金屬頂刊雙語導(dǎo)讀丨Acta Mater. Vol.197,15 Sept. 2020(全)
2020-08-31 來源: Goal Science
本期包含金屬材料領(lǐng)域論文21篇,涵蓋了高熵合金、鋁合金、鈦合金、鋯合金、高錳鋼、雙相不銹鋼、多相鋼、3D打印等,國內(nèi)科研單位包括大連理工大學(xué)、沈陽金屬所、北京科技大學(xué)、東北大學(xué)、中科院固體物理研究所等(通訊作者單位)。
Vol. 197 目錄
ACTA Vol. 197, 15 Sept. 2020, P10-19
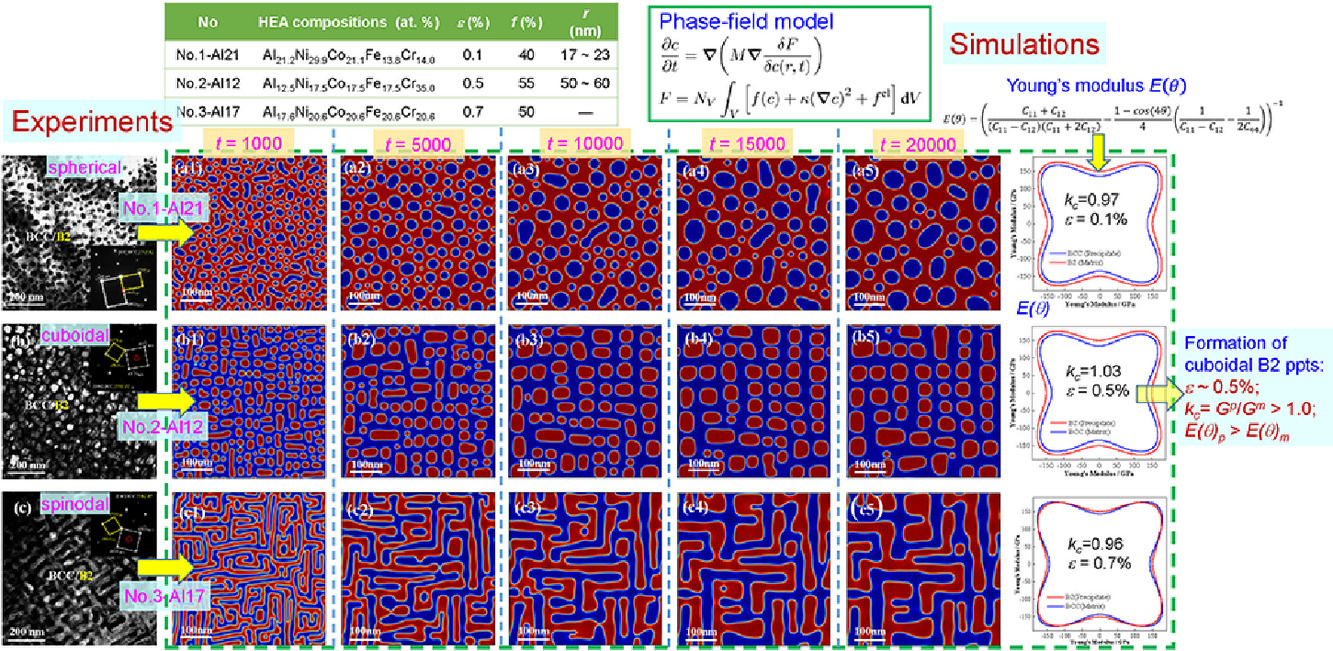
1. Phase-field simulation of coherent BCC/B2 microstructures in high entropy alloys
高熵合金中共格BCC/B2組織的相場模擬
J.L. Li, Z. Li?, Q. Wang?, C. Dong, P.K. Liaw
Z.Li:lizhen@dlut.edu.cn,大連理工大學(xué)
Q.Wang:wangq@dlut.edu.cn,大連理工大學(xué)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.07.030
摘要
在本工作中,我們使用了相場模型模擬了BCC基體的Al-Ni-Co-Fe-Cr 高熵合金中的共格BCC/B2組織。在實(shí)驗(yàn)中,這些共格的BCC/B2組織中含有球形或立方的納米沉析出,并且有時(shí)會(huì)發(fā)生調(diào)幅分解。我們基于Chan-Hilliard方程,利用COMSOL軟件建立了二維相場模型,揭示了高熵合金中這種組織的演化過程。模擬的析出與調(diào)幅分解與實(shí)驗(yàn)結(jié)果吻合較好。析出相與基體之間的晶格錯(cuò)配和楊氏模量各向之間的差異都會(huì)影響析出相的形貌,其中立方納米析出對模量各向異性尤其敏感。基于模擬結(jié)果,我們進(jìn)一步討論了析出物的粗化行為。我們的研究表明,相場模型可以很好地預(yù)測高熵合金的組織演變并輔助新型高熵合金的設(shè)計(jì)。
英文摘要
This present work simulated the coherent BCC/B2 microstructures existing in body-centered-cubic (BCC)-based Al-Ni-Co-Fe-Cr high entropy alloys (HEAs) in light of the phase-field method. These coherent BCC/B2 microstructures contain spherical or cuboidal nanoprecipitates, or exhibit a weave-like spinodal decomposition in experiments. Based on the Chan-Hilliard equation, a two-dimensional phase field model was established using the COMSOL Multiphysics software to reveal the coherent microstructural evolutions of the present HEAs. It was found that the simulations of spherical/cuboidal nanoprecipitations and weave-like spinodal decomposition are well consistent with the experimental results. Both the lattice misfit and the anisotropy difference of Young's moduli between the precipitated phase and matrix phase affect the precipitate morphology, in which the cuboidal nanoprecipitation is especially susceptible to the modulus anisotropy. The coarsening behavior of precipitates is also discussed with the aid of the simulation results. The phase-field simulation will provide an important technique to predict the microstructural evolution and to assist the composition design of new HEAs.
ACTA Vol. 197, 15 Sept. 2020, P20-27
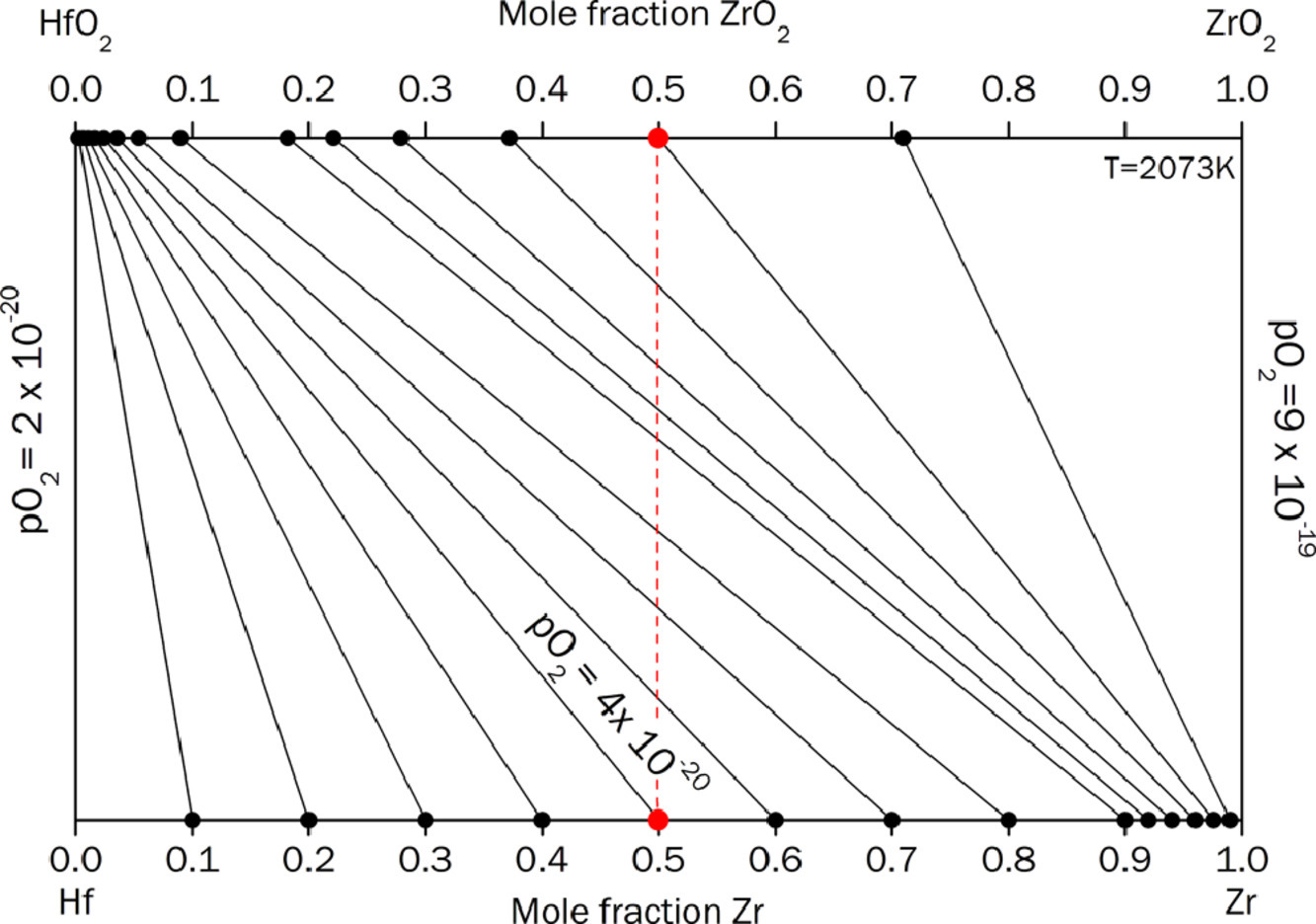
2. Part I: Theoretical predictions of preferential oxidation in refractory high entropy materials
難熔高熵材料中的優(yōu)先氧化(第一部分):理論預(yù)測
Lavina Backman?, Joshua Gild?, Jian Luo?, Elizabeth J. Opila?
L. Backman:lb2ty@virginia.edu
J. Gild:jgild@ucsd.edu
J. Luo:jluo@ucsd.edu
E.J. Opila:opila@virginia.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.07.003
摘要
高熵材料,包括高熵合金、碳化物和硼化物,是目前材料研究的熱點(diǎn)之一,因?yàn)樗鼈兊某煞址秶采w很廣,其中的某些新材料可能能夠填補(bǔ)目前應(yīng)用需求的空白領(lǐng)域。現(xiàn)階段的高端技術(shù)領(lǐng)域?qū)Σ牧系母邷匦阅埽貏e是抗氧化性能具有迫切的需求,因此我們有必要對高熵材料的氧化行為進(jìn)行系統(tǒng)研究。之前的研究已經(jīng)發(fā)現(xiàn),高熵材料氧化過程中,不同氧化物形成的優(yōu)先度具有很大差異。在本工作中,我們基于熱力學(xué)計(jì)算和分析,對以IV、V、VI族元素為主要組成的高熵合金和陶瓷材料中的這種優(yōu)先氧化行為進(jìn)行了量化研究。熱力學(xué)計(jì)算表明,在這些材料中存在較強(qiáng)的優(yōu)先氧化傾向,即使對于那些發(fā)生氧化后熱力學(xué)性質(zhì)差異性較小的元素也是如此。與合金相比較,碳化物中的這種現(xiàn)象相對較弱。此外,高熵材料中的優(yōu)先氧化可能會(huì)導(dǎo)致固溶體的失穩(wěn)或其他競爭相的形成,從而導(dǎo)致材料的性能發(fā)生相應(yīng)的變化。
英文摘要
High entropy materials, which include high entropy alloys, carbides, and borides, are a topic of substantial research interest due to the possibility of a large number of new material compositions that could fill gaps in application needs. There is a current need for materials exhibiting high temperature stability, particularly oxidation resistance. A systematic understanding of the oxidation behavior in high entropy materials is therefore required. Prior work notes large differences in the thermodynamic favorability between oxides formed upon oxidation of high entropy materials. This work uses both analytical and computational thermodynamic approaches to investigate and quantify the effects of this large variation and the resulting potential for preferential component oxidation in refractory high entropy materials including group IV-, V- and VI-element based alloys and ceramics. Thermodynamic calculations show that a large tendency towards preferential oxidation is expected in these materials, even for elements whose oxides exhibit a small difference in thermodynamic favorability. The effect is reduced in carbides, compared to their alloy counterparts. Further, preferential oxidation in high entropy refractory materials could result in possible destabilization of the solid solution or formation of other, competing phases, with corresponding changes in bulk material properties.
ACTA Vol. 197, 15 Sept. 2020, P81-90
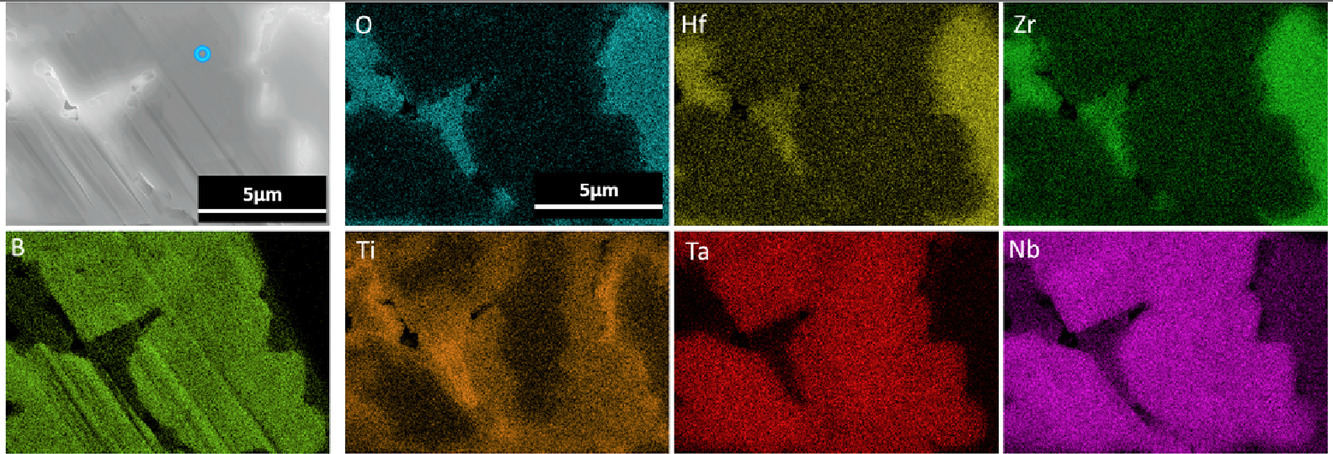
3. Part II: Experimental verification of computationally predicted preferential oxidation of refractory high entropy ultra-high temperature ceramics
難熔高熵材料中的優(yōu)先氧化(第二部分):關(guān)于高熵陶瓷在超高溫條件下優(yōu)先氧化理論預(yù)測的實(shí)驗(yàn)驗(yàn)證
Lavina Backman?, Joshua Gild?, Jian Luo?, Elizabeth J. Opila?
L. Backman:lb2ty@virginia.edu
J. Gild:jgild@ucsd.edu
J. Luo:jluo@ucsd.edu
E.J. Opila:opila@virginia.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.07.004
摘要
高熵材料由于其在高溫結(jié)構(gòu)中的應(yīng)用潛力而受到廣泛關(guān)注。抗氧化是高溫合金設(shè)計(jì)面臨的主要挑戰(zhàn),而我們對于高熵合金獨(dú)特氧化機(jī)制的理解還遠(yuǎn)遠(yuǎn)不夠。之前已有文獻(xiàn)利用熱力學(xué)計(jì)算分析輔助設(shè)計(jì)含有IV族(Hf, Zr, Ti)和V族(Ta, Nb)元素的高熵材料,本工作是對該研究的實(shí)驗(yàn)補(bǔ)充。我們以(Hf0.2Zr0.2Ti0.2Ta0.2Nb0.2)碳化物和二硼化物為研究對象,將試樣在1700℃ 1% O2條件下暴露了5分鐘。研究表明,在相同溫度下,實(shí)驗(yàn)結(jié)果與計(jì)算預(yù)測一致,盡管兩者在氧化區(qū)形貌方面還存在一定差異。碳化物形成了多孔的氧化物,而二硼化物形成了更加致密的外部結(jié)構(gòu)。氧化產(chǎn)物以IV族氧化物為主,由于消耗了下層材料中的對應(yīng)元素,因此下層材料主要由V族碳化物或硼化物組成。本研究為高熵材料在超高溫下的氧化提供了一個(gè)初步的觀察,并驗(yàn)證了模擬計(jì)算所預(yù)測的高熵材料的優(yōu)先氧化性質(zhì)。
英文摘要
Refractory high entropy materials have garnered significant research interest due to their potential ability to fill a need in high temperature structural applications. However, challenges remain with respect to designing for oxidation resistance. A knowledge gap exists with respect to a rigorous understanding of the mechanisms driving oxidation processes unique to high entropy materials. This work provides an experimental complement to a companion publication, which outlines analytical and computational thermodynamic approaches that are envisioned to aid the design of refractory high entropy materials containing group IV (Hf, Zr, Ti) and group V (Ta, Nb) constituents. In this work, (Hf0.2Zr0.2Ti0.2Ta0.2Nb0.2) carbide and diboride specimens were exposed at 1700°C in 1% O2 for 5 min. Experimental results show good agreement with the computational predictions for the same temperature, despite differences in the overall morphology of the oxidized regions. The carbide formed porous oxides, while the diboride formed a denser external scale. Oxidation products are dominated by group IV oxides, depleting the underlying materials, which were found to consist of primarily group V carbides and borides respectively. The results provide a first look at the oxidation of high entropy UHTCs at ultra-high temperatures and validate the preferential nature of high entropy material oxidation predicted by the computational approach developed for the study of this new class of materials.
ACTA Vol. 197, 15 Sept. 2020, P28-39
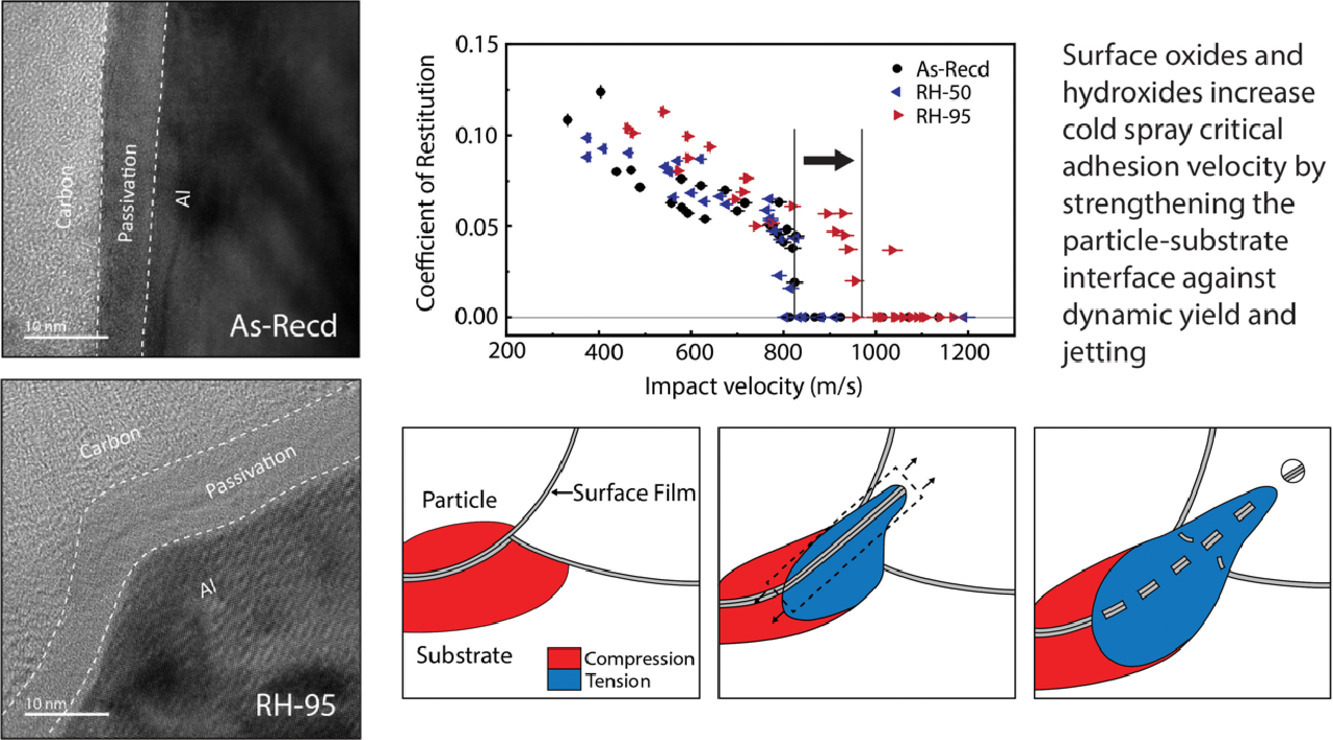
4. Surface oxide and hydroxide effects on aluminum microparticle impact bonding
表面氧化物和氫氧化物對鋁合金中微粒沖擊連接的影響
Jasper Lienhard, Cameron Crook, Maryam Zahiri Azar, Mostafa Hassani, Daniel R. Mumm, David Veysset, Diran Apelian, Keith A. Nelson, Victor Champagne, Aaron Nardi, Christopher A. Schuh?, Lorenzo Valdevit
C.A. Schuh:schuh@mit.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.07.011
摘要
在冷噴沖擊粘接過程中,氧化物、氫氧化物和其他表面會(huì)阻礙冶金結(jié)合,提高臨界附著速度,降低鍍層質(zhì)量。我們利用單粒子沖擊成像方法,研究了暴露在不同溫度和濕度水平下的鈍化表面氧化物對鋁的冷噴涂臨界附著速度的影響。我們通過透射電子顯微鏡(TEM)、X射線光電子能譜(XPS)和傅里葉變換紅外光譜(FTIR)分析了鈍化層的厚度、成分和微觀結(jié)構(gòu),并將其與觀察得到的不同表面的臨界附著速度之間建立了聯(lián)系。研究結(jié)果表明: 在高達(dá)300°C的干燥空氣中暴露240分鐘,或在濕度50%的室溫條件下暴露4天,表面氧化層對臨界附著速度的影響幾乎可以忽略不計(jì)。而在95% 相對濕度的環(huán)境溫度下暴露4天后,臨界附著速度增加了125m /s以上,約14%。我們發(fā)現(xiàn)臨界附著速度的這種明顯變化與暴露在高濕度環(huán)境下導(dǎo)致的鈍化層厚度、均勻性、結(jié)晶度和成分變化有關(guān)。以上結(jié)果表明,顆粒表面處理可以改善冷噴涂工藝。
英文摘要
Oxides, hydroxides, and other surface films act as impediments to metallurgical bonding during cold spray impact adhesion, raising the critical adhesion velocity and reducing the quality of the deposited coating. Using a single-particle impact imaging approach we study how altering the passivating surface oxides with exposures to various levels of heat and humidity affect the cold spray critical adhesion velocity in the case of aluminum. We analyze the thickness, composition and microstructure of the passivation layers with transmission electron microscopy (TEM), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), and Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), and correlate our observations with a direct measurement of the critical adhesion velocity for each surface treatment. We conclude that exposures to temperatures as high as 300 °C for up to 240 min in dry air, or to room-temperature with humidity levels as high as 50% for 4 days, have negligible effect on the surface oxide layers, and by extension do not affect the critical adhesion velocity. In contrast, ambient-temperature exposure to 95% relative humidity levels for 4 days increases the critical adhesion velocity by more than 125 m/s, approximately a 14% percent increase. We observe that this distinct change in critical adhesion velocity is correlated with unique changes in the passivating layer thickness, thickness uniformity, crystallinity and composition resulting from exposure to high humidity. These results speak to particle surface treatments to improve the cold spray process.
ACTA Vol. 197, 15 Sept. 2020, P40-53
5. A solution to the hot cracking problem for aluminium alloys manufactured by laser beam melting
一種激光熔化鋁合金熱裂紋問題的解決方案
Mathieu Opprecht?, Jean-Paul Garandet?, Guilhem Roux?, Camille Flament?, Mathieu Soulier?
M. Opprecht:mathieu.opprecht@cea.fr
J.-P. Garandet:jeanpaul.garandet@cea.fr
G. Roux:guilhem.roux@cea.fr
C. Flament:camille.flflament@cea.fr
M. Soulier:mathieu.soulier@cea.fr
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.07.015
摘要
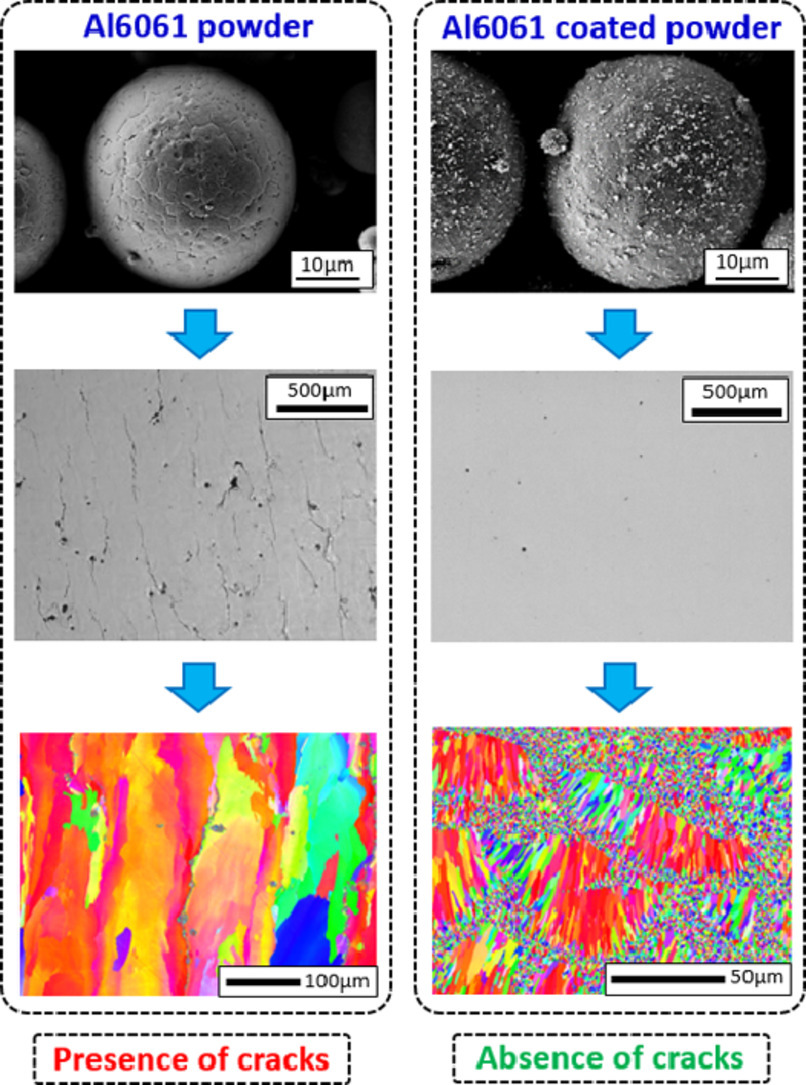
在本研究中,我們提出了一種消除激光熔化鋁合金中熱裂的方法,并以6061合金為例進(jìn)行了驗(yàn)證。6061是一種沉淀強(qiáng)化鋁合金,主要合金元素為鎂和硅。這種合金因其優(yōu)異的重量強(qiáng)度比和高導(dǎo)熱系數(shù)而在航空和汽車工業(yè)中被廣泛使用,但是卻特別容易在激光熔化加工過程中發(fā)生熱裂。我們提出的消除裂紋的方法是:通過引入晶粒細(xì)化阻礙柱狀晶的生長。為此, 我們向Al6061金屬粉末中加入了不同含量的釔穩(wěn)定氧化鋯(YSZ)。實(shí)驗(yàn)發(fā)現(xiàn)添加的YSZ含量對晶粒細(xì)化的效果影響很大。加入1vol %YSZ時(shí),SEM和EBSD結(jié)果顯示材料為雙峰晶粒尺寸分布的等軸柱晶組織。加入2 vol% YSZ時(shí),由于在熔池形成連續(xù)等軸帶,使得熱裂被完全避免。此外,TEM和DRX實(shí)驗(yàn)結(jié)果為3D打印過程中粒子的演化提供了新的認(rèn)識。我們在已有凝固模型的基礎(chǔ)上對實(shí)驗(yàn)結(jié)果進(jìn)行了討論,其中重點(diǎn)討論了建立等軸凝固體系的必要條件。
英文摘要
A method to eliminate hot cracking phenomena for aluminium alloys in Laser Beam Melting (LBM) is presented in this paper, focused here on the 6061 alloy. 6061 is a precipitation-hardened aluminium alloy, containing magnesium and silicon as its major alloying elements. This alloy, commonly used in the aeronautic and automotive industries, thanks to its excellent weight to strength ratio and high thermal conductivity, is particularly prone to hot cracking, in particular during LBM processing. The solution to remove cracks proposed in the present paper is to induce grain refinement to avoid the development of large columnar structures. To this end, various quantities of Yttrium Stabilized Zirconia (YSZ) are added to an Al6061 base powder using a dry mixing (Turbula?) procedure. Experiments highlight a grain refinement effect depending on the added YSZ quantity. From 1 vol% on, SEM and EBSD images reveal an equiaxed-columnar bimodal grain microstructure. Results show that the addition of 2 vol% YSZ allows to fully avoid cracks due to a continuous equiaxed band at melt pool boudaries. Additionally, TEM and DRX investigations provide new insights into the becoming of added particles along the printing process. The experimental results are then discussed on the basis of a number of existing solidification models, with a focus on the necessary conditions for the establishment of an equiaxed solidification regime.
ACTA Vol. 197, 15 Sept. 2020, P54-68
6. Atomistic deformation behavior of single and twin crystalline Cu nanopillars with preexisting dislocations
含有預(yù)存位錯(cuò)的單晶和孿晶Cu納米微柱中原子尺度的變形行為
Won-Seok Ko?, Alexander Stukowski, Raheleh Hadian, Ali Nematollahi, Jong Bae Jeon, Won Seok Choi, Gerhard Dehm, Jörg Neugebauer, Christoph Kirchlechner, Blazej Grabowski
W.-S. Ko:wonsko@ulsan.ac.kr
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.07.029
摘要
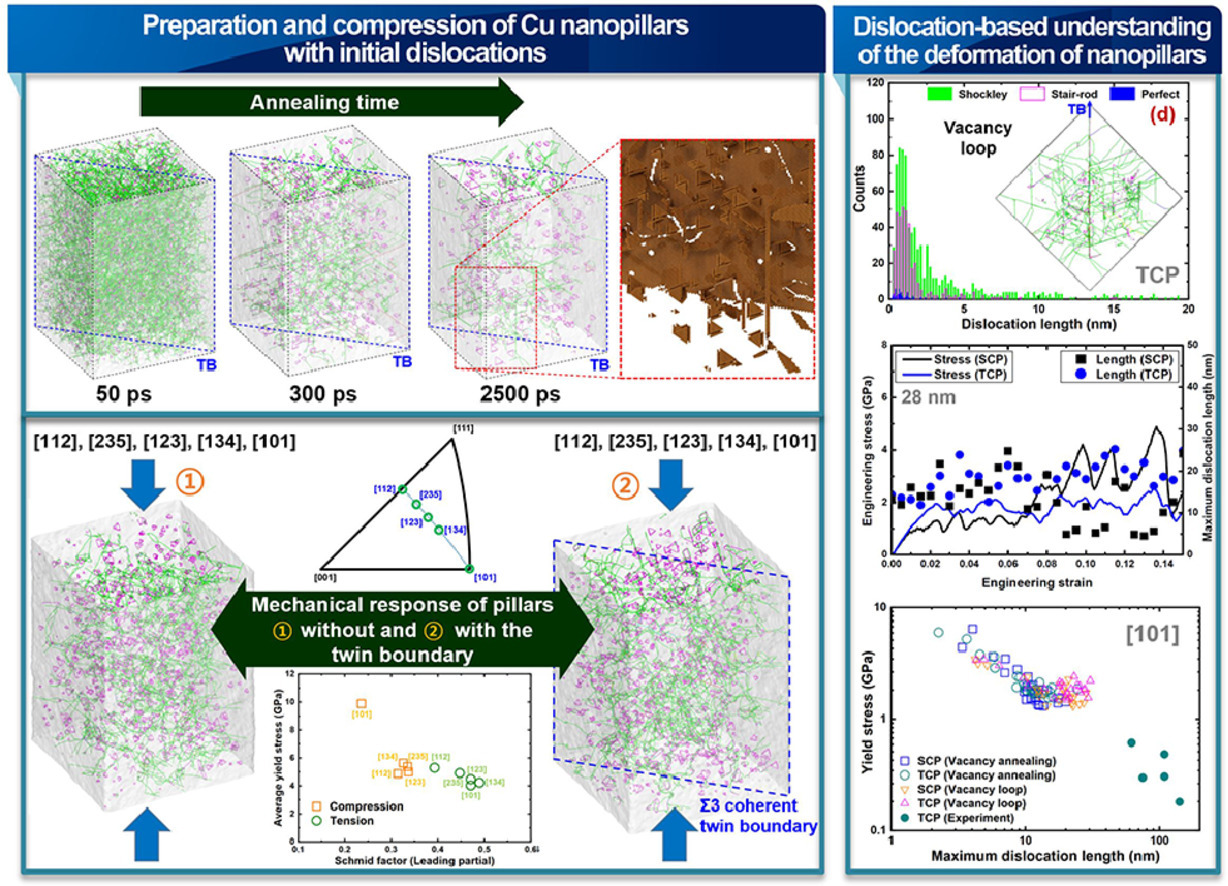
我們使用了分子動(dòng)力學(xué)研究了共格Σ3 (111)孿晶界對Cu納米微柱塑性變形的影響。研究表明,含有孿晶界和不含孿晶界的微柱的力學(xué)響應(yīng)是由初始位錯(cuò)源的特性決定的。在微柱尺寸相對較大,且其中含有大量初始可動(dòng)位錯(cuò)的情況下,屈服強(qiáng)度和流變應(yīng)力取決于最長的那根可動(dòng)位錯(cuò)。我們建立了最長位錯(cuò)的長度與屈服和流變應(yīng)力之間的關(guān)系,并將其與實(shí)驗(yàn)結(jié)果進(jìn)行了比較。含有孿晶和不含孿晶的微柱的屈服和流變應(yīng)力之間的細(xì)微差別極有可能與最大可動(dòng)位錯(cuò)長度有關(guān)。而在微柱尺寸相對較小,且可動(dòng)位錯(cuò)數(shù)量較少的情況下,含有孿晶和不含孿晶的微柱的屈服和流變應(yīng)力則具有明顯區(qū)別。由于孿晶界可以有效釘扎位錯(cuò)網(wǎng)絡(luò),因此這種情況下,變形時(shí)不含孿晶界的微柱中的位錯(cuò)缺乏就極為顯著了。
英文摘要
Molecular dynamics simulations are performed to investigate the impact of a coherent Σ3 (111) twin boundary on the plastic deformation behavior of Cu nanopillars. Our work reveals that the mechanical response of pillars with and without the twin boundary is decisively driven by the characteristics of initial dislocation sources. In the condition of comparably large pillar size and abundant initial mobile dislocations, overall yield and flow stresses are controlled by the longest, available mobile dislocation. An inverse correlation of the yield and flow stresses with the length of the longest dislocation is established and compared to experimental data. The experimentally reported subtle differences in yield and flow stresses between pillars with and without the twin boundary are likely related to the maximum lengths of the mobile dislocations. In the condition of comparably small pillar size, for which a reduction of mobile dislocations during heat treatment and mechanical loading occurs, the mechanical response of pillars with and without the twin boundary can be clearly distinguished. Dislocation starvation during deformation is more pronounced in pillars without the twin boundary than in pillars with the twin boundary because the twin boundary acts as a pinning surface for the dislocation network.
ACTA Vol. 197, 15 Sept. 2020, P69-80
7. Effects of Mo on the mechanical behavior of γ/γ?-strengthened Co-Ti-based alloys
Mo元素對γ/γ?強(qiáng)化Co-Ti基合金力學(xué)性能的影響
Hye Ji Im, Subin Lee, Won Seok Choi, Surendra Kumar Makineni, Dierk Raabe, Won-Seok Ko?, Pyuck-Pa Choi?
W.-S. Ko:wonsko@ulsan.ac.kr
P.-P. Choi:p.choi@kaist.ac.kr
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.07.037
摘要
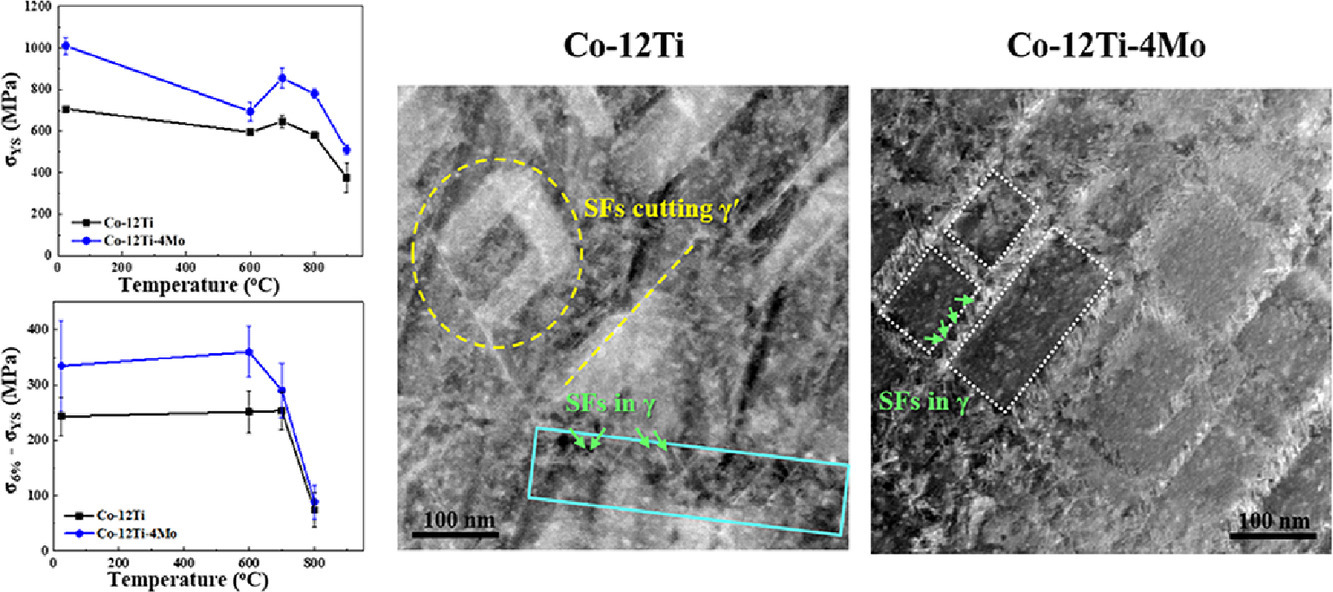
我們使用了電子顯微鏡和密度泛函理論對γ/γ?強(qiáng)化的Co-12Ti和Co-12Ti-4Mo(at.%)合金在室溫和高溫(最高溫度達(dá)900℃)下的流變行為進(jìn)行了研究。與二元對照組合金相比,加入鉬元素后合金的壓縮屈服強(qiáng)化和應(yīng)變硬化能力明顯增強(qiáng)。這是由于Co-12Ti-4Mo合金中的γ? 相體積分?jǐn)?shù)和層錯(cuò)能分別提高了~25%和~7%。利用電子隧道對比成像技術(shù),我們在變形6%的Co-12Ti- 4Mo合金中發(fā)現(xiàn)了不連續(xù)的滑移帶,這與Co-12Ti中沿{111}分布的擴(kuò)展滑移帶有顯著不同,大大增強(qiáng)了應(yīng)變硬化能力。由于通過位錯(cuò)源快速疲憊后,為了切過γ? 析出需要更高的能壘,導(dǎo)致了不連續(xù)滑移帶的形成。這些效應(yīng)是由于γ通道寬度降低、γ? -Co3(Ti,Mo)強(qiáng)化和γ?/γ剪切模量的巨大差異共同引起的。
英文摘要
We investigated the flow behavior of γ/γ?-strengthened Co-12Ti and Co-12Ti-4Mo (at.%) alloys at room and elevated temperatures (up to 900°C) by electron microscopy and density functional theory. The Mo-added alloy exhibited an enhanced compressive yield strength and strain hardening behavior as compared to the reference binary alloy. This behavior could be attributed to a ~25% larger γ? volume fraction and ~7% higher planar fault energies in Co-12Ti-4Mo. Using electron channeling contrast imaging, we observed interrupted slip bands in the Co-12Ti-4Mo alloy deformed to a strain of 6%, which led to enhanced strain hardening, in contrast to extended slip bands along {111} planes in the Co-12Ti alloy. Interrupted slip band formation in Co-12Ti-4Mo could be explained by rapid exhaustion of dislocation sources and a higher energy barrier required to cut the γ? precipitates. These effects are due to a reduced γ channel width and substantial hardening effect of γ?-Co3(Ti,Mo) in the ternary alloy as well as due to the large shear modulus difference between γ? and γ.
ACTA Vol. 197, 15 Sept. 2020, P91-96
8. Unconventional non-uniform local lattice distortion in dilute Ti-Mo solid solution
低固溶Ti-Mo合金中的非均勻局部晶格畸變
Qing-Miao Hu?, Rui Yang
Q.-M. Hu:qmhu@imr.ac.cn,沈陽金屬所
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.07.033
摘要
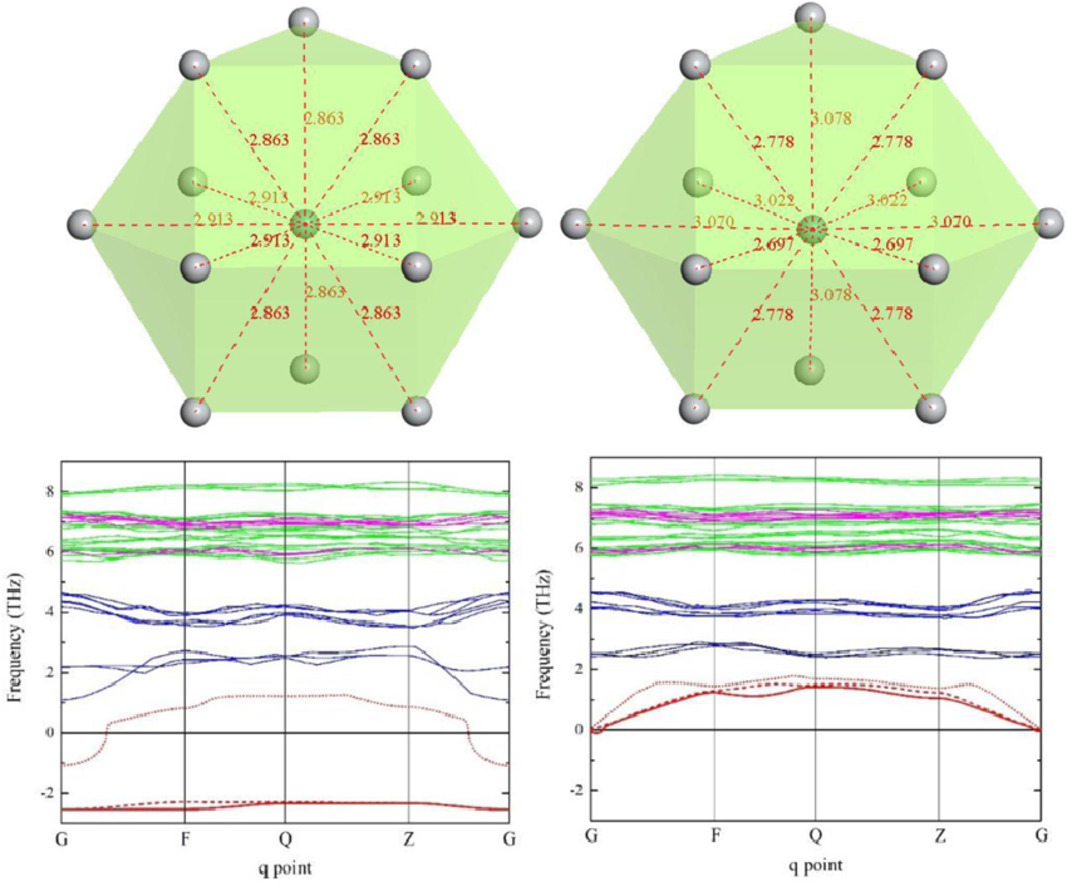
一般而言,我們認(rèn)為低合金固溶體中的溶質(zhì)原子在不破壞晶格點(diǎn)群對稱性的情況下,占據(jù)了高對稱的晶格位點(diǎn),因此導(dǎo)致的局部晶格畸變是均勻的。與傳統(tǒng)的觀點(diǎn)相反,我們報(bào)道了在Ti-Mo合金中,置換原子Mo并沒有占據(jù)高對稱格點(diǎn)位置,而是占據(jù)了遠(yuǎn)離中心的格點(diǎn)位置,導(dǎo)致了高度不均勻的局部晶格畸變。我們的第一原理計(jì)算證明了這一點(diǎn)。我們認(rèn)為Mo原子d軌道的Jahn-Teller分裂是導(dǎo)致其偏心占位和非均勻晶格畸變的基礎(chǔ)物理。基于以上理論模型,我們進(jìn)一步預(yù)測了會(huì)產(chǎn)生非均勻晶格畸變的固溶體體系。非均勻晶格畸變使得基于均勻晶格畸變和球面應(yīng)力假設(shè)的經(jīng)典固溶硬化模型在這類固溶體中的應(yīng)用收到了很大的挑戰(zhàn)。同時(shí),這項(xiàng)研究也對金屬固溶體中的置換型溶質(zhì)原子不引起滯彈性弛豫和內(nèi)摩擦等傳統(tǒng)觀點(diǎn)提出了質(zhì)疑。
英文摘要
The substitutional solute atom induced local lattice distortion (LLD) in dilute metal solid solution was believed to be uniform because the solute atom was supposed to occupy the high symmetry lattice site without breaking the point group symmetry of the crystal lattice. Contrary to this conventional picture, we report in this paper that substitutional Mo atom in Ti-Mo solid solution occupies an off-center position instead of the high symmetry lattice site and leads to highly non-uniform LLD, as evidenced by our first principles calculations. The physics underlying the off-center occupation and non-uniform LLD are shown to be the Jahn-Teller splitting of the degenerated d states of Mo atom. With which, the solid-solutions suffering from non-uniform LLD are predicted. The non-uniform LLD challenges the application of classical solid solution hardening model based on uniform LLD and spherical stress tensor assumption to this kind of solid solutions. This work also questions the traditional view that elementary substitutional solute atoms in metal solid solutions should not induce anelastic relaxation and internal friction.
ACTA Vol. 197, 15 Sept. 2020, P97-107
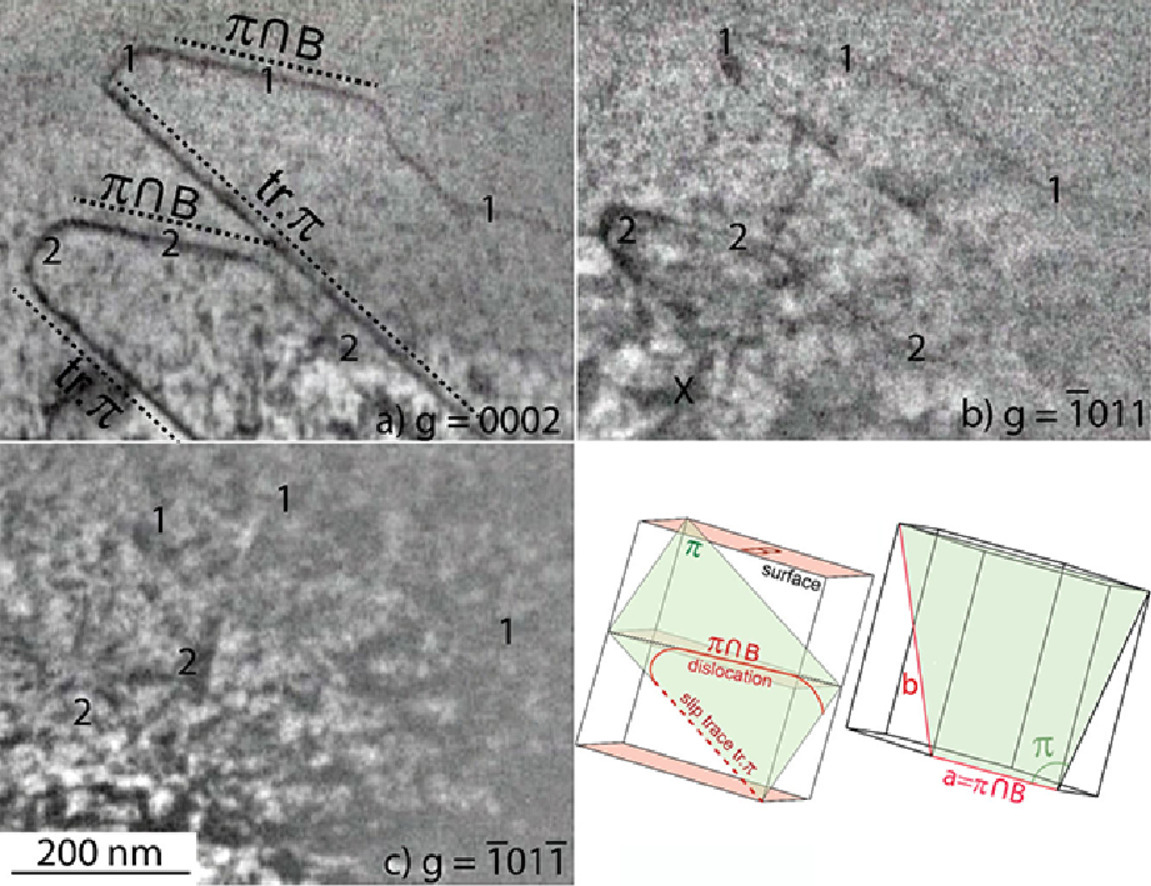
9. Mobility of 〈c+a〉dislocations in zirconium
鋯合金中〈c+a〉位錯(cuò)的運(yùn)動(dòng)
Thomas Soyez, Daniel Caillard, Fabien Onimus, Emmanuel Clouet?
E. Clouet:emmanuel.clouet@cea.fr
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.07.026
摘要
密排六方鋯合金的塑性變形主要受到伯氏矢量為1/3〈1-210〉的位錯(cuò)的滑移控制。由于這些位錯(cuò)不能適應(yīng)[0001]方向的變形,因此體系必須激活〈c+a〉位錯(cuò),也就是伯氏矢量為1/3〈1-213〉的位錯(cuò)的孿晶。我們使用TEM原位應(yīng)變實(shí)驗(yàn)對兩種Zr合金(純Zr和Zircaloy-4)中〈c+a〉位錯(cuò)在室溫下的滑移進(jìn)行了研究。實(shí)驗(yàn)表明,〈c+a〉位錯(cuò)只在一級錐面上滑移,并激活了交叉滑移。當(dāng)它們的〈a〉方向平行于滑移面和底面的交線時(shí),晶格阻力使得這些位錯(cuò)的滑移受到明顯抑制。這導(dǎo)致沿著〈a〉方向滑移的長位錯(cuò)被拉直。〈a〉方向決定了位錯(cuò)具有不同取向部分的其他部分的運(yùn)動(dòng),以使位錯(cuò)的線張力最小。此外,我們在文中對溶質(zhì)原子造成的阻力也進(jìn)行了一定討論。
英文摘要
Plasticity in hexagonal close-packed zirconium is mainly controlled by the glide of dislocations with 1/3〈1-210〉Burgers vectors. As these dislocations cannot accommodate deformation in the [0001] direction, twinning or glide of 〈c+a〉dislocations, i.e. dislocations with 1/3〈1-213〉 Burgers vector, have to be activated. We have performed in situ straining experiments in a transmission electron microscope to study the glide of〈c+a〉dislocations in two different zirconium samples, pure zirconium and Zircaloy-4, at room temperature. These experiments show that 〈c+a〉 dislocations exclusively glide in first-order pyramidal planes with cross-slip being activated. A much stronger lattice friction is opposing the glide of 〈c+a〉 dislocations when their orientation corresponds to the〈a〉direction defined by the intersection of their glide plane with the basal plane. This results in long dislocations straightened along〈a〉which glide either viscously or jerkily. This〈a〉direction governs the motion of segments with other orientations, whose shape is merely driven by the minimization of the line tension. The friction due to solute atoms is also discussed.
ACTA Vol. 197, 15 Sept. 2020, P123-136
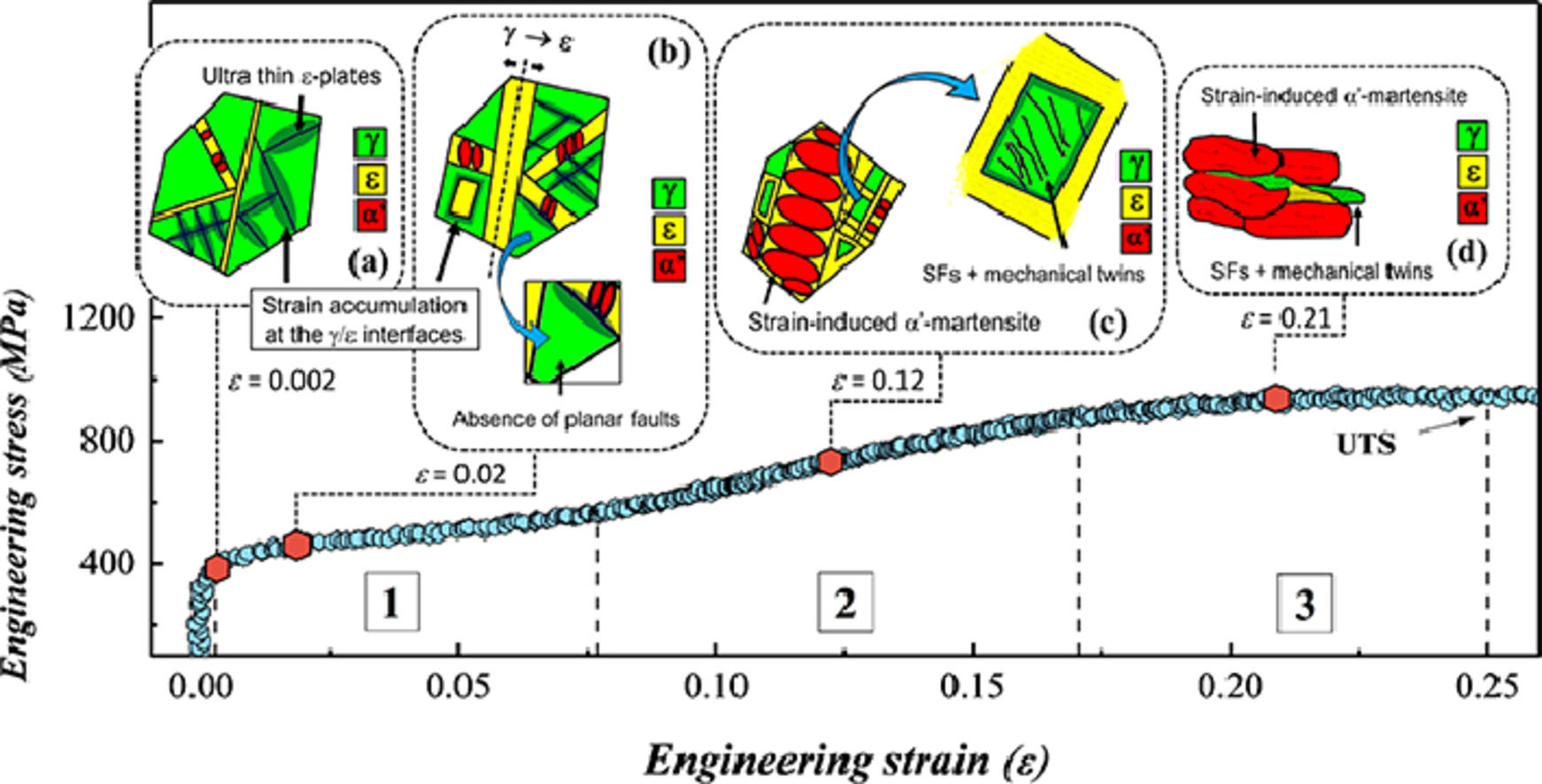
10 The impact of grain-scale strain localization on strain hardening of a high-Mn steel: Real-time tracking of the transition from the γ → ε → α’ transformation to twinning
通過實(shí)時(shí)追蹤γ → ε → α’相變向?qū)\晶的過渡研究晶粒尺度局部應(yīng)變對高錳鋼應(yīng)變硬化的影響
I.R. Souza Filho?, A. Dutta, D.R. Almeida Junior, W. Lu, M.J.R. Sandim, D. Ponge, H.R.Z. Sandim, D. Raabe
I.R. Souza Filho:souza@mpie.de
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.07.038
摘要
我們使用了原位同步輻射X射線衍射,原位DIC和電子顯微技術(shù)研究了一種高M(jìn)n鋼(17.1wt.% Mn)中的應(yīng)變集中。通過結(jié)合DIC和Warren理論,我們觀測到了合金中的面缺陷(層錯(cuò)和機(jī)械孿晶)并且將它們與組織中的應(yīng)變集中建立了聯(lián)系。材料初始組織為奧氏體,ε馬氏體和α’馬氏體。我們發(fā)現(xiàn)拉伸過程中,應(yīng)變優(yōu)先集中到γ/ε界面附近。通過DIC測得的局部微觀Mises應(yīng)變分布圖可知,這些局部應(yīng)變梯度所導(dǎo)致的應(yīng)變峰值能達(dá)到宏觀工程應(yīng)變的兩倍左右,因此在屈服的較早階段就引起了局部ε馬氏體相變。而在殘余奧氏體內(nèi)部,不存在這樣的界面峰值應(yīng)變,因此奧氏體內(nèi)部幾乎沒有面缺陷。局域應(yīng)變驅(qū)動(dòng)下的ε相長大和α’馬氏體生成伴隨發(fā)生。在中等宏觀應(yīng)變下,奧氏體晶粒尺寸不斷減小至幾個(gè)納米,γ/ε界面微觀應(yīng)變峰值發(fā)生數(shù)量級上的增長。當(dāng)工程應(yīng)變達(dá)到0.075以上時(shí),孿晶逐漸成為一種更加優(yōu)先的應(yīng)變硬化競爭機(jī)制。在拉伸應(yīng)變較大時(shí),γ → ε → α’相變停止,孿晶和層錯(cuò)成為應(yīng)變硬化的主要機(jī)制。這些發(fā)現(xiàn)揭示了高M(jìn)n TRIP鋼中不同組成相之間的應(yīng)變集中對多種應(yīng)變硬化機(jī)制之間動(dòng)態(tài)競爭的影響。
英文摘要
Strain partitioning and localization were investigated in a high-Mn steel (17.1 wt.% Mn) during tensile testing by a correlative probing approach including in-situ synchrotron X-ray diffraction, micro- digital image correlation (μ-DIC) and electron microscopy. By combining Warren's theory with the μ-DIC analysis, we monitored the formation of planar faults (stacking faults and mechanical twins) and correlated them with the local strain partitioning behavior within the microstructure. Starting with an initial microstructure of austenite (γ) and athermally formed ε- and α’-martensite, strain accumulates preferentially near the γ/ε interfaces during tensile straining. The local microscopic von Mises strain (εvM) maps obtained from μ-DIC probing show that these local strain gradients produce local strain peaks approximately twice as high as the imposed macroscopic engineering strain (ε), thus locally triggering formation of ε-martensite already at early yielding. The interior of the remaining austenite, without such interfacial strain peaks, remained nearly devoid of planar faults. The local strain-driven growth of the ε-domains occurs concomitantly with the α’-martensite formation. At intermediate macroscopic applied strains, austenite grain size is considerably reduced to a few nanometers and the associated γ/ε interfacial microscopic strain peaks increase in magnitude. This scenario favors twinning to emerge as a competing strain hardening mechanism at engineering strain levels from ε = 0.075 onwards. At large tensile strains, the γ → ε → α’ transformation rates tend to cease making both twinning and SFs formation to operate as the main strain hardening mechanisms. The findings shed light on the transformation micro-mechanisms in multiphase Mn-TRIP steels by revealing how strain localization among the constituents can directly influence the kinetics of the competing strain hardening mechanisms.
ACTA Vol. 197, 15 Sept. 2020, P137-145
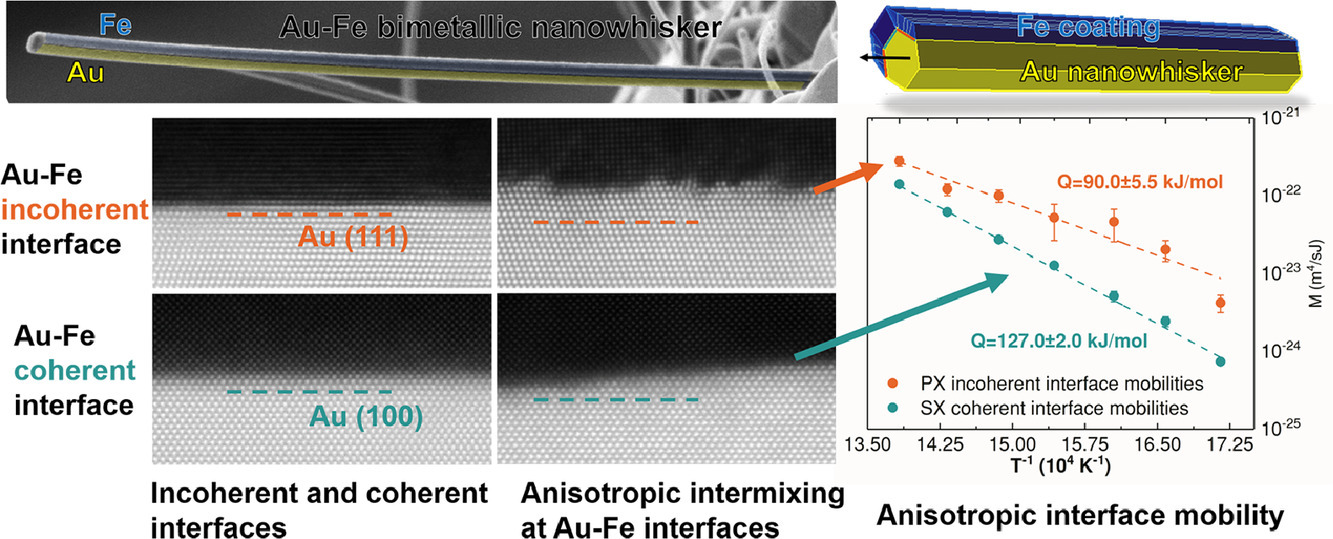
11. Interdiffusion in bimetallic Au–Fe nanowhiskers controlled by interface mobility
Au–Fe雙金屬納米晶須中由界面遷移率控制的互擴(kuò)散過程
Yuanshen Qi?, Gunther Richter, Eylül Suadiye, Leonid Klinger, Eugen Rabkin?
Y. Qi:yuanshen.qi@campus.technion.ac.il
E. Rabkin:erabkin@technion.ac.il.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.07.041
摘要
異相界面上的納米尺度擴(kuò)散是控制多層材料固態(tài)相變和混合的基本過程。在本研究中,我們使用實(shí)驗(yàn)直接地證明了,納米尺度的多相相互擴(kuò)散過程是由界面遷移率控制的。我們在Fe-Au納米晶須中觀察到了各向異性擴(kuò)散混合,其中Fe穿過非共格Fe-Au界面進(jìn)入Au的擴(kuò)散深度比共格對比組要大得多。利用一個(gè)簡單的動(dòng)力學(xué)模型分析測得的結(jié)果后,我們得到了共格和非共格Fe-Au界面遷移率的絕對值,以及描述其與溫度之間的關(guān)系的Arrhenius參數(shù)。分辨率達(dá)到原子尺度的掃描透射電鏡實(shí)驗(yàn)證實(shí)了共格界面的低遷移率是由于界面分離形核困難導(dǎo)致的。我們認(rèn)為這是決定了混合速度的動(dòng)力學(xué)瓶頸。我們的研究結(jié)果表明,界面遷移率的各向異性是導(dǎo)致許多非均相固態(tài)相變中析出相形貌各向異性的主要因素。
英文摘要
Nanoscale interdiffusion at the heterophase interfaces is the elementary process that controls solid-solid phase transformations and intermixing in multilayers. Here, we provide a direct experimental proof that the nanoscale multiphase interdiffusion is controlled by the interface mobility. We observed the anisotropic diffusion intermixing in Au–Fe bimetallic nanowhiskers, where the diffusion penetration depth of Fe into single crystalline Au nanowhisker across the incoherent Au–Fe interface was much greater than across its coherent counterpart. By applying a simple kinetic model to the results of diffusion measurements, we obtained the absolute values of mobilities of coherent and incoherent Fe-Au interfaces, and the Arrhenius parameters describing their temperature dependence. Atomic resolution scanning transmission electron microscopy confirmed that the lower mobility of the coherent interface is associated with the difficulties of the nucleation of interface disconnections. We proposed that the sluggish movement of the latter represents a kinetic “bottleneck” which determines the rate of intermixing. Our results indicate that the anisotropy of interface mobilities is a leading factor determining the anisotropic shape of precipitates formed in many heterogeneous solid-solid phase transformations.
ACTA Vol. 197, 15 Sept. 2020, P146-162
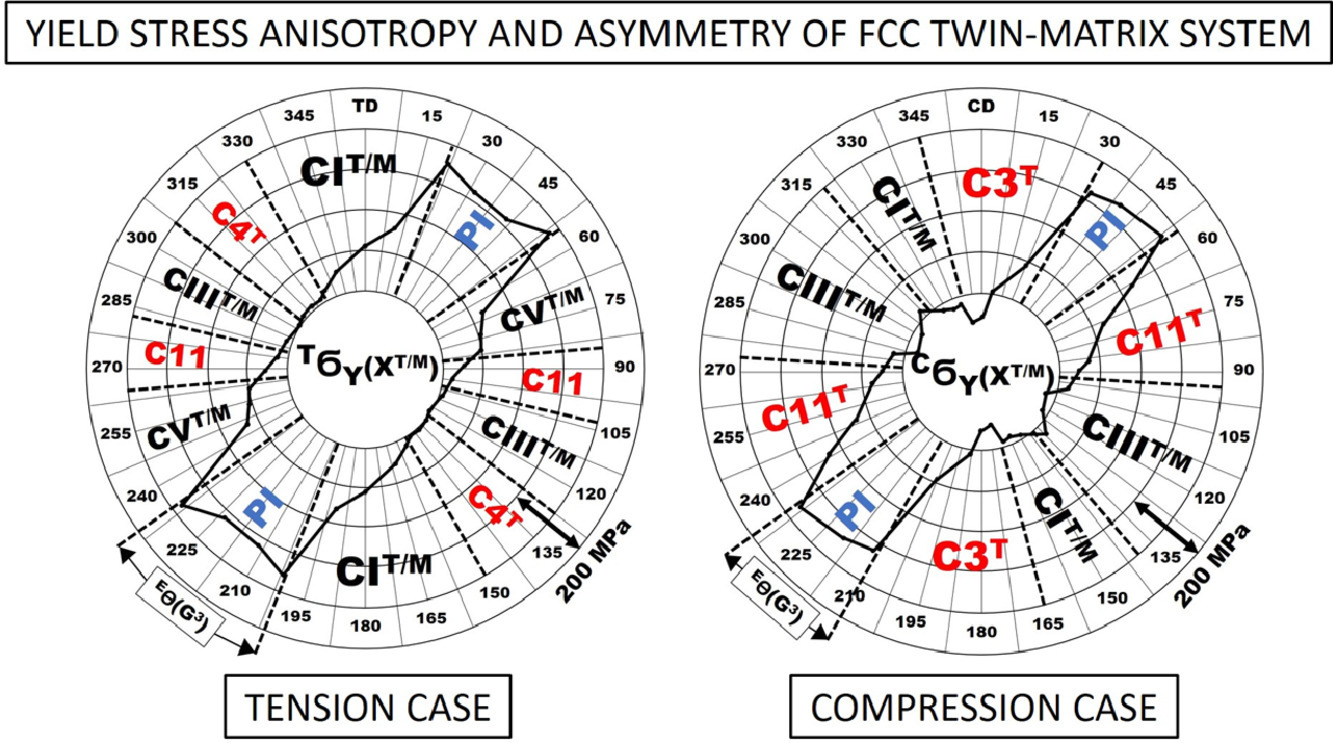
12. A study on crystal plasticity of face-centered cubic structures induced by deformation twinning
關(guān)于FCC晶體中形變孿晶引發(fā)的晶體塑性的研究
M.S. Szczerba, S. Kopacz, M.J. Szczerba?
M.J. Szczerba:m.szczerba@imim.pl
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.07.040
摘要
我們研究了形變孿晶對面心立方結(jié)構(gòu)可開動(dòng)滑移/孿晶切變系統(tǒng)的影響,并分析了其對應(yīng)的臨界應(yīng)力。我們選取了單一滑移取向的Cu-8at.%Al基體,將其在室溫下拉伸至孿晶開始發(fā)生,研究其塑性切變模式;并將其與孿晶不斷發(fā)生后的孿晶/基體層狀結(jié)構(gòu)的塑性切變模式進(jìn)行了比較。研究發(fā)現(xiàn),基體結(jié)構(gòu)內(nèi)所有的孿晶系和滑移系均可獨(dú)立開動(dòng),且其臨界應(yīng)力分布在均值上下15% 附近。然而,對于孿晶/基體而言,并非所有可能的滑移和孿晶系統(tǒng)都能獨(dú)立開動(dòng),且它們的臨界應(yīng)力可能相差四倍以上。這種巨大的臨界應(yīng)力差異導(dǎo)致了孿晶/基體層狀結(jié)呈現(xiàn)出顯著的屈服各向異性;最大和最小屈服應(yīng)力甚至可能相差一個(gè)數(shù)量級。此外,孿晶/基體層狀結(jié)構(gòu)也表現(xiàn)出了顯著的拉/壓屈服應(yīng)力不對稱。我們認(rèn)為,屈服應(yīng)力的各向異性和不對稱的特點(diǎn)具有相同的物理起源,即是由與位于孿晶片內(nèi)的立方擴(kuò)展位錯(cuò)有關(guān)的內(nèi)應(yīng)力場引起的。因此,立方位錯(cuò)產(chǎn)生的應(yīng)力對孿晶面心立方金屬材料的塑性和強(qiáng)化有非常重要的影響。
英文摘要
The effect of deformation twinning on the accessible slip and twin shear systems of a dislocated face-centered cubic structure and their critical stresses is studied. In particular, the plastic shear modes of critical matrix structure – single glide oriented Cu-8at.%Al alloy crystals deformed by room temperature tension up to the onset of deformation twinning - and the plastic shear modes of bimodal twin/matrix layered structure – subsequently twinned Cu-8at.%Al crystals – were examined. It was found that all twin and slip systems of the matrix structure may operate independently and their critical stresses are dispersed by about fifteen percent around the mean value. However, not all of the accessible slip and twin systems of the twin/matrix structure may operate independently and their critical stresses may differ by a factor of well over four. This large discrepancy of the critical stresses is responsible for giant yield stress anisotropy of the twin/matrix layered structure; the maximal and minimal yield stresses may differ even by one order of a magnitude. The twin/matrix layered structure reveals also very strong asymmetry of the tension/compression yield stress. It is suggested, that the giant anisotropy and very strong asymmetry of the yield stress have the same physical origin, i.e. the internal stress field associated with extended configurations of cube dislocations located within a twin lamellae - the deformation twinning induced effect of cube dislocation stress. It is concluded, that the cube dislocation stress effect seems greatly responsible for plasticity and strengthening of mechanically twinned face-centered cubic structures.
ACTA Vol. 197, 15 Sept. 2020, P172-183
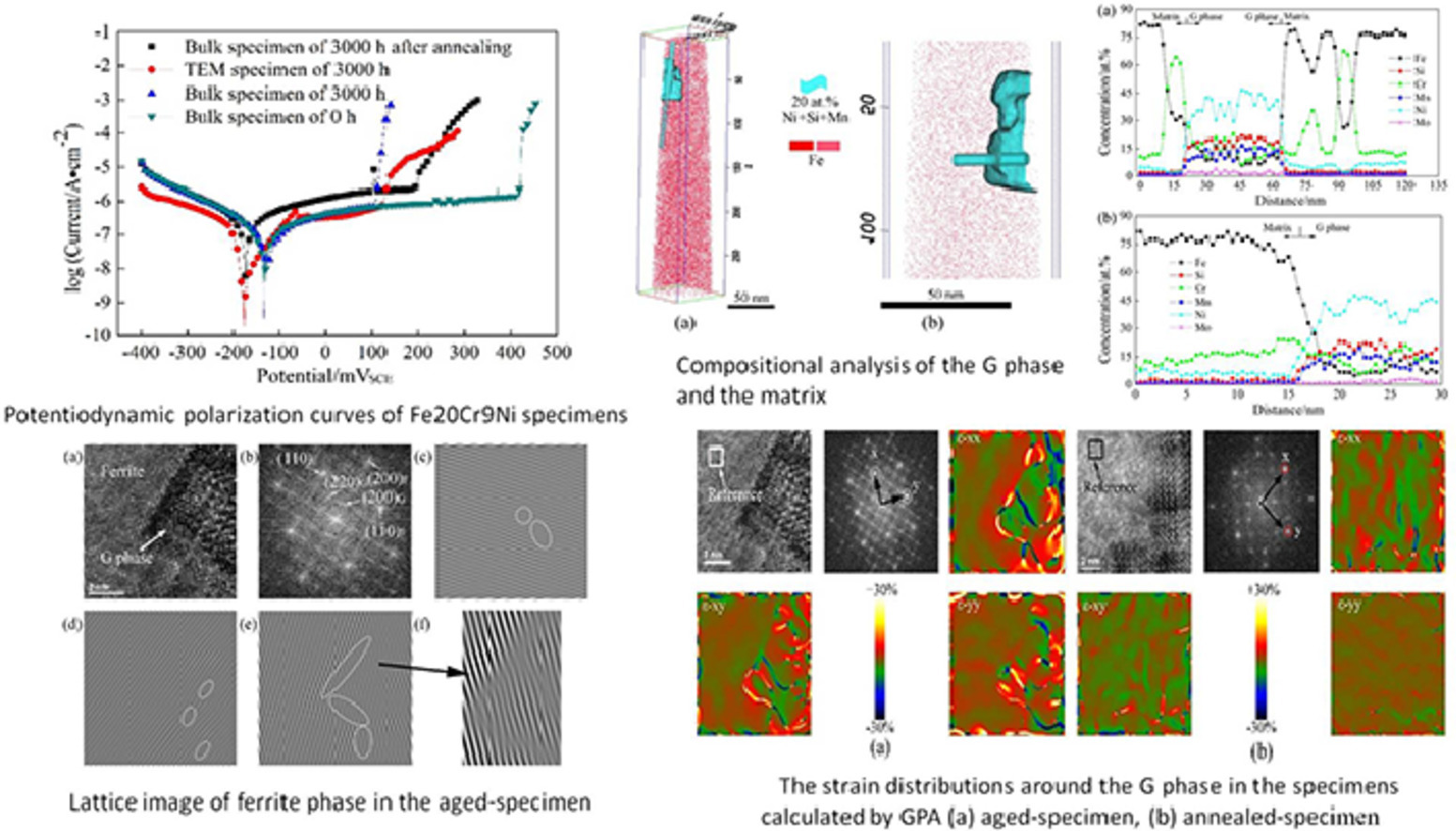
13. Evaluation of pitting corrosion in duplex stainless steel Fe20Cr9Ni for nuclear power application
核電用Fe20Cr9Ni雙相不銹鋼的點(diǎn)腐蝕性能研究
Yuefeng Chen, Bin Yang?, Yangtao Zhou, Yuan Wu, Huihui Zhu
B. Yang:byang@ustb.edu.cn,北京科技大學(xué)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.07.046
摘要
Fe20Cr9Ni鐵素體-奧氏體雙向不銹鋼在280-320°C長時(shí)間服役時(shí)經(jīng)常發(fā)生調(diào)幅分解,從而導(dǎo)致材料的耐蝕性能降低。通常來說,比起G相, 富Fe的α相被更多地認(rèn)為是導(dǎo)致材料時(shí)效后耐蝕性能降低的主要原因。而我們發(fā)現(xiàn),在Fe20Cr9Ni不銹鋼發(fā)生調(diào)幅分解后,約76.8%的耐蝕性降低是由于G相導(dǎo)致的,而僅有23.2%是由于α相導(dǎo)致的。在本研究中,我們采用了合適的熱時(shí)效處理引入了更大尺寸的G相,并研究了該相在腐蝕過程中的作用。通過將475℃ 3000h時(shí)效處理材料的TEM樣品浸入NaCl溶液,我們確定了鐵素體中的優(yōu)先腐蝕位置。通過TEM-EDS, 3DAPT和GPA等技術(shù),我們分析了G相附近的成分變化和應(yīng)變分布。結(jié)果表明,盡管α相和α’相之間Cr的成分差異可高達(dá)60%,但腐蝕卻首先在G相和鐵素體基體的界面處發(fā)生,而非在富Fe的α相內(nèi)發(fā)生,這表明貧Cr理論不能解釋已有的實(shí)驗(yàn)現(xiàn)象。我們發(fā)現(xiàn),G相和鐵素體基體的界面處的應(yīng)變能是最大的。在界面處的原子比在晶粒內(nèi)部具有更高能量,因此更容易與溶液中的Cl−離子反應(yīng)并最終形成腐蝕坑。
英文摘要
A spinodal decomposition is often carried out in the austenite-ferrite duplex stainless steel Fe20Cr9Ni during long-term service at a temperature in the range from 280 to 320°C, resulting in a decrease of pitting corrosion resistance. Fe-rich α phase rather than G-phase has been suggested as the major reason for the deterioration in pitting corrosion resistance of the thermally-aged steel. Here, we found that ∼76.8% of the decline in pitting resistance for the duplex stainless steel Fe20Cr9Ni was attributed to G-phase, and ∼23.2% to Fe-rich α phase after the spinodal decomposition. In this study, a suitable thermal aging treatment was introduced to obtain a larger size of the G-phase and to study the role of the phase in the corrosion process. Through immersing thermally-aged TEM specimen treated at 475°C for 3000 h in NaCl solution, the preferential position of corrosion pits formed in the ferrite was obtained. The composition changes and strain field distribution around the G-phase were analyzed by TEM-EDS, 3DAPT and GPA techniques. We further found that, although the concentration difference of Cr element between α and α’ phases was as high as 60 at.%, corrosion pits were initiated at the interface between the G-phase and the ferrite matrix rather than in the Fe-rich α phase, indicating that the Cr-depleted theory could not explain the aforesaid phenomenon. The strain energy at the interface between the G-phase and the ferrite matrix was found to be the largest. The atoms at the interface have higher energy than in the intracrystalline, and thus easily react with Cl− ions in the solution to form pits finally.
ACTA Vol. 197, 15 Sept. 2020, P184-197
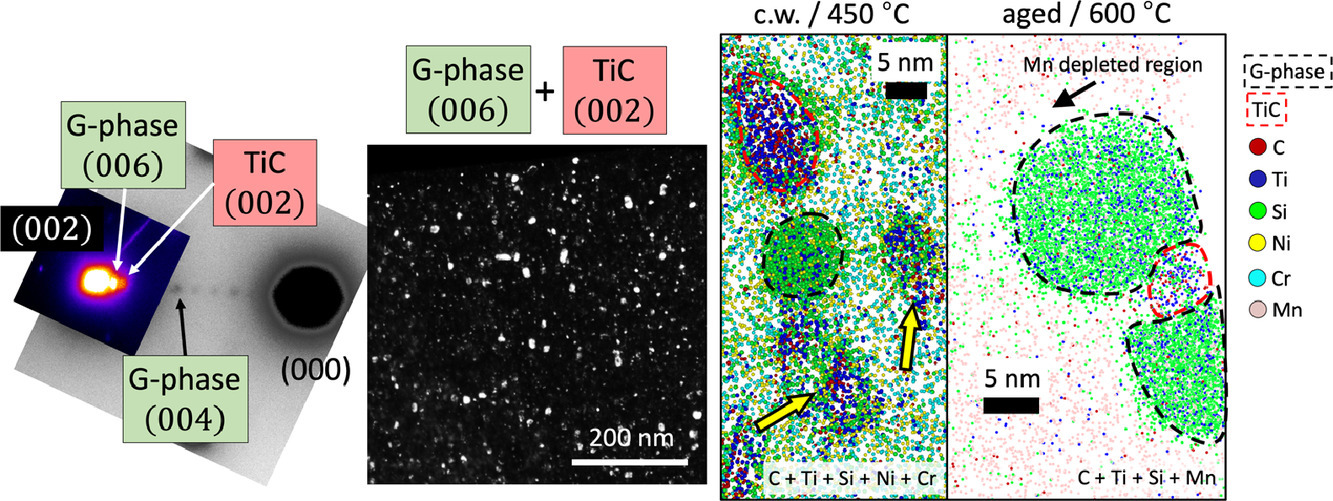
14. The role of Ti and TiC nanoprecipitates in radiation resistant austenitic steel: A nanoscale study
Ti元素和TiC析出對奧氏體鋼抗輻照性能影響的納米尺度研究
Niels Cautaerts?, Rémi Delville, Erich Stergar, Janne Pakarinen,1, Marc Verwerft, Yong Yang, Christina Hofer, Ronald Schnitzer, Steffen Lamm, Peter Felfer, Dominique Schryvers
N. Cautaerts:n.cautaerts@mpie.de
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.07.022
摘要
我們使用了透射電子顯微鏡和原子探針技術(shù)研究了鈦穩(wěn)定奧氏體鋼在鐵離子輻照下的響應(yīng)。研究的重點(diǎn)在于輻照誘導(dǎo)的偏聚和析出,特別是Ti和TiC如何影響這些過程。我們使用了兩種不同狀態(tài)(冷加工態(tài)和時(shí)效態(tài))的15-15Ti鋼作為研究對象,在不同溫度下進(jìn)行輻照,輻照劑量最高達(dá)到40 dpa。我們發(fā)現(xiàn),在較低的輻照溫度下,冷加工和時(shí)效后的材料組織演化類似,組織中以小的Si和Ni團(tuán)簇為主,即發(fā)生點(diǎn)缺陷處的偏聚;且時(shí)效態(tài)材料中已有的TiC析出不穩(wěn)定。提高輻照溫度,則將導(dǎo)致納米級富鉻TiC析出在富Si和富Ni的殼層周圍形核。此外,組織中還形成了富Ti和富Mn的納米級G相(M6Ni16Si7)析出,這些析出通常附著在TiC析出上。輻照后,冷加工態(tài)材料中的TiC密度大于時(shí)效態(tài),這與其較低的G相體積分?jǐn)?shù)有關(guān)。結(jié)果表明,在較高的輻照溫度下,析出相與基體的界面是重要的點(diǎn)缺陷匯,有助于提高材料的抗輻照性能。本研究是首次對Ti穩(wěn)定奧氏體鋼進(jìn)行類似研究,闡明了少量添加鈦原子對輻照過程中組織演變的重要影響。
英文摘要
This work encompasses an in-depth transmission electron microscopy and atom probe tomography study of Ti-stabilized austenitic steel irradiated with Fe-ions. The focus is on radiation induced segregation and precipitation, and in particular on how Ti and TiC affect these processes. A 15-15Ti steel (grade: DIN 1.4970) in two thermo-mechanical states (cold-worked and aged) was irradiated at different temperatures up to a dose of 40 dpa. At low irradiation temperatures, the cold-worked and aged materials evolved to a similar microstructure dominated by small Si and Ni clusters, corresponding to segregation to small point defect clusters. TiC precipitates, initially present in the aged material, were found to be unstable under these irradiation conditions. Elevated irradiation temperatures resulted in the nucleation of nanometer sized Cr enriched TiC precipitates surrounded by Si and Ni enriched shells. In addition, nanometer sized Ti- and Mn-enriched G-phase (M6Ni16Si7) precipitates formed, often attached to TiC precipitates. Post irradiation, larger number densities of TiC were observed in the cold-worked material compared to the aged material. This was correlated with a lower volume fraction of G-phase. The findings suggest that at elevated irradiation temperatures, the precipitate-matrix interface is an important point defect sink and contributes to the improved radiation resistance of this material. The study is a first of its kind on stabilized steel and demonstrates the significance of the small Ti addition to the evolution of the microstructure under irradiation.
ACTA Vol. 197, 15 Sept. 2020, P198-211
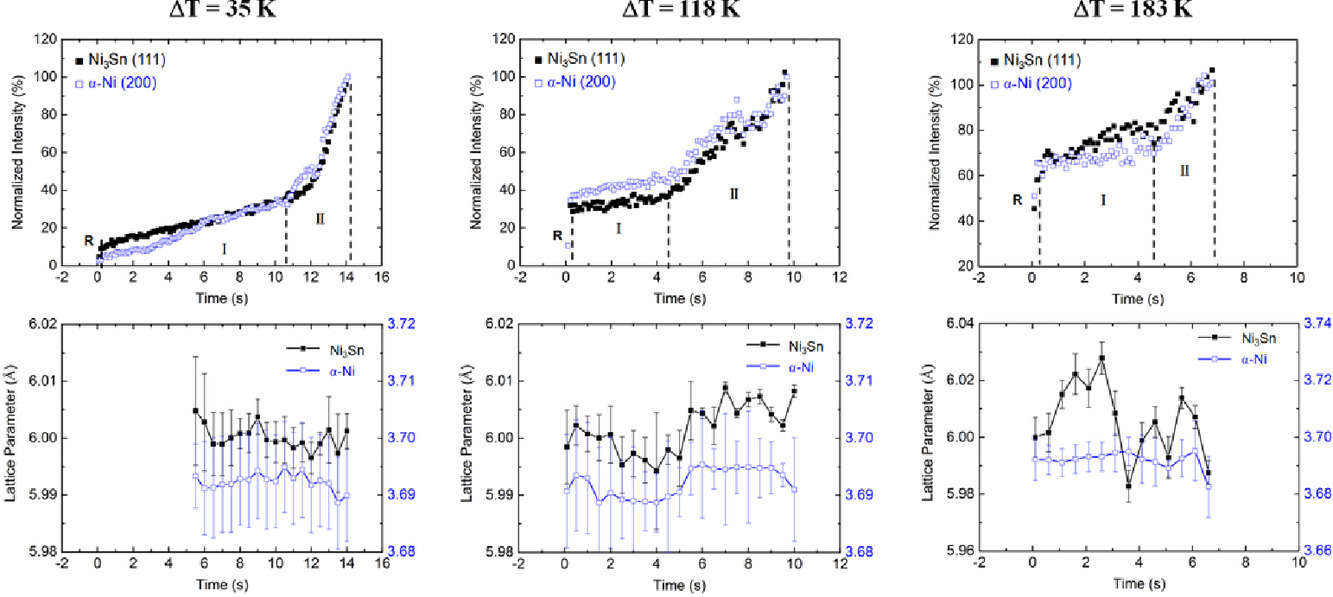
15. In situ and ex situ studies of anomalous eutectic formation in undercooled Ni–Sn alloys
過冷Ni–Sn合金中反常共晶形成的原位和離位研究
Rijie Zhao, Yeqing Wang, Jianrong Gao?, Evan B. Baker, Douglas M. Matson, Matthias Kolbe, Andrew Chih-Pin Chuang, Yang Ren
J. Gao:gao@mail.neu.edu.cn,東北大學(xué)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.07.048
摘要
我們采用原位X射線衍射和非原位重熔和退火,研究了過冷Ni–Sn 合金中的異常共晶形成過程。原位X射線衍射揭示了在凝固前沿一次固溶體的動(dòng)態(tài)再結(jié)晶和部分重熔,以及隨后發(fā)生的共晶反復(fù)形核和生長。非原位實(shí)驗(yàn)表明,共晶或接近共晶成分的凝固合金可以通過部分重熔,將規(guī)則的層狀共晶組織轉(zhuǎn)變?yōu)榉闯9簿В欢硪环矫妫瑢Υ慊鸷蟮念愃瞥煞诌M(jìn)行高溫退火,可以將共晶或雙相枝晶轉(zhuǎn)變?yōu)榉闯9簿АR虼耍c固態(tài)熟化相比,共晶或雙相枝晶的部分重熔是Ni–Sn合金過冷凝固過程中形成異常共晶更可能的機(jī)制。
英文摘要
Anomalous eutectic formation in undercooled Ni–Sn alloys was investigated by in situ X-ray diffraction and ex situ remelting and annealing experiments. Dynamic recrystallization and partial remelting of primary solids followed by repeated nucleation and growth of eutectic grains in the mushy zone were revealed by time-resolved X-ray diffraction. Ex situ experiments demonstrated that partial remelting of near-equilibrium solidified alloys of eutectic or near-eutectic composition can convert regular lamellar eutectic into anomalous eutectic, whereas high-temperature annealing of splat-quenched alloys of similar composition can convert eutectic or two-phase dendrites into anomalous eutectic. It is concluded that compared to ripening in solid-states, partial remelting of eutectic or two-phase dendrites in a mushy zone provides a more realistic mechanism for anomalous eutectic formation in undercooled solidification of Ni–Sn eutectic alloys.
ACTA Vol. 197, 15 Sept. 2020, P212-223
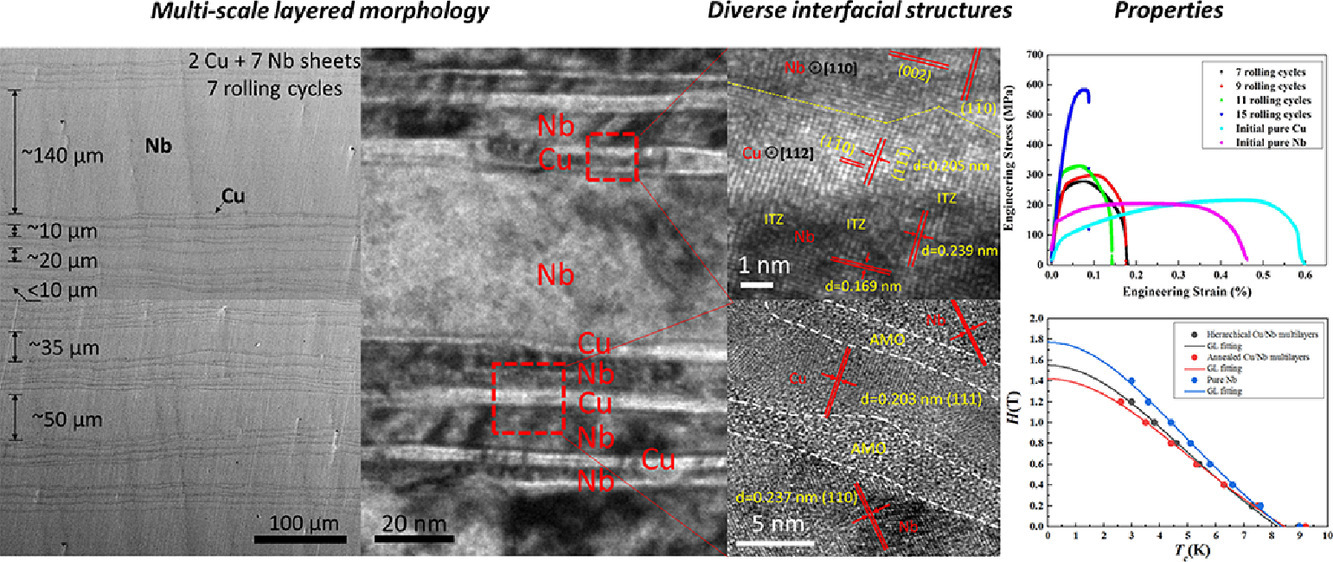
16. Superconducting Cu/Nb nanolaminate by coded accumulative roll bonding and its helium damage characteristics
疊軋制備的超導(dǎo)Cu/Nb納米層片結(jié)構(gòu)及其氦損傷特征
Rui Gao, Miaomiao Jin?, Fei Han, Baoming Wang, Xianping Wang?, Qianfeng Fang, Yanhao Dong, Cheng Sun, Lin Shao, Mingda Li, Ju Li?
M. Jin:mmjin@mit.edu
X. Wang:xpwang@issp.ac.cn,中國科學(xué)院固體物理研究所
J. Li:liju@mit.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.07.031
摘要
能夠在微觀結(jié)構(gòu)尺度上跨越多個(gè)尺度(如從納米到微米)的材料已被證明更有可能具備某些特別的材料性能。本研究中,我們通過改進(jìn)傳統(tǒng)疊軋(ARB)技術(shù),在重復(fù)堆疊和軋制過程中插入Nb薄板,制備出了具有疊層結(jié)構(gòu)的Cu/Nb雙相復(fù)合材料。這種具有多尺度結(jié)構(gòu)的多層材料具有非常大量的相界和界面結(jié)構(gòu)。這種復(fù)合材料表現(xiàn)出了與純Nb累似,但比純Nb強(qiáng)3倍的超導(dǎo)特性。這種材料在理論上也具有更好的抗氧化性能,并保持了相當(dāng)?shù)难诱剐浴T诤ぽ椪諚l件下,其獨(dú)特的化學(xué)混合界面(三維)比原子尖銳界面(二維)更不利于形成大的氦團(tuán)簇,從而屏蔽了輻照損傷,提高了機(jī)械性能。這項(xiàng)研究意味著設(shè)計(jì)類似的疊層結(jié)構(gòu)是一種提高材料性能的有效手段,并且在聚變和裂變領(lǐng)域有廣闊的應(yīng)用前景。
英文摘要
A very broad distribution of microstructural length scales spanning few nm- to the μm-scale has proven effective to achieve exceptional materials properties. Here, we fabricate a Cu/Nb two-phase composite made of a hierarchically layered structure by modifying the conventional accumulative roll bonding (ARB) technique, where fresh Nb sheets are inserted and bonded during a repeated stacking and rolling process. This barcode-like multilayer with a designed hierarchical length scale distribution possesses densely distributed phase boundaries and rich interfacial structures. The composite demonstrates similar superconductivity characteristics as pure Nb, but is 3 × stronger, has theoretically better oxidation resistance, and retains considerable ductility. Under the helium irradiation environment, the unique interfacial structures featuring chemical intermixing zones (3-dimensional) are more immune to the formation of large helium clusters than atomically sharp interfaces (2-dimensional), screening them from radiation damage and improving their long-term mechanical integrity. This work signifies an effective strategy of constructing hierarchical laminates to achieve high-performance materials, which holds promise in fusion and fission energy applications.
ACTA Vol. 197, 15 Sept. 2020, P253-268
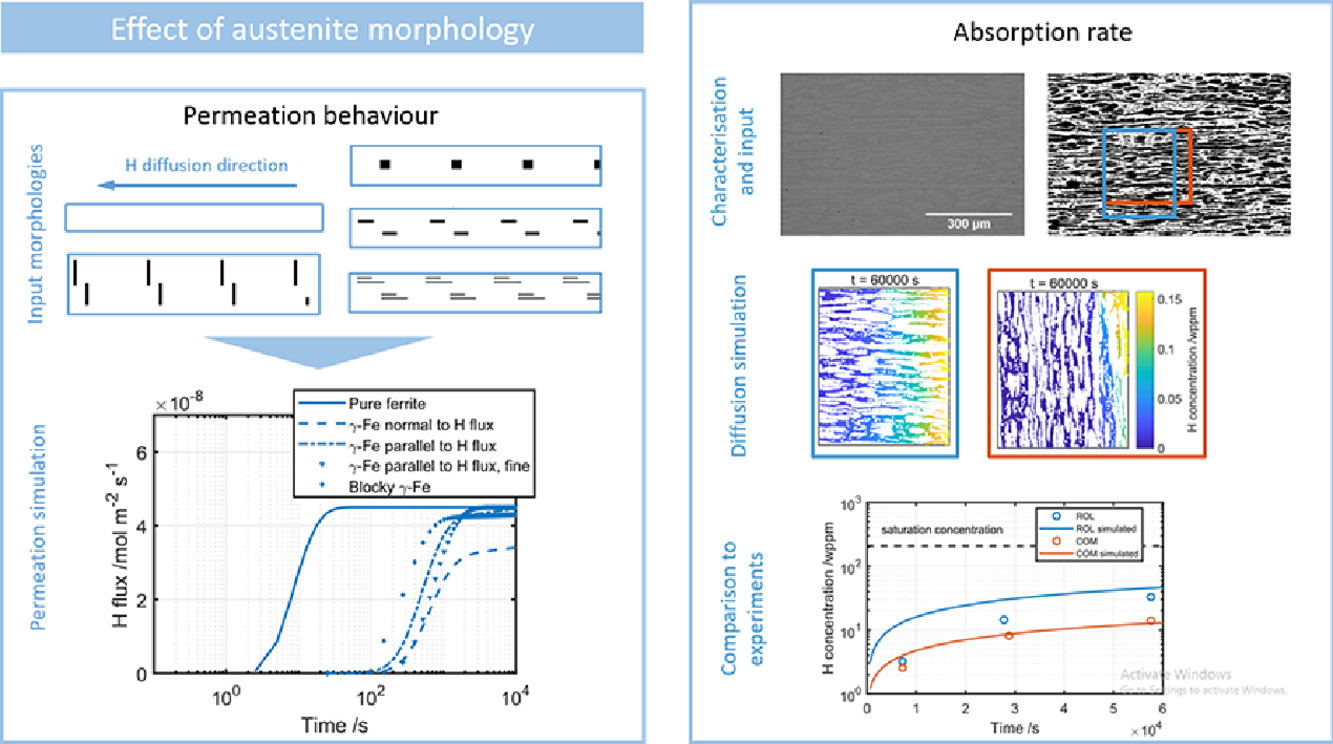
17. Quantification of hydrogen trapping in multiphase steels: Part II – Effect of austenite morphology
多相鋼中氫捕獲的定量研究:第二部分—奧氏體性能的影響
Andrej Turk?, Shengda D. Pu?, David Bomba??, Pedro E.J. Rivera-Díaz-del-Castillo?, Enrique I. Galindo-Nava?
A. Turk:at712@cam.ac.uk
S.D. Pu:shengda.pu@queens.ox.ac.uk
D. Bomba?:david.bombac@ntf.uni-lj.si
P.E.J. Rivera Díaz-del-Castillo:p.rivera1@lancaster.ac.uk
E.I. Galindo-Nava:eg375@cam.ac.uk
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.07.039
摘要
我們首次系統(tǒng)性地研究了多相鋼鐵材料中奧氏體對氫擴(kuò)散的影響。在研究中,我們使用了實(shí)驗(yàn)和模型考慮了一系列因素,如形貌、界面動(dòng)力學(xué)和點(diǎn)陷阱的附加效應(yīng)等。在先前(即第一部分)的研究中,我們發(fā)現(xiàn)奧氏體不能像晶界和位錯(cuò)那樣,在局部平衡假設(shè)下以點(diǎn)陷阱方式進(jìn)行參數(shù)化模擬。為此,我們引入了一個(gè)二維氫擴(kuò)散模型,模擬不同相之間氫擴(kuò)散系數(shù)和溶解度的區(qū)別。我們首先回顧了淬火馬氏體中的氫滲透結(jié)果,發(fā)現(xiàn)馬氏體中極低的氫擴(kuò)散速率可以用奧氏體的新模型來解釋,也可能是由于淬火空位造成的。隨后,我們采用模擬和實(shí)驗(yàn)相結(jié)合的方法,研究了雙相鋼中的吸氫和脫氫速率。結(jié)果表明,吸氫和脫氫速率很大程度上取決于奧氏體的形貌,以及氫從鐵素體到奧氏體的遷移,這種遷移需要跨越一定的能壘。我們發(fā)現(xiàn),氫在鐵素體基體和奧氏體島中的擴(kuò)散速度接近,部分文獻(xiàn)中關(guān)于鐵素體中氫濃度梯度可以忽略的假設(shè)是一種不合理的近似。我們提出的這種研究方法同樣適用于其他含奧氏體的鋼鐵材料以及多相合金。
英文摘要
We tackle the role of austenite in multiphase steels on hydrogen diffusion systematically for the first time, considering a range of factors such as morphology, interface kinetics and the additional effect of point traps using both experiments and modelling. This follows the findings from part I where we showed that austenite cannot be parametrised and modelled as point traps under the assumption of local equilibrium, unlike grain boundaries and dislocations. To solve this, we introduce a 2D hydrogen diffusion model accounting for the difference in diffusivities and solubilities between the phases. We first revisit the as-quenched martensite permeation results from part I and show that the extremely low H diffusivity there can be partly explained with the new description of austenite but is partly likely due to quench vacancies. We then also look at the H absorption and desorption rates in a duplex steel as a case study using a combination of simulations and experiments. The rates are shown to depend heavily on austenite morphology and the kinetics of H transition from ferrite to austenite and that an energy barrier is likely associated to this transition. We show that H diffusion through the ferrite matrix and austenite islands proceeds at similar rates and the assumption of negligible concentration gradients in ferrite occasionally applied in the literature is a poor approximation. This approach is also applicable to other austenite-containing steels as well as other multiphase alloys.
ACTA Vol. 197, 15 Sept. 2020, P269-282
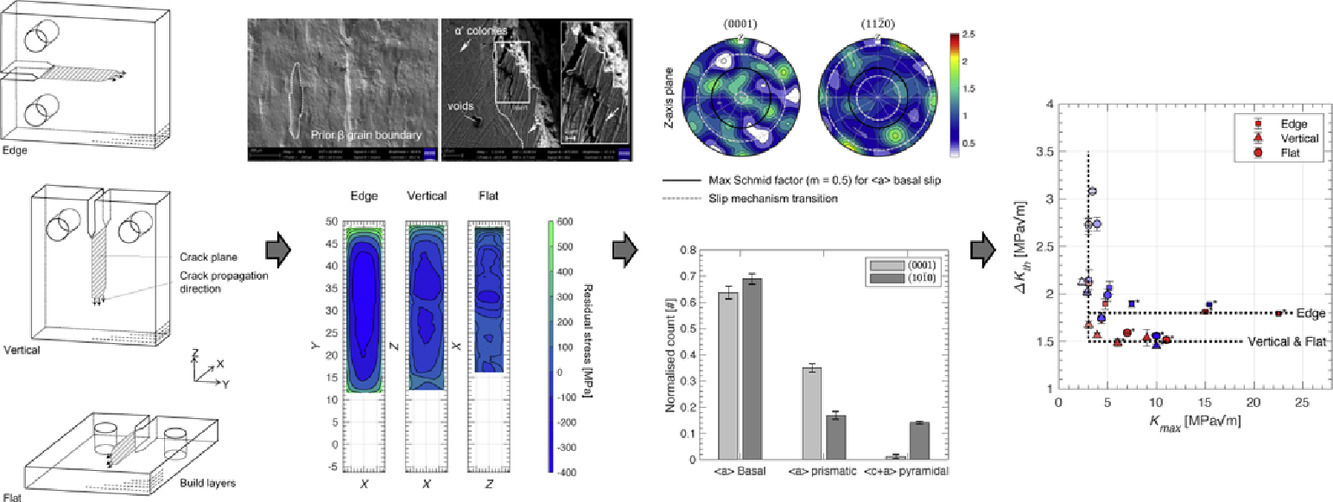
18. Near-threshold fatigue crack growth rates of laser powder bed fusion produced Ti-6Al-4V
激光粉末熔化Ti-6Al-4V的近臨界疲勞裂紋擴(kuò)展速率
Thorsten Hermann Becker?, Nur Mohamed Dhansay?, Gerrit Matthys Ter Haar?, Kim Vanmeensel?
T.H. Becker:tbecker@sun.ac.za
N.M. Dhansay:nurmdhansay@sun.ac.za
G.M.T. Haar:gterhaar@sun.ac.za
K. Vanmeensel:kim.vanmeensel@kuleuven.be
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.07.049
摘要
使用激光粉末熔化制備的Ti-6Al-4V合金通常呈馬氏體組織。內(nèi)應(yīng)力、高表面粗糙度和殘余氣孔都會(huì)影響其在高循環(huán)載荷下的疲勞壽命。目前關(guān)于激光熔化Ti-6Al-4V研究的重點(diǎn)大都集中在疲勞壽命的實(shí)驗(yàn)方法方面,對于疲勞失效機(jī)制缺乏深入的研究。近臨界疲勞裂紋擴(kuò)展速率對于描述疲勞裂紋萌生機(jī)制,以及殘余應(yīng)力、馬氏體組織、制樣方向等因素對裂紋萌生的影響非常重要。我們對不同尺寸的樣品進(jìn)行了疲勞試驗(yàn),用等高線法對樣品的殘余應(yīng)力進(jìn)行了測量,并使用電子背散射衍射對材料的形貌和織構(gòu)進(jìn)行了表征,細(xì)致研究了激光熔化Ti-6Al-4V的近臨界疲勞裂紋擴(kuò)展速率。結(jié)果表明,各向異性的近臨界疲勞裂紋擴(kuò)展速率主要取決于殘余應(yīng)力和載荷比。材料的斷裂模式主要為穿晶準(zhǔn)解理斷裂,斷裂路徑由原β柱晶結(jié)構(gòu)決定,從而導(dǎo)致與取向相關(guān)的裂紋閉合現(xiàn)象。殘余應(yīng)力導(dǎo)致裂紋張開,使近臨界疲勞裂紋擴(kuò)展速率發(fā)生變化。我們測得ΔKth 約為1.6 ± 0.2 MPa√m,Kmax約為 3 MPa√m,且這兩者不受受力狀態(tài)影響,但與取向有關(guān)。進(jìn)一步研究表明,這種各向異性與Ti-6Al-4V的形貌織構(gòu)關(guān)系較大,而與晶體學(xué)織構(gòu)關(guān)系較小。
英文摘要
When Ti-6Al-4V is processed by laser powder bed fusion (LPBF), a material with a martensitic microstructure is obtained. Moreover, the presence of internal stresses, an outer surface with relatively high surface roughness and the presence of remnant porosity all influence the fatigue life of high cyclically loaded components. The majority of investigations on LPBF produced Ti-6Al-4V have focused on a fatigue life method providing valuable, albeit limited, insight into fatigue failure mechanisms. Near-threshold fatigue crack growth rates are vital for describing fatigue crack initiation mechanisms and how these are influenced by residual stress, a martensitic microstructure and build orientation. This study investigates near-threshold fatigue crack growth rates of LPBF produced Ti-6Al-4V. The study makes use of full-size compact tension specimens for fatigue crack growth rate investigations, the contour method for residual stress measurement, and scanning electron microscopy with electron backscatter diffraction to consider both morphological and crystallographic texture. Results show anisotropic near-threshold fatigue crack growth rates that are dependant on residual stress levels and load-ratios. Fracture is predominantly governed by transgranular quasi-cleavage mechanisms, and the fracture path is directed by the columnar prior beta-grain structure resulting in orientation-dependant crack closure effects. Residual stresses result in crack opening that causes a shift of near-threshold fatigue crack growth rates. An intrinsic ΔKth of ~1.6 ± 0.2 MPa√m and critical Kmax of ~ 3 MPa√m is measured that is independent of the stress state but dependant on orientation. It is shown that this anisotropy is linked to morphological texture and to a lesser extent the crystallographic texture of LBPF produced Ti-6Al-4V.
ACTA Vol. 197, 15 Sept. 2020, P283-299
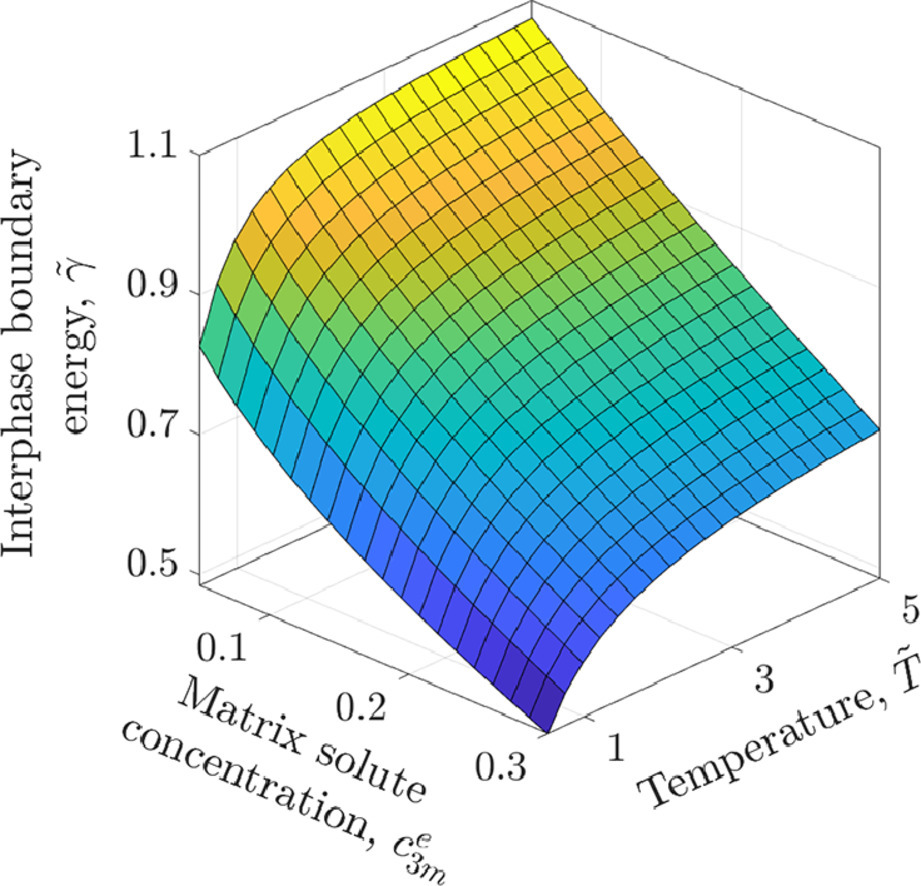
19. Interphase boundary segregation and precipitate coarsening resistance in ternary alloys: An analytic phase-field model describing chemical effects
描述三元合金中界面偏聚和析出相粗化阻力的相場模型
Sourabh B Kadambi, Fadi Abdeljawad, Srikanth Patala?
S. Patala:spatala@ncsu.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.06.052
摘要
許多析出硬化合金的實(shí)驗(yàn)和第一性原理研究表明,合金元素偏聚到基體-析出界面(IB)會(huì)降低界面能量。這種偏聚機(jī)制可以穩(wěn)定材料組織,抑制析出粗化過程,使得結(jié)構(gòu)材料能在更高的溫度服役。在本研究中,我們建立了一個(gè)描述三元合金中基體-析出界面溶質(zhì)偏析的相場模型框架。通過建立基體-析出界面能量和溶質(zhì)濃度的依賴關(guān)系,能夠有效地描述界面熱力學(xué)。界面相平衡通過平行切面確定,類似于經(jīng)典理論中對于自由表面和晶界偏析的處理。我們推導(dǎo)出了一維體系中的穩(wěn)態(tài)解析解,闡明了基體-析出界面性質(zhì)隨體成分、溫度和模型參數(shù)的變化關(guān)系。我們還推導(dǎo)得到了界面能量、溶質(zhì)濃度等經(jīng)典熱力學(xué)量的解析關(guān)系,其結(jié)果與吉布斯吸附方程一致,因此,模型預(yù)測結(jié)果可以與實(shí)驗(yàn)和原子模擬進(jìn)行比較。我們利用了Mg/Mg2Sn體系中Zn的偏聚說明了模型的典型應(yīng)用。我們對界面偏聚導(dǎo)致的析出相粗化進(jìn)行了模擬,結(jié)果表明三元合金的抗粒子粗化能力優(yōu)于二元合金。
英文摘要
Many experimental and first principles studies on precipitation hardening alloys show that segregation of elemental species to the matrix-precipitate interphase boundary (IB) reduces the boundary’s energy. This segregation mechanism can thermally stabilize the microstructure against precipitate coarsening processes and allow for higher operating temperatures in structural applications. In this paper, we develop a phase-field modeling framework to describe IB solute segregation in ternary alloys. The interfacial thermodynamics is effectively described by defining an IB phase with a characteristic free energy-concentration dependence. Equilibrium for the IB phase is established via the parallel tangent plane construction, analogous to classical treatments for segregation to free surfaces and grain boundaries. Analytic steady-steady solutions elucidating the dependence of IB properties on bulk phase composition, temperature and model parameters are derived for a one-dimensional system. Analytic relations for the classical thermodynamic quantities–IB energy and relative solute excess–are derived and the Gibbs adsorption equation is shown to hold; therefore, predictions of the model can be compared with experiments and atomistic simulations. An application of the model is demonstrated for Zn segregation to Mg/Mg2Sn using representative IB parameters. A two-particle coarsening simulation of IB segregation is performed: the result demonstrates enhanced coarsening resistance of the ternary alloy relative to the binary alloy.
ACTA Vol. 197, 15 Sept. 2020, P300-308
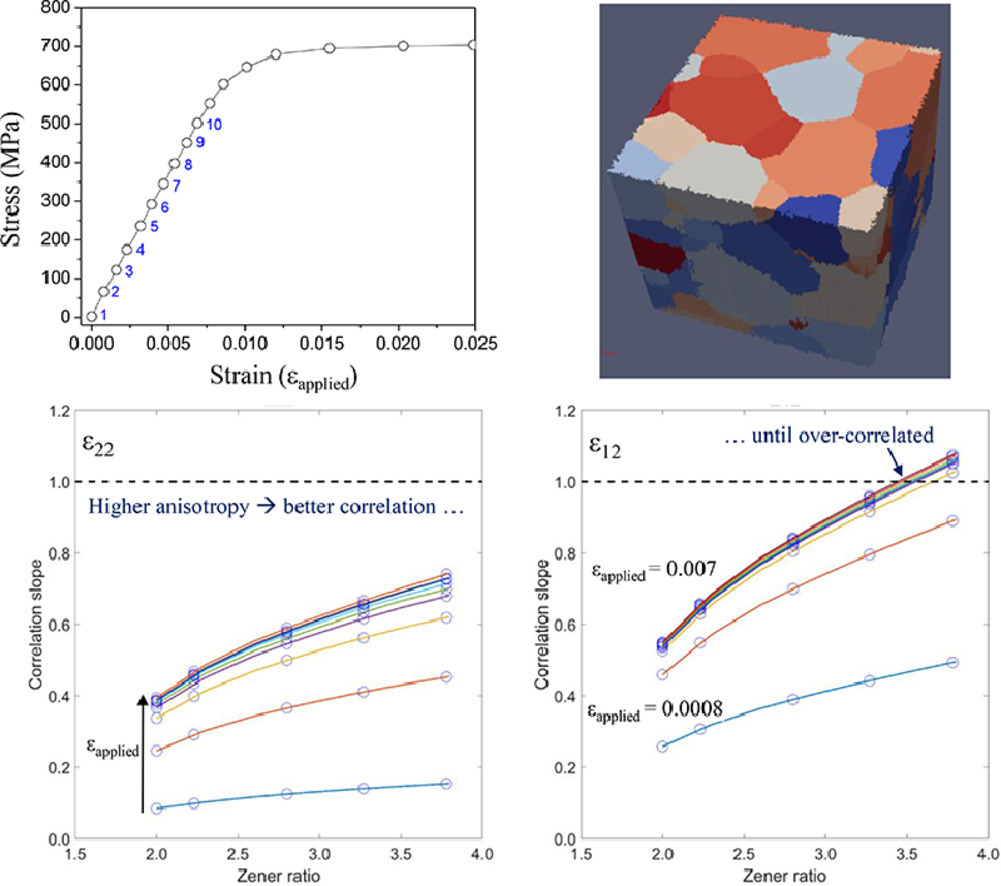
20. In-situ high energy X-ray diffraction study of the elastic response of a metastable β-titanium alloy
亞穩(wěn)β鈦合金彈性響應(yīng)的原位高能X射線衍射研究
Jishnu J Bhattacharyya?, Sriramya Nair, Darren C Pagan, Vahid Tari, Anthony D Rollett, Sean R Agnew
J.J. Bhattacharyya:jb4cp@virginia.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.07.050
摘要
在本研究中,我們使用了原位遠(yuǎn)場和同步輻射近場X射線衍射顯微(HEDM)技術(shù),結(jié)合晶體彈性模擬,研究了一種亞穩(wěn)態(tài)β-Ti合金(Timetal-18)在β淬火條件下的彈性行為。HEDM技術(shù)使我們能夠?qū)ξ覀兊亩嗑?shí)驗(yàn)材料樣品中部每一個(gè)晶粒的三維結(jié)構(gòu)、彈性應(yīng)變張量和晶體學(xué)取向進(jìn)行全面分析。基于約100個(gè)晶粒的彈性應(yīng)變和取向數(shù)據(jù),我們給出了一種能夠直接獲得單晶彈性常數(shù)(SEC)的方法。由此測得的彈性模量(以GPa為單位)分別為:C11 = 118±5、C12 = 79±3、C44 = 39±4,各向異性比(A)為2.0±0.4。我們將近場HEDM測到的微觀組織結(jié)構(gòu)進(jìn)行數(shù)字化構(gòu)建后,作為快速傅里葉變換(MASSIF)應(yīng)力-應(yīng)變不均勻性分析的輸入,模擬材料在晶粒尺度上的本構(gòu)響應(yīng)。模擬預(yù)測的彈性應(yīng)變張量演化與實(shí)驗(yàn)結(jié)果吻合良好。需要注意的是,單個(gè)晶粒之間的相互比較突出了彈性各向異性的影響,因此彈性各向異性參數(shù)A可能大于2。此外,我們也對該模擬方法的準(zhǔn)確性和塑性區(qū)的晶粒本構(gòu)相應(yīng)進(jìn)行了討論。
英文摘要
In the present work, the elastic behavior of a metastable β-Ti alloy, Timetal-18, is studied in the β-quenched condition using in-situ far-field (ff) and near-field (nf) high energy synchrotron X-ray diffraction microscopy (HEDM) techniques and full-field crystal elasticity simulation. HEDM enables assessment of the 3D microstructure as well as the complete (6 components) elastic strain tensor and crystallographic orientation of each grain in the gauge volume of a polycrystalline aggregate. Using this elastic strain and orientation data from ~100 grains, a straightforward strategy to obtain the single crystal elastic constants (SEC) is demonstrated. The elastic moduli thus obtained are (in GPa): C11 = 118 ± 5, C12 = 79 ± 3, C44 = 39 ± 4, with a Zener anisotropy ratio (A) of 2.0 ± 0.4. The nf-HEDM 3D microstructure was used to instantiate a virtual microstructure, as input into the parallelized code, Micromechanical Analysis of Stress-strain Inhomogeneities with fast Fourier transform (MASSIF), in order to simulate the grain level constitutive response. The predicted evolutions of the elastic strain tensor components are shown to be in good agreement with the measured values. However, grain-by-grain comparisons emphasize the strong effect of elastic anisotropy, suggesting it may be even higher than A = 2. The accuracy of the approach and implications for modeling the grain-level constitutive response in the plastic regime are discussed.
ACTA Vol. 197, 15 Sept. 2020, P330-340
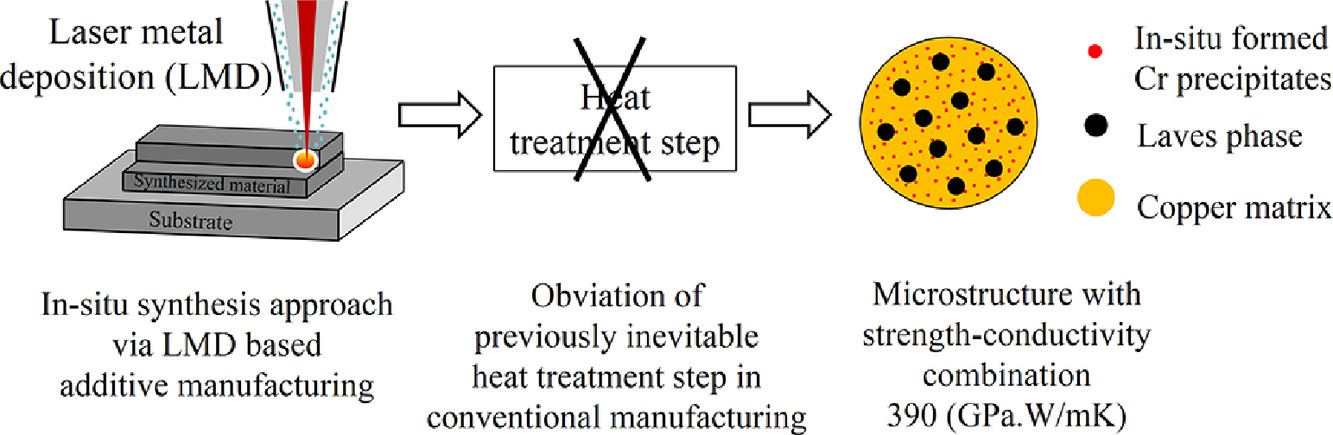
21. In-situ synthesis via laser metal deposition of a lean Cu–3.4Cr–0.6Nb (at%) conductive alloy hardened by Cr nano-scale precipitates and by Laves phase micro-particles
利用原位激光沉積技術(shù)原位制備納米Cr析出和LAVES相顆粒強(qiáng)化的Cu–3.4Cr–0.6Nb(at%)高導(dǎo)電性能合金
Anoop R Kini?, Dora Maischner, Andreas Weisheit, Dirk Ponge, Baptiste Gault, Eric A Jäglea, Dierk Raabe
A.R. Kini:anoopkini@gmail.com
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.07.035
摘要
高強(qiáng)度、高導(dǎo)電性銅合金是電子機(jī)械設(shè)備的重要材料。在本研究中,我們展示了利用激光沉積原位合成Cu-3.4Cr-0.6Nb (at.%) 的新方法。原位形成的納米Cr析出相(直徑約4nm,數(shù)密度約8 × 1023 m−3)和Laves相(直徑< 1 µm,體積分?jǐn)?shù)約為2.2%)在組織中彌散分布,起到了顯著的強(qiáng)化作用。這種幾乎是純銅基體中的雙析出相組織,是通過在激光沉積過程中適量固溶Cr并快速冷卻實(shí)現(xiàn)的。制備得到的材料的導(dǎo)電性在IACS標(biāo)準(zhǔn)下達(dá)到68%,室溫維氏硬度達(dá)到146。這一維氏硬度比目前文獻(xiàn)中報(bào)道的最強(qiáng)的Cu–8Cr–4Nb三元銅合金還要高11%。這種原位合成法避免了傳統(tǒng)制備過程中必不可少的熱處理步驟,實(shí)現(xiàn)了低合金化Cu-Cr體系優(yōu)異的綜合性能。
英文摘要
Conductive and yet strong copper alloys are essential materials in highly mechanically loaded electrical devices. We demonstrate a novel in-situ synthesis approach via laser metal deposition (LMD) in a lean copper alloy, Cu–3.4Cr–0.6Nb (at%). Strengthening in the lean alloy comes from chromium nano-scale precipitates formed in-situ (4 nm diameter; number density 8 × 1023 m−3) and from Laves phase particles (< 1 µm diameter; 2.2 vol%), dispersed across the microstructure. This dual dispersion, in a nearly pure copper matrix, is achieved through a suited combination of chromium alloying and cooling rate during LMD synthesis. The as-synthesized alloy has a conductivity of 68% IACS (International Annealed Copper Standard) and a Vickers hardness of 146, at room temperature. The latter is 11% above the value reported for the strongest lean reference ternary alloy Cu–8Cr–4Nb (at%). The in-situ synthesis approach averts any heat treatment step, which has been an essential step previously in conventional manufacturing, for realizing the property combination in lean Cu–Cr based system.
微信公眾號:Goal Science
投稿郵箱:wechat@gs-metals.com
投稿微信:GSmaterial
