金屬頂刊雙語導讀丨Scripta Mater. Vol.189, Dec. 2020(全)
2020-09-07 來源: Goal Science
本期包含金屬材料領域論文13篇,涵蓋了NiMo合金、Sn-Ni合金、低碳鋼、Ni-Mn-Sn單晶、Ni-30Cr-10Fe合金、高熵合金、純鎢等,國內科研單位包括上海交通大學、蘭州大學、清華大學、浙江大學、東北大學、南京大學、西安交通大學、北京理工大學、南京理工大學、山東大學等(通訊作者單位)。
Vol. 189 目錄
SCRIPTA Vol. 189, Dec. 2020, P1-6
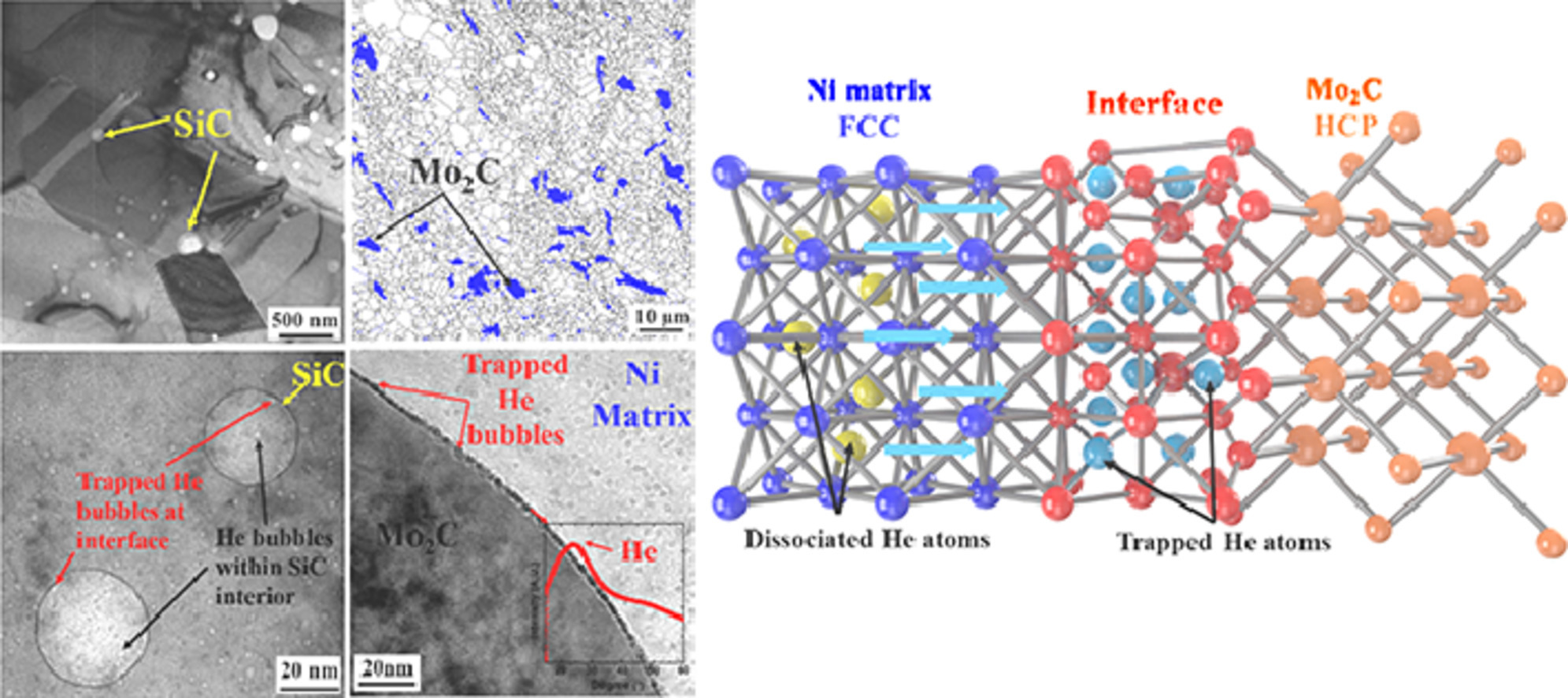
1. Synergistic effect of Mo2C micro-particles and SiC nanoparticles on irradiation-induced hardening in dispersion-precipitation strengthened NiMo alloys
Mo2C微顆粒和SiC納米顆粒對彌散析出強化NiMo合金輻照硬化的協同作用
Chao Yang, Tao Wei, Guoliang Zhu, Da Shu?, Jiang Ju, Wenzhe Zhou, An pingDong, Baode Sun, Mihail Ionescu
Da Shu: dshu@sjtu.edu.cn,上海交通大學
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.07.058
摘要
本工作研究了一種新型彌散析出強化NiMo合金優異的抗氦離子輻照硬化的機理。微觀組織觀察表明Mo2C微顆粒/鎳基體界面和SiC納米顆粒/鎳基體界面可以有效地捕獲氦氣泡,從而協同抑制Ni基體中游離氦氣泡的形成和長大。研究結果表明合理的大量彌散分散的Mo2C微顆粒和SiC納米顆粒可以有效地提高輻照硬化的抑制效率,有利于耐輻照鎳基合金的優化設計。
英文摘要
The mechanism for outstanding resistance to He-ion irradiation-induced hardening of a novel dispersion-precipitation strengthened NiMo alloy has been investigated. Microstructural observations show the interface between Mo2C micro-particles and Ni matrix and between SiC nanoparticles and Ni matrix can effectively trap He bubbles, thus synergistically inhibiting the formation and growth of the dissociated He bubbles in the Ni matrix. It suggests that the reasonable high amounts of well-dispersed Mo2C micro-particles and SiC nanoparticles can effectively improve the inhibition efficiency of irradiation-induced hardening and are beneficial for the optimization and design of irradiation-resistant Ni-based alloys.
SCRIPTA Vol. 189, Dec. 2020, P21-24
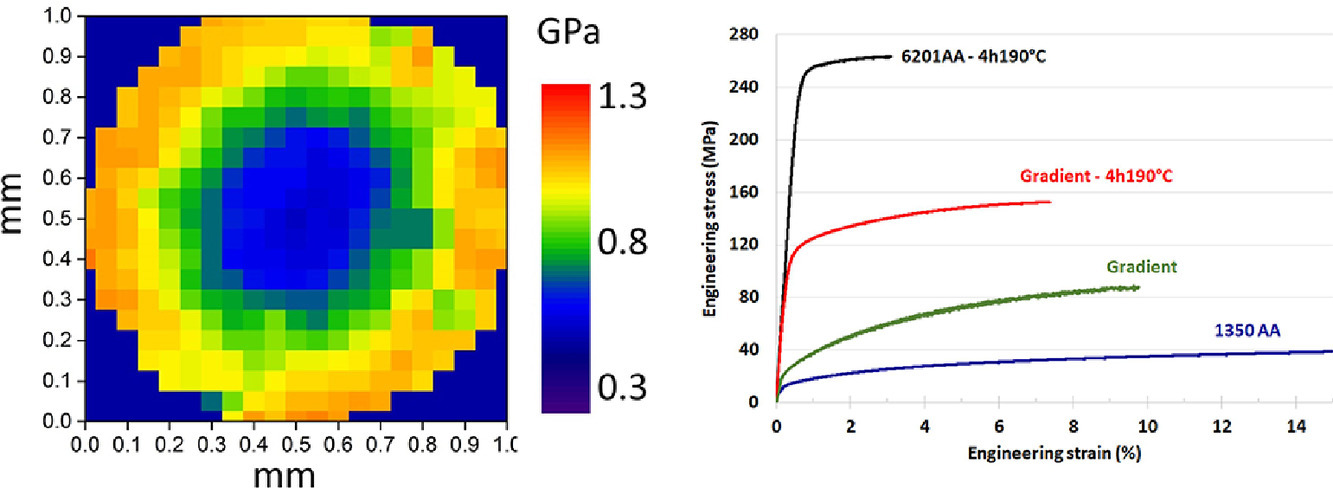
2. Multifunctional properties of composition graded Al wires
成分梯度鋁絲的多功能性研究
Cui Yang, Nicolas Masquellier, Camille Gandiolle, Xavier Sauvage?
Xavier Sauvage: xavier.sauvage@univ-rouen.fr
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.07.052
摘要
本工作研究了利用成分梯度AlMgSi絲優化電導率和扭轉強度的潛力。研究人員將工業純鋁與AlMgSi合金一起拉拔,然后擴散退火,得到了具有成分梯度的鋁絲。借助于納米壓痕測試,對擴散梯度和沉淀處理的局部硬化響應進行了評估。通過透射電子顯微鏡表征了具有納米沉淀空間梯度的微觀組織。結果表明,與基于經典混合原則的預測結果相比,這種梯度結構能提高電導率和扭轉強度。
英文摘要
The potentiality of composition graded AlMgSi wires for optimized combination of electrical conductivity and torsion strength has been investigated. Composition graded wires were obtained by co-drawing commercially pure Al with an AlMgSi alloy followed by diffusion annealing. Diffusion gradients and local hardening response to precipitation treatments were evaluated thanks to nano-indentation measurements. Resulting microstructures with spatial gradients of nanoscaled precipitates were characterized by transmission electron microscopy. Finally, it is shown that such graded structures give rise to an improved combination of electrical conductivity and mechanical strength in torsion as compared to the predictions based on a classical rule of mixture.
SCRIPTA Vol. 189, Dec. 2020, P42-47
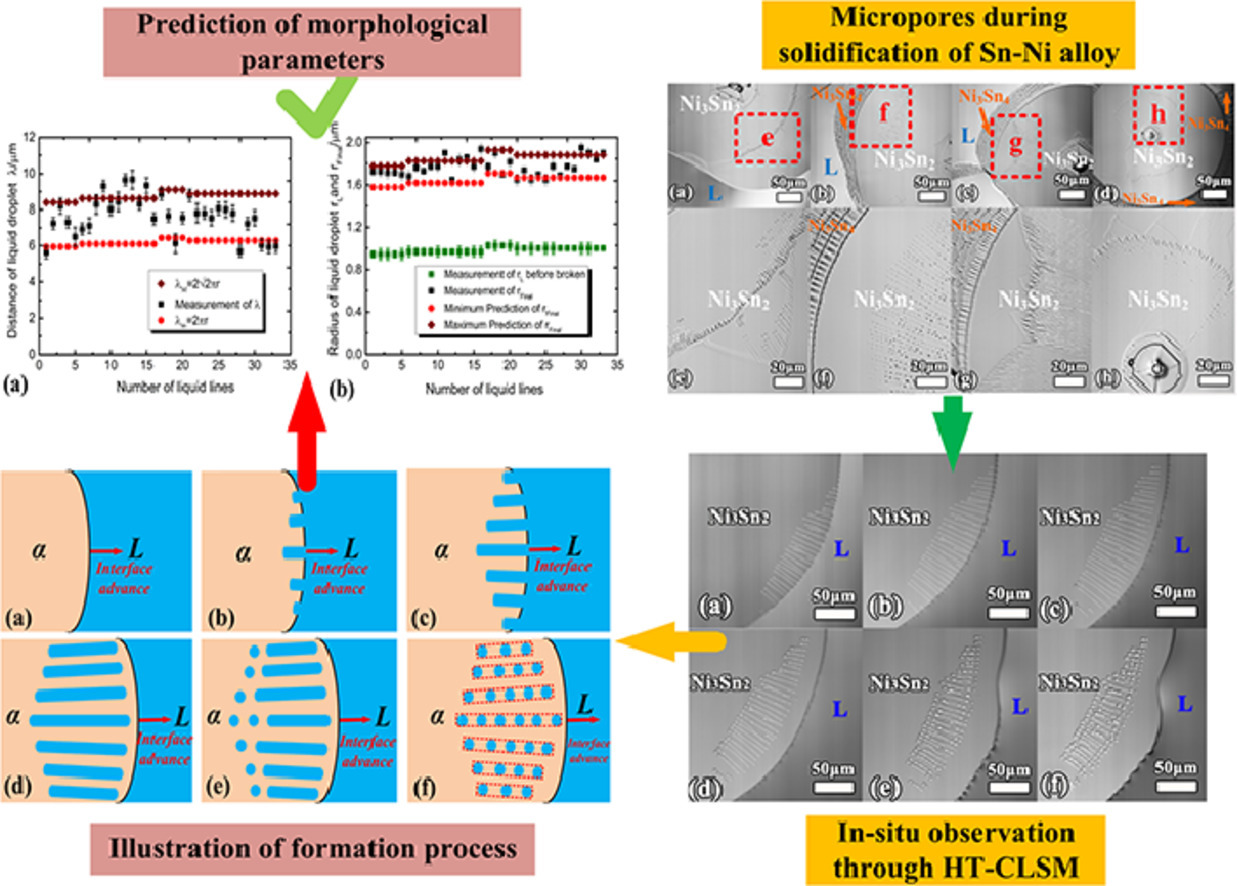
3. In-situ analysis on formation of micropores by Rayleigh instability in solidification of Sn-Ni alloy
Sn-Ni合金凝固過程中瑞利失穩微孔形成的原位分析
Peng Peng?, Jinmian Yue, Anqiao Zhang, Xudong Zhang, Yuanli Xu
Peng Peng: pengp@lzu.edu.cn,蘭州大學
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.07.057
摘要
通過共聚焦激光掃描顯微鏡原位觀察,研究了Sn-Ni合金凝固過程中半徑約為1μm微孔的形成新機理。凝固過程中形成了一系列與生長的L/Ni3Sn2界面的穩定性密切相關的液相線,隨后這些液相線由于固態Ni3Sn2相中的瑞利不穩定性而分解成不同行的液滴。研究人員確認了微孔形成與液滴之間的關系。另外,微孔半徑的分布與瑞利不穩定性理論的預測一致。
英文摘要
A new formation mechanism of micropores whose radii are approximately 1 μm is investigated during solidification of Sn-Ni alloy through the in-situ observation by confocal laser scanning microscope. A series of liquid lines which are closely related to the stability of the growing L/Ni3Sn2 interface were formed during solidification, then, these liquid lines decomposed into different rows of liquid droplets by Rayleigh instability in solid Ni3Sn2 phase. The relationship between the formation of the micropores and the liquid droplets is confirmed. In addition, the distribution of the radii of the micropores agrees with the prediction of the Rayleigh instability theory.
SCRIPTA Vol. 189, Dec. 2020, P48-52
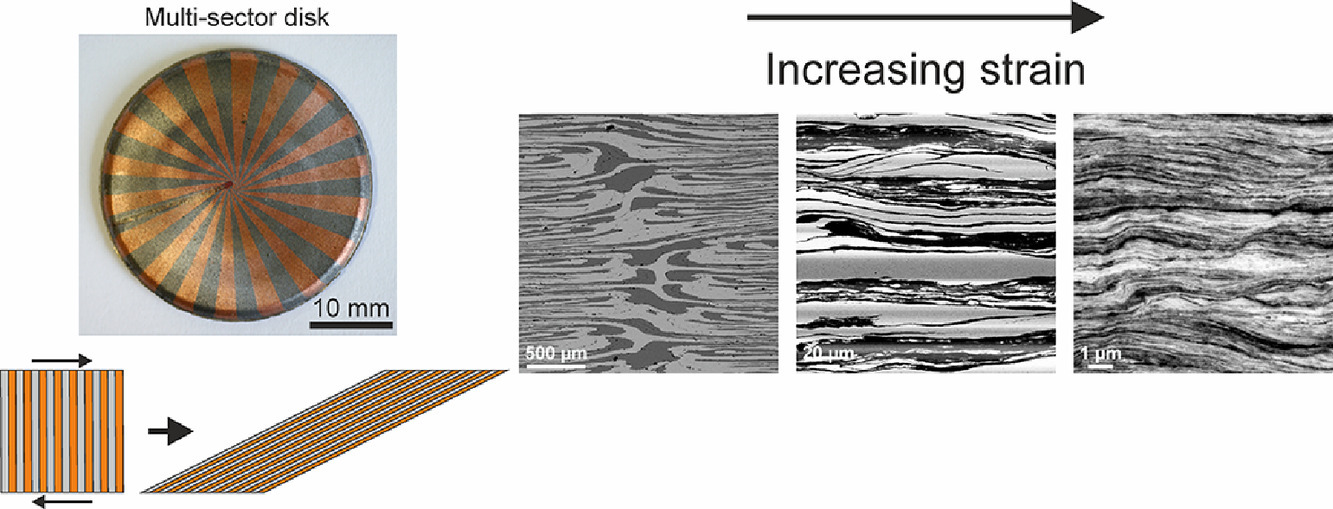
4. Microstructure, strength and fracture toughness of CuNb nanocomposites processed with high pressure torsion using multi-sector disks
多扇區圓盤高壓扭轉加工的CuNb納米復合材料的微觀結構、強度和斷裂韌性
A. Hohenwarter?
A. Hohenwarter: anton.hohenwarter@unileoben.ac.at
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.07.061
摘要
本工作采用特殊設計的圓盤,通過高壓扭轉處理CuNb復合材料。其中,圓盤由預先定義的單個扇形元素組成,稱為多扇形圓盤。通過改變所施加的塑性應變,復合材料的結構可以從相對粗大的多層結構調整為納米層狀結構。本工作首先介紹了該技術,展示了CuNb復合材料的顯微組織和硬度隨應變的演化,并對具有良好抗損傷性能的復合材料的斷裂韌性進行了研究。
英文摘要
CuNb composites were processed by high pressure torsion using specially designed disks consisting of a pre-defined number of single sector elements called multi-sector disks. By variation of the applied plastic strain the composite structure could be tuned ranging from relatively coarse multilayer structures to nanostructured laminates. In this first study the technique is introduced, the microstructural and hardness evolution of CuNb with varying strain is presented and a fracture toughness study of the finest composite structure showing good damage tolerance has been performed.
SCRIPTA Vol. 189, Dec. 2020, P53-57
5. Kinetics of deformation-induced martensitic transformation under cyclic loading conditions
循環加載條件下變形誘導馬氏體轉變的動力學研究
Cheng Luo, Jingyu Sun, Wu Zeng, Huang Yuan?
Huang Yuan: yuan.huang@tsinghua.edu.cn,清華大學
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.08.003
摘要
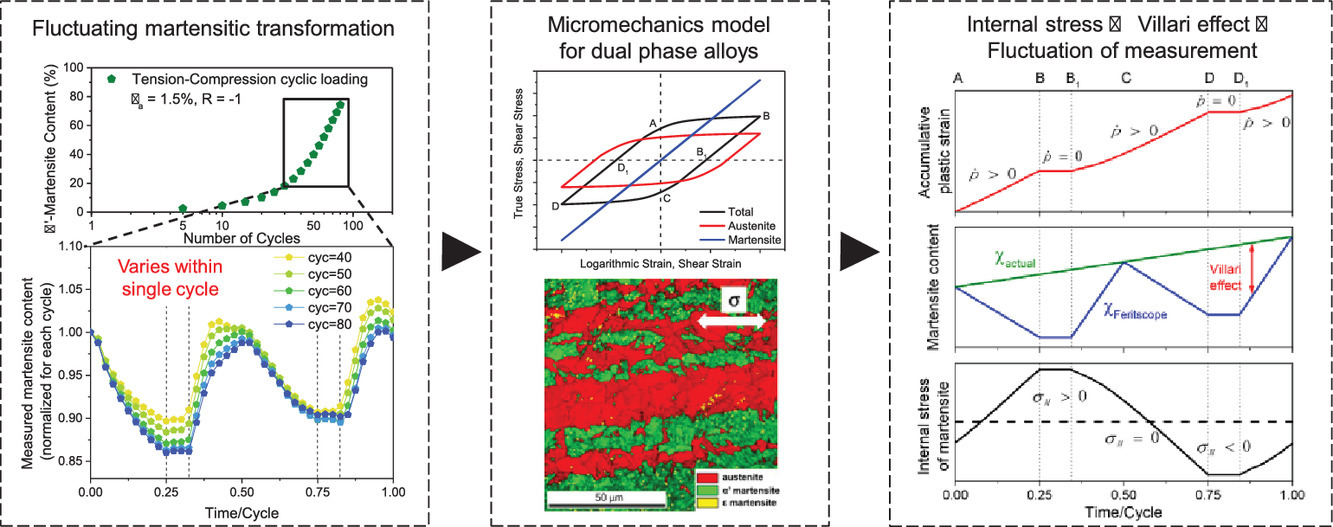
單調加載條件下的形變誘導馬氏體相變(DIMT)已經研究了很多年。但是,非單調加載條件下DIMT的演化卻很少有人研究。本工作通過實驗探索了在拉伸-壓縮以及扭轉循環載荷條件下DIMT的演化,并展示了通過Feritscope測量的奧氏體不銹鋼在循環載荷下的波動行為,這種波動性為在單調載荷下沒有觀察到。本研究表明,測量的馬氏體波動和兩相的特征有關,且可以用馬氏體相中的維拉里效應(Villari effect)來解釋。假定馬氏體含量隨有效塑性應變單調增加,并沿著主應力分布。研究人員提出了針對單調和循環加載條件下DIMT的統一動力學模型,并進行了實驗驗證。DIMT各向異性的建立可以結合模型與循環塑性來描述。
英文摘要
Deformation-induced martensitic transformation (DIMT) has been investigated for many years mainly under monotonic loading conditions. However, the evolution of the DIMT under non-monotonic loading conditions has rarely been studied. The present work experimentally explored the development of DIMT under tension-compression as well as torsion cyclic loading conditions and showed fluctuating behavior within loading cycles in austenitic stainless steels measured by Feritscope, which was not observed under monotonic loadings. The present study showed that the fluctuation of the martensite measurement was related to the dual-phase features and could be explained by the Villari effect in the martensite phase. The martensite contents are assumed to increase monotonically with the effective plastic strain and are distributed along with principal stresses. A unified kinetics model for DIMT was proposed for both monotonic and cyclic loading conditions and verified experimentally. The anisotropic development of DIMT can be described by the model in combining with cyclic plasticity.
SCRIPTA Vol. 189, Dec. 2020, P67-71
6. Enhanced hydrogen embrittlement of low-carbon steel to natural gas/hydrogen mixtures
提高低碳鋼在天然氣/氫混合物中的抗氫脆能力
Juan Shang, Weifeng Chen, Jinyang Zheng, Zhengli Hua?, Lin Zhang, Chengshuang Zhou, Chaohua Gu
Zhengli Hua: huazhengli007@126.com,浙江大學
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.08.011
摘要
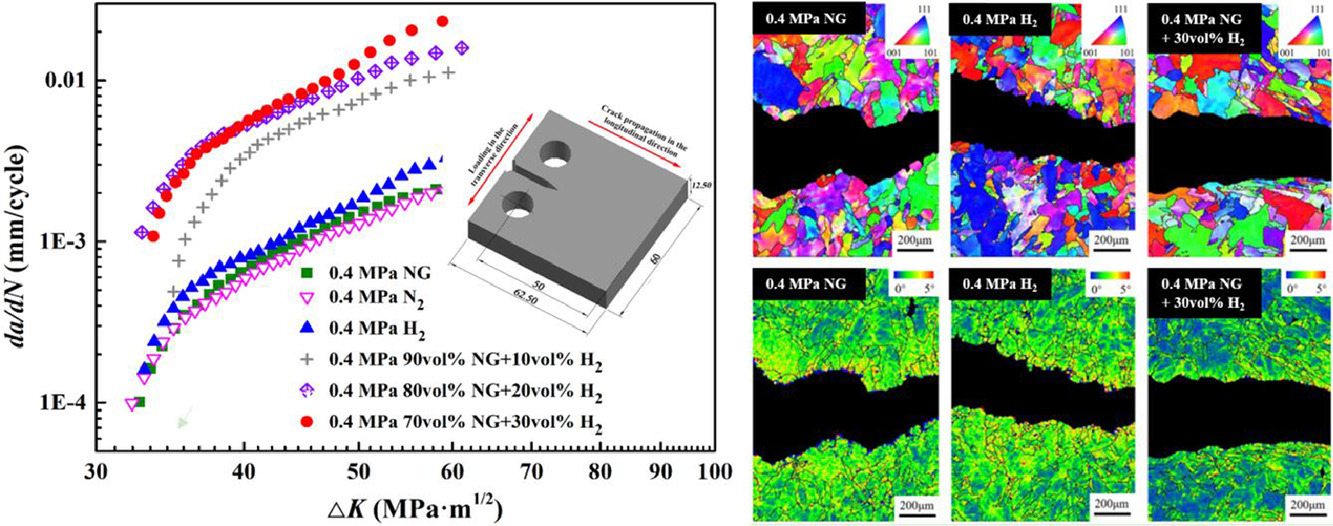
本工作采用疲勞裂紋擴展速率 (FCGR) 試驗研究了低碳鋼在實際天然氣/氫混合氣體和二氧化碳/氫/氮混合氣體中的疲勞性能。研究人員首次發現在混合氣體中FCGR的加速比氫氣或天然氣中的FCGR快得多。天然氣/氫氣混合氣體使斷裂模式從韌性疲勞條紋轉變為脆性解離斷裂,并限制了裂紋周圍的變形行為。二氧化碳和氫氣對材料的協同作用被認為是鋼在混合氣體中性能異常的主要原因。
英文摘要
Fatigue crack growth rate (FCGR) tests were used to investigate the fatigue property of low-carbon steel in actual natural gas/hydrogen mixtures and carbon dioxide/hydrogen/nitrogen mixtures. It is found for the first time that the acceleration of FCGRs in the mixtures are much faster than that in hydrogen or natural gas. Natural gas/hydrogen mixtures changed the fracture mode from ductile fatigue striation to brittle cleavage fracture, and restricted the deformation activities around the crack. Synergy effect of carbon dioxide and hydrogen on the material is proposed to be the major reason for the abnormal performance of steel in the mixtures.
SCRIPTA Vol. 189, Dec. 2020, P78-83
7. Enhanced cyclability of elastocaloric effect in a directionally solidified Ni55Mn18Ga26Ti1 alloy with low hysteresis
提高低滯后定向凝固Ni55Mn18Ga26Ti1合金彈性熱效應的循環能力
Dong Li, Zongbin Li?, Xiaoliang Zhang, Bo Yang, Dunhui Wang?, Xiang Zhao, Liang Zuo
Zongbin Li: lizb@atm.neu.edu.cn,東北大學
Dunhui Wang: wangdh@nju.edu.cn,南京大學
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.08.010
摘要
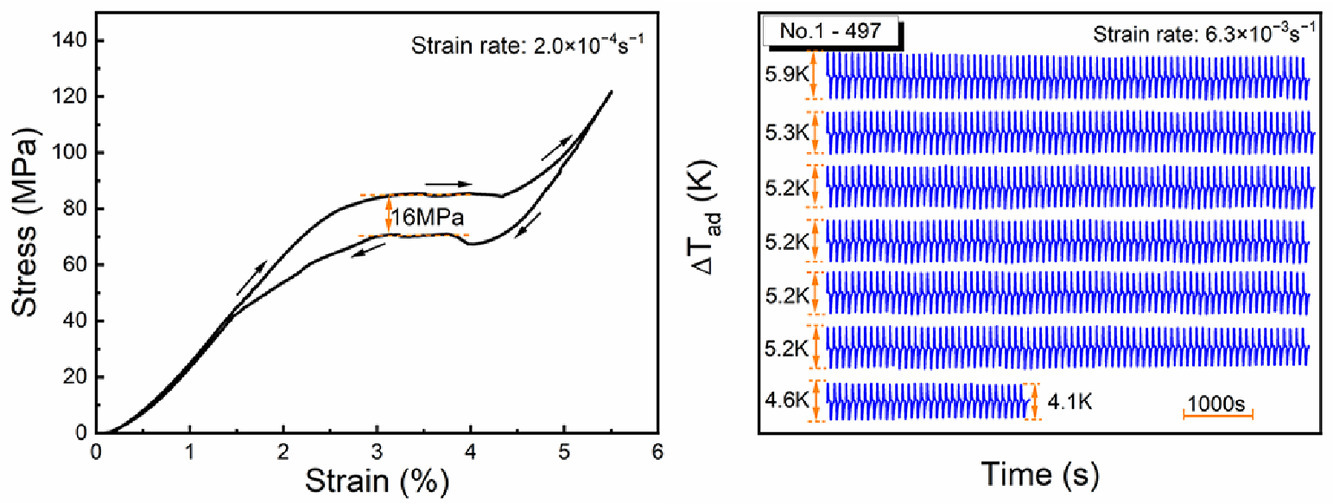
本工作結合成分調整和組織調控,提高了定向凝固Ni55Mn18Ga26Ti1合金的彈性熱性能。由于鈦的引入以及具有粗大柱狀晶粒和強<001>A擇優取向的顯微組織特征,研究人員成功地將熱滯后和應力滯后分別減小到4K和16MPa。在去除一個120MPa的低應力后,大的絕熱溫度變化為-6.2k,由此造成比絕熱溫度變化為51.7K/GPa。此外,該合金熱彈效應的循環性能增強,可達到497次加載/卸載循環,性能系數高達25.6。
英文摘要
Enhanced elastocaloric properties in a directionally solidified Ni55Mn18Ga26Ti1 alloy were achieved by combining composition tuning and microstructural control. Owing to the introduction of Ti and the microstructural feature with coarse columnar grains and strong <001>A preferred orientation, the thermal hysteresis and the stress hysteresis were successfully reduced to 4K and 16MPa, respectively. Large adiabatic temperature change of -6.2K was obtained on removing a low stress of 120MPa, resulting in the specific adiabatic temperature change of 51.7K/GPa. Moreover, the alloy demonstrated enhanced cyclability of elastocaloric effect up to 497 loading/unloading cycles and high coefficient of performance value of 25.6.
SCRIPTA Vol. 189, Dec. 2020, P106-111
8. On the role of atomic shuffling in the 4O, 4M and 8M martensite structures in Ni-Mn-Sn single crystal
Ni-Mn-Sn單晶中原子挪動對4O, 4M和8M馬氏體結構的影響
R. Chulist?, P. Czaja
R. Chulist: r.chulist@imim.pl
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.08.007
摘要
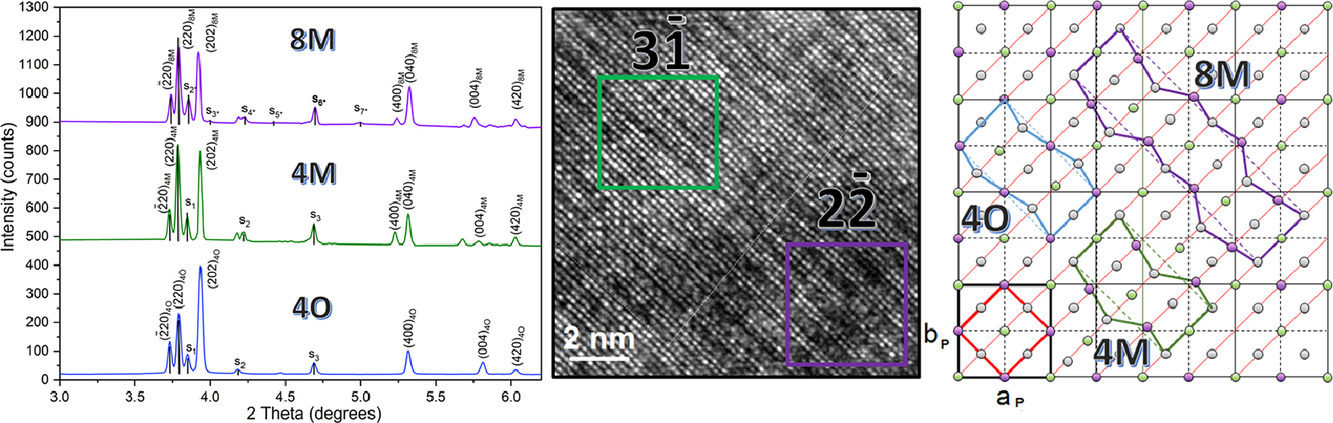
本工作采用高能同步輻射和高分辨透射電子顯微鏡對Ni50Mn37.5Sn12.5單晶中四層馬氏體相的晶體結構進行了研究。根據樣品的變形過程,研究人員發現了3種不同類型的單胞,即4O、4M和8M。最穩定的相是4M馬氏體。通過對調制反射強度的分析,可以確定周期性原子位移為0.3497 Å。研究結果支持周期性原子挪動的概念,而不是自適應納米孿晶的方法。
英文摘要
The crystal structure of a four-layered martensite phase in Ni50Mn37.5Sn12.5 single crystal following various modes of training procedure was examined by high energy synchrotron radiation and high-resolution transmission electron microscopy. Three distinct types of unit cell i.e. 4O, 4M, and 8M were unveiled, depending on the mechanical history of the specimen. The most stable phase turned out to be the 4M martensite. Analysis of the intensity of modulation reflections allowed for defining a periodic atomic displacement of 0.3497 Å. The results support the concept of a periodic atomic shuffling as opposed to the adaptive nanotwining approach.
SCRIPTA Vol. 189, Dec. 2020, P122-128
9. A novel test technique for the mechanistic study of initiation of environmentally assisted cracking on a Ni-30Cr-10Fe alloy in simulated pressurized water reactor primary water
新型測試技術用于研究Ni-30Cr-10Fe合金在模擬壓水反應堆原生水中環境誘導裂紋萌生的機理
Wenjun Kuang?, Han Yue, Xingyu Feng, Bo Yang, Chaowei Guo
Wenjun Kuang: wjkuang66@xjtu.edu.cn,西安交通大學
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.08.016
摘要
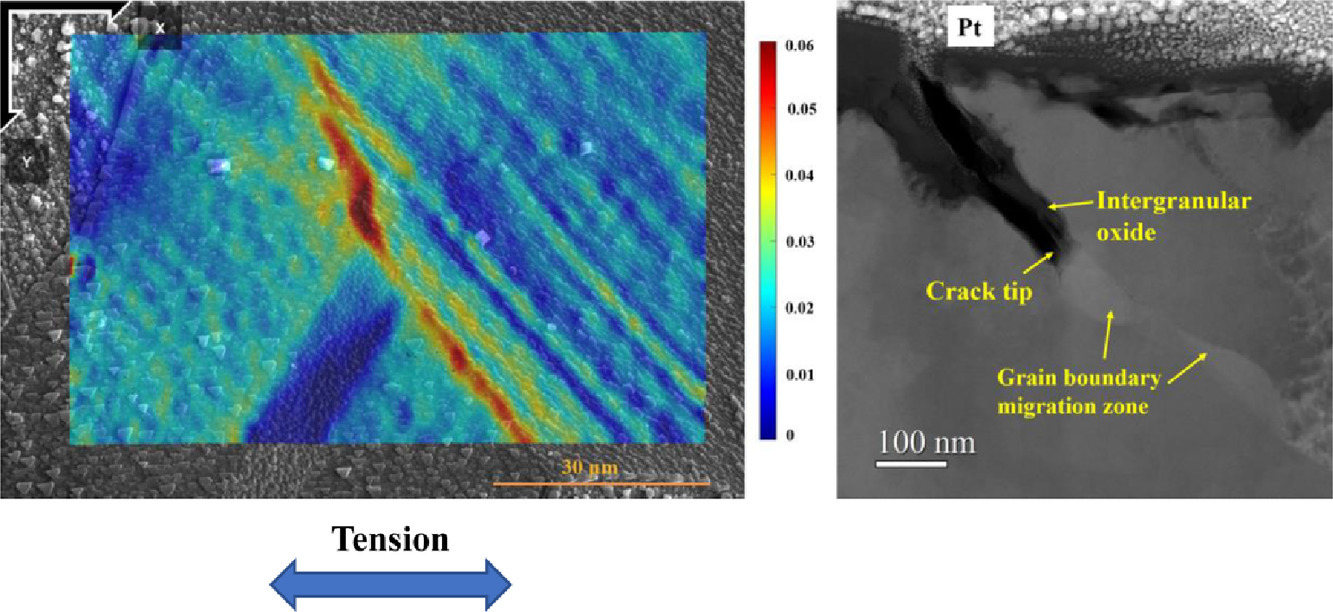
本工作開發了循環步驟應變法,用于研究Ni-30Cr-10Fe合金(690合金)在模擬壓水堆 (PWR) 原生水中環境誘導裂紋(EAC)的萌生。由于該技術,腐蝕和應變在690合金EAC萌生過程中的作用得以去耦合,并再現了應力腐蝕開裂的典型微觀組織,即擴散誘導晶界遷移和氧化進入遷移區。利用表面氧化粒子作為標記的數字圖像相關法(DIC)成功和此技術相結合,并應用于高分辨平面應變測量中。初步結果顯示,沿晶裂紋萌生與相鄰晶粒的高局部應變有關,這表明沿晶界的滑移傳遞促進了裂紋萌生。循環步驟應變法對于機械研究EAC是適合的,因為它使化學和機械過程的單獨作用變得可調整和可追蹤。
英文摘要
Recurring step straining was developed to investigate the environmentally assisted cracking (EAC) initiation of a Ni-30Cr-10Fe alloy (Alloy 690) in simulated pressurized water reactor (PWR) primary water. Thanks to this technique, the roles of corrosion and straining in the EAC initiation of Alloy 690 was decoupled and typical microstructures in stress corrosion cracking, i.e. diffusion induced grain boundary migration and oxidation into the migration zone, were reproduced. Digital image correlation using indigenous surface oxide particles as markers was successfully incorporated into this technique for high-resolution in-plane strain measurement. The preliminary results show that intergranular crack initiation is correlated with the high local strain in both adjacent grains, indicating that slip transfer across the grain boundary promotes crack initiation. Recurring step straining is desirable for the mechanistic study of EAC as it makes the separate roles of chemical and mechanical processes adjustable and traceable.
SCRIPTA Vol. 189, Dec. 2020, P129-134
10. A novel stress-induced martensitic transformation in a single-phase refractory high-entropy alloy
單相耐火高熵合金中一種新型的應力誘導馬氏體相變
Liang Wang, Tangqing Cao, Xudong Liu, Benpeng Wang, Ke Jin, Yaojian Liang, Lu Wang, Fuchi Wang, Yang Ren, Jun Liang, Yunfei Xue?
Yunfei Xue: xueyunfei@bit.edu.cn,北京理工大學
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.08.013
摘要
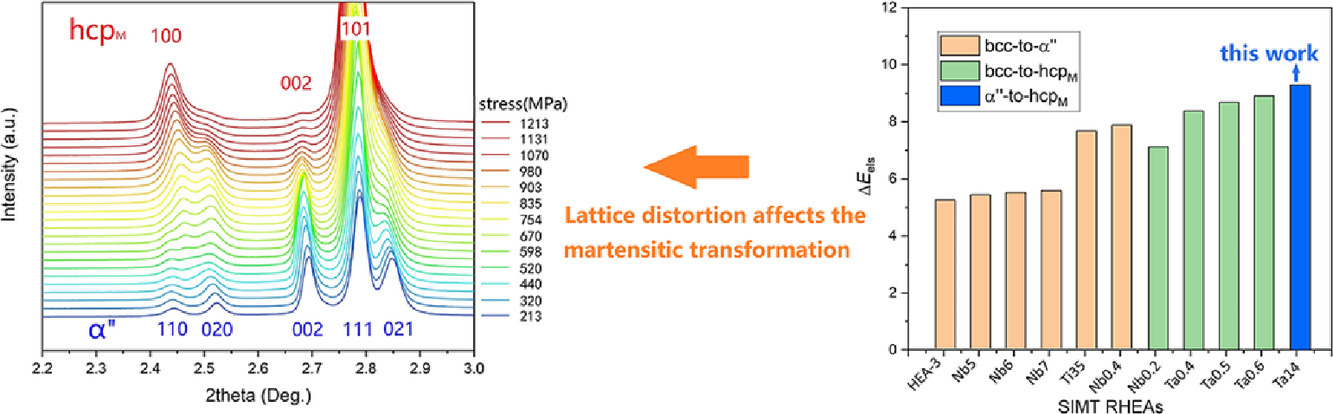
高熵合金(HEA)為設計具有應力誘導馬氏體相變(SIMT)的亞穩態合金提供了新的視角,以克服強度和塑性“此消彼長”的問題。本文在單個正交晶系的耐火HEA(Ti16Zr35Hf35Ta14 RHEA)中報道了一種新型的SIMT,即正交晶系向密排六方的馬氏體相變,該材料顯示出良好的屈服強度-延展性匹配。對Ti16Zr35Hf35Ta14和其他幾種RHEA彈性畸變能(ΔEels)的分析表明,嚴重的晶格畸變是導致此類SIMT的關鍵因素。將“d-電子合金設計”方法與?Eels相結合,可以很好地預測RHEA中的相結構和SIMT過程。此工作為RHEA的晶格畸變和SIMT之間的關系提供了新的見解,有利于亞穩合金的設計開發。
英文摘要
High-entropy alloys (HEAs) provide a new perspective to design metastable alloys with the stress-induced martensitic transformation (SIMT) for overcoming the strength-ductility trade-off. Here, we report a novel SIMT, orthorhombic to hexagonal close-packed martensite, in a single orthorhombic refractory HEA (Ti16Zr35Hf35Ta14 RHEA), showing a good yield strength-ductility matching. The analysis of the elastic distortion energy (?Eels) of Ti16Zr35Hf35Ta14 and several other RHEAs reveals that severe lattice distortion is a key factor which causes this SIMT. Combined the “d-electron alloy design” approach with the ?Eels, the phase configuration and SIMT path in RHEAs can be well predicted. Our work brings new insights between the lattice distortion and SIMT of RHEAs, benefiting the metastable alloy development.
SCRIPTA Vol. 189, Dec. 2020, P135-139
11. Orientation dependence of the nano-indentation behaviour of pure Tungsten
純鎢納米壓痕行為的取向依賴性
Hongbing Yu?, Suchandrima Das, Haiyang Yu, Phani Karamched, Edmund Tarleton, Felix Hofmann?
Hongbing Yu: hongbing.yu@eng.ox.ac.uk
Felix Hofmann: felix.hofmann@eng.ox.ac.uk
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.08.014
摘要
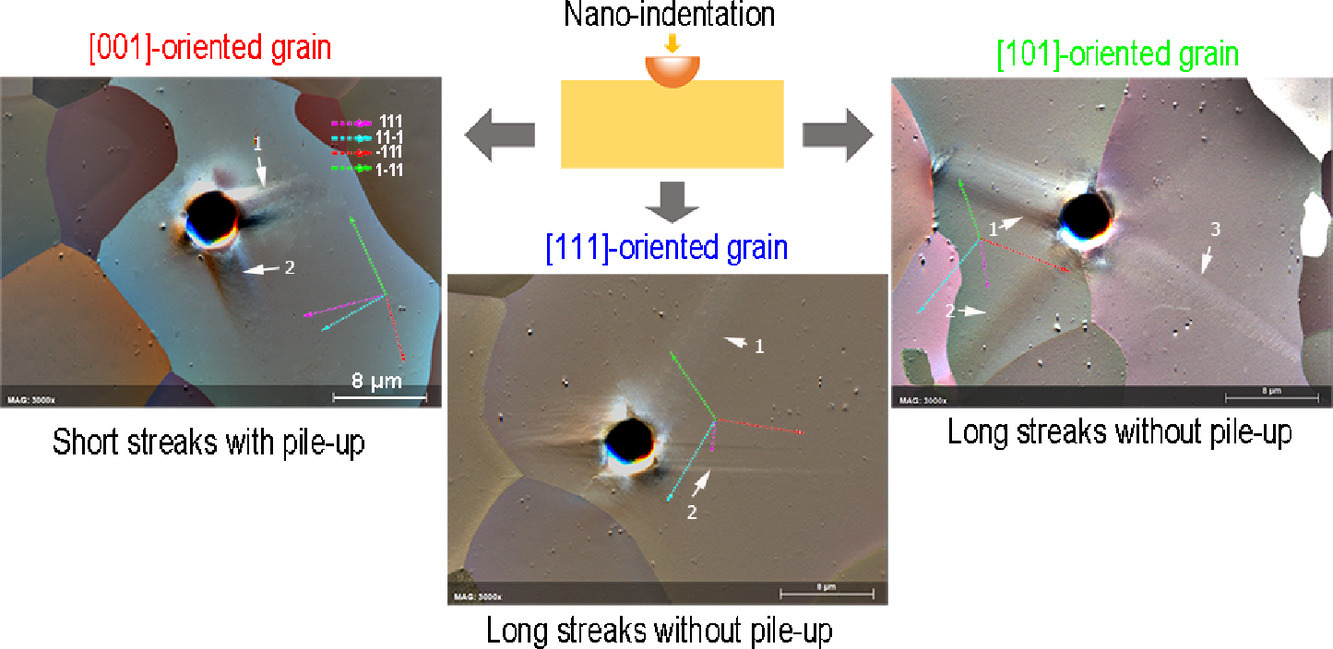
納米壓痕和晶體塑性有限元(CPFE)模擬的耦合被廣泛用于定量測定材料的小尺度力學行為。早期的研究表明,CPFE可以成功地再現不同晶體取向的載荷-位移曲線和表面形貌。本工作報告了鎢中殘余晶格應變花樣和位錯結構的取向依賴性。對于一個或多個近似于平行樣品表面的柏氏矢量,位錯運動和殘余晶格應變被限于狹長的通道中。CPFE無法重現此行為,我們的分析揭示了相應的潛在機制。
英文摘要
Coupling of nano-indentation and crystal plasticity finite element (CPFE) simulations is widely used to quantitatively probe the small-scale mechanical behaviour of materials. Earlier studies showed that CPFE can successfully reproduce the load-displacement curves and surface morphology for different crystal orientations. Here, we report the orientation dependence of residual lattice strain patterns and dislocation structures in tungsten. For orientations with one or more Burgers vectors close to parallel to the sample surface, dislocation movement and residual lattice strains are confined to long, narrow channels. CPFE is unable to reproduce this behaviour, and our analysis reveals the responsible underlying mechanisms.
SCRIPTA Vol. 189, Dec. 2020, P140-144
12. Stiff, strong and ductile heterostructured aluminum composites reinforced with oriented nanoplatelets
用定向納米片晶強化的具有高強高韌高剛度的異質結構鋁基復合材料
Jinfeng Nie?, Yuyao Chen, Xiang Chen, Xiangfa Liu, Guiliang Liu, Yonghao Zhao?, Yuntian Zhu
Jinfeng Nie: niejinfeng@njust.edu.cn,南京理工大學
Yonghao Zhao: xfliu@sdu.edu.cn,山東大學
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.08.017
摘要
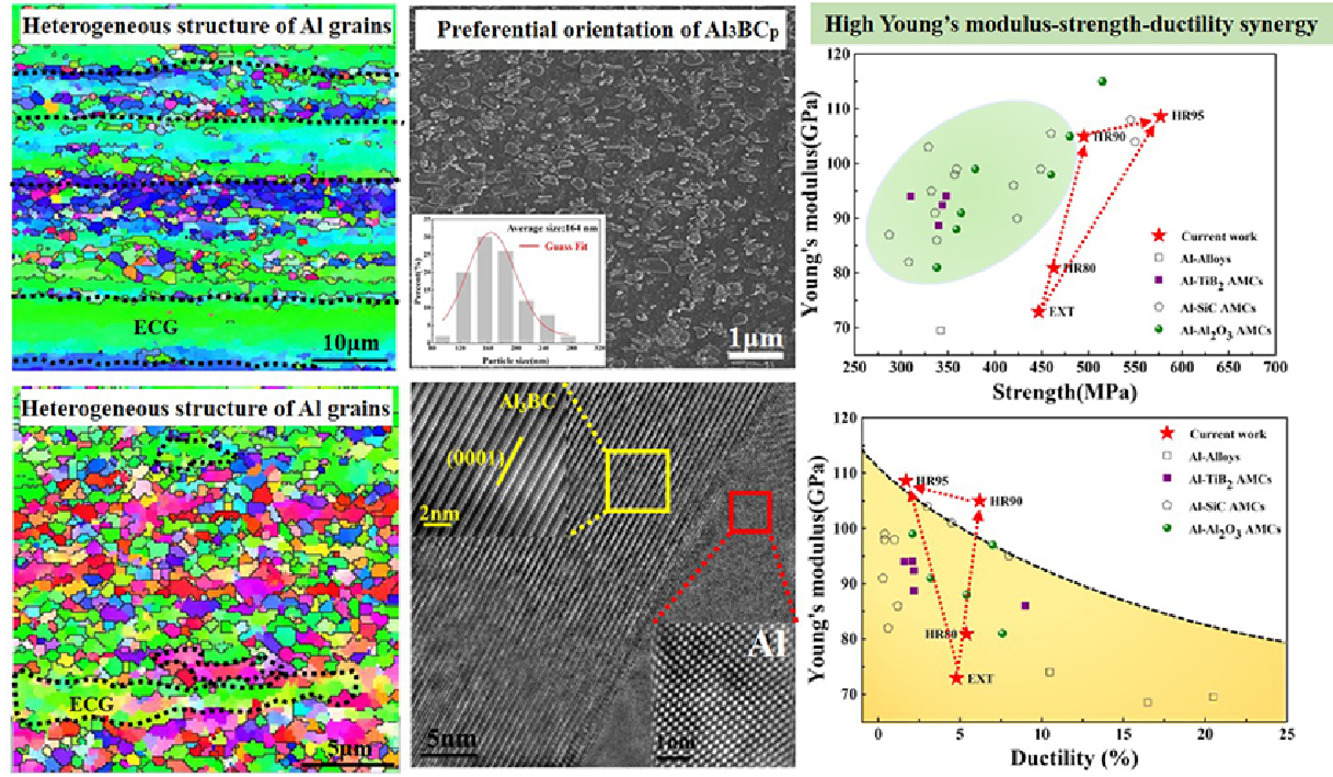
本工作報道了一種結合擇優顆粒取向的液固反應方法,用來制備具有超高楊氏模量(105GPa)、高拉伸強度(495MPa)和合理塑性(6.2%)的Al3BC/6061異質復合材料。Al3BC納米片晶的擇優取向貢獻了超高的剛度,Al基體的異質晶粒結構有助于異質形變誘導應力并提供額外的應變硬化,從而產生高的強度和良好的延展性。這些結果為改善金屬基復合材料的機械性提供了新的無限可能。
英文摘要
In this study, we report a liquid-solid reaction method combined with preferential particle orientation for fabricating a heterostructured Al3BC/6061 composite with ultrahigh Young's modulus (105 GPa), high tensile strength (495 MPa) and reasonable ductility (6.2%). The preferential orientation of Al3BC nanoplatelets contributes to the ultrahigh stiffness, and heterogeneous grain structure of the Al matrix facilitates the development of hetero-deformation induced stress and extra strain hardening, giving rise to high strength and good ductility. These results shed new sights into the untapped potential in improving the mechanical properties of metal matrix composites.
SCRIPTA Vol. 189, Dec. 2020, P145-150
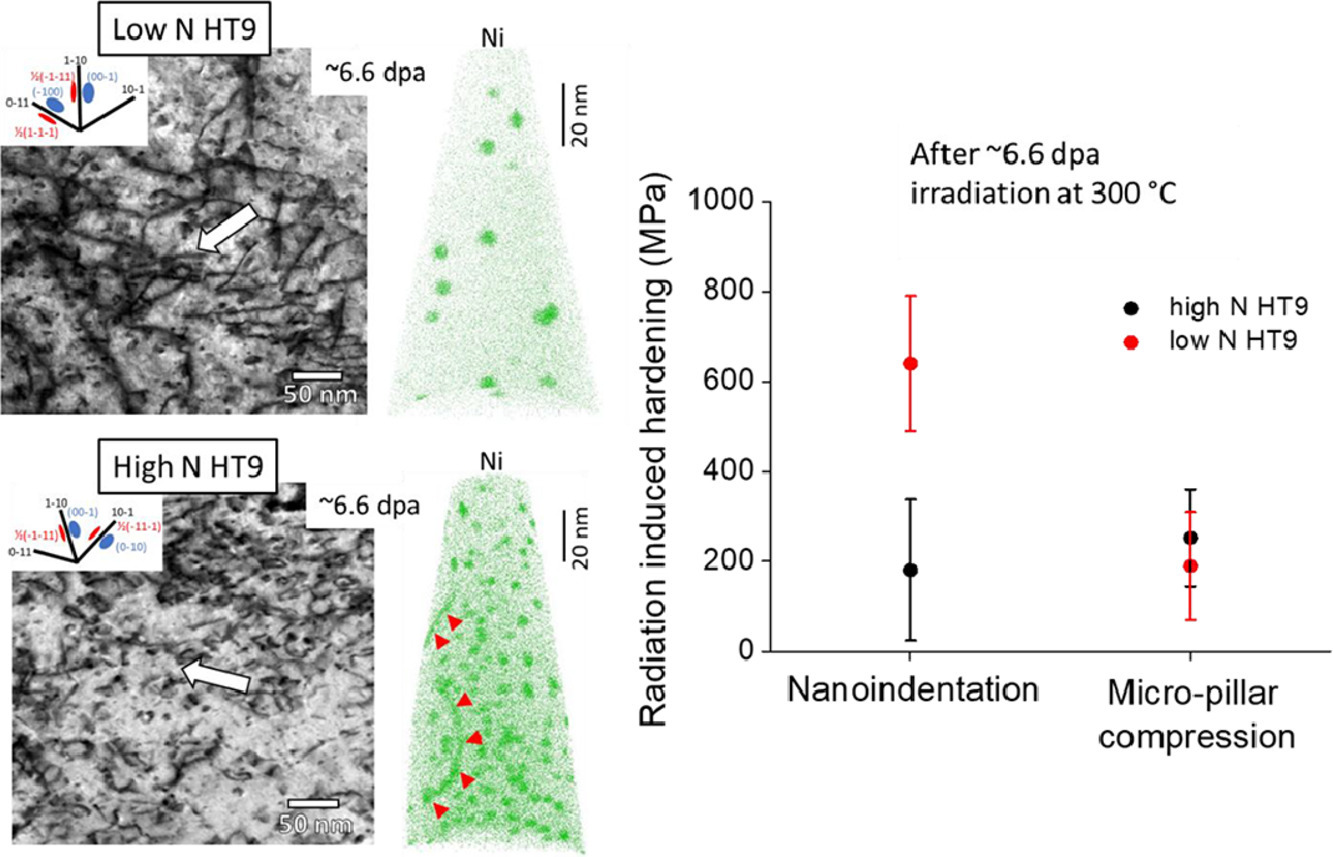
13. Nitrogen effects on radiation response in 12Cr ferritic/martensitic alloys
氮對12Cr鐵素體/馬氏體合金輻照響應的影響
E. Aydogan?, J.G. Gigax, S.S. Parker, B.P. Eftink, M. Chancey, J. Poplawsky, S.A. Maloy
E. Aydogan: aydogane@metu.edu.tr
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.08.005
摘要
鐵素體/馬氏體鋼是下一代核反應堆中應用于高劑量的最佳候選結構材料之一。結構材料的成分必須加以優化,以確保在輻照期間穩定服役。本工作報告了間隙氮對可控氮濃度的12Cr鐵素體/馬氏體HT9鋼輻照響應的影響。結果表明,基質中大量的“游離”氮穩定了間隙團簇,從而導致(i)較大的位錯環尺寸(ii)較低的位錯環密度(iii)輻照誘導硬化略有降低。此外,它還會影響Ni的擴散機理和富Ni/Si析出的形成。
英文摘要
Ferritic/martensitic steels are one of the best candidates for structural materials for high dose applications in next generation nuclear reactors. The composition of structural materials must be optimized for reliable service during irradiation. This study reports the effect of interstitial nitrogen on radiation response in 12Cr ferritic/martensitic HT9 steels having a controlled nitrogen concentration. Results show that a high amount of ‘free’ nitrogen in the matrix stabilizes the interstitial clusters which leads to (i) larger loop sizes (ii) lower loop density and (iii) slightly reduced radiation induced hardening. It also affects diffusion mechanism of Ni and formation of Ni/Si-rich precipitates.
微信公眾號:Goal Science
投稿郵箱:wechat@gs-metals.com
投稿微信:GSmaterial
