.J. Styles, A.J. Studer, Y. Bréchet, A. Arlazarov, C.R. Hutchinson?
C.R. Hutchinson:christopher.hutchinson@monash.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.07.001
摘要
亞穩態奧氏體對先進高強鋼的力學性能有顯著影響,而兩相區退火過程中的奧氏體逆轉變動力學又與初始組織密切相關。我們通過原位中子粉末衍射對一系列Fe-C-Mn 和Fe-C-Mn-Si/Al滲碳體-鐵素體初始組織中的奧氏體逆轉變動力學進行了詳細的研究。取決于滲碳體溶解和奧氏體/鐵素體界面遷移的相對速度關系,可能會存在以下2種不同情況:被包圍的滲碳體受制于奧氏體中的緩慢擴散而沒有完全溶解,導致奧氏體體積分數穩定在一個低于熱力學平衡的值;基體中滲碳體的快速溶解則會導致奧氏體體積分數穩定在一個高于熱力學平衡的值。當我們考慮或者模擬奧氏體的形成動力學時,我們需要同時考慮這兩種情況對動力學的不同貢獻。
英文摘要
Metastable austenite strongly influences the mechanical properties of many advanced high strength steels (AHSS) and its formation kinetics during intercritical annealing strongly depend on the initial microstructure. In this contribution, we have performed detailed kinetic studies of austenite formation from cementite-ferrite aggregate in a range of Fe-C-Mn and Fe-C-Mn-Si/Al alloys via in situ neutron powder diffraction. Depending on the relative contribution of cementite dissolution in respect to migrating interface of austenite/ferrite, the incomplete dissolution of enveloped cementite limited by slow diffusion in austenite could result in austenite plateauing below equilibrium, while fast dissolution of matrix cementite could result in austenite plateau above equilibrium. Both contributions need to be considered and modelled to describe the austenite formation kinetics.
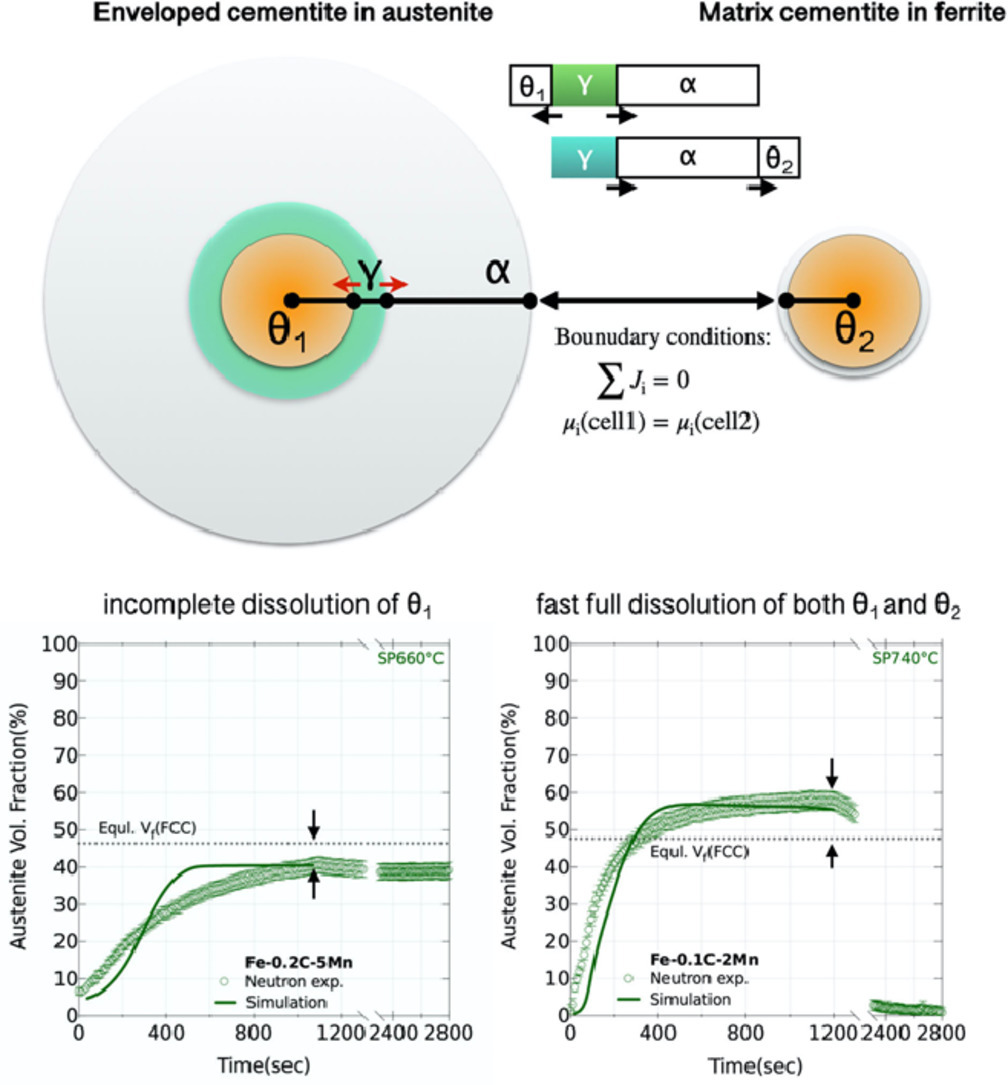
ACTA Vol. 196, 1 Sept. 2020, P488-504
26. Intrinsic coupling between twinning plasticity and transformation plasticity in metastable β Ti-alloys: A symmetry and pathway analysis
基于對稱性和狀態路徑分析亞穩β Ti合金中孿晶塑性和相變塑性的本征耦合
Yipeng Gao?, Yufeng Zheng?, Hamish Fraser, Yunzhi Wang
Y. Gao:gao.108@osu.edu
Y. Zheng:yufengz@unr.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.07.020
摘要
除了常規的位錯滑移之外,機械孿晶和相變是另外兩種重要的晶體塑性發生機制,且他們都是打破晶體對稱性的過程。雖然我們已經很好地建立了它們單一過程的相關理論,但關于這兩種機制的內在耦合卻少有研究。本研究采用了相變圖譜方法系統地分析了由機械孿晶和相變相互作用引起的變形模式。以亞穩態β Ti合金為例,我們成功說明了機械孿晶和相變在打破對稱性的過程中是本征耦合的,并導致了多種相變和非相變情況下的形變路徑和孿晶模式。這項工作不僅揭示了一些獨特孿晶模式(如{3 3 2}、{5 8 11}和{3 9 10} 孿晶)和孿晶界結構(如嵌套孿晶)的物理起源,并且從孿晶、相變耦合的角度為理解β Ti合金的高塑形提供了新的見解。
英文摘要
In addition to conventional dislocation plasticity, mechanical twinning and structural phase transformations are another two important plasticity carriers. Although both are symmetry-breaking processes and theories to treat each of them individually have been well-established, the intrinsic coupling between the two has not been investigated. Here we employ a phase transition graph approach to analyze systematically deformation modes arising from the interplay between mechanical twinning and phase transformations. Using metastable β Ti-alloys as an example, we show that mechanical twinning and phase transformations are intrinsically coupled in the symmetry-breaking processes, which results in multiple interconnected transformation and non-transformation deformation pathways and characteristic twinning modes. This work not only reveals the physical origin of unique twinning modes (e.g., {3 3 2}, {5 8 11} and {3 9 10} twins) and extended core structures of twin boundaries (e.g., nested twins) observed in experiments, but also provides a new insight into the enhanced plasticity of metastable β Ti-alloys through coupled twinning and transformation pathway engineering.
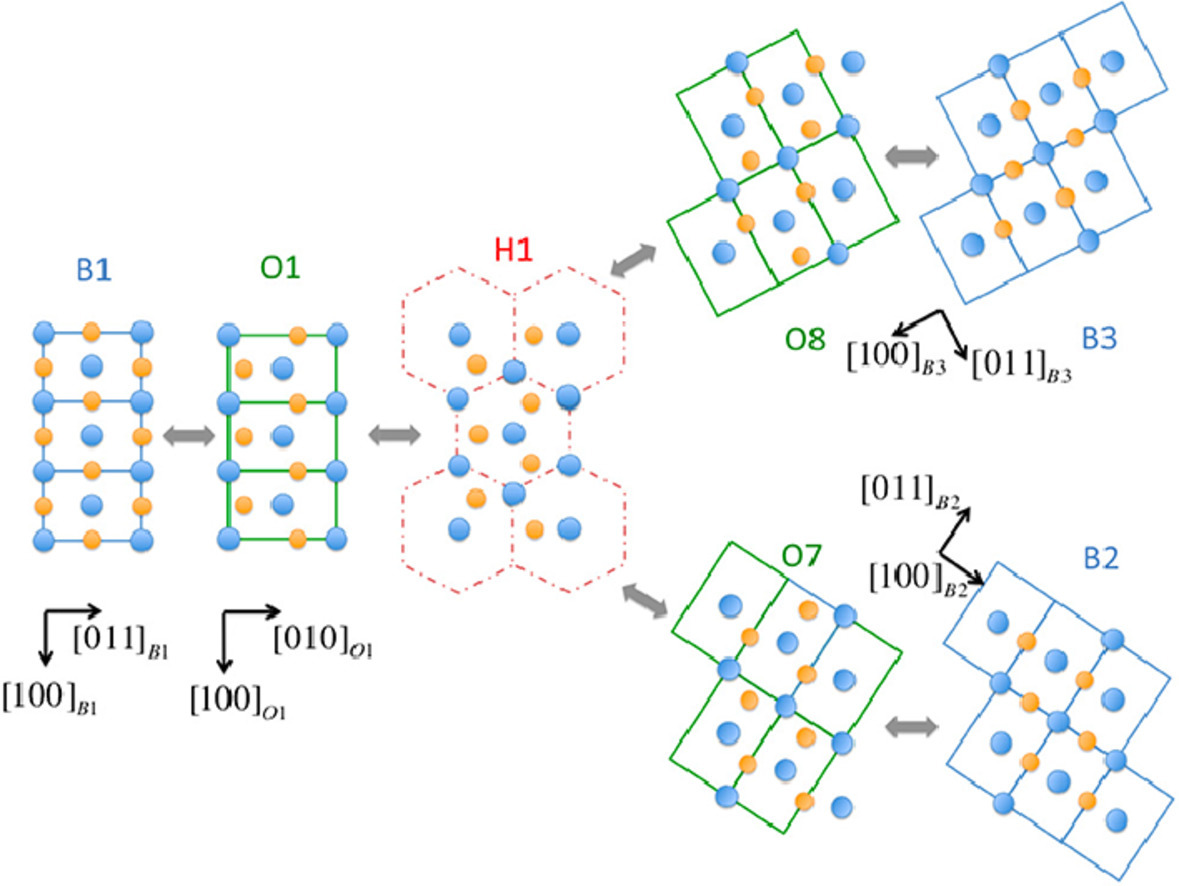
ACTA Vol. 196, 1 Sept. 2020, P505-515
27. Defect behavior and radiation tolerance of MAB phases (MoAlB and Fe2AlB2) with comparison to MAX phases
MAB相(MoAlB和Fe2AlB2)的缺陷行為和抗輻照性能研究及其與MAX相的比較
Hongliang Zhang?, Jun Young Kim?, Ranran Su, Peter Richardson, Jianqi Xi, Erich Kisi, John O’Connor, Liqun Shi?, Izabela Szlufarska?
H. Zhang:zhlcanes@hotmail.com
J.Y. Kim:junyoungkim729@gmail.com
L. Shi:lqshi@fudan.edu.cn,復旦大學
I. Szlufarska:szlufarska@wisc.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.07.002
摘要
MAB相是一種具有多種優異性能的新型層狀三元材料。我們使用了一系列的實驗表征結合第一性原理計算研究了兩種MAB相,即MoAlB 和Fe2AlB2的缺陷演化和抗輻照情況。我們發現,在150℃和300℃下,Fe2AlB2都比MoAlB更能耐受輻射誘導的非晶化。這是由于MoAlB中的Mo Frenkel對不穩定,因此導致輻照后的MoAlB中產生了大量的MoAl反位缺陷,而這些缺陷即使在300℃下退火條件也很難消失。MAB相對輻射誘導的非晶化的抵抗能力比MAX相若,但與SiC相當。但是,在相同的輻照條件下,MAB相中卻并沒有觀測到類似MAX相中出現的輻照裂紋。這項研究表明,MAB極有可能是一種非常有前景的抗輻照應用材料。
英文摘要
MAB phases are a new class of layered ternary materials that have already shown a number of outstanding properties. Here, we investigate defect evolution and radiation tolerance of two MAB phases, MoAlB and Fe2AlB2, using a combination of experimental characterization and first-principles calculations. We find that Fe2AlB2 is more tolerant to radiation-induced amorphization than MoAlB, both at 150 °C and at 300 °C. The results can be explained by the fact that the Mo Frenkel pair is unstable in MoAlB and as a result, irradiated MoAlB is expected to have a significant concentration of MoAl antisites, which are difficult to anneal even at 300 °C. We find that the tolerance to radiation-induced amorphization of MAB phases is lower than in MAX phases, but it is comparable to that of SiC. However, MAB phases do not show radiation-induced cracking which is observed in MAX phases under the same irradiation conditions. This study suggests that MAB phases might be a promising class of materials for applications that involve radiation.
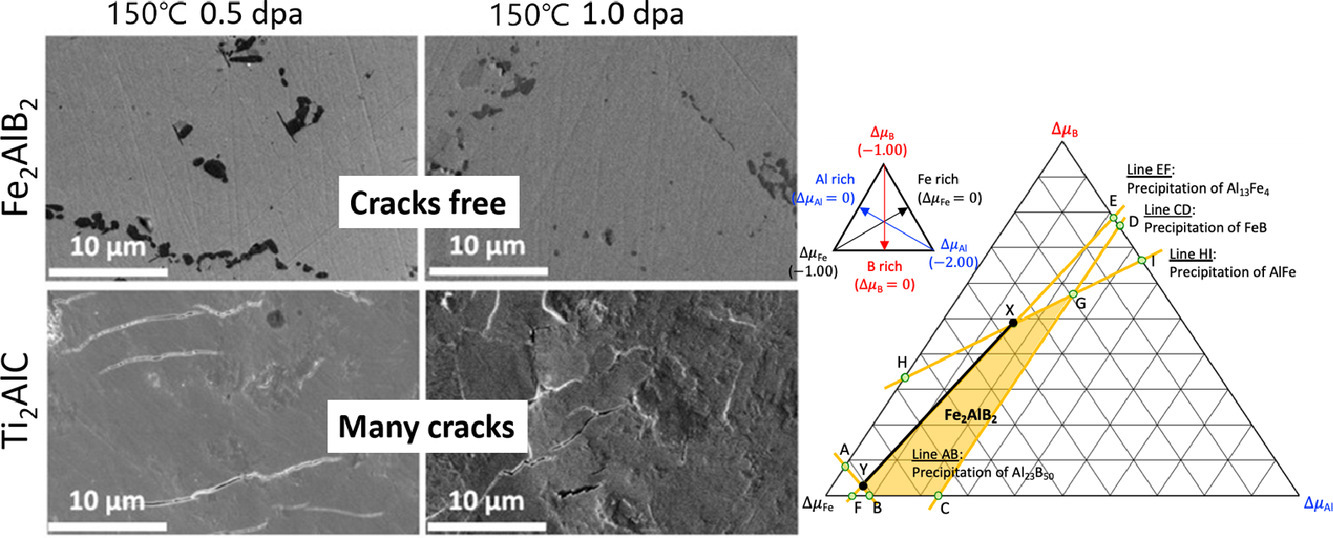
ACTA Vol. 196, 1 Sept. 2020, P516-527
28. Hydrogen trapping and desorption of dual precipitates in tempered low-carbon martensitic steel
低碳回火馬氏體中兩種析出相的捕氫和脫氫行為研究
Yu-Chen Lin, Ingrid E. McCarroll, Yi-Ting Lin, Wei-Chih Chung, Julie M. Cairney?, Hung-Wei Yen?
J.M. Cairney:julie.cairney@sydney.edu.au
H.-W. Yen:homeryen@ntu.edu.tw
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.06.046
摘要
本工作研究了一種低碳鋼中的兩種納米析出相——ε銅析出和TiC,對氫的捕獲行為。通過不同奧氏體化溫度下的淬火和回火對析出相進行調控,利用高分辨率透射電子顯微鏡和原子探針對析出相的納米結構進行了表征。我們進行了氫的熱脫附實驗,通過分析脫附過程反映析出相對于氫原子的捕獲能力。實驗結果表明,H的捕獲行為受TiC析出路徑影響;TiC與Cu的共同析出顯著提高了材料的氫捕獲能力。因此,我們可以使用熱處理工藝對回火馬氏體鋼的抗氫脆性能進行調控。更重要的是,在回火馬氏體鋼中共析出的TiC和Cu表現出了很強的捕氫能力從而提高了材料強度,因此,利用共沉淀提高氫脆性能是一條具有廣闊前景的鋼鐵材料設計思路。
英文摘要
The hydrogen trapping behaviors of dual nanometer-sized ε-copper and TiC carbide precipitates have been investigated in a low-carbon steel. The precipitation fashions were controlled by quenching and tempering at different austenization temperatures. The nanostructures of the dual precipitates were characterized by high-resolution transmission electron microscopy and atom probe tomography. Hydrogen desorption was studied through thermal desorption analysis of steels electrochemically charged with hydrogen. The hydrogen trapping capability of the precipitates was investigated through the release process. The precipitation routes of TiC carbides influenced the behavior of hydrogen trapping and the co-precipitation of copper and TiC carbides significantly increased the hydrogen trapping capability of the steels. These heat treatments can therefore be used to tailor the resistance to hydrogen embrittlement in tempered martensitic steels. Importantly, co-precipitated TiC and ε-copper particles in tempered martensitic steels show an enhanced capacity for hydrogen trapping and provide a range of trapping strengths. Co-precipitation is therefore proposed as a new prospect for designing steels with the capacity for substantial hydrogen trapping.
ACTA Vol. 196, 1 Sept. 2020, P565-575
29. Continuous and discontinuous yielding behaviors in ferrite-cementite steels
鐵素體-滲碳體鋼中的連續和不連續屈服現象
Yanxu Wang?, Yo Tomota, Takahito Ohmura, Wu Gong, Stefanus Harjo, Masahiko Tanaka
Y. Wang:WANG.Yanxu@nims.go.jp
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.07.017
摘要
我們通過納米尺度和宏觀尺度形變試驗,互補地研究了鐵素體-滲碳體鋼的連續和不連續屈服行為。即使在經過應變時效后,仍可觀察到熱處理后具有層狀或球狀組織的試樣中發生了連續屈服;而經過冷軋再結晶的鐵素體-滲碳體鋼中則發生了不連續屈服,同時有Lüders帶形成。電子顯微鏡、同步輻射X射線和中子衍射的結果表明,熱處理后的鐵素體-滲碳體界面是半共格的,具有很強的內應力場;而再結晶試樣的界面則是非共格的,內應力場較弱。此外,共格應變和熱應變是影響峰值展寬的兩個因素,其中前者依賴于鐵素體-滲碳體界面的總面積,而后者受溫度控制。納米壓痕試驗結果表明,半共格界面附近的臨界載荷顯著低于非共格界面和鐵素體晶界,因此半共格界面更容易發射位錯。
英文摘要
The continuous and discontinuous yielding behaviors in ferrite-cementite steels were complementarily investigated via nano- and macro-scale deformation examinations. The continuous yielding behavior was observed in heat-treated specimens with a lamellar or cementite-spheroidal structure even after strain-aging treatment. However, the discontinuous yielding behavior accompanied by the Lüders elongation appeared in ferrite-cementite steel that was recrystallized after cold rolling. The results obtained by electron microscopy, synchrotron X-ray, and neutron diffractions indicate that the ferrite-cementite interface of the heat-treated specimen is semi-coherent with a high internal stress field, whereas that of the recrystallized one is incoherent with a low internal stress field. Moreover, coherency strain, which depends on the total area of the ferrite-cementite interface, and thermal strain, which is governed by temperature, are the two factors that influence peak broadening. The nanoindentation tests revealed that the critical loads are significantly lower near the semi-coherent interface than those near the incoherent interface and the ferrite grain boundary; this suggests that dislocations are easily emitted from the semi-coherent interface.
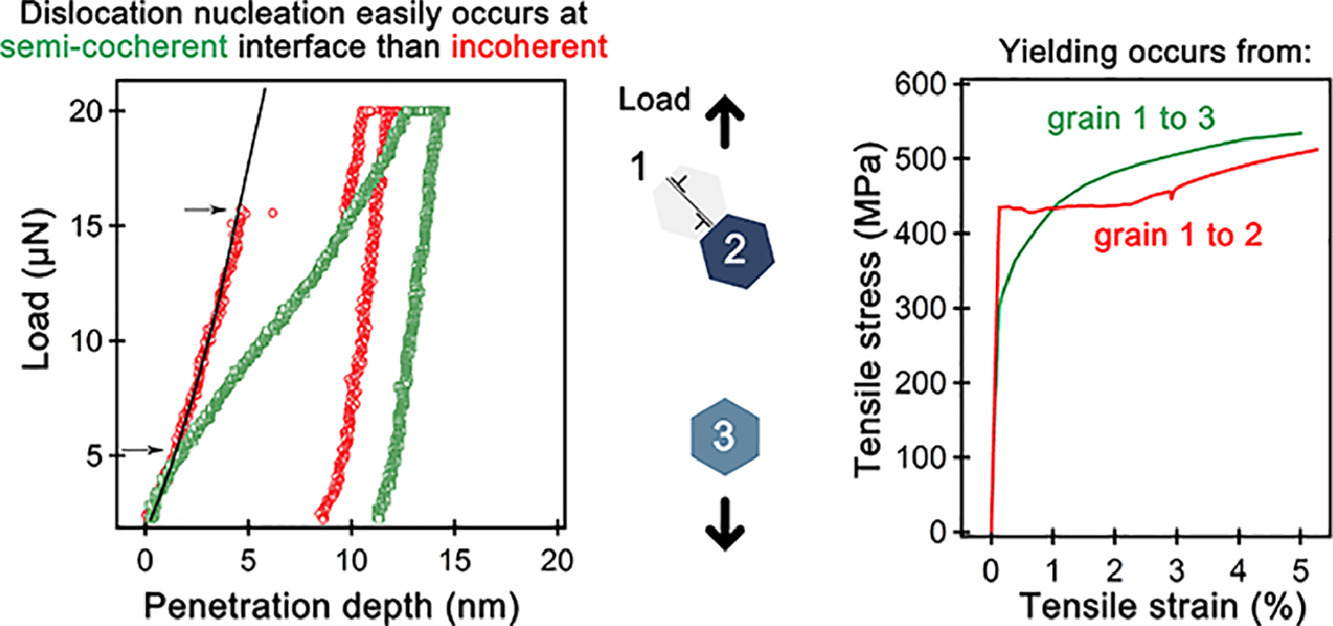
ACTA Vol. 196, 1 Sept. 2020, P584-594
30. Neutron diffraction monitoring of ductile cast iron under cyclic tension–compression
利用中子衍射研究球墨鑄鐵在循環拉壓載荷下的相變
Stefanus Harjo?, Satoru Kubota, Wu Gong, Takuro Kawasaki, Si Gao
S. Harjo:stefanus.harjo@j-parc.jp
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.07.016
摘要
為了深入理解低循環載荷條件下的加工硬化行為,我們采用原位中子衍射,對含有10.1 vol%球狀石墨和19.6 vol%珠光體的鐵素體基體材料進行了4循環拉壓加載行為研究,其中外加應變為±0.01。實驗發現,外應力、包辛格應力和包辛格應變的振幅隨循環次數的增加而增大,表明在循環加載過程中發生了加工硬化。最大和最小外加應變下的鐵素體晶格畸變均隨循環次數的增加而增大,表明鐵素體強度有所提高,因此鐵素體對材料強度的貢獻隨循環加載次數增加而提高。珠光體中的滲碳體作為體系中最硬的相,始終發生彈性變形。由于其體積分數僅為2.2%左右,因此對強度的貢獻十分有限。同時,石墨承受的應力較小。由于循環加載過程中鐵素體中的位錯累積而引起的鐵素體強度的增加對球墨鑄鐵的加工硬化起著重要的作用。同時,石墨承受的應力較小。綜上所述,循環加載過程中鐵素體中的位錯積累導致的強度提高對球墨鑄鐵的加工硬化起著重要的作用。
英文摘要
To understand work hardening behavior during low-cycle loading, ductile cast iron containing 10.1 vol% spheroidal graphite, 19.6 vol% pearlite, and ferrite matrix was investigated in an in situ neutron diffraction study of up to four cycles of tensile–compressive loading with applied strains of ±0.01. The amplitudes of applied stress, Bauschinger stress, and Bauschinger strain were found to increase with increasing cycle number, indicating work hardening as cyclic loading progressed. Absolute values of ferrite lattice strain at maximum and minimum applied strains increased with increasing cycle number, indicating an increase in ferrite strength. Consequently, the stress contribution to the strength from ferrite increased as cyclic loading progressed. Cementite embedded in pearlite behaved as the hardest phase and maintained elastic deformation, but its stress contribution to strength was limited because the volume fraction was only about 2.2%. Meanwhile, graphite accommodated little stress. The increase in ferrite strength, caused by dislocation accumulation in ferrite during cyclic loading, played an important role in the work hardening of the ductile cast iron.
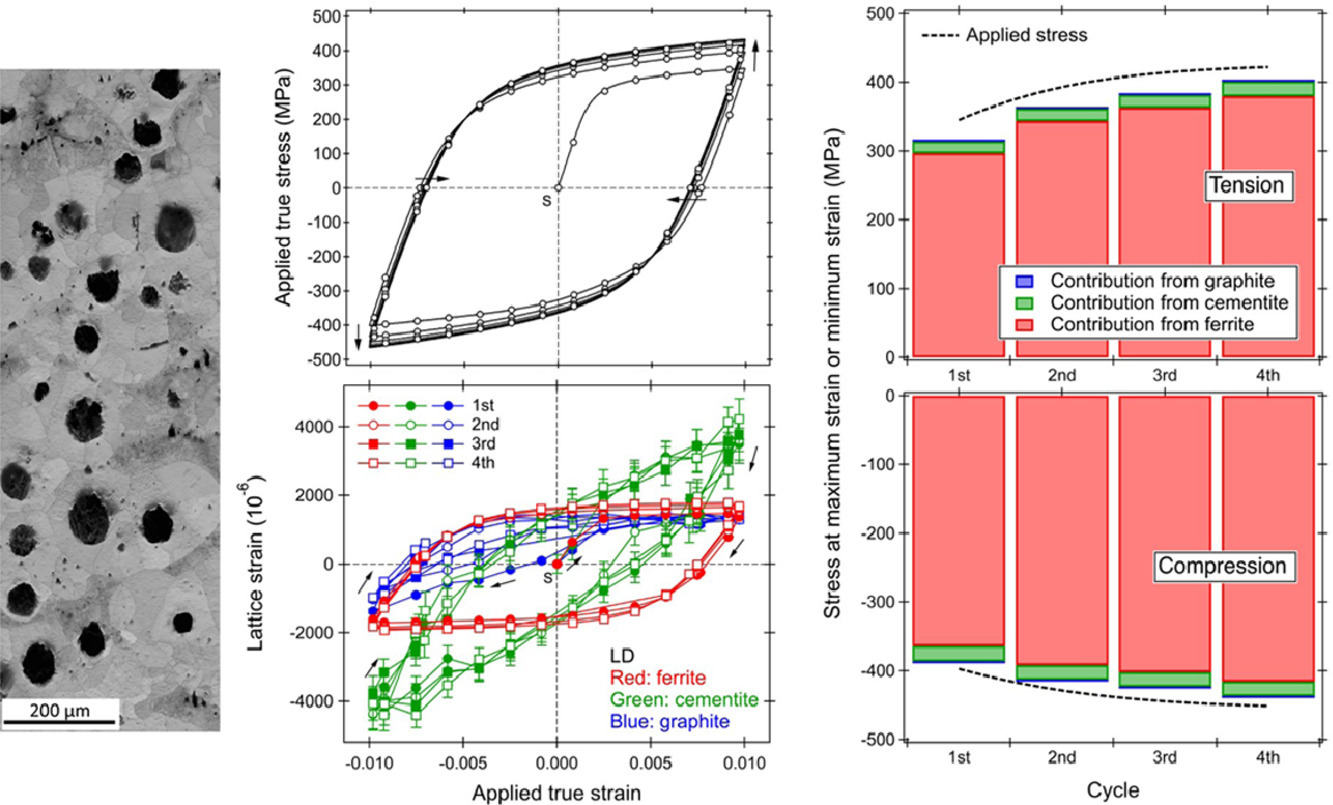
ACTA Vol. 196, 1 Sept. 2020, P595-608
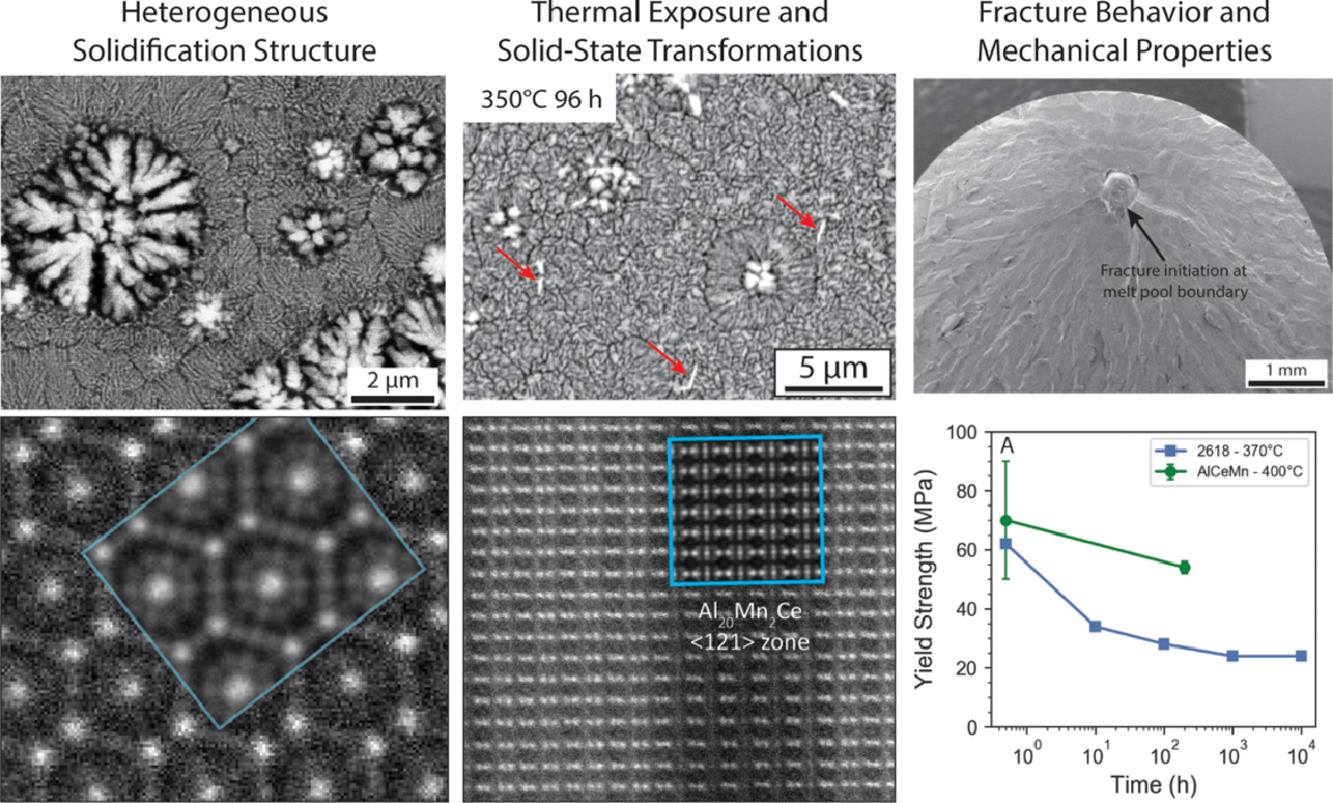
31. Microstructure and properties of a high temperature Al–Ce–Mn alloy produced by additive manufacturing
一種通過增材制造方法制備的高溫合金Al–Ce–Mn的組織和性能
A. Plotkowski?, K. Sisco, S. Bahl, A. Shyam, Y. Yang, L. Allard, P. Nandwana, A. Marquez Rossy, R.R. Dehoff
A. Plotkowski:plotkowskiaj@ornl.gov
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.07.014
摘要
本研究采用激光粉末熔化增材制造工藝設計并制備了一種Al-10Ce-8Mn (wt%)合金。增材制造過程中的快速冷卻速率使我們得到了一種內含大量具有強化作用的金屬間化合物的精細組織。我們對制備態及經過熱處理后的合金分別進行了拉伸性能測試。與鍛造和增材制造的鋁合金相比,制備態合金在400℃的高溫條件下表現出了優異的高溫性能和強度。通過組織表征和熱力學模擬,我們很好地解釋了Al–Ce–Mn 體系的凝固和固態相變過程。此外,我們對制備態及經過熱處理后的合金的相應強化機制進行了分析。
英文摘要
An Al–10Ce-8Mn (wt%) alloy was designed and fabricated by laser powder bed fusion additive manufacturing (AM). The rapid cooling rates of the AM process produced a refined microstructure with a large fraction of reinforcing intermetallic phases. The tensile properties of the alloy were characterized in the as-fabricated state and following thermal exposure. The properties of the as-fabricated microstructure showed exceptional high-temperature performance and strength retention at elevated temperatures up to 400 °C relative to benchmark wrought Al and AM Al alloy properties. Characterization of the microstructure and thermodynamic modeling of the ternary Al–Ce–Mn system rationalized the solidification and solid-state phase transformations. Analysis of the relevant strengthening mechanisms for both the as-fabricated and thermally exposed conditions was performed.
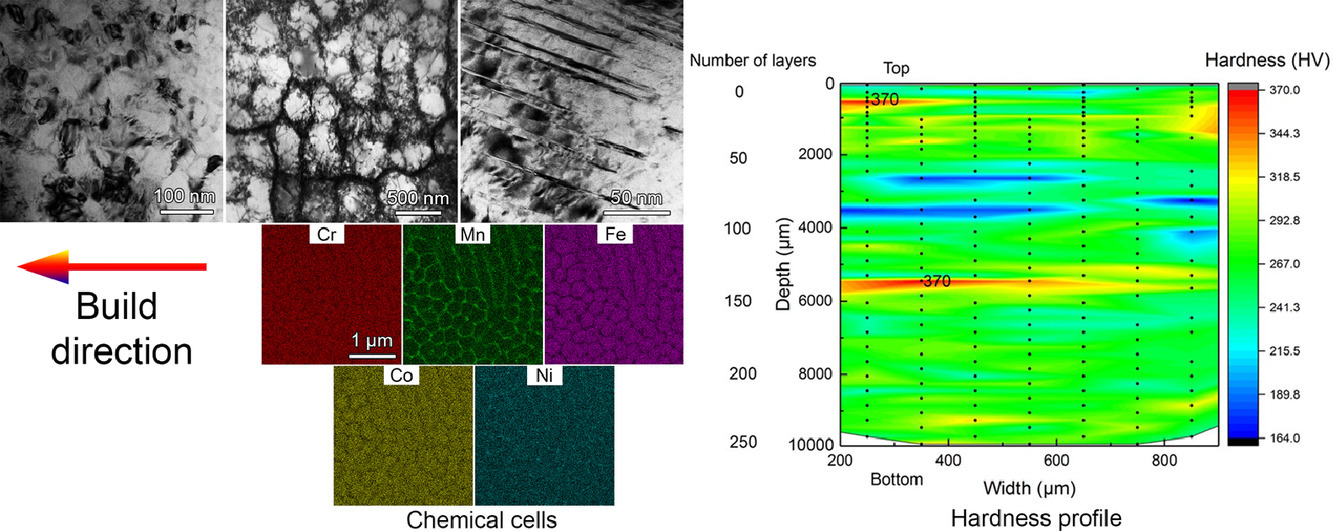
ACTA Vol. 196, 1 Sept. 2020, P609-625
32. Effect of cyclic rapid thermal loadings on the microstructural evolution of a CrMnFeCoNi high-entropy alloy manufactured by selective laser melting
CrMnFeCoNi高熵合金選區激光熔化過程中快速熱循環對組織演變的影響
H. Wang, Z.G. Zhu, H. Chen, A.G. Wang, J.Q. Liu, H.W. Liu, R.K. Zheng, S.M.L. Nai, S. Primig, S.S. Babu, S.P. Ringer?, X.Z. Liao?
S.P. Ringer:simon.ringer@sydney.edu.au
X.Z. Liao:xiaozhou.liao@sydney.edu.au
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.07.006
摘要
增材制造產生的金屬材料在制備方向上會經歷復雜的應力和溫度變化。這將有可能產生復雜的非均勻微觀結構,并導致各種各樣的力學性能。目前對于微觀結構非均勻性的性質和形成機制的研究還很缺乏,這限制了我們通過增材制造對金屬材料進行組織設計的能力。在本文中,我們通過電子顯微鏡對選區激光熔化制備的CrMnFeCoNi高熵合金進行了研究,并且主要關注其在制備方向上的組織演化。研究發現,組織中存在顯著的層次特征,包括納米晶、元素偏聚和析出、胞狀位錯結構、形變孿晶和形變誘導相變。我們的研究闡明了不同特征之間的相互聯系,并為通過增材制造工藝調控材料組織提供了指導。
英文摘要
Metallic materials produced by additive manufacturing experience complex stress and thermal gyrations along the build direction. This has the potential to produce complicated heterogeneous microstructures that may exhibit a wide variety of mechanical properties. There remains a paucity of studies on the nature and the formation mechanisms of the microstructural heterogeneity and this limits our capability for microstructural design in additively manufactured metallic materials. Here, we present an electron microscopy-based investigation of a CrMnFeCoNi high-entropy alloy produced by selective laser melting. We have focussed on a systematic investigation of the microstructural evolution along the build direction. Our results reveal a remarkable hierarchy of microstructures, including the formation of nanocrystalline grains, elemental segregation and precipitation, cellular dislocation structures, deformation twinning, and deformation-induced phase transformation. Our research clarifies the relationships amongst different features, and provides guidance for future structural manipulation of materials produced by additive manufacturing.
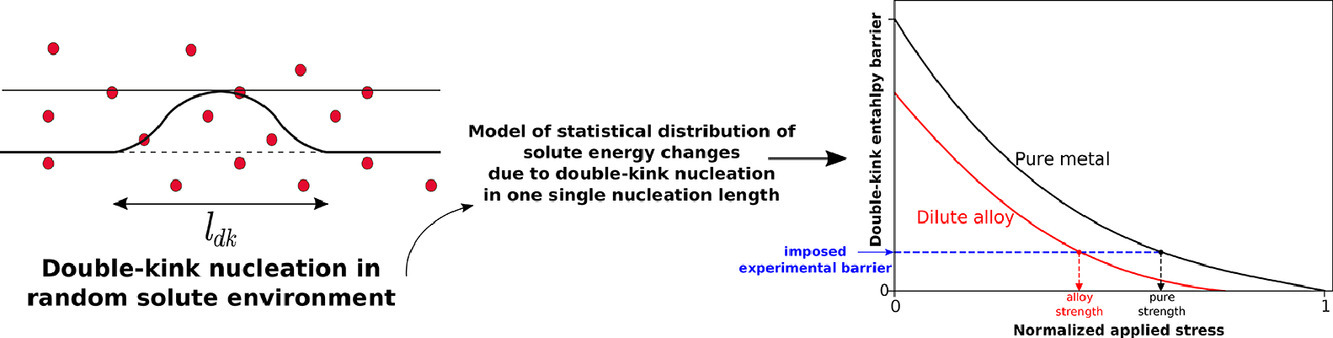
ACTA Vol. 196, 1 Sept. 2020, P635-650
33. Theory of double-kink nucleation in dilute BCC alloys
低固溶BCC合金中的雙彎折形核理論
Alireza Ghafarollahi?, William A. Curtin
A. Ghafarollahi:alireza.ghafarollahi@epflfl.ch
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.07.008
摘要
在純BCC金屬和稀置換元素固溶合金中,屈服通常是通過雙彎折結構沿螺位錯的形核和長大發生的。低溫下,屈服應力由雙彎折的形核控制。本研究中,我們提出了一種統計分析模型,通過考慮純金屬中的雙彎折過程和低合金中溶質原子與螺位錯的相互作用能來預測低合金中與應力和長度有關的雙彎折形核勢壘。與先前的文獻一樣,我們發現低合金化總是降低雙彎折形核勢壘,且這種降低與溶質或基體的元素種類無關。我們通過對Fe-Si模型合金的模擬,驗證了我們的模型。隨后,我們將模型結果與實際的Fe-Si、W-Ta和W-Re合金的實驗結果進行了比較,發現模型與實驗結果能夠定性吻合。我們利用提出的理論模型結合Maresca等人提出的非稀溶體理論,對稀固溶體到非稀固溶體的過渡進行了分析。結果表明Fe-Si合金的理論結果與實驗一致,而與W-Ta和W-Re合金則定性一致。本理論模型和Maresca的模型一起為較寬成分范圍的合金,從?1 at.%到幾個原子百分比,甚至高熵合金,提供了一個統一的預測框架,用于預測螺位錯的強化作用。
英文摘要
Yielding in pure BCC metals and dilute substitutional alloys occurs by double-kink nucleation and propagation along screw dislocations. At low temperatures, the yield stress is controlled by double-kink nucleation. Here, an analytical statistical model is presented to predict the stress- and length-dependent double-kink nucleation barrier in dilute BCC alloys solely in terms of the double-kink process in the pure metal and the solute/screw-dislocation interaction energies in the dilute alloy. Consistent with early literature, dilute alloying always reduces the double-kink nucleation barrier (softening) independent of solutes or matrix. The model is extensively validated via simulations in model Fe-Si alloys described by interatomic potentials. The model is then compared to experiments on real Fe-Si, W-Ta, and W-Re alloys, showing qualitative agreement consistent with the accuracy of the inputs. A cross-over from the dilute limit to the non-dilute limit, where there is hardening, is analyzed using the present theory and the non-dilute theory of Maresca et al. The analysis for Fe-Si is consistent with a cross-over at Si, as observed experimentally, and qualitatively consistent with W-Ta and W-Re. The present theory plus the recent theory of Maresca et al. together provide a coherent predictive framework for strengthening of screw dislocations over the full range of concentrations from extremely dilute (?1 at.%), to dilute (up to a few at.%) and non-dilute alloys including High Entropy Alloys.
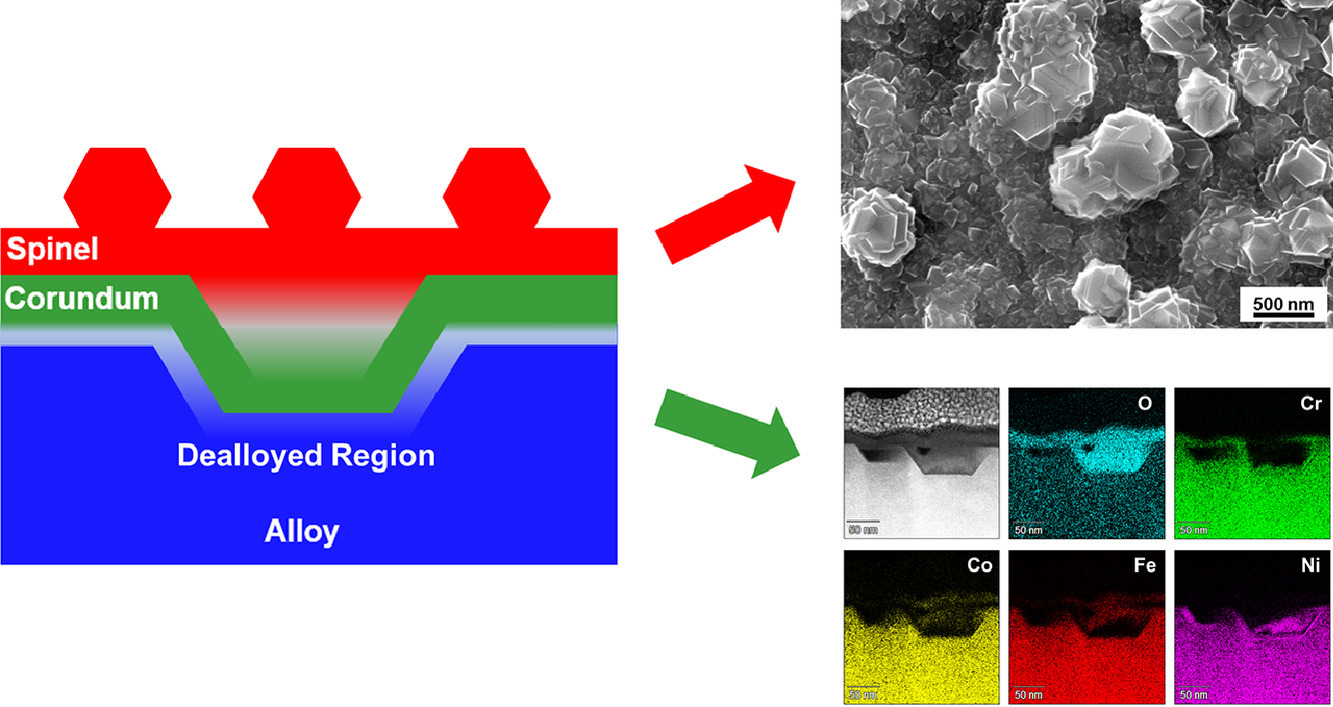
ACTA Vol. 196, 1 Sept. 2020, P651-659
34. Competition between thermodynamics, kinetics and growth mode in the early-stage oxidation of an equimolar CoCrFeNi alloy
一種等原子比CoCrFeNi合金氧化早期階段的熱力學、動力學和生長模式競爭
Xiao-Xiang Yu?, Matthew A. Taylor, John H. Perepezko, Laurence D. Marks
X.-X. Yu:yuxx07@gmail.com;
xiaoxiang.yu@northwestern.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.06.056
摘要
我們闡明了CoCrFeNi多主元素合金中的早期氧化取決于動力學和熱力學之間的競爭,包括陽離子和氧的相對擴散速率,以及它們如何與氧化物的內延或外延生長耦合。我們使用透射電子顯微鏡對500 ~ 800℃下0.5 小時形成的氧化層的微觀結構和化學成分進行了研究。觀測到一種三層結構,外層為富鐵尖晶石結構氧化物,中間為富鉻剛玉結構,內層是富Ni但貧Fe、貧Co、貧Cr的金屬/氧化物界面區。在800℃以下,剛玉結構中占主導的氧擴散導致剛玉結構向內生長,而尖晶石氧化物的生長則主要受陽離子擴散控制,因此向外生長。Cr被隔離在剛玉層中,從而促進了貧Cr富Fe且同時摻雜了Co和Ni的尖晶石氧化物的形成。由于Ni不能輕易地通過剛玉結構擴散,因此Ni傾向于留在合金相中,導致形成了金屬/氧化物界面的富鎳區域。除了以上這些微觀組織結果以外,我們還利用二次電子衍射說明了氧化物的摻雜性質,尖晶石結構為p型而剛玉結構為n型。
英文摘要
We demonstrate that the early-stage oxidation of a CoCrFeNi multi-principal element alloy depends upon a competition between kinetic and thermodynamic factors involving the relative diffusion rate of cations and oxygen, and how this couples to inward or outward oxide growth. The microstructures of oxide layers formed at temperatures from 500 to 800 °C for 0.5 h, as well as their chemical compositions, were investigated by transmission electron microscopy. A triple layer microstructure with an outer Fe-rich spinel oxide, an intermediate Cr-rich corundum structure, and a Ni-rich (Fe, Co, and Cr depleted) dealloyed region at the metal/oxide interface was observed. The dominant oxygen transport in corundum at 800 °C and below led to an inward growth of the corundum phase; the spinel oxide growth was dominated by cation diffusion, so it grew outward. The chromium was sequestered in the corundum layer, thereby favoring the formation of the chromium-free, Fe-rich spinel oxides with Co and Ni dopants. Since nickel cannot readily diffuse through corundum, it tends to remain in the alloy phase leading to the Ni-rich dealloyed region at the metal/oxide interface. Beyond the microstructure results, we exploit secondary electron image contrast to show the doping nature of the oxides, a p-type spinel and a n-type corundum growing on the metal surface.
ACTA Vol. 196, 1 Sept. 2020, P660-668
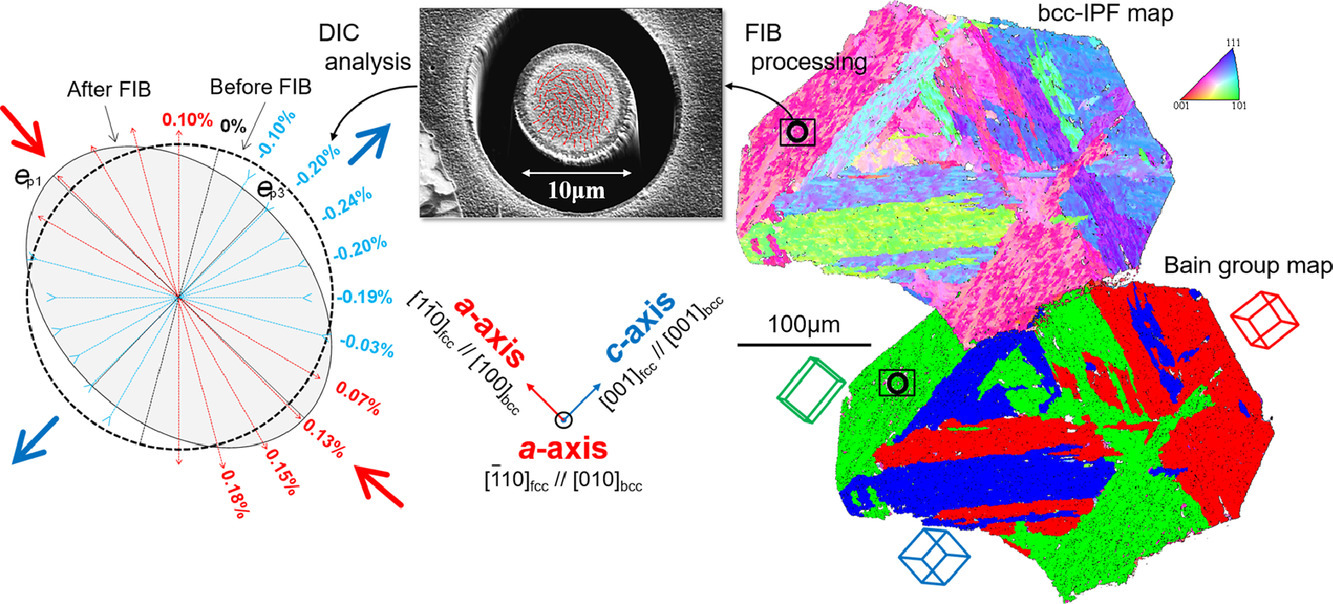
35. Internal residual stress originated from Bain strain and its effect on hardness in Fe–Ni martensite
Fe-Ni馬氏體中由于貝恩應變導致的殘余內應力及其對硬度的影響
Daisuke Fukui?, Nobuo Nakada?, Susumu Onaka?
D. Fukui:fukui.d.aa@m.titech.ac.jp
N. Nakada:nakada.n.aa@m.titech.ac.jp
S. Onaka:onaka.s.aa@m.titech.ac.jp
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.07.013
摘要
為了進一步理解鋼鐵材料中馬氏體相變導致的微觀內部殘余應力, 我們從宏觀和微觀兩個方面對無間隙原子Fe-16%Ni馬氏體中由于FCC和BCC相之間的貝恩關系所導致的內應力以及這種內應力對硬度的影響進行了研究。中子衍射和背散射電子衍射分析表明,即使在無碳情況下,BCC淬火馬氏體結構中也包含彈性畸變,這種畸變引起了一定的四方性,從而導致馬氏體的BCC[001] 傾向于平行于原奧氏體的FCC<001>。此外,微觀尺度下的聚焦離子束(FIB)和高精度數顯技術顯示, 經FIB加工的微柱會由于四方變形的淬火馬氏體殘余應力釋放而發生各項異性形變。這一結果表明,在馬氏體相變后,一小部分貝恩應變以彈性殘余應變的方式被保留在馬氏體半條的貝恩群中。更進一步地,殘余應變導致了內部的靜壓力,因此材料的納米硬度由于微柱加工過程中伴隨的內應力釋放而顯著降低。這意味著馬氏體的殘余內應力對馬氏體鋼的力學性能有不可忽視的影響。
英文摘要
To further understand the internal residual stress that is microscopically generated via martensitic transformation in steels, the origin of internal strain attributed to Bain correspondence between face-centered cubic (fcc) and body-centered cubic (bcc) was evaluated from macro- and micro-viewpoints and its effect on hardness was investigated in an interstitial free Fe-16%Ni martensite. Neutron diffractometry and electron backscatter diffraction analysis showed that body-centered cubic (bcc) crystal structure of as-quenched martensite contained elastic distortions leading to small tetragonality, even in martensitic steels without solute carbon, and that the extended [001]bcc of martensite tended to be parallel to <001>fcc of prior fcc austenite. In addition, the combination of micro-scale focused ion beam (FIB) and high-precision digital image correlation techniques revealed that a micropillar fabricated by FIB processing within a martensite block was anisotropically deformed by the release of the residual strain distributed in as-quenched martensite in correspondence with the tetragonal distortions of the bcc crystal structure. These results prove that a small part of the Bain strain remained as an internal elastic residual strain and was microscopically distributed among Bain groups in lath martensite after martensitic transformation. Furthermore, the residual strain generated a hydrostatic internal stress, and therefore, the nanohardness decreased considerably by the micropillar fabrication accompanied by the release of the internal stress. This means that the internal residual stress in martensite among Bain groups influences the mechanical properties of martensitic steel.
ACTA Vol. 196, 1 Sept. 2020, P690-703
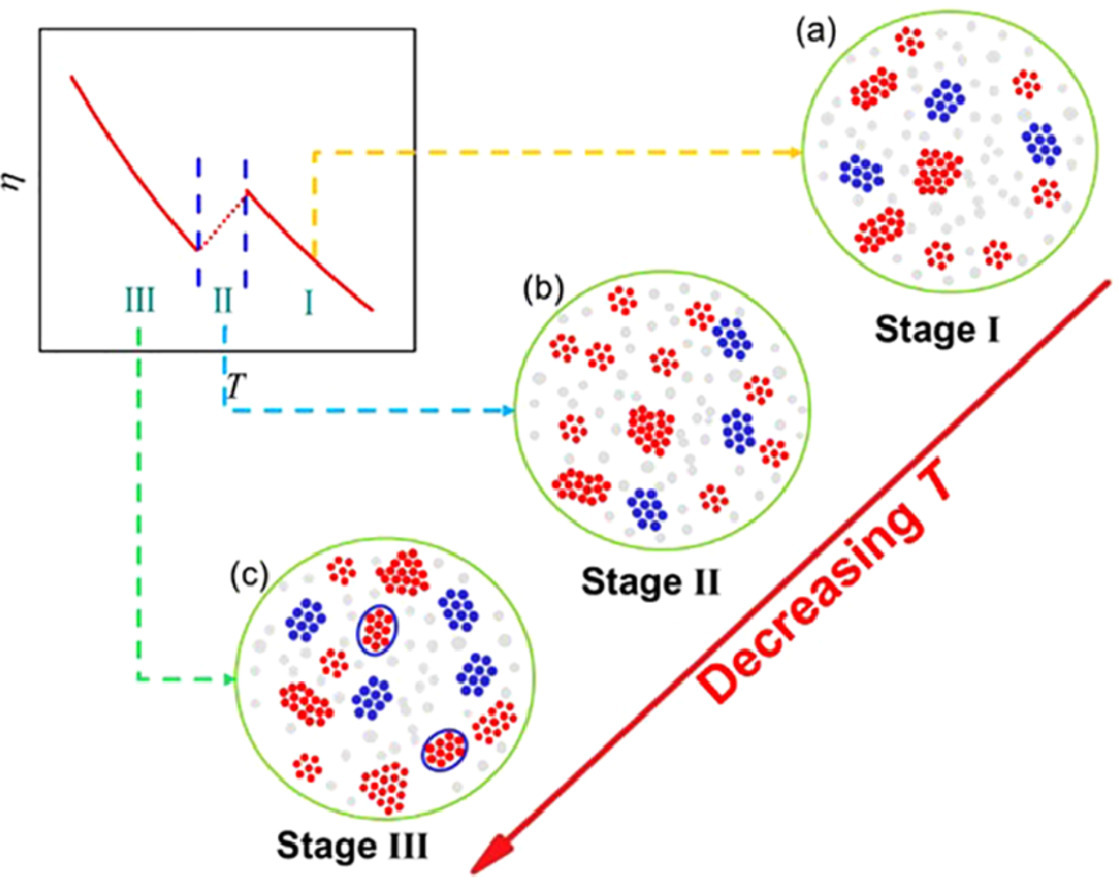
36. Generality of abnormal viscosity drop on cooling of CuZr alloy melts and its structural origin
CuZr合金熔體冷卻過程中粘度異常下降的普遍性及結構成因
Wei Chu, Jixiang Shang, Kuibo Yin, Nannan Ren, Lina Hu?, Yunbo Zhao, Bangshao Dong
L. Hu:hulina0850@sina.com;
hulina0614@sdu.edu.cn,山東大學
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.07.018
摘要
當超過液相線溫度后,合金熔體的粘度隨溫度降低單調增加,這一觀點已被廣泛接受。然而,我們在之前的工作中,發現當溫度升高時,一些合金熔體的粘度發生了明顯的降低。為了進一步了解這種異常現象,我們逐漸改變合金體系的組成,對CuZrAl和CuZrTiNi熔體的粘度進行了研究。結果表明,當摻雜元素(Al、Ti、Ni)的量足夠大時,這種異常的粘度降低現象消失。對于CuZr二元合金,當Zr含量在27.3-66.7%之間時存在異常現象,這與CuZr塊體金屬玻璃中Zr的可能含量十分接近。通過分子動力學模擬,我們發現了Cu62Zr38熔體中四種高脆性二十面體團簇隨溫度變化的機理。與冷卻過程中一般發生的團簇聚集或長大不同,當溫度升高至400 K左右時,這些團簇令人意外地趨向于分離,使液體中的分散度增大,而這也正是我們實驗中觀測到粘度開始下降的溫度。而在1300K以下,這些二十面體團簇再次突然聚集起來。熱差分析(DSC)和高分辨率透射電子顯微鏡(HRTEM)的實驗結果進一步證實了這些脆性的二十面體團簇對結晶過程的影響。這一發現揭示了塊體金屬玻璃形成和熔體動態異常的共同結構起源,闡明了脆性二十面體團簇在液體動力學特征中的主導作用。
英文摘要
It has been widely accepted that the viscosity of alloy melts increases monotonically with temperature decreasing after exceeding the liquidus temperature. However, a distinct viscosity-drop has been observed in several alloy melts in our previous works. To further understand this dynamic anomaly, we investigated the viscosity of CuZrAl and CuZrTiNi melts by gradually changing the compositions of alloy systems. The results suggest that when the amounts of doping elements (Al, Ti, Ni) become large enough, this abnormal viscosity-drop disappears. For CuZr binary alloys, the anomaly exists when the composition of Zr ranges between 27.3–66.7%, which nearly corresponds to the available content of Zr in CuZr bulk metallic glasses. By conducting molecular dynamics simulation, the mechanism that four icosahedron-like clusters with high fragility evolves with temperature in Cu62Zr38 melts has been recognized. In contrast to general aggregation or growth of clusters during cooling process, an unexpected tendency that more segregations are formed among these clusters and the clusters become further dispersed in liquids has been discovered around 1400 K; meanwhile, the viscosity-drop in our experiments begins simultaneously at this temperature. Below 1300 K, these icosahedron-like clusters aggregate abruptly again. Experimental results from differential scanning calorimeter (DSC) and high-resolution transmission electron microscope (HRTEM) further approve the influence of these fragile icosahedron-like clusters on crystallization processes. This finding uncovers the same structural origin that underlies both the formation of bulk metallic glasses and the dynamic anomaly in melts, and demonstrates the dominant role of fragile icosahedron-like clusters in the feature of liquid dynamics.
ACTA Vol. 196, 1 Sept. 2020, P710-722
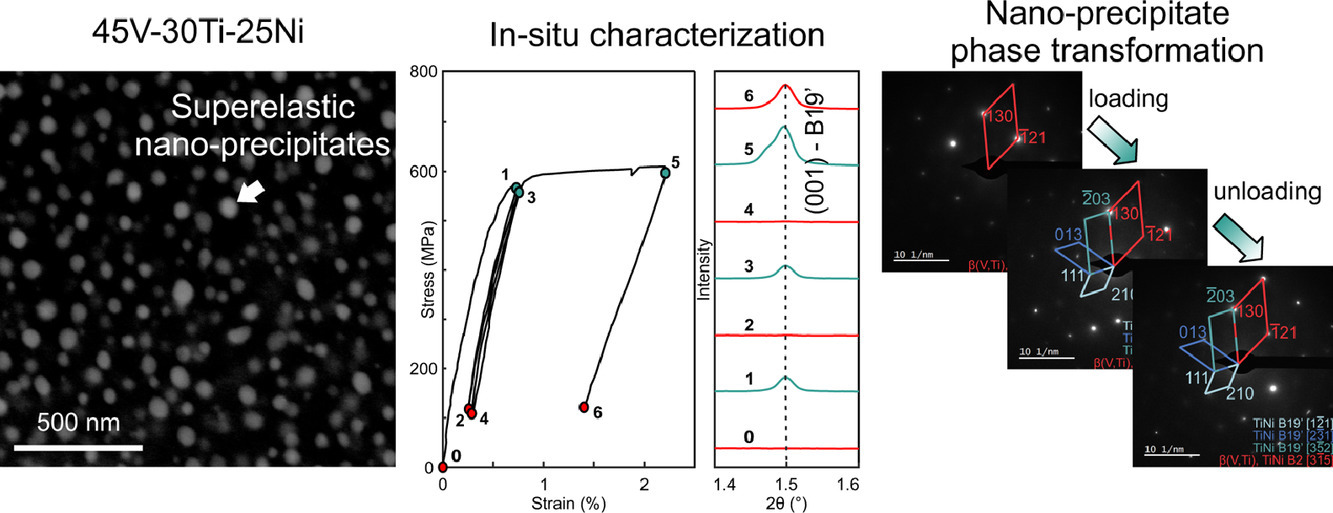
37. Design of a V–Ti–Ni alloy with superelastic nano-precipitates
基于超彈性納米析出相的V–Ti–Ni合金設計思路
J.-L. Zhang, J.L. Cann, S.B. Maisel, K. Qu, E. Plancher, H. Springer, E. Povoden-Karadeniz, P. Gao, Y. Ren, B. Grabowski, C.C. Tasan?
C.C. Tasan:tasan@mit.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.07.023
摘要
相變誘發塑性鋼(TRIP)使亞穩態合金表現出很強的應變硬化能力,從而提高成形性和韌性。TRIP效應產生的馬氏體由于其固有的脆性,會限制材料的延展性和疲勞壽命。在這項研究中,我們探索出了一種合金設計策略,利用應力誘導馬氏體相變,但卻不保留馬氏體相。這一策略的要點在于引入超彈性納米析出,這種析出在發生應力誘導相變后,會進一步發生反向相變。為此,我們利用第一性原理模擬和熱力學計算,設計并制造了一種V45Ti30Ni25 (at%)合金。在該合金中,TiNi以納米析出相形式均勻分布在韌性的富釩BCC基體中。我們通過掃描電鏡(SEM)和透射電鏡(TEM)對合金的微觀組織結構進行了表征;通過拉伸實驗測試了合金力學性能;通過原位TEM微柱壓縮實驗、原位高能衍射循環拉伸實驗、壓痕實驗和熱差掃描實驗證實了TiNi的可逆相變。此外,我們對實驗觀測到的影響TiNi穩定性的的相變路徑和變量進行了重點討論。
英文摘要
Stress-induced martensitic transformations enable metastable alloys to exhibit enhanced strain hardening capacity, leading to improved formability and toughness. As is well-known from transformation-induced plasticity (TRIP) steels, however, the resulting martensite can limit ductility and fatigue life due to its intrinsic brittleness. In this work, we explore an alloy design strategy that utilizes stress-induced martensitic transformations but does not retain the martensite phase. This strategy is based on the introduction of superelastic nano-precipitates, which exhibit reverse transformation after initial stress-induced forward transformation. To this end, utilizing ab-initio simulations and thermodynamic calculations we designed and produced a V45Ti30Ni25 (at%) alloy. In this alloy, TiNi is present as nano-precipitates uniformly distributed within a ductile V-rich base-centered cubic (bcc) β matrix, as well as being present as a larger matrix phase. We characterized the microstructure of the produced alloy using various scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) methods. The bulk mechanical properties of the alloy are demonstrated through tensile tests, and the reversible transformation in each of the TiNi morphologies were confirmed by in-situ TEM micro-pillar compression experiments, in-situ high-energy diffraction synchrotron cyclic tensile tests, indentation experiments, and differential scanning calorimetry experiments. The observed transformation pathways and variables impacting phase stability are critically discussed.
ACTA Vol. 196, 1 Sept. 2020, P733-746
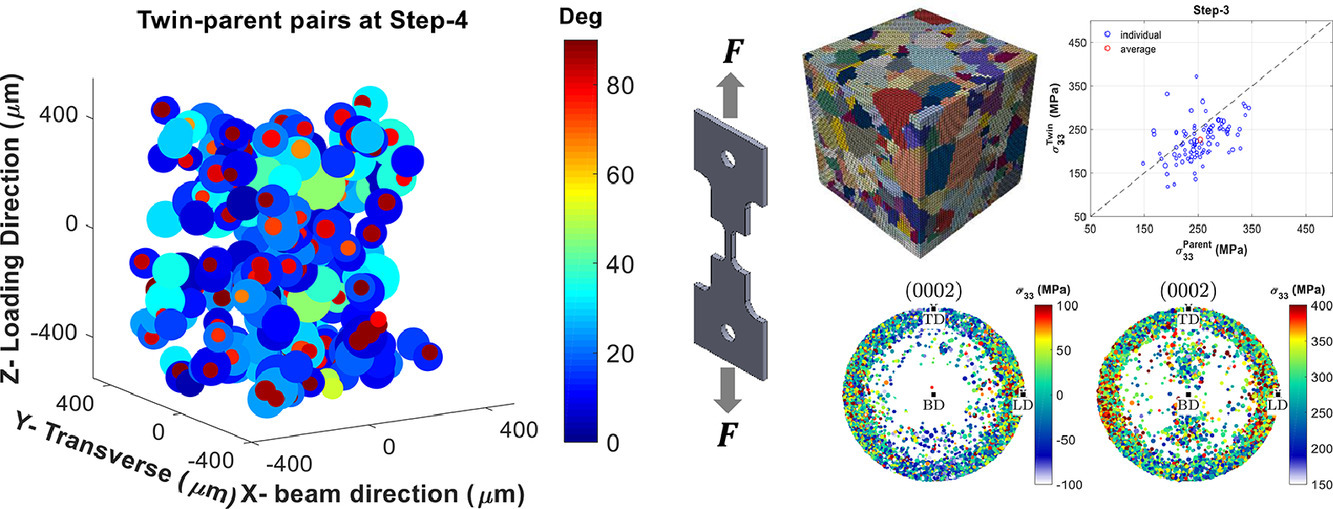
38. On the nucleation of deformation twins at the early stages of plasticity
塑性形變早期的形變孿晶形核過程研究
Hamidreza Abdolvand?, Karim Louca, Charles Mareau, Marta Majkut, Jonathan Wright
H. Abdolvand:hamid.abdolvand@uwo.ca
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.07.010
摘要
在晶粒尺度理解六方密堆晶體(HCP)的變形機制對于建立宏觀和微觀尺度的預測模型都是十分重要的。滑移和孿晶是HCP多晶在室溫下兩種主要的變形機制。在本工作中,我們對孿晶形核和長大過程中晶粒尺度上應力張量的變化進行了研究。我們采用三維同步輻射X射線衍射(3D-XRD),對HCP純鋯試樣變形過程中,測量了單一晶粒的質心、取向、彈性應變和應力進行了原位測量。隨后將觀測到的微觀結構導入晶體塑性有限元(CPFE)模型來模擬多晶的變形。我們詳細研究了塑性發生初期、塑性變形階段和卸載過程中孿晶和母晶中的應力演化過程,發現應力松弛在孿晶的形核階段并不明顯,但在塑性變形階段,應力松弛區孿晶與母晶之間的應力差顯著增大。在塑性的早期階段,所有六個孿晶變體都被激活,利用測得的晶粒應力張量可以對激活的變體進行一個較好的估計。
英文摘要
Understanding the deformation mechanisms of hexagonal close-packed (HCP) polycrystals at the grain scale is crucial for developing both macro and micro scale predictive models. Slip and twinning are the two main deformation mechanisms of HCP polycrystals at room temperature. In this paper, the development of grain-level stress tensors during nucleation and growth of twins is investigated. A pure zirconium specimen with HCP crystals is deformed in-situ while the centre-of-mass, orientation, elastic strain, and stress of individual grains are measured by three-dimensional synchrotron X-ray diffraction (3D-XRD). The observed microstructure is subsequently imported into a crystal plasticity finite element (CPFE) model to simulate the deformation of the polycrystal. The evolution of stress in twin-parent pairs at the early stages of plasticity, further into plasticity zone, and unload is studied. It is shown that twins do not relax very much at the nucleation step, but the difference between the measured stress in the twin and parent increases further into plastic zone where twins relax. While at the early stages of plasticity all six twin variants are active, a slightly better estimation of active variants is obtained using the measured grain-resolved stress tensors.
ACTA Vol. 196, 1 Sept. 2020, P747-758
39. Solute-vacancy clustering in aluminum
鋁合金中的溶質原子-空位團簇
Jian Peng, Sumit Bahl, Amit Shyam, J. Allen Haynes, Dongwon Shin?
D. Shin:shind@ornl.gov
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.06.062
摘要
在本研究中,我們建立了一個鋁合金中溶質原子-空位、同種溶質原子、異種原子和溶質原子-溶質原子-空位結合能的第一原理數據庫。我們重點關注了鋁合金中最主要的幾種合金元素,例如Cu、Mg、Si。計算得到的溶質原子-空位結合能、溶液原子對結合能和溶原子-溶質原子-空位結合能與文獻中已有的實驗和理論結果一致。我們考慮了溶質原子尺寸、金屬間化合物形成能等物理因素,將它們與結合能建立聯系。對于同種原子形成的溶質原子-溶質原子-空位復合體和(Cu/Mg/Si)-溶質原子空位復合體的系統研究表明空位對于穩定溶質原子對具有決定性的作用。結合能數據庫闡明了鋁合金中溶質原子團簇與空位之間的相互作用,并為Al合金的設計和性能調控提供了有效的指導。
英文摘要
We present an extensive first-principles database of solute-vacancy, homoatomic, heteroatomic solute-solute, and solute-solute-vacancy binding energies of relevant alloying elements in aluminum. We particularly focus on the systems with major alloying elements in aluminum, i.e., Cu, Mg, and Si. The computed binding energies of solute-vacancy, solute-solute pairs, and solute-solute-vacancy triplets agree with available experiments and theoretical results in literature. We consider physical factors such as solute size and formation energies of intermetallic compounds to correlate with binding energies. Systematic studies of the homoatomic solute-solute-vacancy and heteroatomic (Cu, Mg, or Si)-solute-vacancy complexes reveal the overarching effect of the vacancy in stabilizing solute-solute pairs. The binding energy database presented here elucidates the interaction between solute cluster and vacancy in aluminum, and it is expected to provide insight into the design of advanced Al alloys with tailored properties.
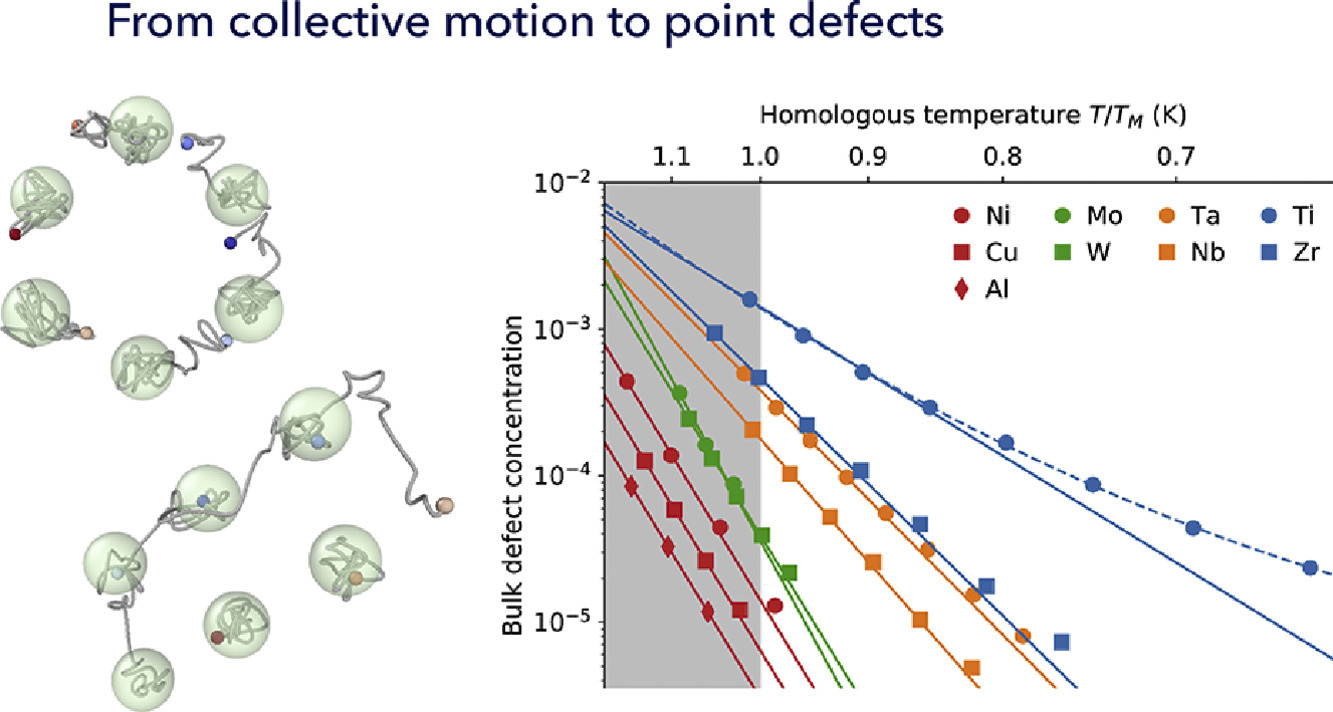
ACTA Vol. 196, 1 Sept. 2020, P770-775
40. Defects from phonons: Atomic transport by concerted motion in simple crystalline metals
聲子缺陷:簡單金屬晶體中協調運動導致的原子遷移
Erik Fransson, Paul Erhart?
P. Erhart:erhart@chalmers.se
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.06.040
摘要
點缺陷在晶體材料中有至關重要的作用,它們同時影響熱力學性質和動力學過程。雖然它們在熱力學平衡中是必要的,但一般認為,除了在接近熔點的溫度以外,體系中很自發形成大量點缺陷。在本研究中,我們通過原子模擬的方法說明了,在體心立方金屬中,即使在低至熔點溫度50%的情況下,由于原子協調運動過程導致點缺陷形成實際上是經常發生的。研究表明,這種行為與晶格振動的非諧性和沿某些晶體方向的能量分布密切相關,而這一特征在面心立方等結構中并不存在。這一結果對我們對材料的一般理解很有幫助,并為所謂的第4族過渡金屬中的反常擴散提供了補充解釋。
英文摘要
Point defects play a crucial role in crystalline materials as they do not only impact the thermodynamic properties but are also central to kinetic processes. While they are necessary in thermodynamic equilibrium spontaneous defect formation in the bulk is normally considered highly improbable except for temperatures close to the melting point. Here, we demonstrate by means of atomistic simulations that processes involving concerted atomic motion that give rise to defect formation are in fact frequent in body-centered cubic metals even down to about 50% of the melting temperature. It is shown that this behavior is intimately related to the anharmonicity of the lattice vibrations and a flat energy landscape along certain crystallographic directions, a feature that is absent in, e.g., face-centered cubic lattice structures. This insight has implications for our general understanding of these materials and furthermore provides a complementary explanation for the so-called anomalous diffusion in group 4 transition metals.
ACTA Vol. 196, 1 Sept. 2020, P776-789
41. Creating, probing and confirming tetragonality in bulk FeNi alloys
創造、檢測并確認塊體Fe-Ni合金的四方性
N. Maât, I. McDonald, R. Barua, B. Lejeune, X. Zhang, G.M. Stephen, A. Fisher, D. Heiman, I.V. Soldatov, R. Schäfer, L.H. Lewis?
L.H. Lewis:lhlewis@northeastern.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.07.019
摘要
本文中,我們報導了采用一種獨特而簡單的工具——多驅動爐,對材料進行長時間退火的同時施加無源均勻飽和磁場和拉應力對材料產生的影響。我們以經強烈變形后退火的等原子比Fe-Ni合金為研究對象,通過高能同步輻射X射線衍射和磁光科爾顯微鏡對其晶體結構和磁疇狀態的演化進行了研究。這種材料在天文時間尺度上才會發生一級相變,轉變為化學有序的L10結構。我們發現,經多驅動爐處理后的樣本與在相同條件下退火但未受磁場和應力作用的樣品相比,會保持立方晶體結構以及和之前形變態相同的織構,同時晶胞體積減小,c/a增大。對磁疇的觀測結果表明:鑄態Fe-Ni合金表現出與應力改性立方磁性晶體各向異性相一致的磁疇狀態,而經多驅動爐退火的樣品中則出現了大面積的單軸各向異性磁疇。盡管樣品中還未形成化學有序,但我們提出的這種策略——即使用無源梯度磁場加快擴散,還是能夠在一定程度上實現合金中的有序態轉變。
英文摘要
Effects derived from the simultaneous application of passive, uniform saturating magnetic field and tensile stress during long-time annealing utilizing a unique and simple processing tool, the MultiDriver furnace, are reported. In particular, the evolution of the crystalline structure and the magnetic domain configuration of severely deformed and subsequently annealed equiatomic FeNi alloys were revealed by high-energy synchrotron X-Ray diffraction and Magneto-Optic Kerr Microscopy. These alloys are known to undergo a first-order magnetic phase transformation to a chemically ordered tetragonal (L10) structure in astronomical timeframes. MultiDriver-annealed specimens are found to retain a tetragonal crystallographic state and texture that is similar to that of the precursor deformed state, with a smaller unit cell volume and a larger c/a ratio relative to those of control samples that were annealed under the same conditions but without magnetic field and stress drivers. Magnetic domain images echo these observations: while as-cast FeNi alloys exhibit domain patterns consistent with the presence of a stress-modified cubic magnetocrystalline anisotropy, large areas of domains with uniaxial anisotropy are present in MultiDriver-annealed samples. While no chemical order was demonstrated in these samples, a strategy is proposed for achieving the ordered state by employing a passive magnetic gradient in the MultiDriver furnace to enhance diffusion.
微信公眾號:Goal Science
投稿郵箱:wechat@gs-metals.com
投稿微信:GSmaterial
