金屬頂刊雙語導(dǎo)讀丨Acta Mater. Vol.198,1 Oct. 2020(全)
2020-09-12 來源: Goal Science
本期包含金屬材料領(lǐng)域論文17篇,涵蓋了單晶鎢、記憶合金、鎂合金、T91鋼、銀薄膜、多主元合金、高熵合金、不銹鋼等,國內(nèi)科研單位包括西南交通大學(xué)、北京科技大學(xué)等(通訊作者單位)。
Vol. 198 目錄
ACTA Vol. 198, 1 Oct. 2020, P1-9
1. Trends in vacancy distribution and hardness of high temperature neutron irradiated single crystal tungsten
單晶鎢經(jīng)高溫中子輻照后空位分布和硬度的變化趨勢
G. Bonny?, M.J. Konstantinovic, A. Bakaeva, C. Yin, N. Castin, K. Mergia, V. Chatzikos, S. Dellis, T. Khvan, A. Bakaev, A. Dubinko, D. Terentyev
G. Bonny: gbonny@sckcen.be
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.07.047
摘要
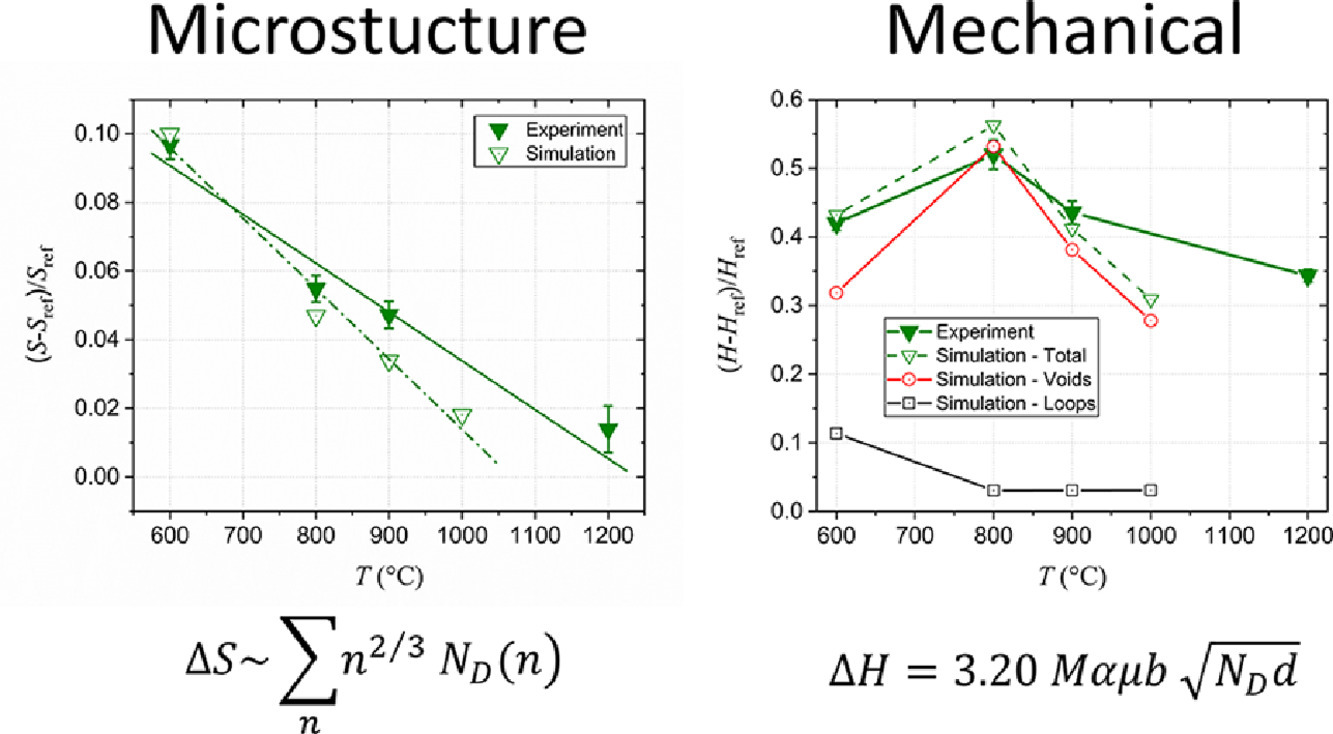
本研究的主要目的是提高我們對鎢在中子輻照條件下的空位缺陷和熱穩(wěn)定性的認(rèn)識,從而對ITER偏濾器中的溫度和中子通量進(jìn)行模擬。我們在600-1200℃的溫度范圍內(nèi)對單晶(100)進(jìn)行了中子輻照,輻照劑量最高達(dá)到0.12 dpa。我們采用正電子湮沒光譜法對體系中的缺陷進(jìn)行了測量,并通過硬度實驗聯(lián)立了輻照缺陷與力學(xué)性能變化之間的聯(lián)系。通過采用蒙特卡羅方法模擬中子輻照過程下微觀結(jié)構(gòu)的演化,進(jìn)一步增強(qiáng)了實驗結(jié)果的合理性。我們采用分散屏障模型對輻照后顯微組織與硬度之間的關(guān)系進(jìn)行了解釋。
英文摘要
The aim of the present study is to extend the knowledge about the formation and thermal stability of vacancy-type defects in tungsten under neutron irradiation, thereby mimicking the temperature and neutron flux expected in the ITER divertor. Neutron irradiation of single crystal tungsten, W(100), in the temperature range 600-1200 °C is performed up to 0.12 dpa. Positron annihilation spectroscopy is employed to detect the presence of open volume defects, while hardness tests are applied to relate the irradiation-induced defects with the modification of mechanical properties. Rationalization of the experimental results is enhanced by the application of a kinetic Monte Carlo simulation tool, applied to model the microstructural evolution under the neutron irradiation process. The relation between radiation microstructure and hardness is explained via a dispersed barrier model.
ACTA Vol. 198, 1 Oct. 2020, P10-24
2. Modeling the two-way shape memory and elastocaloric effects of bamboo-grained oligocrystalline shape memory alloy microwire
對竹子結(jié)構(gòu)寡晶形狀記憶合金的雙向形狀記憶效應(yīng)和熱彈性效應(yīng)的模擬
Ting Zhou, Guozheng Kang, Hao Yin, Chao Yu?
C. Yu: chaoyu@home.swjtu.edu.cn,西南交通大學(xué)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.07.057
摘要
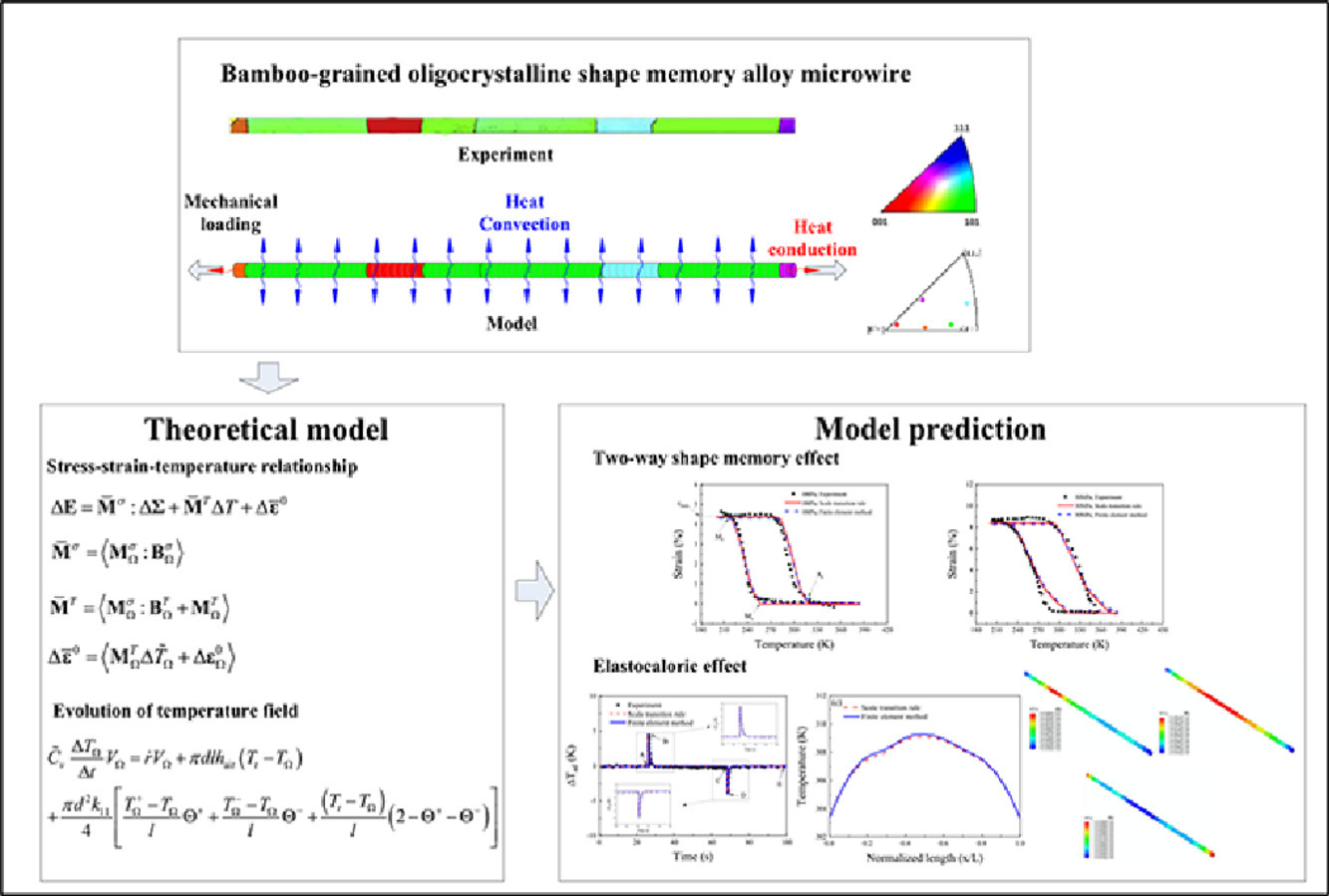
近年來的實驗研究表明,由于減少了晶界約束,竹子結(jié)構(gòu)的寡晶記憶合金(SMA)具有良好的雙向形狀記憶效應(yīng)(TWSME)和彈性熱效應(yīng)(eCE)。在本研究中,我們建立了一個理論模型來預(yù)測這類合金的雙向形狀記憶效應(yīng)和彈性熱效應(yīng)。我們首先在單晶尺度上,基于晶體塑性理論,提出了一種各向異性熱-機(jī)械耦合本構(gòu)模型來描述熱彈性馬氏體相變。在不可逆熱力學(xué)的框架下,成功推導(dǎo)出了馬氏體相變的驅(qū)動力、內(nèi)熱的釋放/吸收、以及內(nèi)部溫度的演化過程。為了計算SMA中的溫度、應(yīng)力和應(yīng)變場并獲取其整體熱機(jī)械響應(yīng),我們通過編寫用戶自定義的子程序,將提出的本構(gòu)模型應(yīng)用于有限元程序ABAQUS/Explicit中。同時,為了降低利用有限元方法進(jìn)行熱力耦合分析的計算成本,我們基于一種考慮了SMA幾何特征的區(qū)域整合方法,構(gòu)造了一種從單晶到宏觀寡晶的過渡規(guī)則。通過與實驗數(shù)據(jù)的比較,我們驗證了該模型對SMA雙向形狀記憶效應(yīng)和彈性熱效應(yīng)的預(yù)測能力。此外,我們對晶粒取向的影響進(jìn)行了討論。該模型可為晶粒組織的優(yōu)化設(shè)計提供理論指導(dǎo),幫助獲得具有優(yōu)良雙向形狀記憶效應(yīng)和彈性熱效應(yīng)的SMAs。
英文摘要
Recent experimental studies reported that the bamboo-grained oligocrystalline shape memory alloy (SMA) microwire showed excellent two-way shape memory effect (TWSME) and elastocaloric effect (eCE) due to the reduced constraints from grain boundary. In this paper, a theoretical model is established to predict the TWSME and eCE of such a kind of SMAs. At single crystal scale, an anisotropic thermo-mechanically coupled constitutive model is proposed to describe the thermo-elastic martensitic transformation based on the crystal plasticity theory. The driving force of martensite transformation, the internal heat release/absorption, and the evolutions of internal variables and temperature are deduced within the framework of irreversible thermodynamics. To calculate the temperature, stress and strain fields in the bamboo-grained oligocrystalline SMA microwire and obtain the overall thermo-mechanical response of the microwire, the proposed constitutive model is implemented into the finite element program ABAQUS/Explicit by writing a user-defined material subroutine. Meanwhile, to reduce the computational cost faced in the fully coupled thermo-mechanical analysis by using the finite element method, a scale transition rule from single crystal scale to macroscopic oligocrystalline one is constructed based on a new proposed sub-region integral method by considering the special geometric characteristics of the microwire. The capability of proposed model to describe the TWSME and eCE of bamboo-grained oligocrystalline SMA microwire is validated by comparing the predictions with the experimental data. In addition, the effect of grain orientation is discussed. The proposed model can provide a theoretical guidance for the optimal design of grain microstructures to obtain the SMAs with excellent TWSME and eCE.
ACTA Vol. 198, 1 Oct. 2020, P35-46
3. Transition of dominant deformation mode in bulk polycrystalline pure Mg by ultra-grain refinement down to sub-micrometer
通過對塊體純Mg進(jìn)行亞微米尺度晶粒細(xì)化引起合金形變模式轉(zhuǎn)變
Ruixiao Zheng?,Jun-Ping Du,Si Gao,Hidetoshi Somekawa,Shigenobu Ogata?,Nobuhiro Tsuji?
R. Zheng: zhengruixiao@buaa.edu.cn,
S. Ogata: ogata@me.es.osakau.ac.jp
N. Tsuji: nobuhiro-tsuji@mtl.kyoto-u.ac.jp
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.07.055
摘要
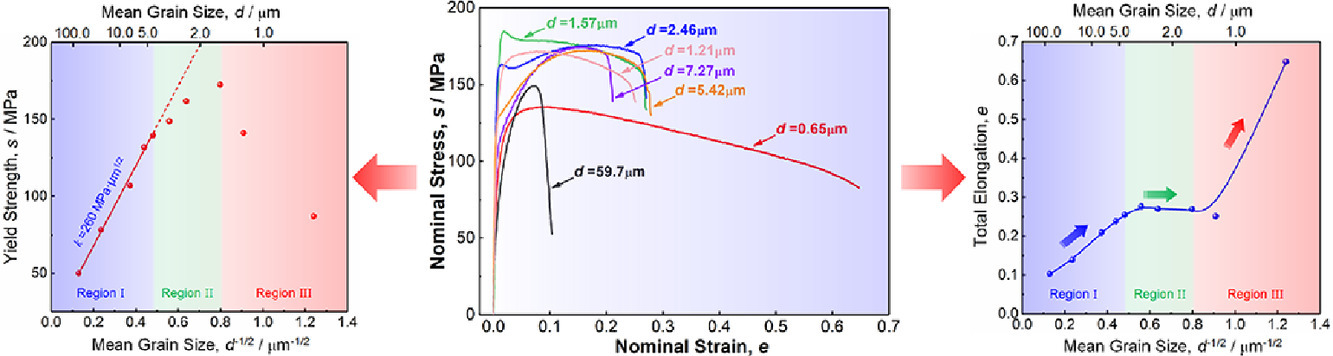
由于鎂合金的各向異性密排六方(HCP)結(jié)構(gòu)限制了獨(dú)立滑移體系的數(shù)量,因此鎂合金在室溫下的強(qiáng)度和延展性往往較差。本研究中,我們發(fā)現(xiàn)通過調(diào)整主要變形模式,可以在塊體多晶純鎂中實現(xiàn)優(yōu)異的強(qiáng)度和延展性耦合。我們成功制備了一系列具有不同平均晶粒尺寸的純鎂完全再結(jié)晶試樣(其中最小的平均晶粒尺寸為650 nm),并系統(tǒng)地闡明了室溫力學(xué)性能、變形機(jī)理與晶粒尺寸之間的關(guān)系。在常規(guī)粗晶區(qū),塑性變形受形變孿晶和滑移控制;當(dāng)晶粒細(xì)化到幾微米時,孿晶被抑制;而在平均晶粒尺寸小于1μm的超細(xì)晶(UFG)試樣中,晶界滑移占主導(dǎo)地位。形變模式的轉(zhuǎn)換使得拉伸延伸率顯著提高,且不再遵循Hall-Petch公式。通過詳細(xì)的微觀組織觀察和理論計算,我們定量地證實了:強(qiáng)度和延展性的變化是由于不同尺寸的晶粒激活不同形變模式的臨界剪切應(yīng)力不同而導(dǎo)致的。
英文摘要
Magnesium (Mg) and its alloys usually show relatively low strength and poor ductility at room temperature due to their anisotropic hexagonal close-packed (HCP) crystal structure that provides a limited number of independent slip systems. Here we report that unique combinations of strength and ductility can be realized in bulk polycrystalline pure Mg by tuning the predominant deformation mode. We succeeded in obtaining the fully recrystallized specimens of pure Mg having a wide range of average grain sizes, of which minimum grain size was 650 nm, and clarified mechanical properties and deformation mechanisms at room temperature systematically as a function of the grain size. Deformation twinning and basal slip governed plastic deformation in the conventional coarse-grained region, but twinning was suppressed when the grain size was refined down to several micro-meters. Eventually, grain boundary mediated plasticity, i.e., grain boundary sliding became dominant in the ultrafine-grained (UFG) specimen having a mean grain size smaller than 1 μm. The transition of the deformation modes led to a significant increase of tensile elongation and breakdown of Hall-Petch relationship. It was quantitatively confirmed by detailed microstructural observation and theoretical calculation that the change in strength and ductility arose from the distinct grain size dependence of the critical shear stress for activating different deformation modes.
ACTA Vol. 198, 1 Oct. 2020, P47-60
4. Understanding bubble and void nucleation in dual ion irradiated T91 steel using single parameter experiments
采用單參數(shù)實驗探究T91鋼在雙離子輻照過程中的氦泡和孔洞形核過程
Stephen Taller?, Gary S. Was
S. Taller: STaller@umich.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.07.060
摘要
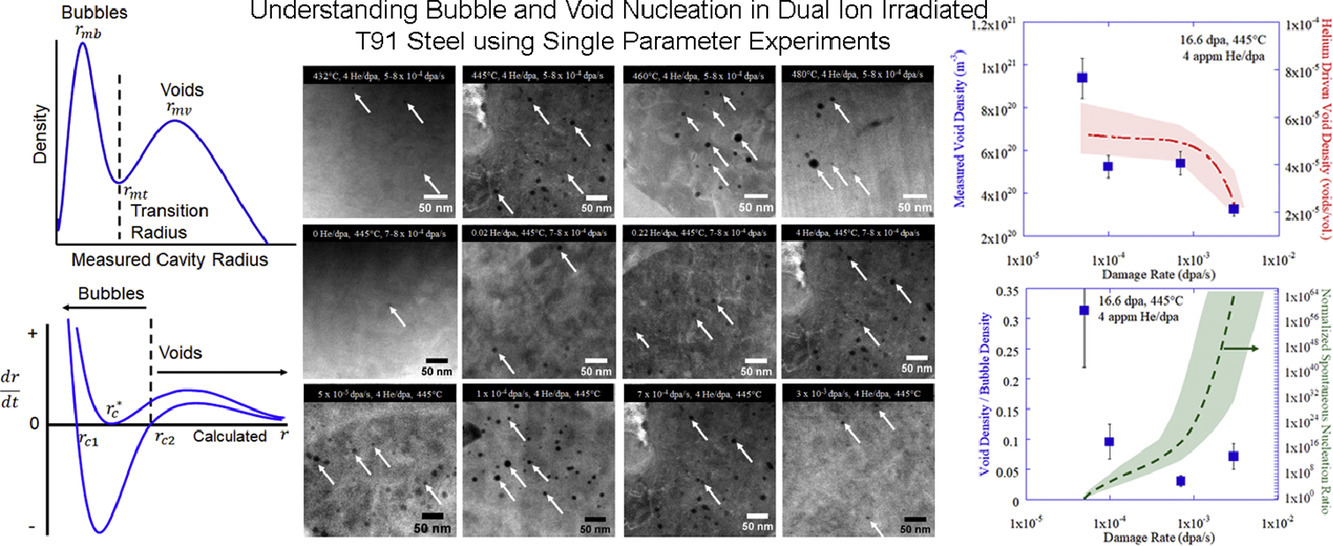
由于鐵素體-馬氏體鋼具有抗輻照膨脹的特性,是下一代核反應(yīng)堆系統(tǒng)結(jié)構(gòu)材料的理想候選材料。我們設(shè)計了一系列實驗,在雙離子輻照條件下,對T91鋼的空洞和位錯環(huán)演化進(jìn)行了表征,考察其與溫度、氦注入率和損傷率這三個單一參數(shù)之間的關(guān)系。在幾乎所有實驗中,輻照都導(dǎo)致了孔洞的產(chǎn)生,且這些孔洞的尺寸呈雙峰分布。實驗結(jié)果表明,溫度和氦注入率對氦泡穩(wěn)定性和氦泡向孔洞過渡的影響比損傷率更大。在較低的氦注入率條件下,所有的氦都集中在空位團(tuán)簇中并演化成氦泡或孔洞。在較高的氦注入率條件下,氦泡中氦達(dá)到飽和,導(dǎo)致氦在其他缺陷處(如位錯環(huán))積聚。中等水平的氦注入率條件下,得益于鐵素體-馬氏體組織中存在的高密度缺陷,氦泡形核膨脹被顯著抑制。當(dāng)溫度足夠高時,因為組織中沒有形成位錯環(huán)等其他強(qiáng)氦阱,因此氦只存在于氦泡中。研究發(fā)現(xiàn),氦泡向孔洞轉(zhuǎn)變的機(jī)理在低損傷率下,是由于氦在臨界氦泡積聚;而在高損傷率下,則是由于隨機(jī)空位起伏導(dǎo)致的自發(fā)過程。
英文摘要
Ferritic-martensitic steels are attractive candidates for structural materials in next generation nuclear reactor systems due to their resistance to radiation induced swelling. Cavity and dislocation loop evolution was characterized in dual ion irradiated T91 steel in three separate irradiation campaigns examining single parameter dependencies of temperature, helium co-injection rate, and damage rate. Irradiations resulted in bimodal cavity size distributions across nearly all ranges of experimental parameters. It was determined that irradiation temperature and helium co-injection rate are stronger influences on bubble stability and the transition from bubbles to voids than is the irradiation damage rate. At low helium injection rates all helium is in vacancy clusters that evolve into bubbles or voids. At high helium injection rates, bubbles become saturated with helium resulting in accumulation of helium at other traps such as dislocation loops. At intermediate levels of He that should aid in the nucleation of bubbles and enhance swelling, the high density of sinks in the F-M microstructure suppresses bubble nucleation and therefore, the onset of swelling. At high enough temperatures, helium is only in bubbles as other strong helium traps, such as dislocation loops, did not form. The mechanism of bubble to void transition was found to shift from being driven by the accumulation of helium to the critical bubble at low damage rates to being driven by spontaneous formation by stochastic vacancy fluctuation at high damage rates.
ACTA Vol. 198, 1 Oct. 2020, P61-71
5. Dislocation plasticity and detwinning under thermal stresses in nanotwinned Ag thin films
納米孿晶Ag薄膜在熱應(yīng)力下的位錯塑性和去孿晶過程
Maya K. Kini?, Claudia Merola, Benjamin Breitbach, Dennis Klapproth, Bastian Philippi, Jean-Baptiste Molin, Christoph Kirchlechner, Gerhard Dehm
M.K. Kini: m.kini@mpie.de
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.07.056
摘要
文獻(xiàn)中對于硬基板上多晶硅(通常有織構(gòu))和外延FCC金屬薄膜的曲率測量表明這兩類薄膜都具有獨(dú)特的應(yīng)力-溫度演化特征。外延薄膜具有獨(dú)特的彈性特點——無存儲位錯且在循環(huán)應(yīng)變過程中具有高可重復(fù)性的理想塑性;而多晶薄膜除了會在高溫下通過擴(kuò)散蠕變產(chǎn)生松弛外,還會在冷卻過程中發(fā)生顯著硬化。在本研究中,我們研究了一種利用電子束沉積方法在(111)Si基板上沉積的外延納米孿晶Ag的形變特點。我們通過熱處理對孿晶Ag的孿晶間距λ進(jìn)行調(diào)控,并且通過測量晶片曲率記錄了熱變形特征隨孿晶間距的變化曲線,其中孿晶間距從20nm變化到1μm。此外,我們還將其與外延雙晶薄膜、含共格孿晶界的雙晶微柱和納米孿晶微柱等其他FCC金屬在微米或亞微米尺度的變形進(jìn)行了比較。
英文摘要
Wafer curvature measurements reported in literature for polycrystalline (often textured) and epitaxial fcc metal thin films on hard substrates show a characteristic “signature” in the stress-temperature evolution for either type of films. While epitaxial films reveal characteristic elastic – ideal plastic deformation with no dislocation storage and highly repeatable cycles, polycrystalline films show considerable hardening upon cooling in addition to the relaxation by diffusional creep at elevated temperatures. In the present study, we study the deformation characteristics of an electron beam deposited epitaxial nanotwinned Ag on Si (111) substrate. The twin spacing λ of the nanotwinned Ag is controlled by suitable heat treatment and the “signature” thermomechanical deformation curves by wafer curvature measurements are recorded for twin spacings varying from 20 nm to 1 μm. Further, deformation is compared to other small scale deformation studies on fcc metals such as epitaxial bicrystal films, bicrystal micropillars containing a coherent twin boundary and nanotwinned micropillars.
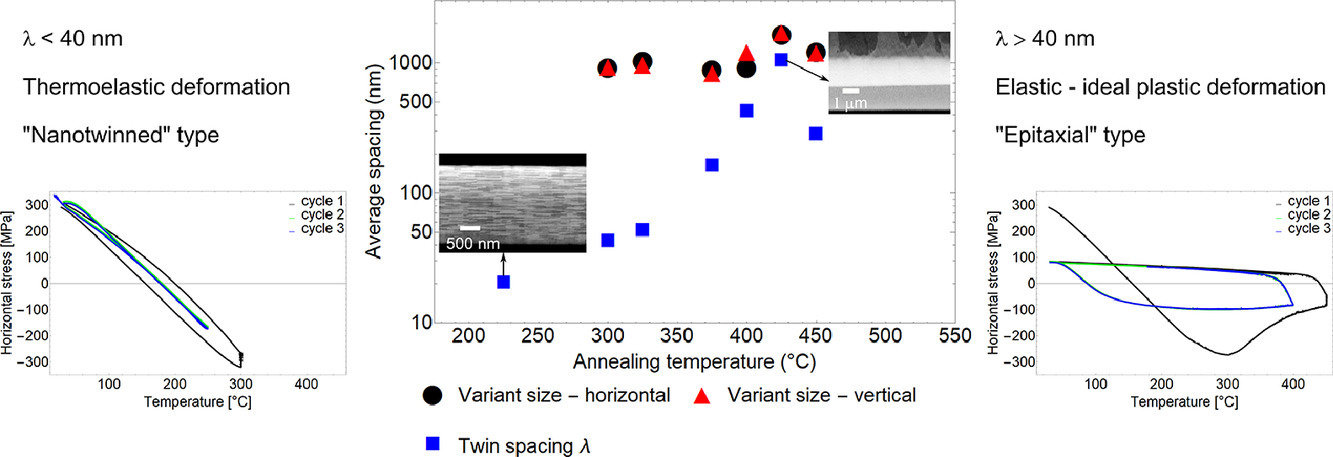
ACTA Vol. 198, 1 Oct. 2020, P72-84
6. Giant shape- and size-dependent compressive strength of molybdenum nano- and microparticles
納米/微米Mo粒子的極高壓縮強(qiáng)度及其與粒子形狀和尺寸的關(guān)系
A. Sharma, R. Kositski, O. Kovalenko, D. Mordehai?, E. Rabkin?
D. Mordehai : danmord@me.technion.ac.il
E. Rabkin : erabkin@technion.ac.il
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.07.054
摘要
在亞微米尺度上對金屬樣品進(jìn)行加工可以使得純金屬的強(qiáng)度極限達(dá)到GPa量級。在本研究中,我們制備了一種Mo的納米顆粒,其壓縮強(qiáng)度超過了所有已知的金屬材料。我們通過在藍(lán)寶石基體上對Mo薄膜進(jìn)行二步固態(tài)除濕過程中調(diào)節(jié)退火氣氛制備了圓形和多面體兩種顆粒。圓形顆粒在突然屈服之前發(fā)生了巨大的彈性變形。通過有限元模擬,我們發(fā)現(xiàn)對于圓形顆粒而言,無論顆粒大小,沖頭下{112}< 110 >滑移系統(tǒng)的剪切分應(yīng)力在屈服時都達(dá)到了20±1 GPa。而多面體顆粒則遵循“尺寸越小,強(qiáng)度越高”的規(guī)律,最小納米粒子的單軸抗壓強(qiáng)度達(dá)到了46GPa。分子動力學(xué)模擬表明,這種強(qiáng)度對尺寸的依賴關(guān)系隨著粒子邊緣的圓潤程度增加而減小。這項研究闡明了如何通過調(diào)控顆粒的形狀和尺寸,大幅提高粒子的強(qiáng)度。
英文摘要
The ability to process metallic samples at the sub-micrometer scale raised the strength limits of pure metals to the Giga Pascal (GPa) range. Here, we fabricated Mo nanoparticles with a giant compressive strength surpassing the previous strength records of metallic materials. Round and faceted particles were produced by manipulating the annealing atmosphere during two-stage solid-state dewetting of Mo thin films deposited on sapphire. The round particle underwent a huge elastic deformation before yielding abruptly. Using finite element analysis, we found that the resolved shear stress on a {112}〈110〉 slip system beneath the punch reaches an enormous value of 20±1 GPa at yield, regardless of particle size. The faceted nanoparticles, contrarily, followed a “smaller is stronger” rule, with uniaxial compressive strength of up to 46 GPa for the smallest nanoparticles. Molecular dynamics simulations indicated that the size effect diminishes with increasing roundness of the particle edges. This work demonstrates how shape and size of particles can be manipulated to achieve giant strength.
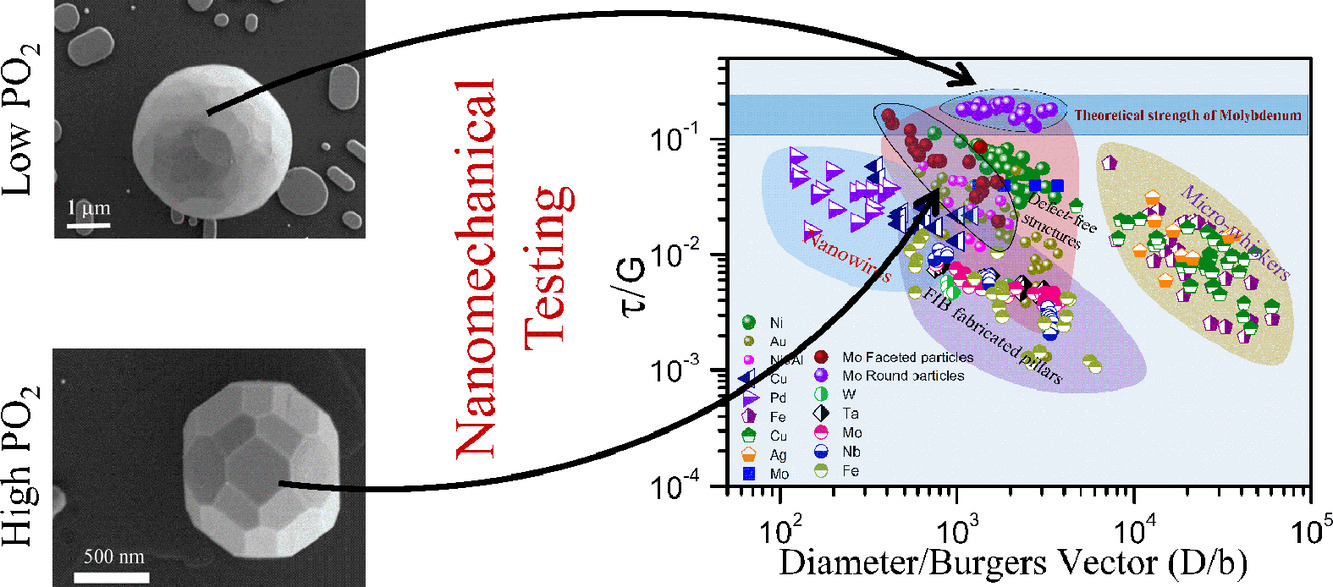
ACTA Vol. 198, 1 Oct. 2020, P85-99
7. In situ microstructural evolution in face-centered and body-centered cubic complex concentrated solid-solution alloys under heavy ion irradiation
對FCC和BCC多組分合金在重離子輻照條件下組織演化的原位研究
Calvin Parkin?, Michael Moorehead, Mohamed Elbakhshwan, Jing Hu, Wei-Ying Chen, Meimei Li, Lingfeng He, Kumar Sridharan, Adrien Couet
C. Parkin: cparkin@wisc.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.07.066
摘要
本研究對單相復(fù)雜組分固溶體合金(CSA)在重離子輻照條件下的組織演變進(jìn)行了表征,以分析其在先進(jìn)裂變系統(tǒng)中的抗輻照機(jī)制。我們結(jié)合了原位透射電子顯微鏡技術(shù)對3種CSA合金和3種對照組材料在50 K和773 K下進(jìn)行了不同程度輻照劑量的1 MeV Kr++離子輻照實驗。其中三種CSA合金分別為:Cr18Fe27Mn27Ni28、 Cr15Fe35Mn15Ni35和等原子比的NbTaTiV合金;3種對照組材料分別為純Ni、E90合金(作為CrFeMnNi合金對照組),以及純V(作為NbTaTiV合金對照組)。低溫輻照條件下,面心立方CSAs中產(chǎn)生了小型缺陷團(tuán)簇和12nm左右的位錯環(huán)。低溫下熱擴(kuò)散被抑制,所有CSAs的缺陷密度都低于其對照組材料,這表明在位移級聯(lián)階段產(chǎn)生的點缺陷減少了。高溫輻照條件下,在Cr18Fe27Mn27Ni28和Cr15Fe35Mn15Ni35兩種FCC結(jié)構(gòu)CSA中觀測到了間隙位錯環(huán)的形成,在2dpa的輻照劑量下,其間隙位錯環(huán)的平均尺寸分別為27 nm和10 nm。這種位錯環(huán)的形成長大動力學(xué)差異是由于錳含量不同所導(dǎo)致,錳元素通過增加空位遷移率或降低層錯能影響位錯環(huán)的形核率。
英文摘要
This study characterizes the microstructural evolution of single-phase complex concentrated solid-solution alloy (CSA) compositions under heavy ion irradiation with the goal of evaluating mechanisms for CSA radiation tolerance in advanced fission systems. Three such alloys, Cr18Fe27Mn27Ni28, Cr15Fe35Mn15Ni35, and equimolar NbTaTiV, along with reference materials (pure Ni and E90 for the CrFeMnNi family and pure V for NbTaTiV) were irradiated at 50 K and 773 K with 1 MeV Kr++ ions to various levels of displacements per atom (dpa) using in-situ transmission electron microscopy. Cryogenic irradiation resulted in small defect clusters and faulted dislocation loops as large as 12 nm in face-centered cubic (FCC) CSAs. With thermal diffusion suppressed at cryogenic temperatures, defect densities were lower in all CSAs than in their less compositionally complex reference materials indicating that point defect production is reduced during the displacement cascade stage. High temperature irradiation of the two FCC CSA resulted in the formation of interstitial dislocation loops which by 2 dpa grew to an average size of 27 nm in Cr18Fe27Mn27Ni28 and 10 nm in Cr15Fe35Mn15Ni35. This difference in loop growth kinetics was attributed to the difference in Mn-content due to its effect on the nucleation rate by increasing vacancy mobility or reducing the stacking-fault energy.
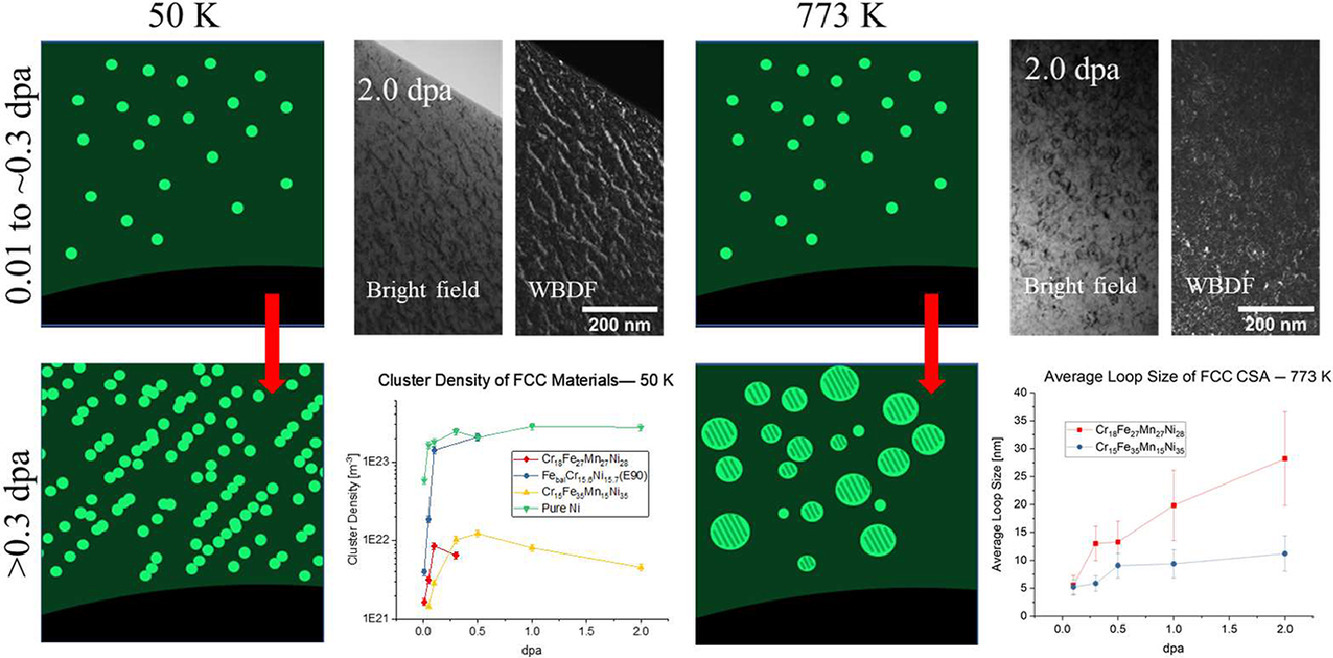
ACTA Vol. 198, 1 Oct. 2020, P111-120
8. Direct atomistic modeling of solute drag by moving grain boundaries
關(guān)于遷移界面處的溶質(zhì)拖曳效應(yīng)的直接原子尺度模擬
R.K. Koju, Y. Mishin?
Y. Mishin: ymishin@gmu.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.07.052
摘要
我們研究發(fā)現(xiàn),分子動力學(xué)模擬能夠很好地展現(xiàn)移動晶界處的溶質(zhì)拖曳。盡管晶格擴(kuò)散在分子動力學(xué)的時間尺度上處于近似停止?fàn)顟B(tài),但晶界處的快速擴(kuò)散使得偏聚溶質(zhì)原子的運(yùn)動能夠跟得上晶界的遷移。這一研究結(jié)果為我們提供了基于分子動力學(xué)方法,在原子尺度上精確研究溶質(zhì)拖曳效應(yīng)的可能性。我們發(fā)現(xiàn),晶界在遷移過程中激活了其掃過位置處的晶界擴(kuò)散,改變了晶格的短程有序態(tài)。同時,我們還發(fā)現(xiàn),移動的晶界同時還在拖拽非平衡空位,使得附近晶格區(qū)域的擴(kuò)散大大加快。
英文摘要
We show that molecular dynamics (MD) simulations are capable of reproducing the drag of solute segregation atmospheres by moving grain boundaries (GBs). Although lattice diffusion is frozen out on the MD timescale, the accelerated GB diffusion provides enough atomic mobility to allow the segregated atoms to follow the moving GB. This finding opens the possibility of studying the solute drag effect with atomic precision using the MD approach. We demonstrate that a moving GB activates diffusion and alters the short-range order in the lattice regions swept during its motion. It is also shown that a moving GB drags an atmosphere of non-equilibrium vacancies, which accelerate diffusion in surrounding lattice regions.
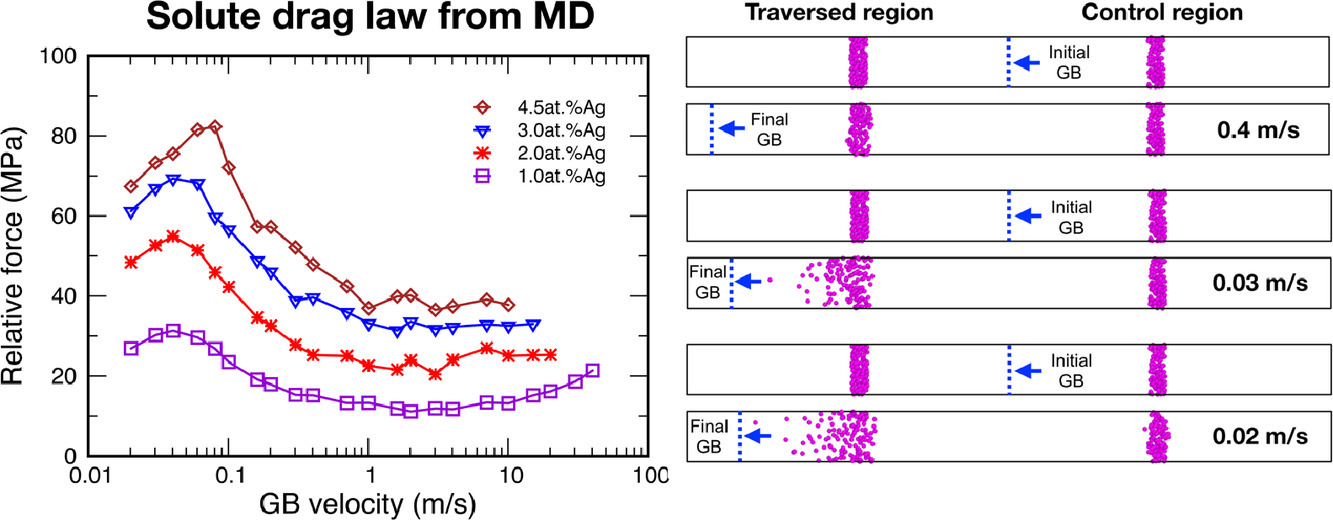
ACTA Vol. 198, 1 Oct. 2020, P121-133
9. Aqueous passivation of multi-principal element alloy Ni38Fe20Cr22Mn10Co10: Unexpected high Cr enrichment within the passive film
Ni38Fe20Cr22Mn10Co10多主元合金液體鈍化膜中顯著的Cr富集現(xiàn)象
Angela Y. Gerard?, Junsoo Han, Stephen J. McDonnell, Kevin Ogle, Elizabeth J. Kautz, Daniel K. Schreiber, Pin Lu, James E. Saal, Gerald S. Frankel, John R. Scully
A.Y. Gerard: ayg8ap@virginia.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.07.024
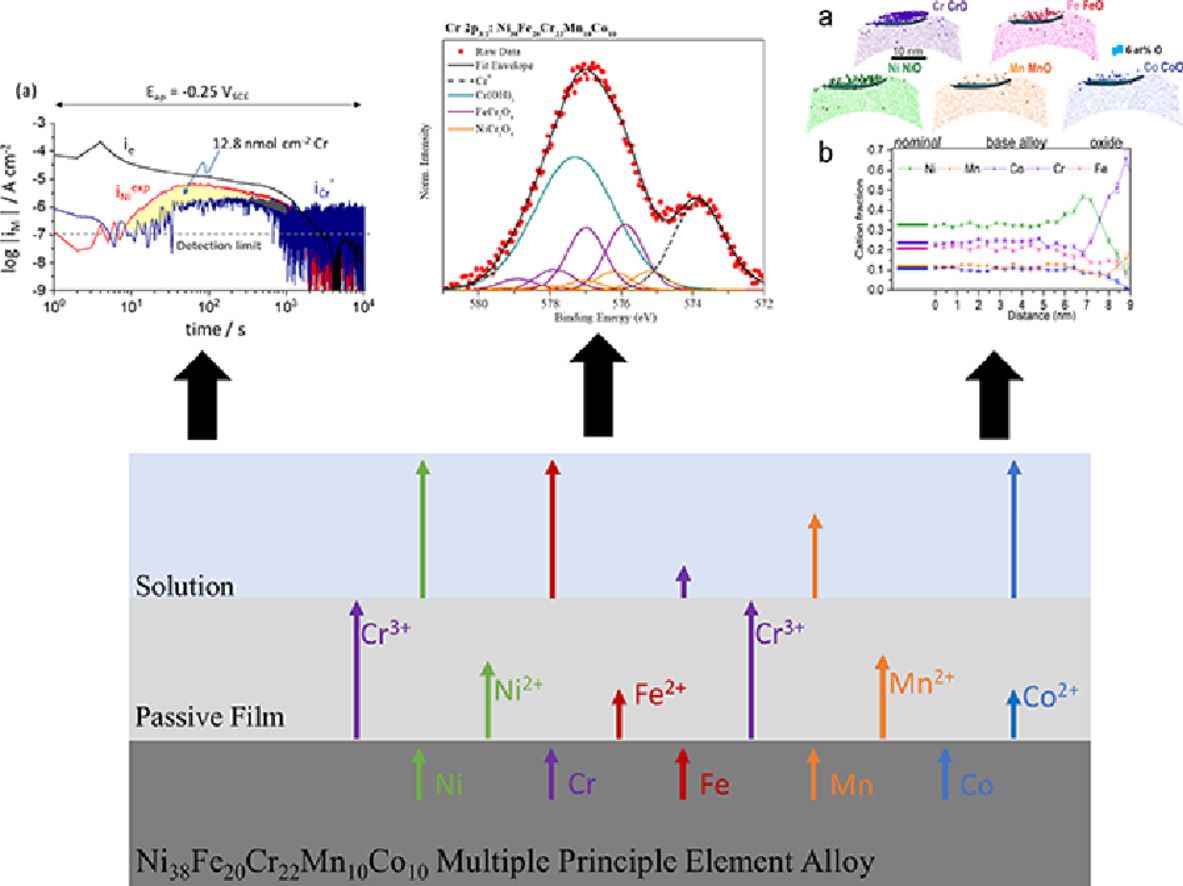
摘要
我們研究了Ni38Fe20Cr22Mn10Co10 at.%(Ni40Fe20Cr20Mn10Co10 wt.%)合金在PH=4條件下在0.1M NaCl溶液中的鈍化過程,并將其與傳統(tǒng)二元合金Ni76Cr24 at.% (Ni78Cr22 wt.%)進(jìn)行了比較。我們使用原位電化學(xué)手段和離位表面技術(shù)對樣品的電化學(xué)行為和氧化膜特點進(jìn)行了表征。通過原位原子發(fā)射譜、離位X射線光電子能譜和原子探針等實驗手段研究了鈍化膜的組成、厚度和元素價態(tài)。研究表明,Ni38Fe20Cr22Mn10Co10合金的耐腐蝕性能略優(yōu)于Ni76Cr24合金。Ni38Fe20Cr22Mn10Co10合金的鈍化膜主要由Cr元素組成,并含有少量的Ni、Fe、Co和Mn。同時,我們還觀測到了Ni、Fe、Co的溶解。氧化膜和金屬界面處富Ni0貧Cr。Ni38Fe20Cr22Mn10Co10合金中Cr在鈍化膜中的富集程度比二元合金中更高。我們對這種富集的原因和影響因素進(jìn)行了討論。
英文摘要
The aqueous passivation of a non-equiatomic Ni38Fe20Cr22Mn10Co10 - at.% (Ni40Fe20Cr20Mn10Co10- wt.%) multi-principal element alloy (MPEA) was investigated in 0.1 M NaCl at pH 4 and compared to a conventional binary Ni76Cr24 – at.% (Ni78Cr22–wt.%) alloy. The electrochemical behavior and oxide film characteristics were explored utilizing in-situ electrochemical and ex-situ surface-sensitive techniques. The passive film composition, thickness, and elemental valence states, as well as, the fate of each element were studied by in-situ atomic emission spectro-electrochemistry, ex-situ X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, and atom probe tomography. The Ni38Fe20Cr22Mn10Co10 MPEA demonstrated slightly better corrosion resistance compared to the binary Ni76Cr24, alloy. Passive films on the MPEA contained primarily Cr, and small amounts of Ni, Fe, Co and Mn, while dissolution of Ni, Fe, Co was observed. Ni0 was enriched at the oxide/metal interface while Cr was depleted. Enrichment of Cr in the passive film occurred to a greater extent in the MPEA than for the Ni-Cr binary alloy. Enrichment factors were determined and the origins of enrichment are discussed.
ACTA Vol. 198, 1 Oct. 2020, P168-177
10. Forensic analyses of microstructure evolution of stage II & III: New assimilated model for work-hardening in FCC metals
分析FCC金屬加工硬化過程中階段II和階段III的組織演變建立新型吸收模型
Shigeo Saimoto?, Bradley J. Diak, Anna Kula, Marek Niewczas
S. Saimoto: shigeo.saimoto@queensu.ca
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.08.002
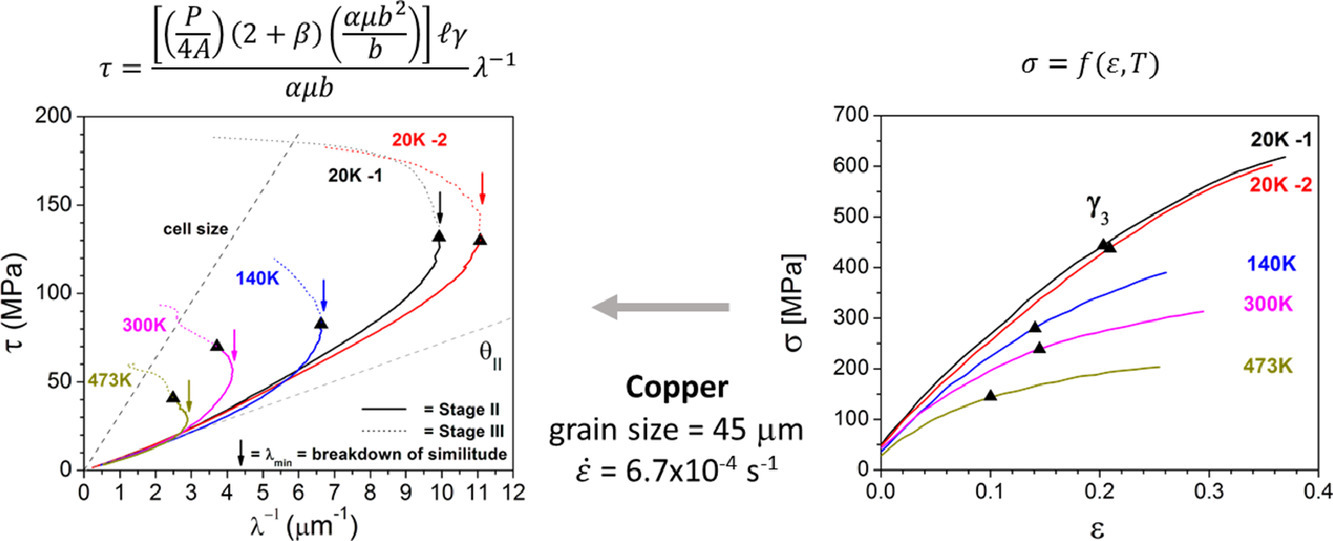
摘要
自人們開始對晶體塑性進(jìn)行研究開始,為什么應(yīng)變過程中,外界施加功的一小部分會被存儲在晶體之中的原因就一直是一個難題。一些塑性變形過程的原位研究表明,當(dāng)滑移發(fā)生在以平均滑移距離為尺度的小區(qū)域內(nèi)時,會導(dǎo)致位錯的共面湮滅。一個較為簡單的模型預(yù)測:消耗能量和儲存能量之間的非熱湮滅因子A約為20,這與儲存功約為5% 的實驗觀測結(jié)果相當(dāng)。對銅而言,模型推導(dǎo)出溫度為20K時A為19,而在300 K時為25。通過使用能夠較好反映應(yīng)力-應(yīng)變關(guān)系的本構(gòu)模型,引入外加剪切應(yīng)變,對滑移平面進(jìn)行分析,我們發(fā)現(xiàn)單極位錯的演化引起了這種相似性。當(dāng)發(fā)生交滑移和伴隨的雙交滑移時,滑移面之間的高度增加,使得Ⅱ階段結(jié)構(gòu)被破壞。這一機(jī)制導(dǎo)致的結(jié)果是,隨著平均滑移距離的增加,位錯由隨機(jī)陣列變?yōu)閳F(tuán)簇形式,從而促進(jìn)了胞結(jié)構(gòu)的形成。這一演化過程可以通過平均滑移距離的倒數(shù)隨剪切流變應(yīng)力的變化關(guān)系進(jìn)行驗證。綜上所述,基于本構(gòu)關(guān)系探究面心立方的加工硬化是一種行之有效的研究方法。
英文摘要
From the beginning of crystal plasticity studies, the cause for the small percentage of expended work retained as stored work has been a quandary. From forensic analyses of plastic deformation studies, it was deduced that coplanar annihilation of dislocations occur since slip takes place in small slip-patch areas of mean slip distance squared. A simple model predicts that the athermal annihilation factor A between expended and stored energy is about 20 comparable to the observed 5% for stored work. The derived A ranged from 19 at 20 K to 25 at 300 K for copper. Using the functional constitutive relation which can replicate the stress-strain diagram, analyses invoking the imposed shear strain to assess the height between coplanar slip planes indicate that structure evolution due to monopole dislocations result in the principle of similitude. However, the break-down of this Stage II structure occurs when cross-slip and the accompanying double cross-slip is incurred resulting in increasing height between slip planes. The consequences of these bypass mechanisms are the change of the random array of dislocations to that of clustered patterns with the increase in mean slip distance leading to cell structure formation. This evolution can be examined using the shear flow stress versus the inverse mean slip distance plot. Hence the bases for decoding work-hardening of face-centred cubic metals using constitutive relations have become possible.
ACTA Vol. 198, 1 Oct. 2020, P178-222
11. Searching for high entropy alloys: A machine learning approach
利用機(jī)器學(xué)習(xí)方法搜尋高熵合金
Kevin Kaufmann, Kenneth S. Vecchio?
K.S. Vecchio: kvecchio@eng.ucsd.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.07.065
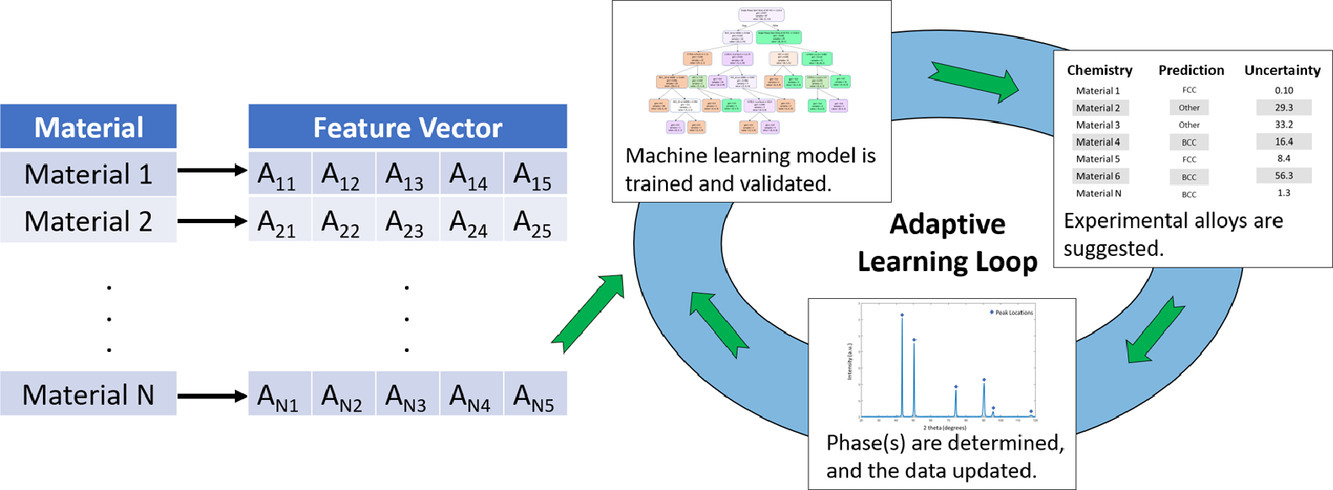
摘要
過去十年中,大量研究工作致力于單相高熵系統(tǒng)的計算搜尋和實驗驗證。但對于高熵系統(tǒng)的預(yù)測目前仍是一個極大的挑戰(zhàn)。以往的研究主要利用密度泛函理論獲取相關(guān)參數(shù),并將其與已有數(shù)據(jù)進(jìn)行擬合,但由于成分范圍廣,計算成本大,導(dǎo)致這一方法難以實際應(yīng)用。而使用機(jī)器學(xué)習(xí)方法加速材料設(shè)計研發(fā),并減少計算和實驗成本則是近來快速發(fā)展的一個領(lǐng)域。機(jī)器學(xué)習(xí)相比傳統(tǒng)模擬具有很多內(nèi)在優(yōu)勢,例如它能夠靈活應(yīng)用最新的實驗數(shù)據(jù),并且能夠快速構(gòu)建輸入數(shù)據(jù)和目標(biāo)輸出之間的關(guān)系。在研究中,我們提出了一種新的高通量機(jī)器學(xué)習(xí)方法,我們把它稱為“ML-HEA”。利用隨機(jī)森林模型耦合熱力學(xué)和化學(xué)特征,預(yù)測固溶體形成能力。該模型既可以單獨(dú)作為一種基本工具,也可以集成到現(xiàn)有的合金設(shè)計工作框架中。我們通過與二、三、四、五元系統(tǒng)的實驗數(shù)據(jù)進(jìn)行比較,驗證了該方法的有效性。我們同樣將其與其他模擬方法(包括CALPHAD和LTVC模型)進(jìn)行了比較,以評估機(jī)器學(xué)習(xí)在標(biāo)記和未標(biāo)記數(shù)據(jù)上集的性能。通過輸出單個預(yù)測樹,我們探討了該模型在預(yù)測每個成分對應(yīng)相時的不確定性。更重要的是,我們開發(fā)的這一模型可以不受約束地隨時進(jìn)行更新,以反映最新的實驗成果。
英文摘要
For the past decade, considerable research effort has been devoted toward computationally identifying and experimentally verifying single phase, high-entropy systems. However, predicting the resultant crystal structure(s) “in silico” remains a major challenge. Previous studies have primarily used density functional theory to obtain correlated parameters and fit them to existing data, but this is impractical given the extensive regions of unexplored composition space and considerable computational cost. A rapidly developing area of materials science is the application of machine learning to accelerate materials discovery and reduce computational and experimental costs. Machine learning has inherent advantages over traditional modeling, owing to its flexibility as new data becomes available and its rapid ability to construct relationships between input data and target outputs. In this article, we propose a novel high-throughput approach, called “ML-HEA”, for coupling thermodynamic and chemical features with a random forest machine learning model for predicting the solid solution forming ability. The model can be a primary tool or integrated into existing alloy discovery workflows. The ML-HEA method is validated by comparing the results with reliable experimental data for binary, ternary, quaternary, and quinary systems. Comparison to other modeling approaches, including CALPHAD and the LTVC model, are also made to assess the performance of the machine learning model on labeled and unlabeled data. The uncertainty of the model in predicting the resultant phase of each composition is explored via the output of individual predictor trees. Importantly, the developed model can be immediately applied to explore material space in an unconstrained manner, and is readily updated to reflect the results of new experiments.
ACTA Vol. 198, 1 Oct. 2020, P223-229
12. Crystallographic anisotropy of nonequilibrium solute capture
非平衡溶質(zhì)捕獲的晶體學(xué)各向異性
Xiao-Xiang Yu?, John H. Perepezko, Laurence D. Marks
X.-X. Yu: yuxx07@gmail.com
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.07.059
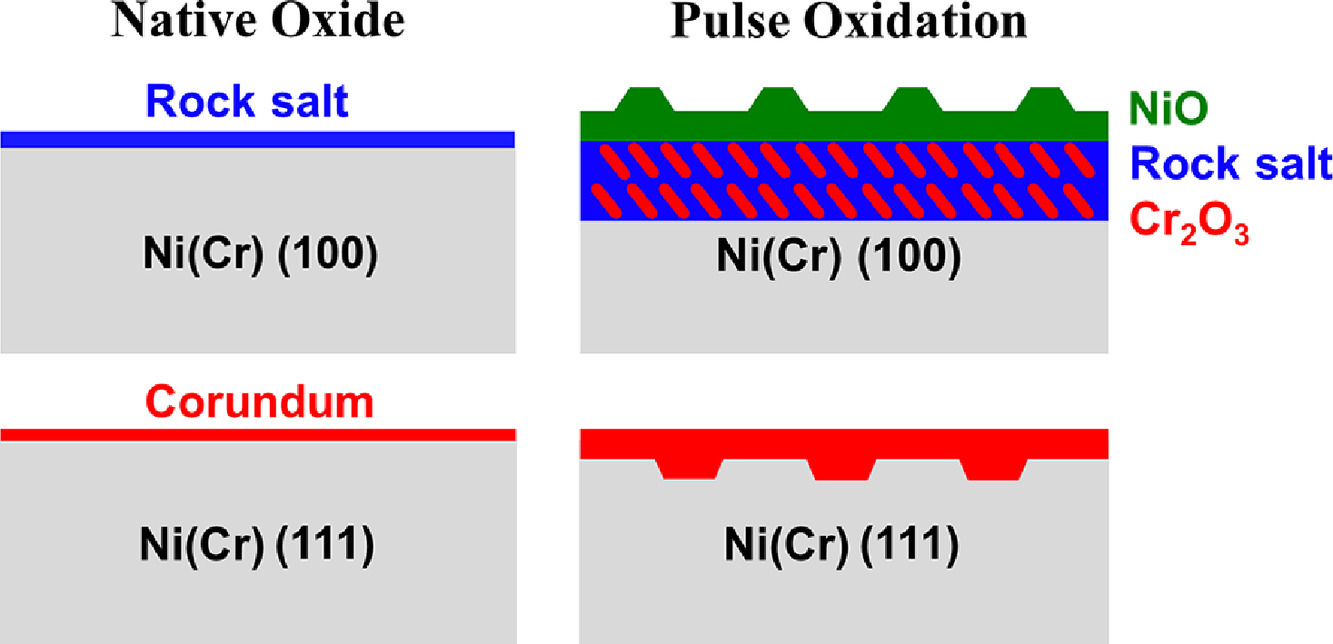
摘要
在本文中,我們闡明了晶體中的非平衡溶質(zhì)捕獲具有各向異性。我們在相同條件下,將不同取向的Ni-30Cr (wt.%)晶粒在600℃ 氧化了60 s。(100)取向晶粒通過溶質(zhì)捕獲,形成了立方-立方外延取向的巖鹽氧化物。而對于(111)晶粒則通過溶質(zhì)捕獲形成了(0001)//(111)的剛玉氧化物。通過形貌可以推斷,氧化物生長是由動力學(xué)因素而非熱力學(xué)因素控制的,從巖鹽氧化物向外生長,而剛玉氧化物向內(nèi)生長。由于在金屬/氧化物邊界在移動(如(111)晶粒對應(yīng)實驗)和靜止(如(100)晶粒對應(yīng)實驗)狀態(tài)下對于溶質(zhì)的捕獲是不同的,因此晶體學(xué)上的各向異性對材料的氧化或腐蝕有不可忽略的影響。
英文摘要
We demonstrate large, crystallographic anisotropy in nonequilibrium solute capture. Under identical conditions, differently oriented grains of a Ni-30Cr (wt.%) alloy were oxidized at 600°C for 60 s. For a Ni(Cr) (100) oriented grain, a solute captured rock salt oxide formed with a cube-cube epitaxial orientation. In contrast, for a Ni(Cr) (111) oriented grain, a solute captured corundum oxide formed with the (0001) basal plane parallel to (111). There are clear indications from the morphologies that are present – islands growing outwards for rock salt and islands growing inwards for corundum – that the oxide growth is dominated by kinetics, not thermodynamic factors. Since the interfacial conditions for nonequilibrium solute capture differ for cases where the metal/oxide boundary is moving (the (111) case) and where it is not (the (100) case), these results indicate that crystallographic anisotropy will have substantial effects which cannot be ignored in oxidation or corrosion.
ACTA Vol. 198, 1 Oct. 2020, P230-241
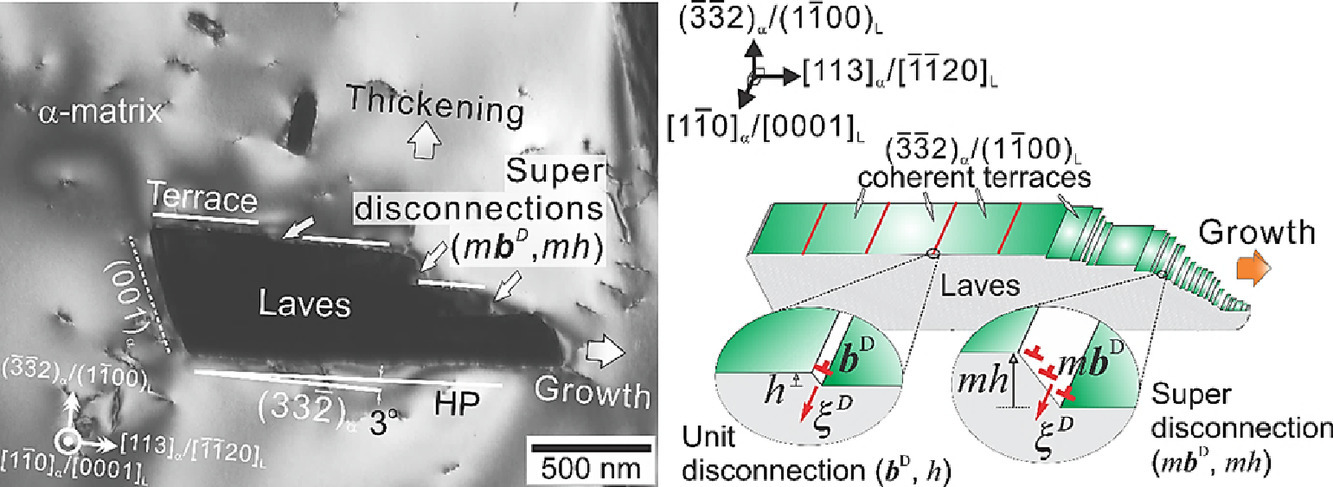
13. Disconnections and Laves (C14) precipitation in high-Cr ferritic stainless steels
高Cr鐵素體不銹鋼中的分離帶與Laves (C14)析出相
Yaw Wang Chai?, Ko Kato, Chieri Yabu, Shin Ishikawa, Yoshisato Kimura
Y.W. Chai: chai.y.aa@m.titech.ac.jp
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.08.006
摘要
盡管目前學(xué)界廣泛認(rèn)為Laves相可以對含Cr不銹鋼起到強(qiáng)化作用,但我們對于Laves相的組織演化卻知之甚少。在此,我們研究了高Cr鐵素體不銹鋼Fe-20Cr-2Mo-0.5Nb (at%)在1073K退火不同時間Laves (C14)相的演化。退火過程中,α相中形成了大量(Fe,Cr)2(Mo,Nb)析出。Laves相的形貌演化遵循以下順序:球形→橢球形→針形→盤形。Laves相和基體有兩套位向關(guān)系,OR1: [-1-12] α/[1-210]L、[111]α/[0-110]L、[1-10]α/[000-1]L,OR-2: [1-10]α/[0001]L、[113]α/[-1-120]L、[-3-32]α/[1-100]L。Laves相的慣析面略微偏離。實驗觀測到界面缺陷,即所謂的分離帶(bD, h)和超分離帶(mbD, mh)沿慣析面分布,這與OR2參考坐標(biāo)系下的理論預(yù)測相一致。bD伯氏矢量的邊緣分量byD (0.1539 nm)平行于Y/[113]α/[-1-120]L,并有一垂直于臺階的bzD分量(0.0747 nm)。同時,重疊步長高度h =d[1-100]L。我們通過分離帶和超分離帶在{-3-32}α/{1-100}L臺階上沿<113>α/<-1-120>L方向的橫向運(yùn)動對Laves析出相的演化進(jìn)行了描述,并發(fā)現(xiàn)分離帶陣列能夠適應(yīng){-3-32}α/{1-100}L臺階引起的錯配應(yīng)變。
英文摘要
Even though it is widely accepted that the Laves phase is a promising strengthener for chromium-containing stainless steels, there is little information available on its microstructural evolution and growth. Therefore, in this study, we analysed the behaviour of Laves (C14) precipitates in high-Cr ferritic stainless steel, Fe-20Cr-2Mo-0.5Nb (at%), annealed at 1073 K for different time periods. A high density of (Fe,Cr)2(Mo,Nb) precipitates was formed in the α matrix during annealing. Morphological evolution in the Laves phase followed the sequence of spheroidal → faceted ellipsoidal → faceted needle-like → faceted plate-like. The Laves phase is related to the α matrix by two sets of orientation relationships, viz. OR1: [-1-12] α/[1-210]L、[111]α/[0-110]L、and [1-10]α/[000-1]L,and OR-2: [1-10]α/[0001]L、[113]α/[-1-120]L、and [-3-32]α/[1-100]L. The habit plane of the Laves phase was found to deviate slightly from the plane. Interfacial defects, namely disconnections (bD, h) and super disconnections (mbD, mh), observed experimentally along the habit plane, were consistent with theoretical results based on OR-2 as the reference coordinate frame. The Burgers vector bD exhibited an edge component byD (0.1539 nm) parallel to Y/[113]α/[-1-120]L and a small normal component bzD (0.0747 nm) perpendicular to the terraces; meanwhile, the overlap step height h =d[1-100]L. The morphological evolution of Laves precipitates was described based on the lateral motion of disconnections and super disconnections on {-3-32}α/{1-100}L terraces in the direction. Arrays of the disconnections (bD, h) were found to be capable of accommodating the misfit strain on {-3-32}α/{1-100}L terraces.
ACTA Vol. 198, 1 Oct. 2020, P242-256
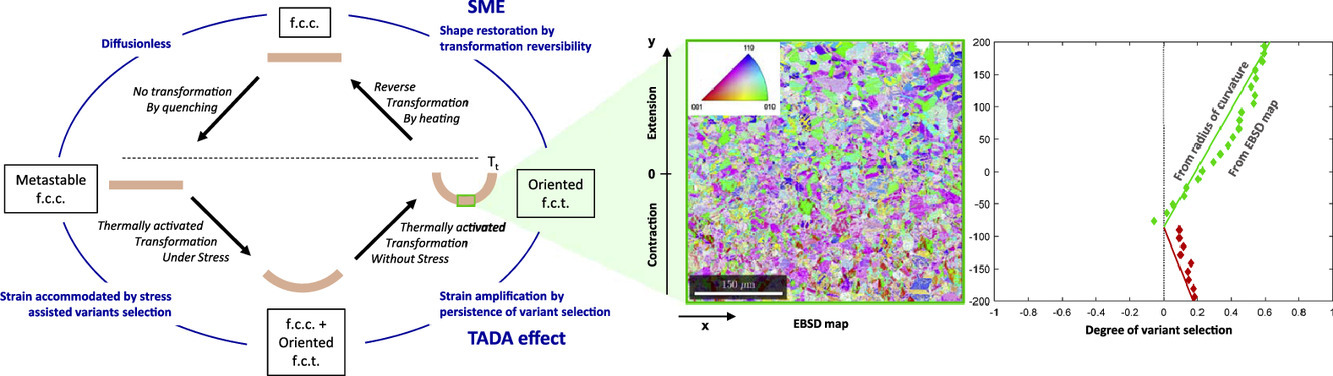
14. The thermally activated distortion with amplification effect and related variant selection in red gold alloys
金紅石合金中具有放大效應(yīng)的熱激活畸變和與之有關(guān)的變體選擇
Margaux N.D. Larcher?, Cyril Cayron, Andreas Blatter, Raphaëlle Soulignac, Roland E. Logé
M.N.D. Larcher: margaux.larcher@epfl.ch
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.07.064
摘要
在之前發(fā)表的工作中,我們利用電子背散射衍射(EBSD)技術(shù),對接近等原子比的金紅石結(jié)構(gòu)多晶Au-Cu合金在A1→L10相變過程中的變體選擇進(jìn)行了研究。通過對晶格畸變進(jìn)行數(shù)學(xué)描述,并結(jié)合最大功準(zhǔn)則,我們成功地對變體選擇的程度進(jìn)行了量化。基于同樣的方法,我們研究了一種20年前在等原子比AuCu-Ga合金中發(fā)現(xiàn)的有趣的形狀畸變效應(yīng)。具體來說,我們詳細(xì)研究了彎曲后再熱處理這整個過程中,薄片試樣的形狀畸變。通過對相變過程和樣本曲率的觀察測量,我們探究了合金奇特的形狀記憶和畸變放大效應(yīng),我們把這稱之為TADA效應(yīng)。樣本的EBSD分析結(jié)果揭示了樣品變體選擇的潛在機(jī)制。我們將實驗測得的變選擇分布與歐拉-伯努利光束理論的預(yù)測結(jié)果進(jìn)行了比較。兩者具有較好的一致性,這表明變體選擇是導(dǎo)致金紅石結(jié)構(gòu)合金發(fā)生宏觀變形的原因。當(dāng)外部應(yīng)力被釋放時,TADA效應(yīng)就會發(fā)生,并且TADA效應(yīng)強(qiáng)烈地依賴于相變初始階段的應(yīng)力。這種不尋常的現(xiàn)象被認(rèn)為是由于在整個相變過程中持續(xù)發(fā)生變體選擇而導(dǎo)致的。
英文摘要
Variant selection during the A1→L10 transformation in a polycrystalline red gold alloy close to equiatomic Au-Cu composition has been extensively studied by Electron Backscatter Diffraction (EBSD) in our previous work. The use of a mathematical description of the lattice distortion and the maximal work criterion allowed us to quantify the degree of selection. With the same approach, we investigate here an interesting shape distortion effect, discovered twenty years ago in equiatomic AuCu-Ga. The shape distortion of thin samples placed in bending condition and then heat-treated under stress is studied in details. The singular shape memory effect and the remarkable distortion amplification, which we call TADA effect, are explored by monitoring the sample radius of curvature and the advancement of the transformation. The underlying mechanisms of variant selection are revealed by EBSD analysis across the samples. The experimental crystallographic variant selection distribution is compared with the expected profile calculated with the Euler-Bernoulli beam theory. The good agreement demonstrates that variant selection during the transformation is at the origin of the macroscopic distortion of red gold alloys. The TADA effect was found to occur when external stresses are released, and strongly depends on the stress at the initial stage of the transformation. This unusual effect is assumed to result from the persistence of variant selection throughout the transformation.
ACTA Vol. 198, 1 Oct. 2020, P258-270
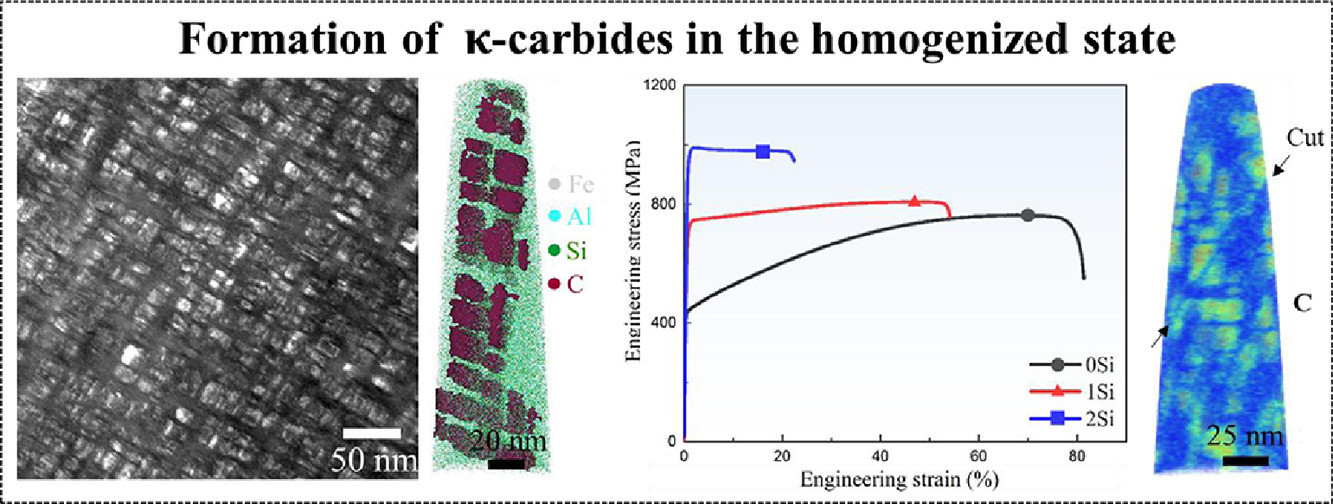
15. Formation mechanism of κκ-carbides and deformation behavior in Si-alloyed FeMnAlC lightweight steels
含Si的FeMnAlC輕量鋼中的κ碳化物形成機(jī)制及變形行為
Zhangwei Wang?, Wenjun Lu?, Huan Zhao, Junyang He, Kang Wang, Bicheng Zhou, Dirk Ponge, Dierk Raabe, Zhiming Li?
Z. Wang: zh.wang@mpie.de
W. Lu: w.lu@mpie.de
Z. Li: lizhiming@csu.edu.cn
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.08.003
摘要
熱力學(xué)計算表明,Si元素的添加能顯著增Al和C的活度,因此向Fe-30Mn-9Al-1.2C (wt. %)奧氏體輕量鋼中添加0、1、2wt.%不等的Si 可以有效調(diào)控κ碳化物的形成。在不含Si的情況下,我們在材料中觀測到了無配分的納米級L12有序微區(qū)(尺寸<1nm);而當(dāng)添加2 wt.%的Si后,材料晶內(nèi)形成了大量的立方 L′12 κ碳化物,其平均尺寸11.5 nm,體積分?jǐn)?shù)達(dá)25.9%。這些κ碳化物與之前報導(dǎo)的時效過程中析出的κ碳化物析出路徑不同。同時,我們在添加了2 wt.% Si的合金的奧氏體晶界上還觀測到了L′12 κ0碳化物析出和DO3相。晶粒內(nèi)的κ析出使得材料的屈服強(qiáng)度大幅提高,從不含Si的~450MPa 提高到2% Si的~950MPa。在三種添加了不同含量Si的鋼鐵材料中,變形機(jī)制都以滑移帶形成為主,其中包括了納米微區(qū)或κ碳化物的切變。由于動態(tài)滑移帶細(xì)化導(dǎo)致滑移帶均勻分布,因此無Si鋼的能夠發(fā)生顯著的應(yīng)變硬化。而含2 wt. % Si鋼則由于局部滑移帶粗化,導(dǎo)致應(yīng)變硬化降低。以上實驗結(jié)果為高性能輕量鋼的設(shè)計提供了富有價值的指導(dǎo)。
英文摘要
The formation of κ-carbides in austenite Fe-30Mn-9Al-1.2C (wt. %) lightweight steels is tuned via alloying of Si (0, 1, 2 wt. %), an element that can remarkably raise the activities of Al and C based on thermodynamic calculations. Ordered L12 nano-domains (with a size <1 nm), lacking elemental partition, were observed in the solution-treated steel without Si alloying, while with the increase of Si to 2 wt. %, cuboidal L′12 intragranular κ-carbides were well developed with an average size of 11.5 nm and a volume fraction of 25.9 %. These κ-carbides found in the solution-treated steel with 2 wt. % Si follow a different precipitation route from previous pathways that require aging. Also, particle-shaped L′12 intergranular κ0-carbides and DO3 phase were formed at austenite grain boundaries in the steel with 2 wt. % Si. The precipitation of κ-carbides in grain interiors leads to an improvement of the yield strength from ~450 MPa to ~950 MPa as the Si content increases from 0 to 2 wt. %. The primary deformation mechanism is the formation of slip bands in all three steels, which involves the shear of ordered nano-domains or κ-carbides. The uniform distribution of the slip bands is essential for the high strain hardening, provided by the dynamic slip band refinement in the steel without Si. Lower strain hardening is seen in the steel with 2 wt. % Si due to the formation of localized coarse slip bands. These findings offer valuable insights into the design of high-performance lightweight steels.
ACTA Vol. 198, 1 Oct. 2020, P271-280
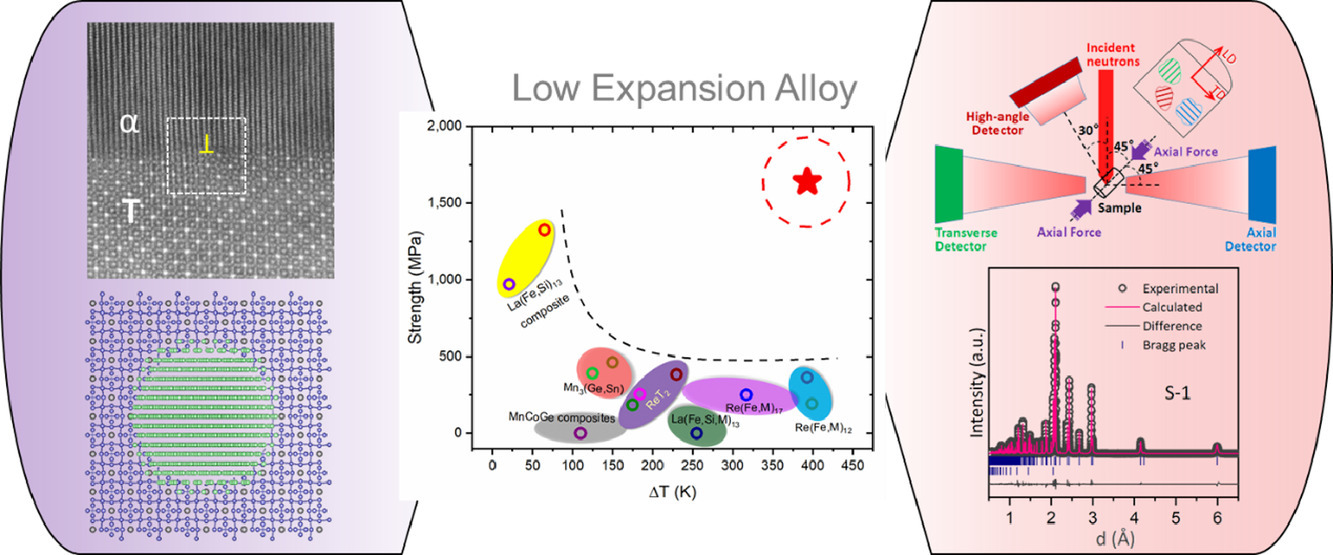
16. High performance and low thermal expansion in Er-Fe-V-Mo dual-phase alloys
具有優(yōu)異力學(xué)性能和低熱膨脹系數(shù)的Er-Fe-V-Mo雙相合金
Kun Lin, Wenjie Li, Chengyi Yu, Suihe Jiang, Yili Cao, Qiang Li, Jun Chen, Minghe Zhang, Min Xia, Yan Chen, Ke An, Xiaobing Li, Qinghua Zhang, Lin Gu, Xianran Xing?
X. Xing: xing@ustb.edu.cn,北京科技大學(xué)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.08.012
摘要
低熱膨脹合金由于其在熱沖擊下的尺寸穩(wěn)定性,而在高精度儀器設(shè)備中具有重要作用。然而,低熱膨脹率合金往往機(jī)械性能差,韌性差,抗斷裂能力低,這大大限制了其作為功能材料的應(yīng)用。在本研究中,我們通過在具有顯著磁體積效應(yīng)的硬質(zhì)金屬間化合物基體中析出一種韌性相,制備出了一種同時具有優(yōu)異機(jī)械性能和功能特性的新型的Er-Fe-V-Mo金屬間化合物雙相合金。研究發(fā)現(xiàn),當(dāng)含有12.8±0.1vol% 沉淀相時,合金的強(qiáng)度和韌性提高了一個數(shù)量級,同時在較寬的溫度范圍內(nèi)(100 ~ 493 K)保持了較低的體熱膨脹系數(shù)(1.87±0.02×10−6 K−1)。實時原位中子衍射、同步輻射X射線衍射和顯微分析實驗表明,析出相的熱膨脹和力學(xué)性能均與基體通過半共格界面相互耦合; 更重要的是,析出相通過位錯滑移產(chǎn)生了顯著的應(yīng)變硬化,減輕了局部應(yīng)力,從而阻礙了微裂紋在金屬間化合物基體中的擴(kuò)展。該合金制備工藝簡單,熱循環(huán)穩(wěn)定性好,具有很大的應(yīng)用潛力。這項研究對于低熱膨脹合金以及其他高性能金屬間化合物材料的設(shè)計具有重要的啟發(fā)意義。
英文摘要
Low thermal expansion alloy plays a unique role in high precision instruments and devices owing to its size stability under thermal shocks. However, a low thermal expansion generally produces a poor mechanical performance, such as brittleness and low fracture resistance, which is a bottle-neck for their applications as functional materials. Here, we demonstrate a novel intermetallic compound-based dual-phase alloy of Er-Fe-V-Mo with excellent structural and functional integrity achieved by precipitating a ductile phase in the hard-intermetallic matrix with large magnetovolume effect. It is found that the compound with 12.8 ± 0.1vol% precipitate phase improves the alloy's strength and toughness by one order of magnitude, while keeping a low bulk coefficient of thermal expansion (1.87±0.02 × 10−6 K − 1) over a wide temperature range (100 to 493 K). The combined analyses of real-time in-situ neutron diffraction, synchrotron X-ray diffraction, and microscopy reveal that both the thermal expansion and the mechanical properties of the precipitate phase are coupled with the matrix phase via semi-coherent interfacial constraint; more importantly, the precipitate phase undergoes a pronounced strain hardening with dislocation slips, which relieves the stress localization and thus hinders the microcrack propagation in the intermetallic matrix. Moreover, the alloys are easy to fabricate and stable during thermal cycling with great application potentials. This study shed light on the development of low thermal expansion alloys as well as the implications to other high-performance intermetallic -compound-based material design.
ACTA Vol. 198, 1 Oct. 2020, P281-289
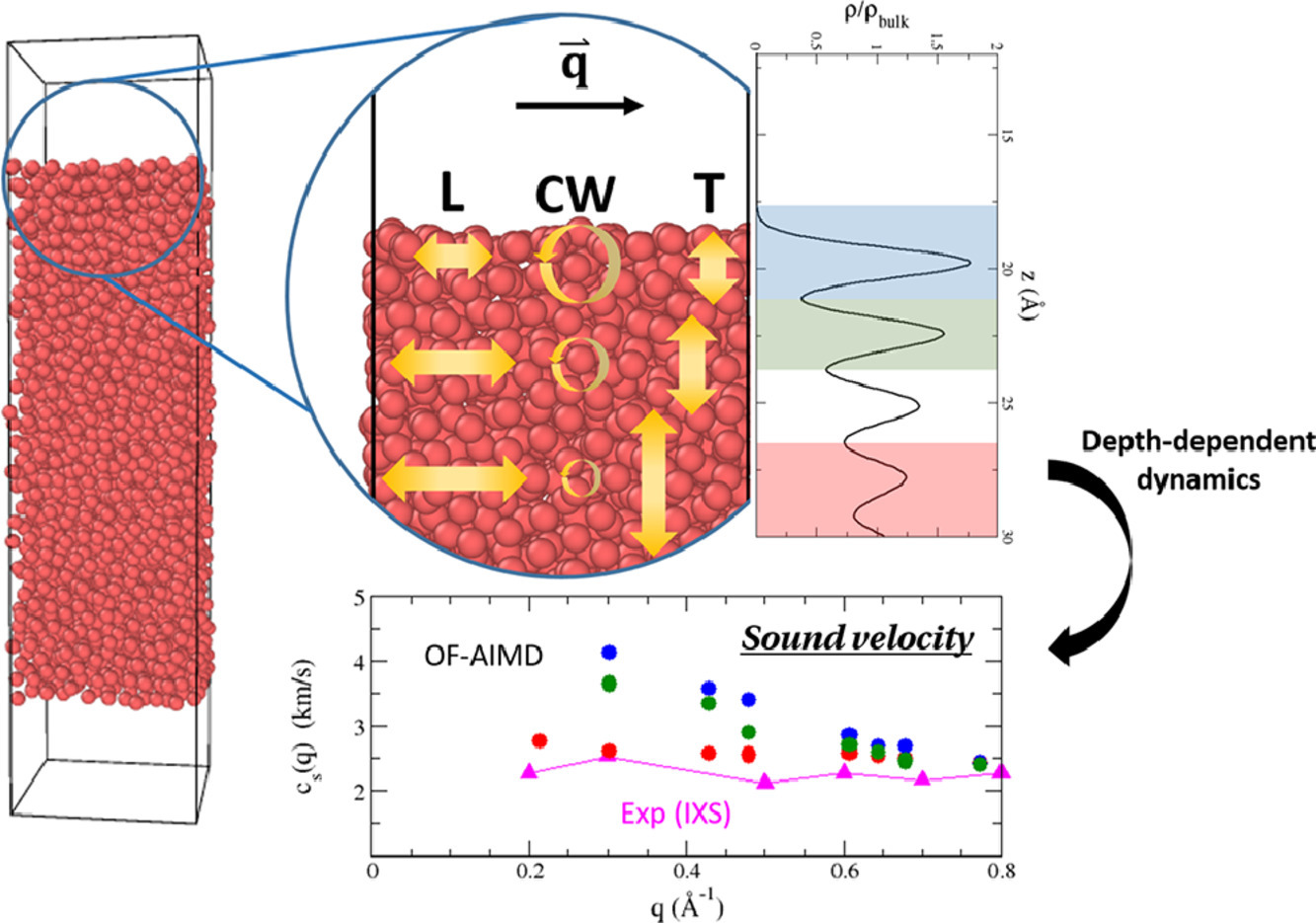
17. Depth-dependent dynamics of liquid metal surfaces with first principles simulations
利用第一性原理模擬液體金屬表面動力學(xué)隨深度的變化
Beatriz G. del Rio, Luis E. González?
L.E. González: luisen@metodos.fam.cie.uva.es
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.07.071
摘要
近年來,液態(tài)金屬表面由于其在二維材料合成、催化或聚變反應(yīng)堆中的應(yīng)用而受到了越來越多的關(guān)注。許多液態(tài)金屬或合金的靜態(tài)性質(zhì),如反射率、密度等,已經(jīng)通過實驗和計算得到了確定。然而,對于液態(tài)金屬動態(tài)性質(zhì)的表征卻仍是一個具有挑戰(zhàn)性的任務(wù),僅有Reichert等人對于液態(tài)銦的動態(tài)性質(zhì)隨表面深度的變化進(jìn)行過一次實驗研究。在本文中,我們對同一體系在不同深度下的動態(tài)特性進(jìn)行了較全面的第一性原理分子動力學(xué)研究。模擬結(jié)果與實驗數(shù)據(jù)表現(xiàn)出了較好的一致性。此外,通過計算,我們能夠獲得比實驗更接近表面的性能,并發(fā)現(xiàn)較淺深度的性能與較深處具有顯著不同。因此,本研究揭示了原子界面處的動態(tài)特性行為,并重點反映了第一性原理分子動力學(xué)在研究目前實驗所無法達(dá)到的液態(tài)金屬表面的動態(tài)行為的能力,這對于液態(tài)表面物理至關(guān)重要。
英文摘要
Liquid metal surfaces have gained increased interest over the last decade due to new applications in synthesis of 2D materials, catalysis, or fusion reactors. Static properties such as the reflectivity and density profile have been determined, both experimentally and computationally, for numerous liquid metals and alloys. However, the characterization of the dynamic properties has remained a challenging task and only one experimental study by Reichert et al. has evaluated the depth-dependence of different dynamic properties in the liquid indium (l-In) surface. In this paper, we present an ab inito molecular dynamics study of the collective dynamic properties of this same system at different depths, obtaining very good agreement with the experimental data. In addition, we are able to compute the properties much closer to the surface than experimentally attainable, and have discovered that at these shallower depths, the properties drastically differ from those deeper in the slab. Therefore, this study sheds light into the behavior of dynamic properties at the atomic interface and highlights the ability of ab initio molecular dynamics to study such unknown dynamic behavior of liquid metals surfaces at depths not yet attainable experimentally but of crucial importance for liquid surface physics.
微信公眾號:Goal Science
投稿郵箱:wechat@gs-metals.com
投稿微信:GSmaterial
