金屬頂刊雙語導讀丨Acta Mater. Vol.200,Nov. 2020(上)
2020-10-29 來源: Goal Science
本期包含金屬材料領域論文25篇,涵蓋了高熵合金、金屬玻璃、420不銹鋼、鈦合金、鎂合金、形狀記憶合金、純錫、單晶鎢、高溫合金、316不銹鋼、中熵合金、增材制造等,國內科研單位包括哈爾濱工業大學、大連理工大學、臺灣成功大學、臺灣中央大學、上海交通大學等(通訊作者單位)。
Vol. 200 目錄
ACTA Vol. 200,Nov. 2020, P1-11
1. Simultaneous twinning and microband formation under dynamic compression in a high entropy alloy with a complex energetic landscape
復雜能量場下高熵合金動態壓縮同步孿晶和微帶形成的研究
D.L.Foley,S.H.Huang,E.Anbera,L.Shanahan,Y.Shen,A.C.Lang,C.M.Barr,D.Spearot,L.Lamberson,M.L.Taheri?
M.L.Taheri:mtaheri4@jhu.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.08.047
摘要
高熵合金(HEAs)由于其優異的力學性能和獨特的微觀組織,近年來成為研究的熱點。這些合金中的化學無序性被認為會導致復雜的能量環境,從而影響位錯的形核與運動。在本文研究中,評估了Cantor高熵合金(CoCrFeMnNi)中由準靜態與動態壓縮而產生的形變微結構的演變。掃描和透射電子顯微鏡(SEM/TEM)技術被用來成像與量化位錯密度。當應變率從10−3 s−1增加到5000 s−1時,可以觀察到整體位錯密度增加,從而導致變形孿晶的形成。此外,在8000 s−1的速率下,變形孿晶和微帶都成為塑性變形機制,這部分通常與層錯能大小緊密相關。為了將這種塑性變形機制與化學無序性聯系起來,通過原子計算用于計算廣義層錯能曲線,并近似計算Contor合金受溫度變化顯著的內稟層錯能,揭示了這些與位錯和孿晶行為有關的能量參數的顯著局部變化。
英文摘要
High entropy alloys (HEAs) have been the subject of significant research in recent years due in part to their excellent mechanical properties and unique microstructure. Chemical disorder in these alloys is thought to lead to a complex energetic environment that affects the nucleation and movement of dislocations. In this study the development of deformation substructures is assessed in the Cantor HEA (CoCrFeMnNi) due to quasistatic and dynamic compression. Scanning and transmission electron microscopy (SEM/TEM) techniques are used to image and quantify dislocation density. When increasing the strain rate from 10−3 s−1 to 5000 s−1 we observe an increase in the overall dislocation density which leads to the formation of deformation twins. Further at a rate of 8000 s−1, both deformation twins and microbands become operative plasticity modes, which are usually associated with different extremes of stacking fault energy. To relate this plastic response to chemical disorder, atomistic calculations are used to compute the generalized stacking fault energy curve and approximate the temperature dependence of the intrinsic stacking fault energy for the Cantor alloy, which reveals significant local variation in these critical energetic parameters associated with dislocation and twinning behaviors.
ACTA Vol. 200, Nov. 2020, P12-23
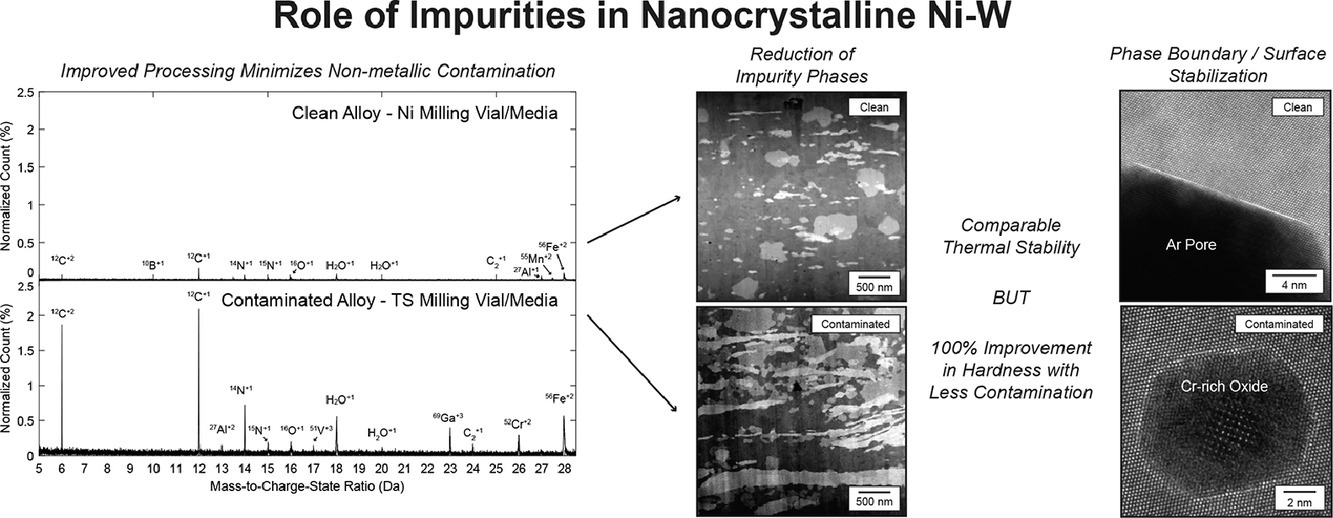
2. On the reduction and effect of non-metallic impurities in mechanically alloyed nanocrystalline Ni-W alloys
機械合金化對納米晶Ni-W合金中非金屬雜質的減少及影響
C.J. Marvel?,J.A. Smeltzer,B.C. Hornbuckle,K.A. Darling,M.P. Harmer
C.J. Marvel:cjm312@lehigh.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.08.083
摘要
非金屬污染是商業合成過程中不可避免的副產品。然而,在考慮納米結構材料的材料設計與性能時,非金屬雜質往往被忽視。重要的是,關于非金屬污染是否穩定或破壞納米晶材料的晶粒生長仍然存在爭議。此外,非金屬污染是否對納米晶系統的硬度有顯著影響尚不清楚。本工作采用機械合金化方法制備了兩種不同雜質濃度的Ni-28at%W納米晶合金,來評估非金屬污染對納米材料熱穩定性和硬度的影響。合金在不同溫度下進行等溫回火處理,采用原子探針層析成像和像差校正掃描電鏡對合金的顯微組織進行比對分析。通過使用特定的研磨介質和預研磨還原工藝,可以顯著降低雜質濃度。此外,清潔合金與受污染合金在防止晶粒長大表現出相似的熱穩定性,盡管晶粒尺寸與第二相分布相似,清潔合金的硬度提高了100%。受污染合金中的雜質項包括CrOx,Ni6W6C與捕獲Ar孔被識別,并且在本研究中觀察到其對熱穩定性和機械性能有貢獻。總的來說,這項工作表明雜質并不總是對納米晶體系統的熱機械行為是有害的。
英文摘要
Non-metallic contamination is a practically unavoidable byproduct of commercial synthesis processes; however, non-metallic impurities are often overlooked when considering material design and performance of nanostructured materials. Importantly, there is disputing evidence as to whether non-metallic contamination stabilize or destabilize nanocrystalline materials against grain growth. Furthermore, it is unclear if non-metallic contamination has a significant impact on hardness of nanocrystalline systems. In this work, two nanocrystalline Ni-28at%W alloys with different impurity concentrations were produced via mechanical alloying to directly evaluate the effect of contamination on thermal stability and hardness of nanostructured materials. The alloys were isothermally annealed at several temperatures, and the microstructures were compared by applying atom probe tomography and aberration-corrected scanning transmission electron microscopy. It was determined that impurity concentrations can be substantially reduced by using specific milling media and pre-milling reduction processes. Furthermore, the clean and contaminated alloys exhibited similar thermal stabilities against grain growth, but the clean alloy displayed a 100% improvement in hardness despite a similar grain size and distribution of second phases. Impurity phases including CrOx, Ni6W6C, and trapped Ar pores were also identified and likely contributed to the thermal stability and mechanical properties observed in this study. Overall, this work suggests that impurities my not always be detrimental to thermomechanical behavior of nanocrystalline systems.
ACTA Vol. 200, Nov. 2020, P24-34
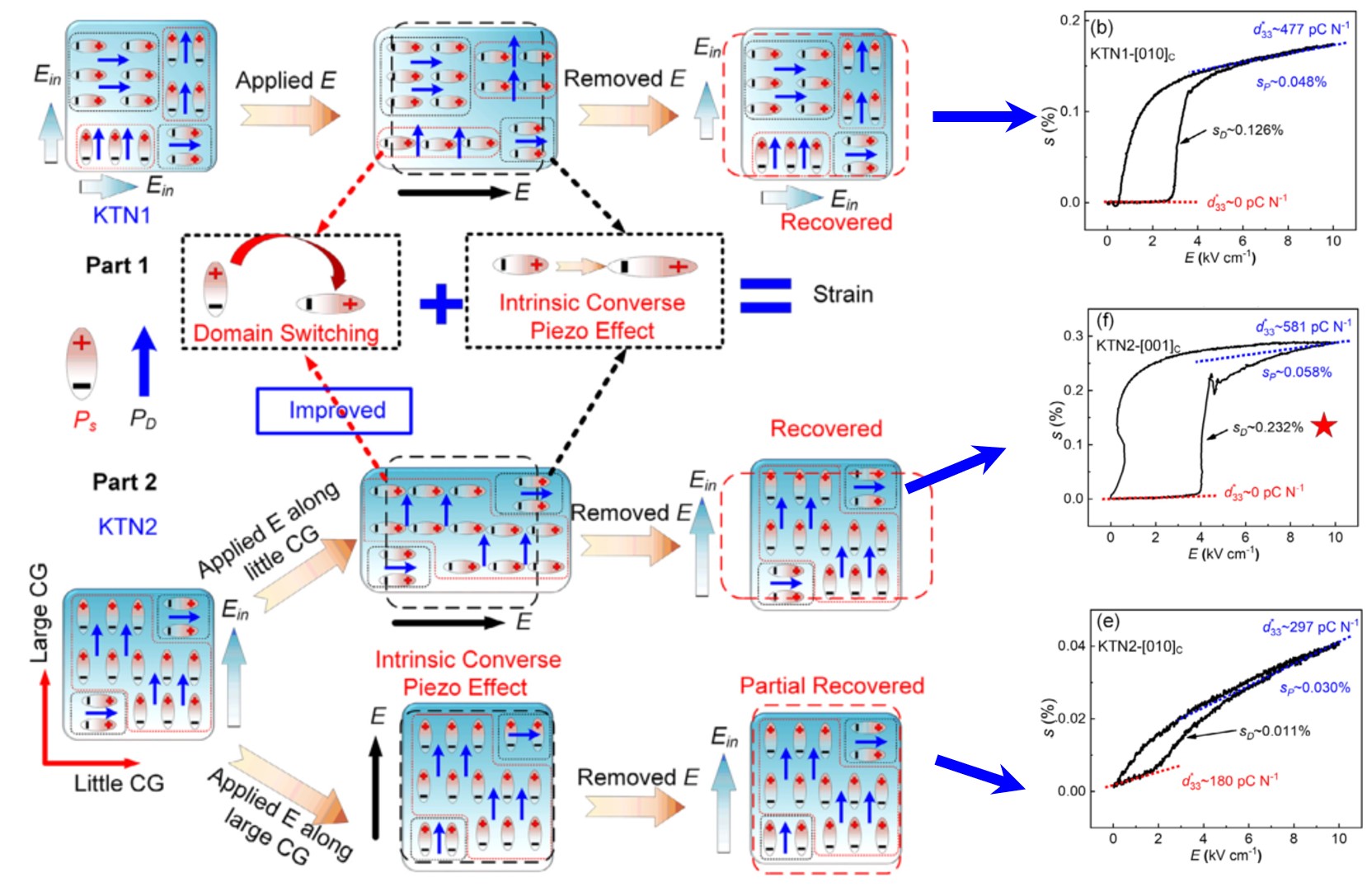
3. Improving strain in single crystal by composition-gradients design
成分梯度設計提高單晶疇變
Fei Huang,Chengpeng Hu?,Zhongxiang Zhou,Xiangda Meng,Peng Tan,Yu Wang,Chuanzhi Wang,Hao Tian
Chengpeng Hu:huchengpeng1988@163.com,哈爾濱工業大學
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.09.004
摘要
疇變是鐵電材料在形變時的重要貢獻之一。在這項工作中,我們利用各向異性成分梯度(CGs)來誘導缺陷和自發偶極子的各向異性取向,以提高KTa1–xNbxO3單晶形變中疇變的貢獻。這樣,KTa0.58Nb0.42O3單晶沿最小CG方向的形變顯著改善(超過60%),在低驅動電場10kV·cm–1時,獲得了較大的單極應變達0.29%。這歸因于缺陷和自發偶極子沿最大CG方向的擇優取向,從而提高了沿最小CG方向的疇變貢獻。特別是,由于撓曲電場和缺陷釘扎效應的共同作用,KTN在小CG方向上表現出的殘余應變(srem)幾乎為零,對應于雙P-E環。此外,V-PFM圖像證實了CGs可以影響微疇結構。因此,設計特殊的各向異性CGs材料有望成為一種改善鐵電材料應變特性的新方法,也是下一代各向異性壓電材料柔性化設計的潛在途徑。
英文摘要
Domain switching is one of the essential contributions for strain in ferroelectric materials. In this work, we utilize anisotropic composition gradients (CGs) to induce anisotropic orientation of both defects and spontaneous dipoles, aiming to enhance the contribution of domain switching on strain in KTa1–xNbxO3 single crystal. In this way, a remarkable improvement (over 60%) of strain is obtained in KTa0.58Nb0.42O3 single crystal along the smallest CG direction, achieving a large unipolar strain, i.e. 0.29%, at low driving electric field 10 kV cm–1. It is attributed to the preferred orientation of both defects and spontaneous dipoles along the largest CG directions, then improving the contribution of domain switching on strain along the smallest CG direction. Particularly, owing to the existence of Ein as recoverable forces caused by both flexoelectric fields and defects pinning effect, KTN show nearly zero remnant strain (srem) along with the small CG directions, corresponding to the double P-E loops. Moreover, the V–PFM images confirm that CGs can influence the microdomain structures. Thus, designing special anisotropic CGs materials is expected to be a novel method to improve the strain properties and a potential way to flexibly design next-generation anisotropic piezoelectric materials.
ACTA Vol. 200, Nov. 2020, P42-55
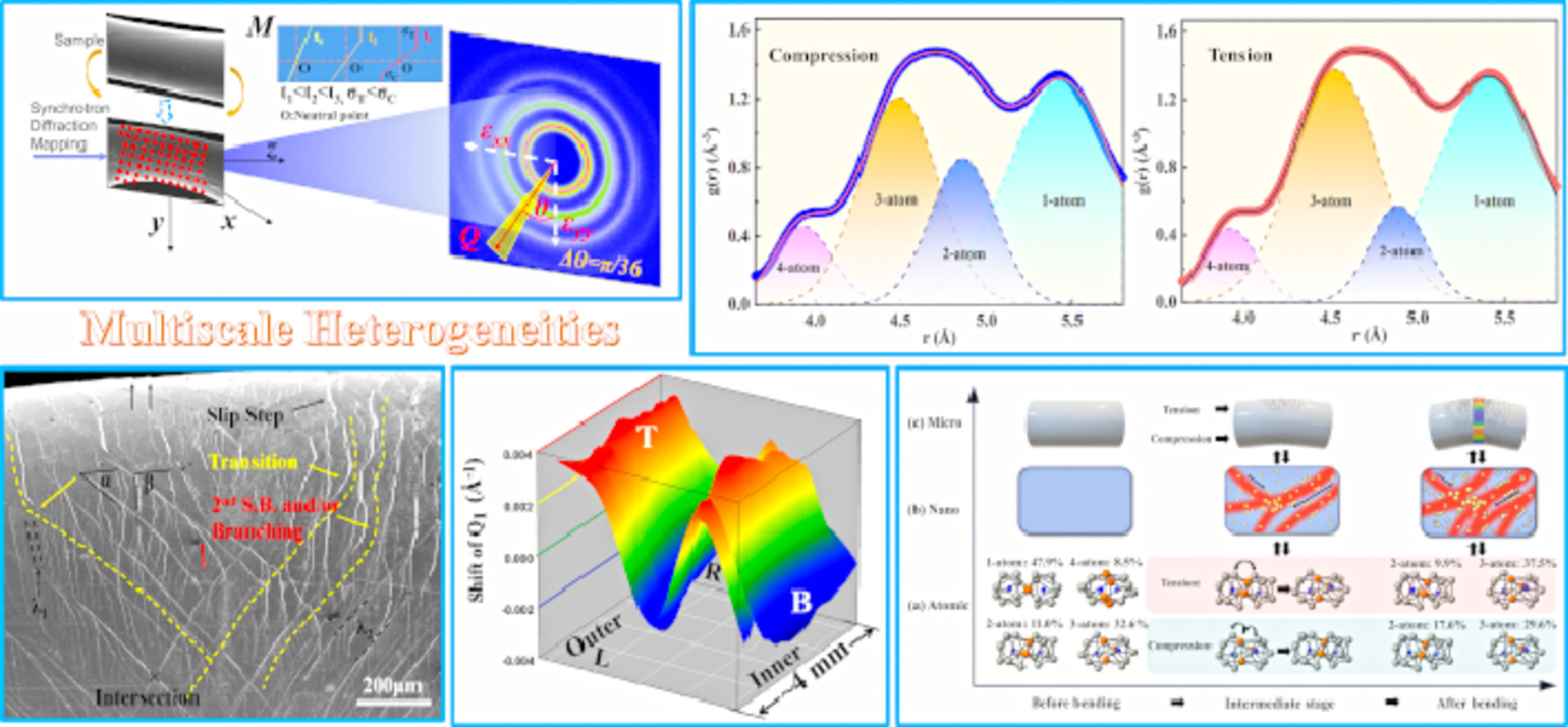
4. Deformation-enhanced hierarchical multiscale structure heterogeneity in a Pd-Si bulk metallic glass
形變增強大塊Pd-Si金屬玻璃的多長度尺度分層結構非均勻性
Sinan Liu,Lifeng Wang,Jiacheng Ge,Zhenduo Wu,Yubin Ke,Qiang Li,Baoan Sun,Tao Feng,Yuan Wu,J.T. Wang,Horst Hahn,Yang Ren,Jonathan D. Almer,Xun-li Wang,Si Lan?
Si Lan:lansi@njust.edu.cn,南京科技大學,香港城市大學
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.08.077
摘要
利用電子顯微鏡、高能同步輻射X射線衍射和小角散射技術研究了Pd82Si18二元塊狀金屬玻璃變形前后的多尺度結構。實驗結果表明,變形后的多長度尺度上分層結構的非均勻性增強。彎曲后觀察到高密度的分層多剪切帶,引入復雜但周期性分布的殘余應變。對分布函數分析表明,短程團簇在中程尺度上的連通性決定了彎曲后樣品拉伸側和壓縮側的堆積密度差異。原位同步輻射X射線衍射研究還揭示了短程團簇在單軸拉伸和壓縮作用下的連接模式的轉變,這與Pd82Si18玻璃合金中彎曲時三軸拉伸/壓縮部分的轉變一致。通過小角散射和透射電子顯微鏡觀察到金屬玻璃變形后的納米尺度非均相,可能是由于塑性變形增強的納米級非晶相分離和多剪切帶相互作用的結果。我們的研究結果表明,在多長度尺度上分層結構非均勻性增強可以解釋Pd-Si玻璃合金具有良好的塑性,加深了對金屬玻璃塑性變形過程中結構-性能關系的理解。
英文摘要
The multiscale structures in a Pd82Si18 binary bulk metallic glass before and after deformation were studied using electron microscopies, high-energy synchrotron X-ray diffraction, and small-angle scattering techniques. The experimental results revealed an enhancement of hierarchical structure heterogeneities on multiple length scales after deformation. Hierarchical multiple shear bands of high number density were observed after bending, introducing complex but periodically distributed residual strain. Pair distribution function analysis revealed that the connectivity of the short-range clusters on the medium-range scale determines the packing density difference between the tension side and the compression side in the sample after bending. In-situ synchrotron X-ray diffraction study also revealed a transformation of connection modes among short-range clusters under uniaxial tension and compression, which is consistent with those of triaxial tension/compression parts upon bending in Pd82Si18 glassy alloys. The nanoscale heterogeneities for metallic glasses after deformation observed by small-angle scattering and transmission electron microscopy may be attributed to the nanoscale amorphous phase separation and interacting multiple shear bands enhanced by plastic deformation. Our findings suggested that the enhancement of hierarchical heterogeneous structure on multiple length scales may explain the excellent plasticity of Pd-Si glassy alloys, deepening the understanding of structure-property relation during plastic deformation in metallic glasses.
ACTA Vol. 200, Nov. 2020, P56-65
5. Dendritic and seaweed growth of proeutectic scandium tri-aluminide in hypereutectic Al-Sc undercooled melt
過共晶Al-Sc過冷熔體中先共晶鈧三鋁化物的枝晶和海藻生長
Aoke Jiang,Xiaoming Wang?
Xiaoming Wang:wang1747@purdue.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.08.078
摘要
在電子顯微鏡下觀察了不同冷卻速率下過冷過共晶Al-2wt.%Sc合金熔體中生長的先共晶Al3Sc的形貌,以揭示其不同的生長機制。在低冷卻速率下(~1k·s−1),正如預期的那樣,先共晶Al3Sc的形成受橫向生長的控制,暴露出六個{100}平面。在中等冷卻速率(~400k·s−1)下,先共晶Al3Sc以枝晶方式生長,具有沿八個〈111〉方向延伸的明確骨架和拋物線形枝晶尖端,盡管枝晶尖端和側枝在生長后期變成多面臺階,這時橫向生長再次盛行。在高冷卻速率(~1000k·s−1)下,先共析Al3Sc主要凝固成完全海藻顆粒,由內部致密海藻和外部分形海藻組成。在后兩種情況下,作者對先共析Al3Sc的形成機理在本工作中首先用生長模型闡明了。通過檢查結構中的特征長度尺度,如枝晶尖端半徑、海藻分枝間距和生長早期不穩定球體的大小,使用各種形態穩定準則來驗證所提出的樹枝狀和海藻生長模型。
英文摘要
The morphologies of proeutectic Al3Sc growing in an undercooled hypereutectic Al-2 wt.% Sc alloy melt with varied cooling rates were carefully examined under electron microscopes, in order to reveal its different growth mechanisms. At a low cooling rate (~1 K·s − 1), as expected, the formation of proeutectic Al3Sc was governed by the lateral growth, exposing six flat {100} facets. At an intermediate cooling rate (~400 K·s − 1), proeutectic Al3Sc grew in a dendritic manner, with well-defined backbones extending in its eight 〈111〉 directions and paraboloidal dendrite tips, although the dendrite tips and side-branches turned into faceted steps at a late growth stage, when the lateral growth prevailed again. At a high cooling rate (~1000 K·s − 1), proeutectic Al3Sc primarily solidified into an entirely seaweed particle, which was composed of interior compact seaweeds and exterior fractal seaweeds. The detailed formation mechanisms of the proeutectic Al3Sc in the latter two situations, to the author's knowledge, are first clarified with growth models in the present work. Various morphological stability criteria were used to verify the proposed dendritic and seaweed growth models, by examining characteristic length scales in the structure, such as the radius of the dendrite tip, the interspacing between seaweed branches, and the size of destabilized sphere at an early growth stage.
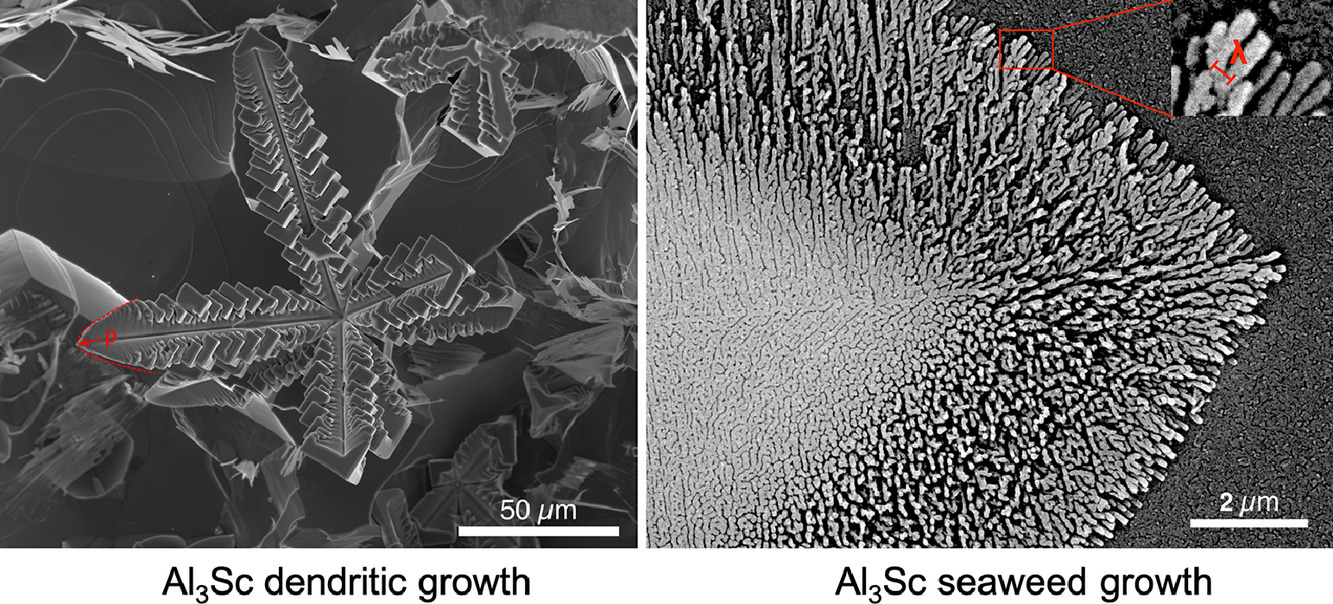

ACTA Vol. 200, Nov. 2020, P74-90
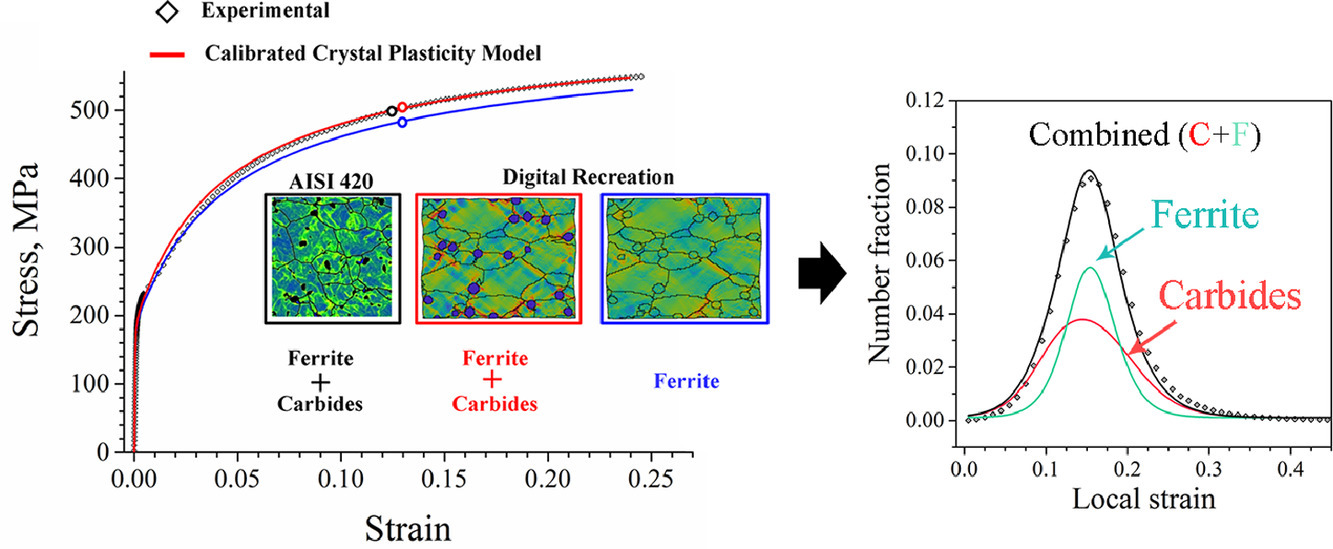
6. Influence of M23C6 carbides on the heterogeneous strain development in annealed 420 stainless steel
M23C6碳化物對退火420不銹鋼非均勻應變發展的影響
J. Hidalgo?,M. Vittorietti,H. Farahani,F. Vercruysse,R. Petrov,J. Sietsma
J. Hidalgo:J.HidalgoGarcia@tudelft.nl
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.08.072
摘要
理解金屬合金中由于微觀結構的不同而引起的局部應變增強和晶格畸變在許多工程過程中是至關重要的。非均相應變的發展不僅在材料的加工硬化過程中起著重要作用,而且在其他過程如再結晶、損傷遺傳和斷裂中也起著重要作用。由于晶界或其他微觀結構特征的存在導致不明確的解釋,分離析出物對非均相應變發展的貢獻可能具有挑戰性。本文通過電子背散射衍射測量的局部應變的統計分析和基于晶體塑性的模擬相結合來確定M23C6碳化物對退火的AISI420鋼變形的影響。結果表明,與純鐵素體組織相比,碳化物通過主要的長程有序作用機制在低塑性應變下具有更有效的硬化作用。碳化物不僅直接通過與鐵素體基體的彈性不相容性直接影響局部應變,而且還影響鐵素體晶粒間的空間相互作用。晶界處的碳化物促進了鐵素體晶界附近應變的發展。然而,在碳化物和鐵素體晶界密度較高的區域,碳化物和晶界對產生高局部應變的積極作用會減弱。
英文摘要
Understanding the local strain enhancement and lattice distortion resulting from different microstructure features in metal alloys is crucial in many engineering processes. The development of heterogeneous strain not only plays an important role in the work hardening of the material but also in other processes such as recrystallization and damage inheritance and fracture. Isolating the contribution of precipitates to the development of heterogeneous strain can be challenging due to the presence of grain boundaries or other microstructure features that might cause ambiguous interpretation. In this work a statistical analysis of local strains measured by electron back scatter diffraction and crystal plasticity based simulations are combined to determine the effect of M23C6 carbides on the deformation of an annealed AISI 420 steel. Results suggest that carbides provide a more effective hardening at low plastic strain by a predominant long-range interaction mechanism than that of a pure ferritic microstructure. Carbides not only influence local strain directly by elastic incompatibilities with the ferritic matrix, but also the spatial interactions between ferrite grains. Carbides placed at the grain boundaries enhanced the development of strain near ferrite grain boundaries. However the positive effect of carbides and grain boundaries to develop high local strains is mitigated at regions with high density of carbides and ferrite grain boundaries.
ACTA Vol. 200, Nov. 2020, P91-100
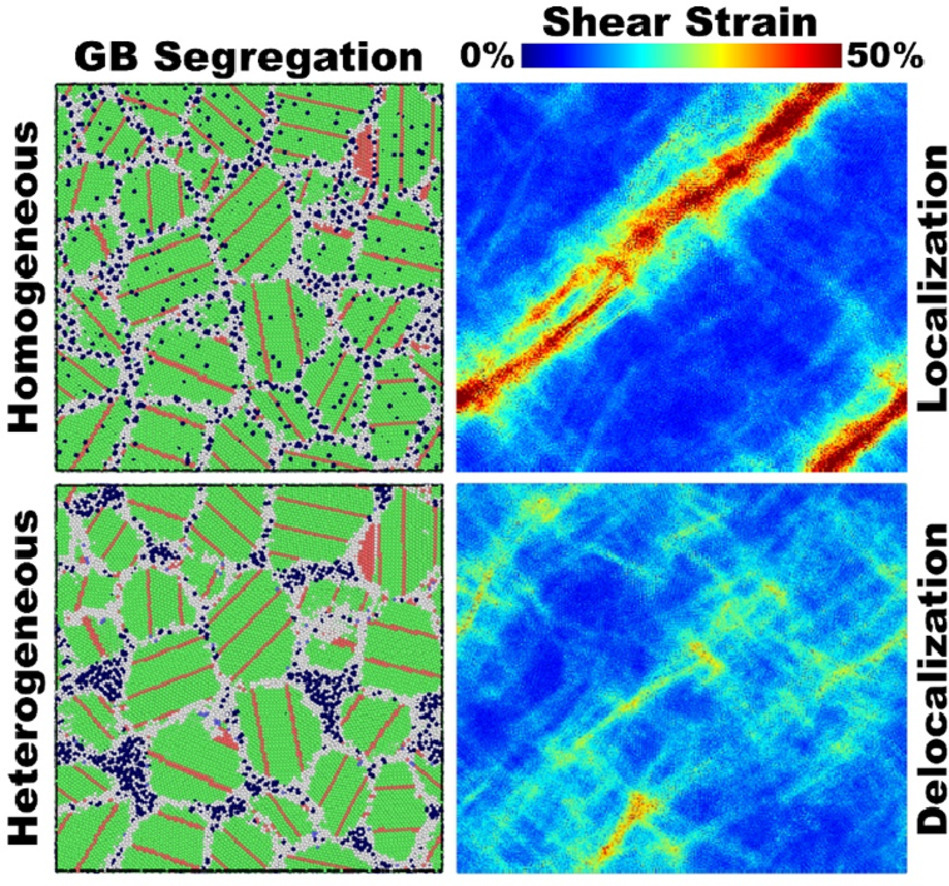
7. Heterogeneous solute segregation suppresses strain localization in nanocrystalline Ag-Ni alloys
非均勻溶質偏析抑制納米晶Ag-Ni合金的應變局部化
Zhiliang Pan,Frederic Sansoz?
Frederic Sansoz:frederic.sansoz@uvm.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.08.074
摘要
溶質向單個晶界的偏析被用來設計生產堅固而穩定的納米金屬合金。然而,眾所周知,晶界偏析會因應變局部化失效機制而導致不利的脆化效應,該機制對結構應用時造成了重大的材料限制。通過原子模擬發現,納米晶Ni-Ag合金中的非均勻Ni偏析在塑性變形過程中顯著地切斷了局部剪切帶,同時提高了合金的拉伸強度。由于晶界誘導的玻璃狀局部剪切帶,納米晶Cu-Ag金屬中溶質濃度比例在8%時達到飽和,呈現出標準的均相銅偏析和拉伸強度。相比之下,納米晶Ag-Ni合金中Ni的非均相偏析沿界面形成富溶質團簇,導致高應變下的應變離域以及溶質濃度增加至15at.%的持續強化。這項研究揭示了非均相和均相偏析行為對應變局部化的重要性,并指出了通過晶界偏析工程設計抗失效納米結構材料的一種全新策略。
英文摘要
Solute segregation to individual grain boundaries is used by design to produce strong and stable nanocrystalline metallic alloys. Grain-boundary segregation, however, is known to cause adverse embrittlement effects from a strain-localization failure mechanism that imposes significant material limitations for structural applications. Here, using atomistic simulations, it is discovered that heterogeneous Ni segregation in nanocrystalline Ni-mixed Ag alloys dramatically shuts down localized shear bands during plastic deformation, while simultaneously increasing the tensile strength. Nanocrystalline Cu-mixed Ag metals are predicted to exhibit standard homogeneous Cu segregation and a tensile strength that saturates above a solute concentration of 8 at.% due to glass-like shear localization induced by grain boundaries. By contrast, it is found that heterogeneous Ni segregation in nanocrystalline Ag-Ni alloys forms solute-rich clusters along interfaces leading to strain delocalization at high strain and continuous strengthening at high solute concentrations up to 15 at.%. This study reveals the importance of heterogeneous versus homogeneous segregation behaviors on strain localization and points to a fundamentally new strategy to design failure-resistant nanostructured materials through grain boundary segregation engineering.
ACTA Vol. 200, Nov. 2020, P101-115
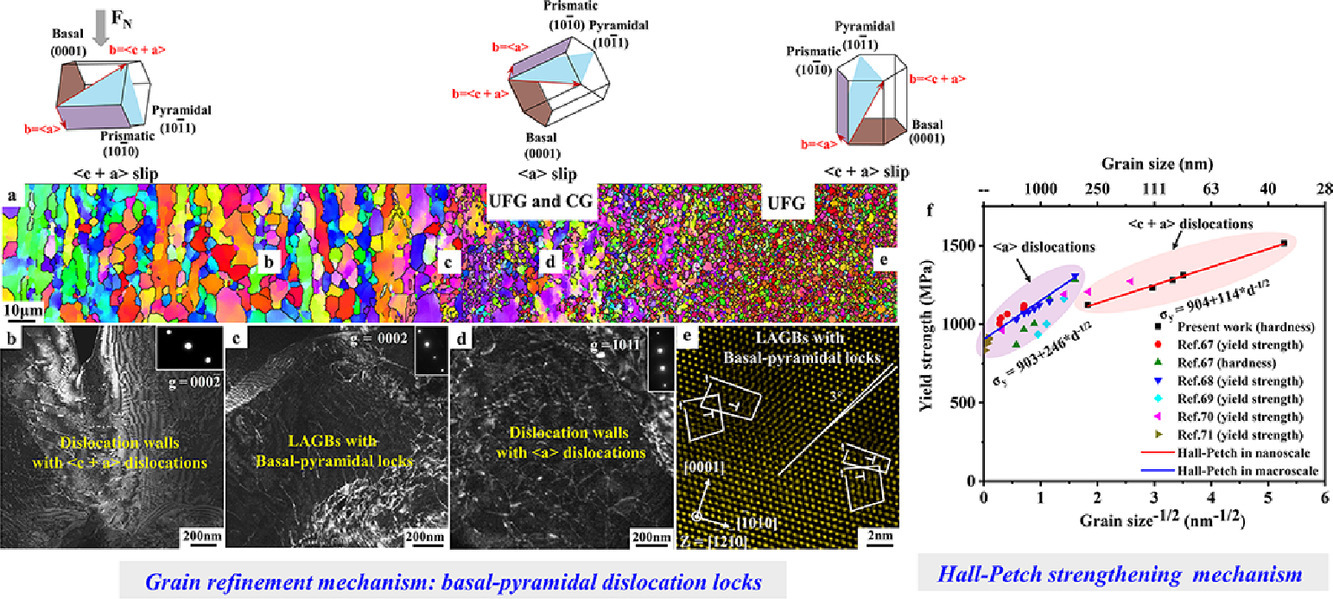
8. The role of pyramidal 〈c + a〉 dislocations in the grain refinement mechanism in Ti-6Al-4V alloy processed by severe plastic deformation
金字塔形〈c+a〉位錯對Ti-6Al-4V合金強塑性變形晶粒細化機制的作用
Chenglin Wang,Dapeng Yu,Zhiqiang Niu,Wenlong Zhou,Guoqing Chen,Zhiqiang Li,Xuesong Fu?
Xuesong Fu:xsfu@dlut.edu.cn,大連理工大學
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.08.076
摘要
本文研究了具有{1120}<1010>初始軋制織構的Ti-6Al-4V合金中金字塔形〈c+a〉位錯對晶粒細化機制的作用。經過劇烈噴丸處理的試樣中,大量的金字塔形〈c+a〉位錯被激活。本文發現了金字塔形〈c+a〉位錯的兩個重要作用。首先,金字塔形〈c+a〉滑移與c軸大的應變協調變化,從而實現了廣義塑性流動,特別是在納米晶中。第二,通過金字塔形〈c+a〉與基底〈a〉位錯相互作用,首次產生了具有金字塔-基底位錯鎖(棱柱狀位錯〈c〉和棱柱狀〈c+a〉位錯)獨特的低角度晶界(LAGBs)。這種獨特的低能晶界極大地提高了應變誘導晶界的穩定性以及位錯密度(納米晶粒中約6.6×1015 m−2)。晶粒細化處理包括三種細分模式:1)粗晶中具有金字塔形〈c+a〉位錯的位錯墻;2)粗晶中與棱柱狀〈a〉位錯相交的基底〈a〉位錯;3)粗晶、超細晶以及納米晶中與金字塔形〈c+a〉位錯相交的基底〈a〉位錯。滑移模式的產生取決于動態再結晶過程中的初始織構和織構演化。此外,本文還發現了納米尺度的Hall-Petch擊穿,其原因是納米尺度金字塔形〈c+a〉滑移的臨界切應力降低所致。本研究通過獨特的金字塔形-基底位錯鎖LAGBs設計穩定的納米六方密排堆積金屬提供了一種新的途徑。
英文摘要
This study focuses on the role of pyramidal 〈c + a〉 dislocations in the grain refinement mechanism in the Ti-6Al-4V alloy with an initial rolling texture. A large number of pyramidal 〈c + a〉 dislocations were activated in the sample subjected to the severe shot peening process. Two important roles of pyramidal 〈c + a〉 dislocations were discovered. First, pyramidal 〈c + a〉 slip coordinates the large c-axis strain, thereby achieving generalized plastic flow, especially in nanograins. Second, the unique low-angle grain boundaries (LAGBs) with basal-pyramidal dislocation locks (prismatic 〈c〉 and prismatic 〈c + a〉 dislocations) were produced for the first time by pyramidal 〈c + a〉 interacting with basal 〈a〉 dislocations. This unique low-energy boundary greatly enhances the stability of the strain-induced grain boundary and dislocation density (~6.6 × 1015 m − 2 in nanograins). The grain refinement process contains three types of subdivision modes: (I) dislocation walls with pyramidal 〈c + a〉 dislocations in coarse grains; (II) basal 〈a〉 intersecting with prismatic 〈a〉 dislocations in coarse grains; and (III) basal 〈a〉 intersecting with pyramidal 〈c + a〉 dislocations in coarse grains, ultrafine-grains and nanograins. The occurrence of slip modes depends on the initial texture and texture evolution during dynamic recrystallization. Besides, Hall-Petch breakdown at the nanoscale was found and is attributed to the decreasing critical resolved shear stress of pyramidal 〈c + a〉 slip at the nanoscale. This study provides a new approach for the design of stable nanostructured hexagonal close-packed metals by the unique LAGBs with basal-pyramidal dislocation locks.
ACTA Vol. 200, Nov. 2020, P116-126
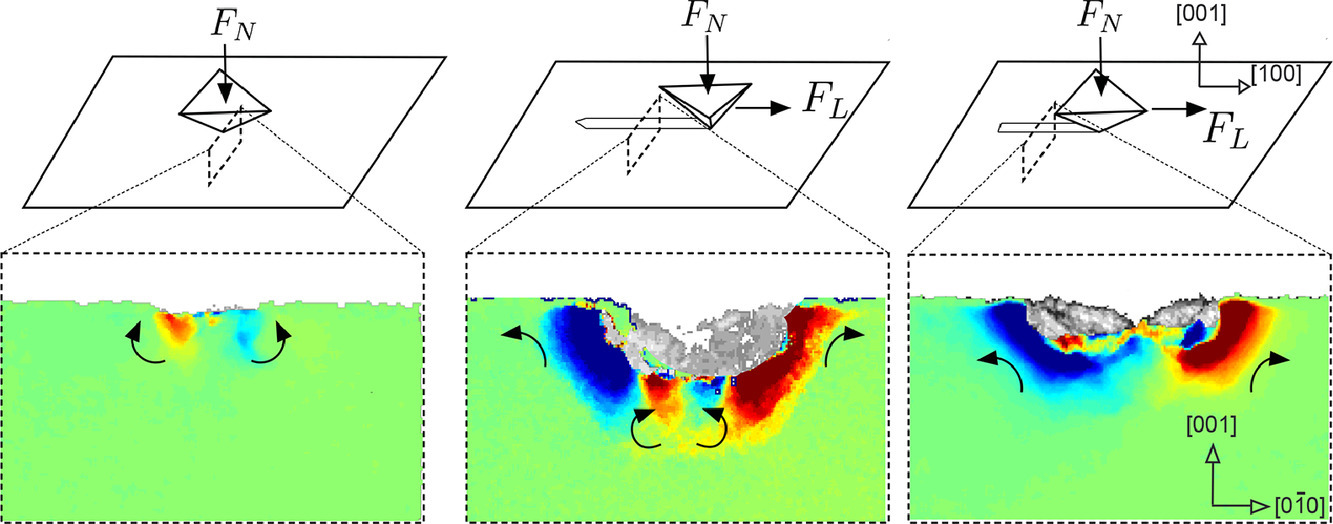
9. Scratching the surface: Elastic rotations beneath nanoscratch and nanoindentation tests
表面劃痕:納米裂紋和納米壓痕試驗下的彈性旋轉
Anna Kareer?,Edmund Tarleton,Christopher Hardie,Sarah V. Hainsworth,Angus J. Wilkinson
Anna Kareer:anna.kareer@materials.ox.ac.uk
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.08.051
摘要
在本文中,我們使用(001)Cu單晶上的玻氏壓針的兩個取向來研究納米劃痕試驗附近的殘余變形場。為了理解切向滑動中的變形機制,我們將變形與壓痕變形進行了比較。利用高分辨電子背散射衍射(HR-EBSD)對聚焦離子束(FIB)制備的截面上實驗性地映射晶格旋轉場。基于物理的晶體塑性有限元模型(CPFEM)模擬晶格旋轉場,并對從初始靜態壓痕過渡到穩態劃痕時納米劃痕實驗的3D旋轉場進行了深入了解。CPFEM模擬以很好的保真度捕捉了實驗旋轉場,并展示了當壓頭遠離初始壓痕時,劃痕方向的旋轉是如何反轉的。
英文摘要
In this paper, we investigate the residual deformation field in the vicinity of nanoscratch tests using two orientations of a Berkovich tip on an (001) Cu single crystal. We compare the deformation with that from indentation, in an attempt to understand the mechanisms of deformation in tangential sliding. The lattice rotation fields are mapped experimentally using high-resolution electron backscatter diffraction (HR-EBSD) on cross-sections prepared using focused ion beam (FIB). A physically-based crystal plasticity finite element model (CPFEM) is used to simulate the lattice rotation fields, and provide insight into the 3D rotation field surrounding a nano-scratch experiment, as it transitions from an initial static indentation to a steady-state scratch. The CPFEM simulations capture the experimental rotation fields with good fidelity, and show how the rotations about the scratch direction are reversed as the indenter moves away from the initial indentation.
ACTA Vol. 200, Nov. 2020, P136-147
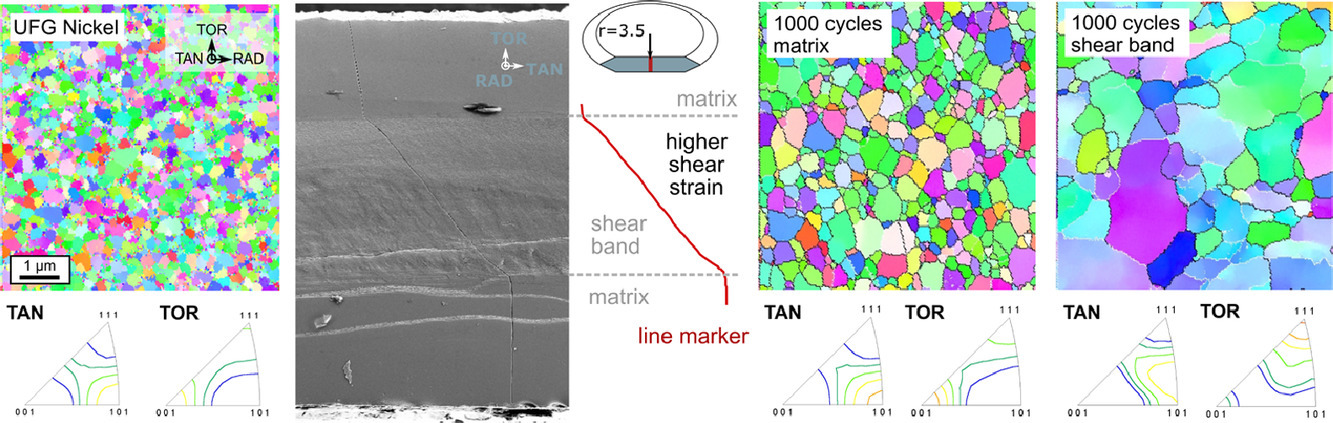
10. Plastic strain triggers structural instabilities upon cyclic loading in ultrafine-grained nickel
循環加載下塑性應變引發超細晶鎳的結構不穩定性
M.W. Kapp,O. Renk,P. Ghosh,T. Leitner,B. Yang,R. Pippan
O. Renk:oliver.renk@oeaw.ac.at
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.08.049
摘要
伴隨剪切帶形成的晶粒長大縮短了在循環載荷下納米結構金屬的壽命。盡管結構不穩定性經常被報道,但使用標準測試程序檢測和跟蹤其起始和演變的困難阻礙了對潛在機制的深入理解。使用不同合成路線的樣品,在不同的條件下測試,進一步使問題復雜化。在這里,循環高壓扭轉是模擬低周疲勞的另一種方法,它能夠研究可重復達到巨大累積應變下結構不穩定性的起始和演變,這在常規疲勞試驗中是無法獲得的。它使人們對用不同參數(如應變大小或溫度)測試的納米結構鎳中引起結構不穩定性的過程有了全面的了解。晶粒粗化從最初的循環開始,并在剪切帶中引發應變局部化。循環應變的累積導致剪切帶厚度的逐漸增長,并伴隨著這些剪切帶內晶粒的進一步增長。很明顯,循環應變強化了晶粒粗化,這表明非外加應力使得晶界運動。這進一步表明了優先織構組分能夠促進循環滑移。雖然施加的循環應變會推動晶粒長大,但它會在晶粒達到一定尺寸下出現停滯。在77K下的實驗展示了同樣的不穩定性,證明鎳的晶界遷移主要由機械驅動。
英文摘要
Grain growth accompanied by shear band formation shortens lifetime of nanostructured metals upon cyclic loading. Although the occurrence of structural instabilities was reported frequently, the difficulty to detect and track their initiation and evolution using standard testing routines prevents an in-depth understanding of the underlying mechanisms. Usage of samples from different synthesis routes tested under varying conditions further complicates this issue. Here, cyclic high pressure torsion is presented as an alternative method to mimic low cycle fatigue. It allows to study initiation and evolution of structural instabilities reproducibly up to enormous accumulated strains, not accessible in conventional fatigue tests. It enabled a general understanding of the processes causing structural instabilities in nanostructured nickel tested with different parameters such as strain amplitude or temperature. Grain coarsening starts from the very first cycles and initiates strain localization in shear bands. Accumulation of cyclic strain induces progressive growth of the shear band thickness accompanied by further grain growth within these bands. Clearly, cyclic strain amplifies grain coarsening suggesting that not the applied stress alone forces boundary motion. This is emphasized further as preferential texture components which facilitate cyclic slip evolve. Although the imposed cyclic strain drives grain growth it stagnates at certain grain sizes. Experiments at 77 K revealed identical instabilities, proving that for nickel boundary migration occurred predominantly mechanically driven.
ACTA Vol. 200, Nov. 2020, P148-161
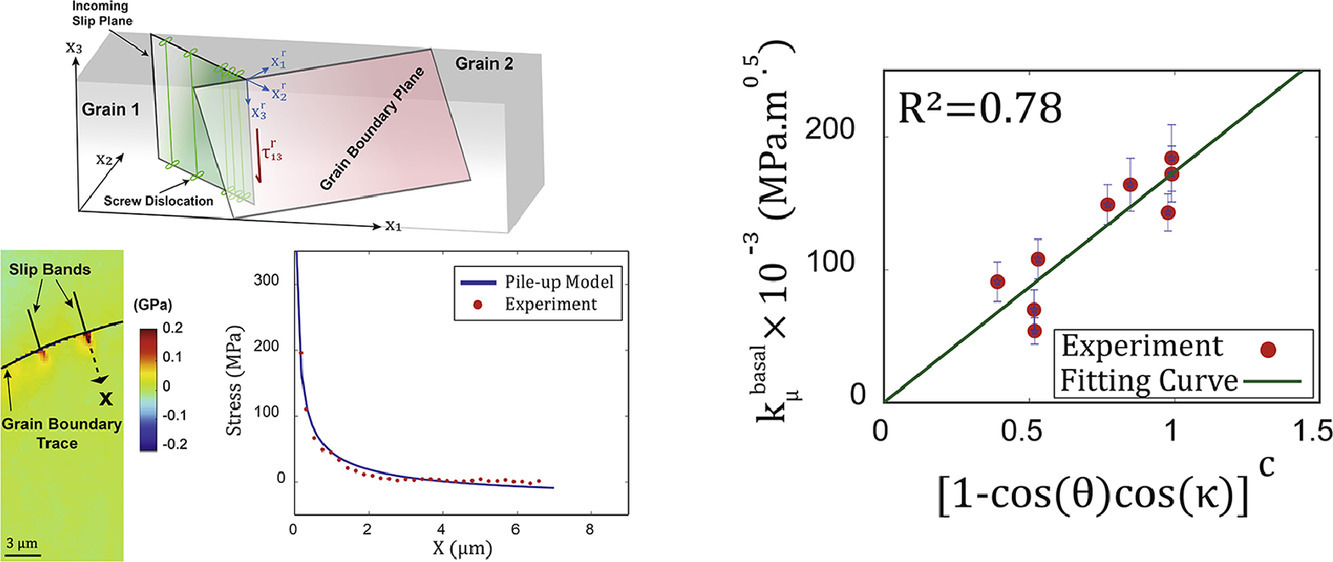
11. Quantitative study of the effect of grain boundary parameters on the slip system level Hall-Petch slope for basal slip system in Mg-4Al
晶界參數對Mg-4Al基底滑移系Hall-Petch斜率影響的定量研究
Mohsen Taheri Andani?, Aaditya Lakshmanan?, Veera Sundararaghavan?, John Allison?, Amit Misra?
Mohsen Taheri Andani:mtaheri@umich.edu
Aaditya Lakshmanan:aadityal@umich.edu
Veera Sundararaghavan:veeras@umich.edu
John Allison:johnea@umich.edu
Amit Misra:amitmis@umich.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.08.079
摘要
一些理論研究表明,多晶材料中晶界的幾何形狀和結構會對Hall-Petch斜率產生顯著影響。然而,實驗觀察主要受限于技術精確量化晶界強度和驗證這些理論模型的能力。利用高分辨電子背散射衍射(HR-EBSD),對被晶界阻擋的滑移帶前的局部應力張量進行量化,并與連續位錯堆積模型耦合,以評估特定晶界對特定滑移系統的阻擋強度,即微Hall-Petch系數。對于Mg-4Al變形合金中的基礎滑移系,九種不同晶界的微Hall-Petch系數(kμ基底)變化顯著,從0.054到0.184MPa−m1/2。這些結果與各自晶界的幾何描述相關聯,并通過聚焦離子束銑削測量了三維晶界形貌。結果表明,晶界面上兩條滑移面跡線之間的夾角是影響kμ基底的最敏感參數,然后是滑動方向之間的角度。本文提出了一種基于這兩個角度計算kμ基底的函數形式,以增強晶體塑性本構模型,其抗滑移性依賴于晶粒尺寸的某些度量。該方法為校正晶體塑性模型中的晶粒尺寸強化參數提供了一條新的途徑,可以對織構、晶粒形態和Hall-Petch效應之間的相互關系進行進一步的計算研究。
英文摘要
Several theoretical studies have reported that the geometry and structure of grain boundaries in polycrystalline materials could impose a significant effect on the Hall-Petch slope. However, experimental observations are primarily limited by the ability of the techniques to accurately quantify the grain boundary strength and validate these theoretical models. Using high-resolution electron backscatter diffraction (HR-EBSD), the local stress tensor ahead of a slip band blocked by a grain boundary was quantified and coupled with a continuum dislocation pile-up model to assess the barrier strength of specific grain boundaries to specific slip systems, referred to as micro-Hall-Petch coefficient. For basal slip system in a deformed Mg-4Al alloy, the micro-Hall-Petch coefficient varied significantly, from 0.054 to 0.184 for nine different grain boundaries. These results were correlated with geometric descriptors of the respective grain boundaries, with three-dimensional GB profile additionally measured via focused ion beam milling. It was found that the angle between the two slip plane traces on the grain boundary plane was the most sensitive parameter affecting , followed by the angle between the slip directions. A functional form for calculation of depending on these two angles is proposed to augment crystal plasticity constitutive models with slip resistance dependent on some measure of the grain size. The method allows a new pathway to calibrate grain size strengthening parameters in crystal plasticity models, allowing further computational investigations of the interrelationship between texture, grain morphology, and the Hall Petch effect.
ACTA Vol. 200, Nov. 2020, P162-170
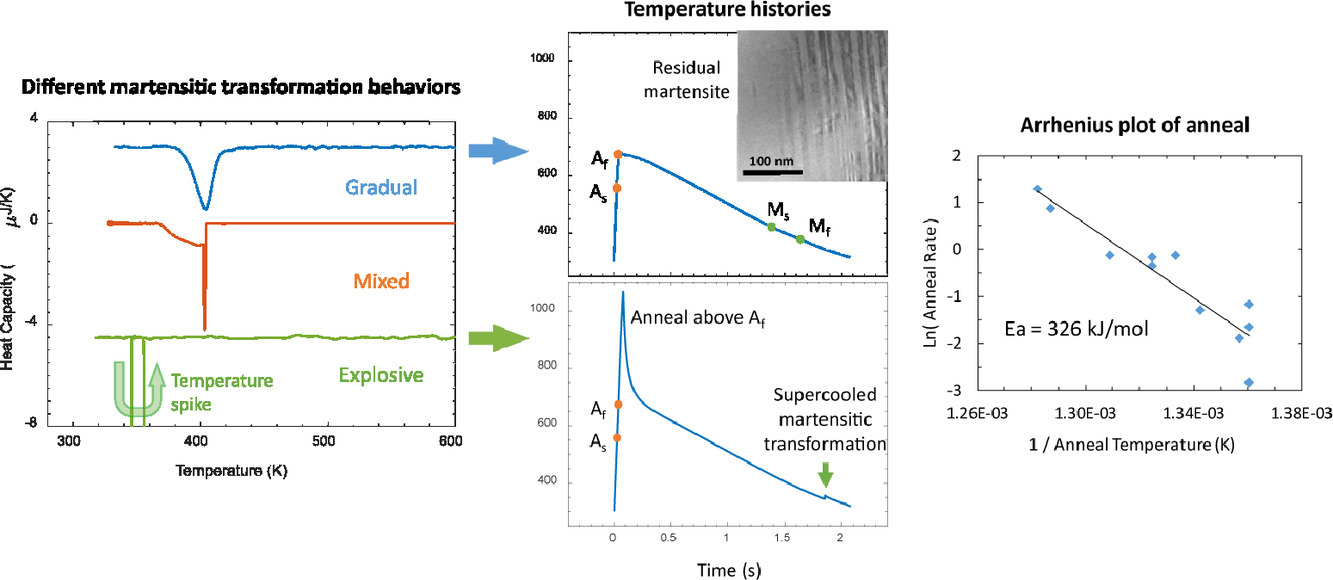
12. Explosive martensitic transformation of supercooled austenite in CuZr-based thin-film shape memory alloys
CuZr基薄膜形狀記憶合金過冷奧氏體的極速馬氏體相變
Yucong Miao,Joost J. Vlassak?
Joost J. Vlassak:vlassak@seas.harvard.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.08.081
摘要
CuZr基合金被認為是一種應用于高溫領域的潛在形狀記憶合金。利用多晶薄膜樣品研究了幾種合金元素對合金形狀記憶性能的影響。本文報道了過冷CuZr、CuZrNi和CuZrCo樣品中馬氏體的極速形成。這種極速轉變行為的特點是:1)高溫奧氏體相在馬氏體臨界轉變溫度Mf以下可以過冷。在低于Mf的臨界溫度下,整個樣品中的奧氏體在不到一微秒的時間內轉變為馬氏體。2) 臨界溫度分布較窄,隨著冷卻速率的增加,臨界溫度略有下降。3) 過冷和極速轉變行為的觀察取決于奧氏體臨界轉變溫度Af以上的溫度歷史記錄。如果樣品在加熱到Af以上后立即淬火,冷卻到Ms以下會逐漸形成馬氏體;如果樣品在Af以上停留幾秒,則馬氏體會極速地形成。我們認為,逐漸轉變是通過馬氏體在連續轉變周期中積累的缺陷上生長的。然而,如果允許樣品在高于Af的溫度下停留,則這些缺陷會湮滅,相變形核會受到限制。馬氏體的形核需要顯著的過冷度。缺陷湮滅過程對溫度高度敏感,表面活化能為326kj/mol,對于簡單的擴散限制過程來說,這一數值太大了。CuZrCo樣品的透射電鏡觀察表明,缺陷可能與殘余馬氏體的存在有關。
英文摘要
CuZr-based alloys are being considered as potential shape memory alloys for use in high-temperature applications. We have conducted a study on the effects of several alloying elements on the shape memory properties of these alloys using polycrystalline thin-film samples. Here we report on the explosive formation of martensite in supercooled CuZr, CuZrNi and CuZrCo samples. This explosive transformation behavior is characterized by the following observations: 1) The high-temperature austenitic phase can be supercooled below the martensite finish temperature Mf. At a critical temperature below Mf, austenite transforms to martensite across the entire sample in less than a microsecond. 2) The critical temperature has a narrow distribution and decreases slightly with higher cooling rate. 3) Observation of supercooling and explosive transformation behavior depends on the temperature history above the austenite finish temperature Af. If a sample is quenched immediately after heating above Af, martensite forms gradually on cooling below Ms; if a sample is allowed to dwell a few seconds above Af, the martensite forms explosively. We suggest that the gradual transformation proceeds by martensite growth on defects that accumulate during successive transformation cycles. If the sample is allowed to dwell at a temperature above Af, however, these defects are annihilated and the transformation is nucleation-limited. Nucleation of martensite then requires significant supercooling. The defect annihilation process is highly sensitive to temperature and has an apparent activation energy of 326 kJ/mol, which is too large for a simple diffusion-limited process. Transmission electron microscopy of CuZrCo samples suggests that the defects may be related to the presence of residual martensite.
ACTA Vol. 200, Nov. 2020, P171-186
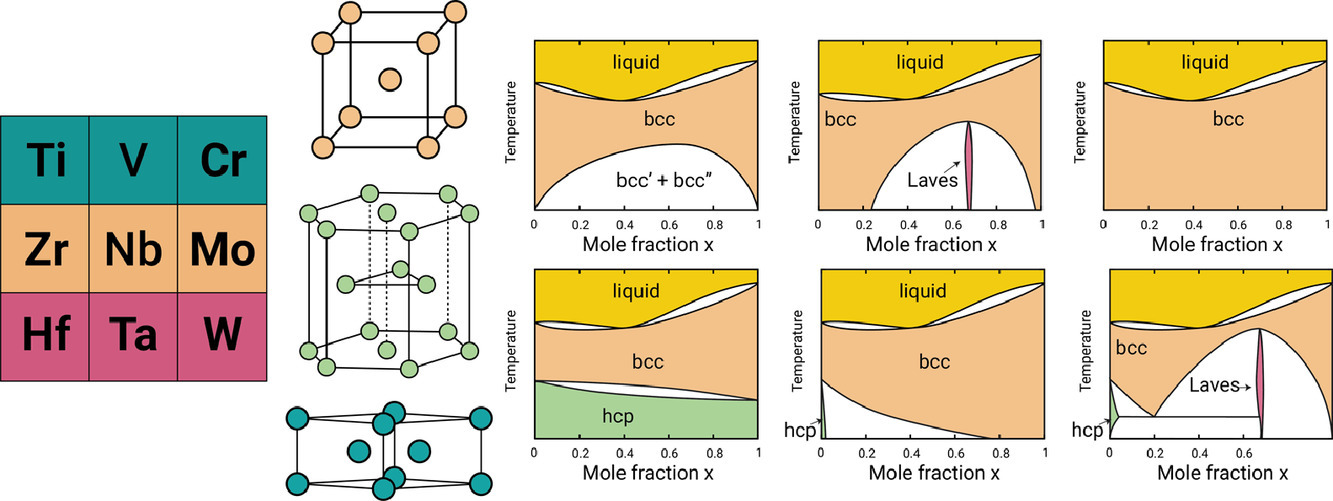
13. Crystallography, thermodynamics and phase transitions in refractory binary alloys
難熔二元合金的晶體學、熱力學和相變
Anirudh Raju Natarajan?, Pavel Dolin, Anton Van der Ven?
Anirudh Raju Natarajan:anirudh@ucsb.edu
Anton Van der Ven:avdv@ucsb.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.08.034
摘要
我們研究了元素周期表第4族(Ti,Zr,Hf)、第五族(V,Nb,Ta)和第6族(Cr,Mo,W)元素組成的所有二元合金的相穩定性。第一性原理計算了bcc與hcp、bcc與ω的晶體學路徑上的能量分布,結果表明,第4族元素與第5、第6族元素非常不同。第5、6族元素在bcc中是穩定的,而第4族元素有利于hcp和ω,并被預測在bcc中是動態不穩定的。利用統計力學技術對36種難熔二元體系進行了第一性原理的全面研究,揭示了六種不同的合金類別,每一種合金都具有獨特的相圖拓撲結構。這項研究的預測與之前的實驗結果非常吻合。一個例外是一類具有高溫混溶間隙的難熔合金,這類合金無法用本工作中使用的方法進行預測。我們的計算預測了Nb-V二元系中低溫Laves相的穩定性,這一點尚待實驗觀察。本研究揭示了合金化學與高溫相穩定性的關系,為多元無序耐火合金的系統設計提供了依據。
英文摘要
We investigate phase stability in all binary alloys comprised of elements from groups 4 (Ti, Zr, Hf), 5 (V, Nb, Ta) and 6 (Cr, Mo, W) of the periodic table. First-principles calculations of the energy landscapes along crystallographic pathways that connect bcc to hcp and bcc to ω show that group 4 elements are very distinct from group 5 and 6 elements. While group 5 and 6 elements are stable in bcc, group 4 elements favor hcp and ω and are predicted to be dynamically unstable in bcc. A comprehensive first-principles investigation of the 36 refractory binary systems using statistical mechanics techniques reveals six distinct classes of alloys, each with a unique phase diagram topology. The predictions of this study are in excellent agreement with previous experimental work. One exception is a class of refractory alloys with high temperature miscibility gaps that are not predicted with the methods used in this work. Our calculations predict the stability of a low-temperature Laves phase in the Nb-V binary that has yet to be observed experimentally. The relationships between alloy chemistry and high-temperature phase stability revealed in this study provide a basis for the systematic design of multicomponent disordered refractory alloys.
ACTA Vol. 200, Nov. 2020, P200-210
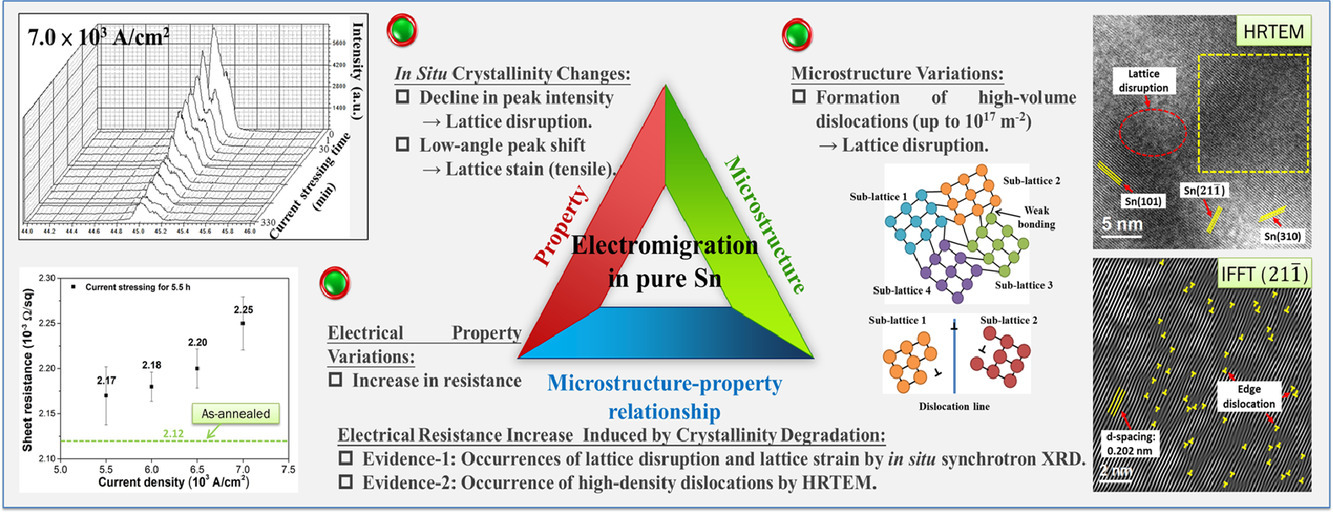
14. A comprehensive study of electromigration in pure Sn: Effects on crystallinity, microstructure, and electrical property
純錫中電遷移的綜合研究:結晶度、微觀結構和電性能的影響
Yi-Han Liao?, Chang-Hsien Chen?, Chien-Lung Liang?, Kwang-Lung Lin?, Albert T. Wu?
Yi-Han Liao:n56014372@mail.ncku.edu.tw,臺灣成功大學
Chang-Hsien Chen:n56054368@mail.ncku.edu.tw,臺灣成功大學
Chien-Lung Liang:clliang@gs.ncku.edu.tw,臺灣成功大學
Kwang-Lung Lin:matkllin@mail.ncku.edu.tw,臺灣成功大學
Albert T. Wu:atwu@ncu.edu.tw,臺灣中央大學
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.09.010
摘要
文獻中有大量關于純錫中電遷移誘導現象的有趣發現。大多數研究揭示了材料在電遷移作用下的熱力學穩定狀態。本文對純錫在5.5~7.5×103a/cm2下5.5h的電遷移進行了綜合研究,揭示了其對結晶度、顯微結構和電性能的影響。本文從結晶度變化的角度對電遷移過程中電性能的變化給出了不同的解釋,并用同步輻射X射線衍射(XRD)和高分辨透射電子顯微鏡(HRTEM)進行了研究。原位XRD分析表明,純Sn條中衍射峰的綜合強度下降(降低率達90%)和晶格應變的累積(超過屈服點0.68%),揭示了電遷移下的結晶度退化現象。原子尺度晶格外觀顯示了塑性變形下電遷移產生位錯的直接證據。位錯的引入形成了不同晶向的亞晶格,導致了整體強度的下降。電遷移實驗后電阻的增加對應于觀察到的晶格破壞與晶格應變累積現象的結果。熱基準實驗表明,非熱電遷移效應而非熱效應對結晶度和電遷移電阻響應的影響顯著。
英文摘要
The literature has accumulated plenty of interesting findings of electromigration-induced phenomena in pure Sn. Most of the researches revealed the thermodynamically steady states of materials under electromigration. We presented a comprehensive study of electromigration in pure Sn at 5.5–7.5 × 103 A/cm2 for 5.5 h revealing the effects on crystallinity, microstructure, and electrical property. The present work provided a divergent explanation about the electrical property variation under electromigration by introducing the crystallinity change aspect, as evidenced by the in situ synchrotron X-ray diffraction (XRD) and high-resolution transmission electron microscope (HRTEM) investigations. The in situ XRD analysis showed an integrated intensity decline of diffraction peaks (up to a 90% reduction rate) and the buildup of lattice strain (up to 0.68% beyond the yield point) within the pure Sn strip, revealing a crystallinity degradation phenomenon under electromigration. The atomic-scale lattice appearance showed direct evidence of dislocation production under electromigration as a result of the plastic deformation. The introduction of dislocations formed sub-lattices with various crystal orientations that were responsible for the integrated intensity decline. The increase in electrical resistance after the electromigration experiment corresponded to the consequences of the observed lattice disruption and lattice strain accumulation phenomena. The thermal benchmark experiments evidenced the predominant athermal electromigration effect, rather than the thermal one, on the crystallinity and electrical resistance responses to electromigration.
ACTA Vol. 200, Nov. 2020, P211-222
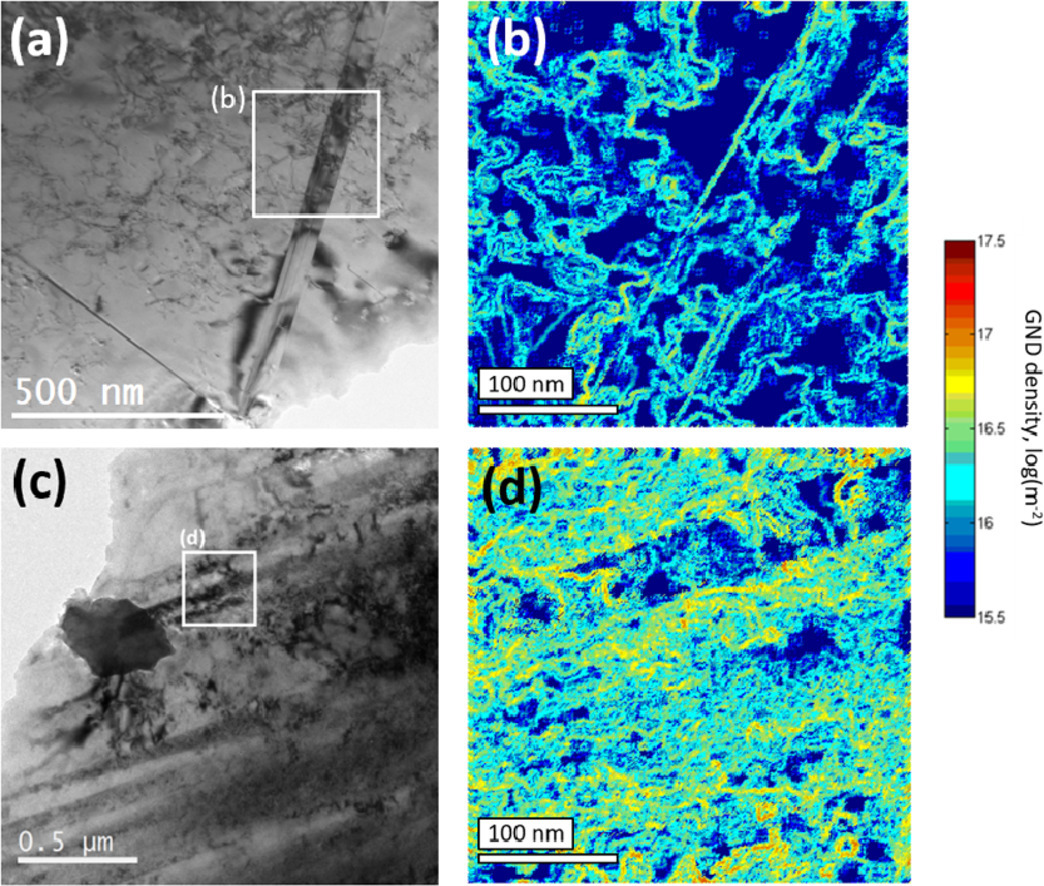
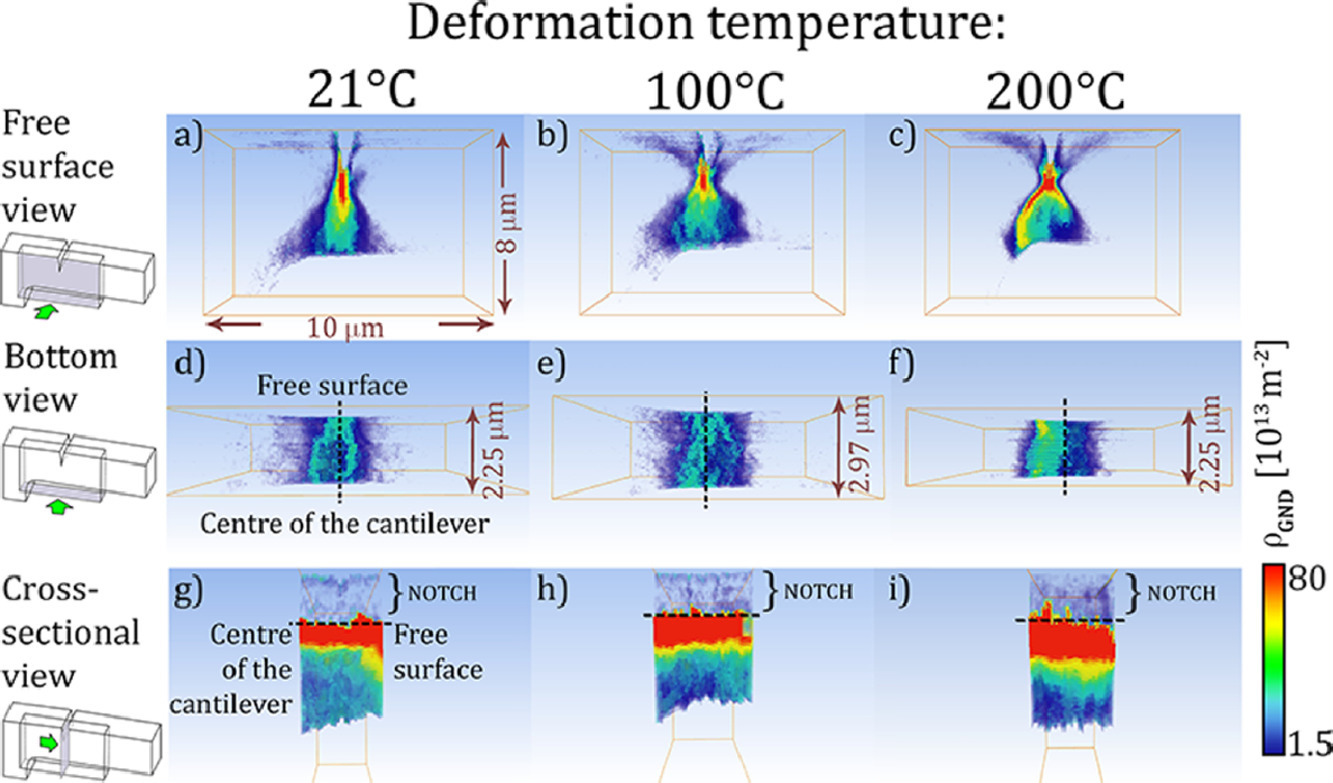
15. 3D HR-EBSD Characterization of the plastic zone around crack tips in tungsten single crystals at the micron scale
微米尺度單晶鎢裂紋尖端塑性區的三維HR-EBSD表征
Szilvia Kalácska?, Johannes Ast, Péter Dusán Ispánovity, Johann Michler, Xavier Maeder
Szilvia Kalácska:szilvia.kalacska@empa.ch
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.09.009
摘要
采用高角分辨率電子背散射衍射(HR-EBSD)和聚焦離子束(FIB)切片相結合的方法,對W單晶三維塑性區的幾何必要位錯(GND)進行了表征。用FIB制備了具有切口的相似尺寸懸臂,在掃描電子顯微鏡下以略高于微尺度脆韌轉變(BDT)溫度(21℃、100℃和200℃)變形。采用J積分試驗分析裂紋擴展,并確定斷裂韌度。在所有三種溫度下,發現靠近自由表面的塑性區比試樣內部的大,類似于宏觀拉伸試驗。然而,在較高的溫度下,塑性區的三維形狀從局限于裂紋尖端前方變為蝴蝶狀分布,更有效地屏蔽了裂紋尖端,抑制了裂紋擴展。將兩個相同變形的樣品從兩個不同的方向進行切片比較,以評估HR-EBSD進行的GND密度估計的可靠性。通過對Nye張量分量分布的分析,來區分樣品中GNDs成核的類型。討論了不同類型的位錯在塑性區中的作用,證實了早期的研究結果,即W的微觀BDT主要受裂紋尖端前螺旋位錯的形核控制。
英文摘要
High angular resolution electron backscatter diffraction (HR-EBSD) was coupled with focused ion beam (FIB) slicing to characterize the shape of the plastic zone in terms of geometrically necessary dislocations (GNDs) in W single crystal in 3 dimensions. Cantilevers of similar size with a notch were fabricated by FIB and were deformed inside a scanning electron microscope at different temperatures (21 °C, 100 °C and 200 °C) just above the micro-scale brittle-to-ductile transition (BDT). J-integral testing was performed to analyse crack growth and determine the fracture toughness. At all three temperatures the plastic zone was found to be larger close to the free surface than inside the specimen, similar to macro-scale tension tests. However, at higher temperature, the 3D shape of the plastic zone changes from being localized in front of the crack tip to a butterfly-like distribution, shielding more efficiently the crack tip and inhibiting crack propagation. A comparison was made between two identically deformed samples, which were FIB-sliced from two different directions, to evaluate the reliability of the GND density estimation by HR-EBSD. The analysis of the distribution of the Nye tensor components was used to differentiate between the types of GNDs nucleated in the sample. The role of different types of dislocations in the plastic zone is discussed and we confirm earlier findings that the micro-scale BDT of W is mainly controlled by the nucleation of screw dislocations in front of the crack tip.
ACTA Vol. 200, Nov. 2020, P223-235
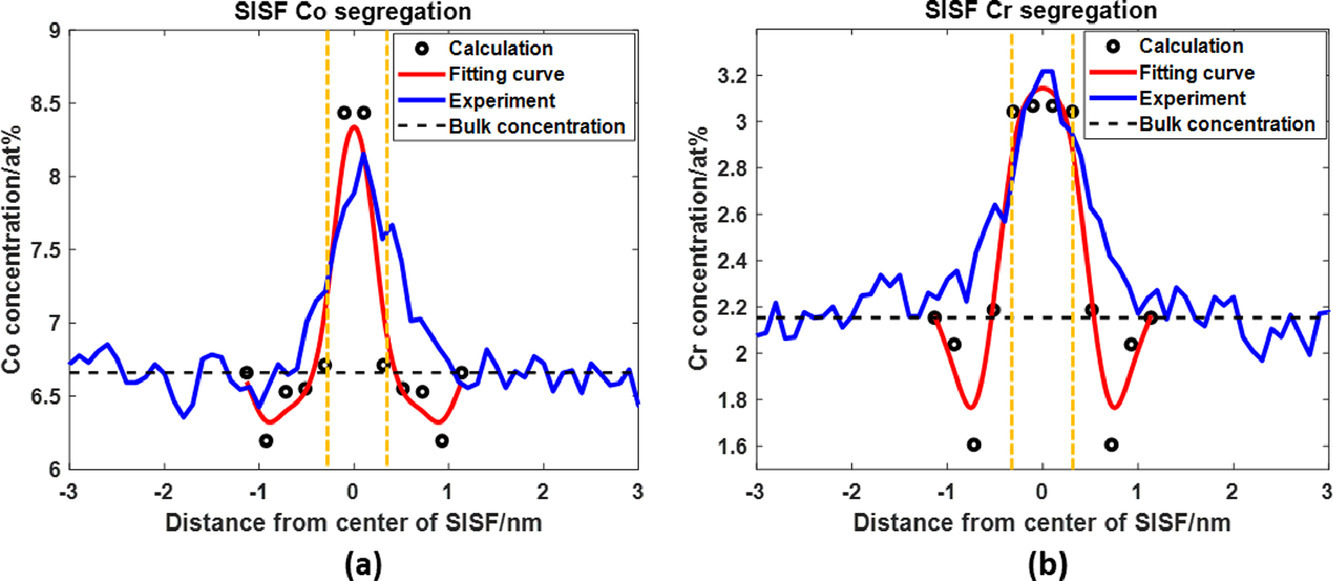
16. Quantitative prediction of Suzuki segregation at stacking faults of the γ’ phase in Ni-base superalloys
鎳基高溫合金γ′相層錯處Suzuki偏析的定量預測
Longsheng Feng, You Rao, Maryam Ghazisaeidi, Michael J. Mills, Yunzhi Wang?
Yunzhi Wang:wang.363@osu.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.08.056
摘要
最近的實驗表明,Suzuki偏析在鎳基高溫合金的中溫變形過程中起著重要作用。本文提出了一個結合從頭計算的偏析焓的偏聚等溫線模型,用以定量預測鎳基高溫合金中γ′析出相中超晶格本征層錯(SISF)處溶質的富集。用亞晶格模型描述了γ′相。偏析焓與溶質富集有很強的相關性。盡管偏聚焓相對較小,但預測的溶質富集與實驗觀測結果一致。模擬預測還表明,不同合金元素之間存在很強的交叉相關性。例如,結果表明, Co在Ni亞晶格上的偏析,導致Cr在沒有Co的情況下在層錯處的偏析焓為正值從而產生偏析現象。這種γ′析出物中溶質在堆垛層錯處的平衡偏析及其對層錯能的影響的定量預測,有助于變形機制的研究和高溫合金的設計。
英文摘要
Recent experiments suggest that Suzuki segregation may play an important role during deformation in Ni-base superalloys at intermediate temperatures. In this study, a segregation isotherm model incorporating segregation enthalpy from ab initio calculations is proposed to predict quantitatively solute enrichment at superlattice intrinsic stacking faults (SISF) within the γ’ precipitates in Ni-base superalloys. A sublattice model is employed to describe the γ’ phase. A strong correlation between segregation enthalpy and solute enrichment is found. Even though the segregation enthalpy is relatively small, the predicted solute enrichment is consistent with experimental observations. The simulation predictions also suggest a strong cross-correlation among different alloying elements. For example, it is found that segregation of Co on the Ni sublattice at the fault draws segregation of Cr that has a positive segregation enthalpy at the fault without the presence of Co. Such quantitative predictions of equilibrium segregation of solutes at stacking faults in γ’ precipitates and its effect on the stacking fault energy could aid the investigation of deformation mechanisms and help the design of superalloys.
ACTA Vol. 200, Nov. 2020, P236-245
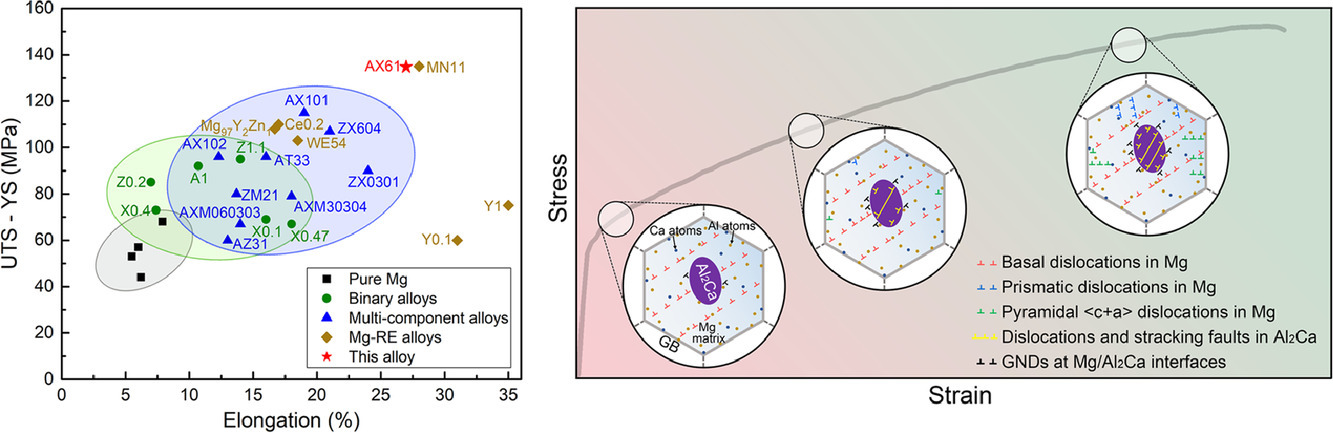
17. Highly deformable Mg–Al–Ca alloy with Al2Ca precipitates
具有Al2Ca析出物的高變形Mg–Al–Ca合金
Gaoming Zhu, Leyun Wang?, Jie Wang, Jian Wang, Jun-Sang Park,Xiaoqin Zeng
Leyun Wang:leyunwang@sjtu.edu.cn,上海交通大學
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.09.006
摘要
鎂是最輕的結構金屬。然而,鎂合金較差的成形性在很大程度上限制了其在結構件制造中的應用。成形性與高拉伸延伸率和大的加工硬化能力密切相關。在這里,我們報道了一種新的Mg−Al−Ca合金,其中大部分可變形的Al2Ca析出,而Mg17Al12和Mg2Ca的Laves相的形成似乎受到抑制。Al2Ca沉淀阻礙位錯運動,導致大的加工硬化。隨后,Al2Ca析出物在增強的流動應力作用下發生變形,出現位錯和堆垛層錯,緩解了局部應力集中,提高了拉伸伸長率。此外,溶質Al和Ca抑制了孿晶形核,促進了Mg中〈c+a〉位錯。這種新的Mg−Al−Ca合金展示了現有鎂合金中拉伸延伸率和加工硬化能力最高的組合之一。
英文摘要
Magnesium (Mg) is the lightest structural metal. However, the poor formability of Mg alloys to great extent limits their applications in making structural parts. Formability is strongly correlated to both high tensile elongation and large work hardening capacity. Here, we report a new Mg−Al−Ca alloy in which a majority of deformable Al2Ca precipitates form while the formation of Laves phases of Mg17Al12 and Mg2Ca seems suppressed. Al2Ca precipitates impede dislocation motion, leading to large work hardening. Then, Al2Ca precipitates deform with dislocations and stacking faults under the enhanced flow stress, which relieve local stress concentration and improve tensile elongation. In addition, solutes Al and Ca suppress twin nucleation while promoting 〈c + a〉 dislocations in Mg. This new Mg−Al−Ca alloy demonstrates one of the highest combinations of tensile elongation and work hardening capacity among existing Mg alloys.
ACTA Vol. 200, Nov. 2020, P246-255
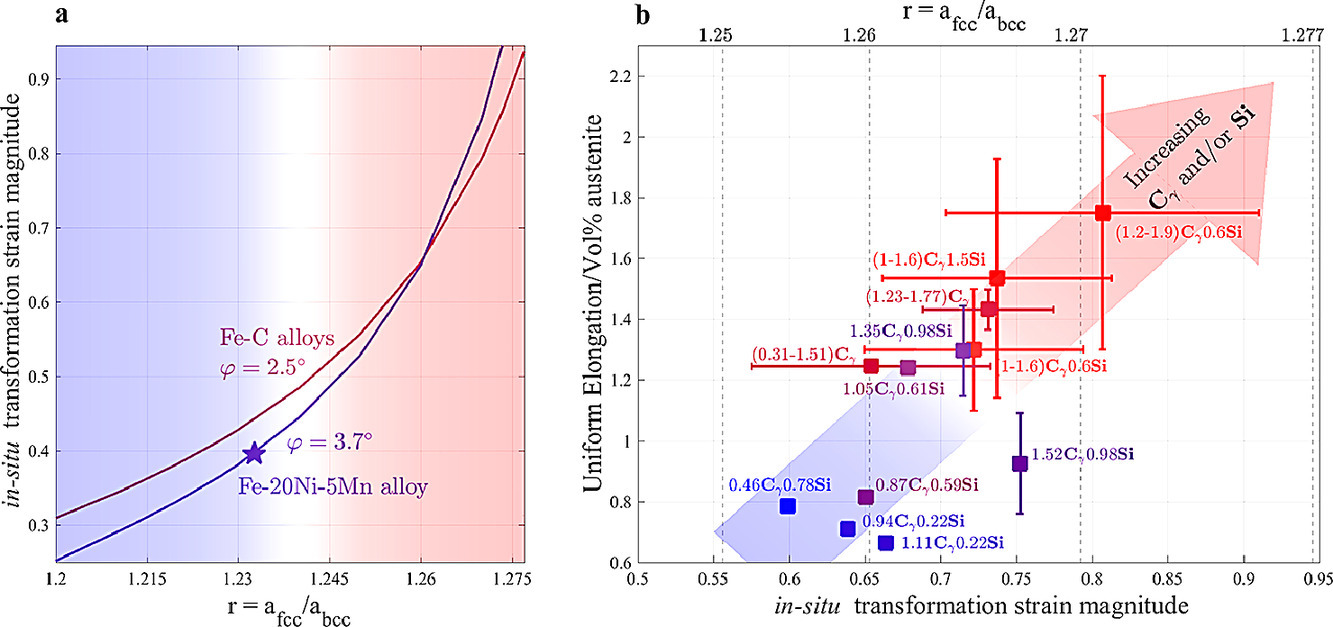
18. Measurement and prediction of the transformation strain that controls ductility and toughness in advanced steels
通過對先進鋼相變應變的測量與預測來控制塑性和韌性
Francesco Maresca?, Efthymios Polatidis, Miroslav Šmíd, Helena Van Swygenhoven, William A. Curtin
Francesco Maresca:f.maresca@rug.nl
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.08.028
摘要
新一代多相馬氏體鋼的高強度來自體心立方(BCC)相,而高韌性來自于亞穩態面心立方(FCC)奧氏體的轉變,后者在加載后轉變為馬氏體。盡管原位相變應變(或“形狀變形”張量)非常重要,但從未在任何形成BCC板條馬氏體的合金中測量到,也從未與底層材料的特性有關。本文利用高分辨率數字圖像相關(HR-DIC)測量了一種典型的Fe-Ni-Mn合金的原位相變應變。實驗結果只能用板條馬氏體晶體學的最新理論來解釋。現場應變預測值與實測值吻合較好,同時驗證了方法和理論的正確性。理論預測,增加FCC與BCC晶格參數的比值會顯著增加原位相變應變的大小。利用現有鋼材的數據證明了這種新的相關性。這些結果為韌性和韌性合金建立了新的附加基本設計原則:通過合金化控制晶格參數比。這為開發更韌性的先進高強鋼提供了新的途徑。
英文摘要
New-generation multi-phase martensitic steels derive their high strength from the body-centered cubic (BCC) phase and high toughness from transformation of the metastable face-centered cubic (FCC) austenite that transforms into martensite upon loading. In spite of its critical importance, the in-situ transformation strain (or “shape deformation” tensor), which controls ductility and toughness, has never been measured in any alloy where the BCC lath martensite forms and has never been connected to underlying material properties. Here, we measure the in-situ transformation strain in a classic Fe-Ni-Mn alloy using high-resolution digital image correlation (HR-DIC). The experimentally obtained results can only be interpreted using a recent theory of lath martensite crystallography. The predicted in-situ transformation strain agrees with the measurements, simultaneously demonstrating the method and validating the theory. Theory then predicts that increasing the FCC to BCC lattice parameter ratio substantially increases the in-situ transformation strain magnitude. This new correlation is demonstrated using data on existing steels. These results thus establish a new additional basic design principle for ductile and tough alloys: control of the lattice parameter ratio by alloying. This provides a new path for development of even tougher advanced high-strength steels.
ACTA Vol. 200, Nov. 2020, P274-286
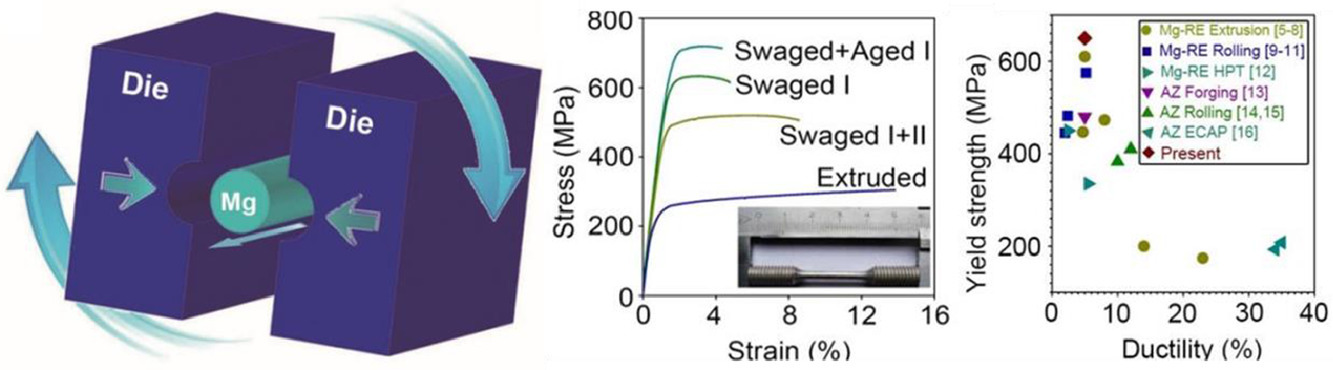
19. Bulk nanocrystalline high-strength magnesium alloys prepared via rotary swaging
旋鍛法制備大塊納米晶高強度鎂合金
Yingchun Wan, Bei Tang, Yonghao Gao, Lingling Tang, Gang Sha,Bo Zhang,Ningning Liang,Chuming Liu?,Shunong Jiang,Zhiyong Chen,Xueyi Guo?,Yonghao Zhao?
Chuming Liu:cmliu@csu.edu.cn
Xueyi Guo:xyguo@csu.edu.cn
Yonghao Zhao:yhzhao@njust.edu.cn
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.09.024
摘要
鎂合金具有重量輕、節能、環保,在各種工業應用中具有巨大的潛力。但是,它們的力學性能相對較低,需要加強。在過去的十年中,人們一直致力于制備強納米晶(NC)鎂合金,盡管由于HCP金屬固有的有限塑性,Mg的晶粒尺寸很少細化到1000nm以下,屈服強度很少超過500MPa。在這里,我們采用傳統的工業旋轉旋鍛方法,制備了平均晶粒尺寸為80nm,尺寸為∅3mm×1000mm的大塊NC Mg–Gd–Y–Zr合金。進一步時效的NC-Mg合金的屈服強度為650MPa,極限抗拉強度為710MPa,這是大塊Mg合金的最高值。斷口觀察表明,NC-Mg合金中存在韌性晶間斷裂。高強度是由于納米晶粒、晶內富Gd團簇、晶間溶質偏析、β′析出、位錯和溶液強化貢獻,其中以納米晶強化為主。納米晶粒的形成是由于高應變速率的旋鍛過程中產生大量的機械孿晶、變形帶和層錯。我們的工作通過探索一種簡單、低成本的制備工藝,促進了大塊數控鎂合金的工業化生產。
英文摘要
Being lightweight, energy-efficient and environmentally benign, magnesium alloys present great potential for various industrial applications. However, they possess relatively low mechanical properties and need to be strengthened. During the last decade, significant effort has been directed towards preparation of strong nanocrystalline (NC) Mg alloys, although because of the limited plasticity inherent to HCP metals, the grain size of Mg was rarely refined below 1000 nm and the yield strength seldom exceeded 500 MPa. Here, by means of a conventional industrial method of rotary swaging, we prepared bulk NC Mg–Gd–Y–Zr alloys with an average grain size of 80 nm and a dimension of ∅3 mm × 1000 mm. The further-aged NC Mg alloy exhibits the yield strength of 650 MPa and the ultimate tensile strength of 710 MPa, the highest such values published for bulk Mg alloys. Fracture surface observation suggested a ductile inter-granular fracture in the NC Mg alloys. The high strength are attributed to nano-grain, intra-granular Gd rich clustering, inter-granular solutes segregation, β′ precipitation, dislocation and solution strengthening contributions, among which the nano-grain strengthening is dominant. The nano-grain formation results from the large number of mechanical twins, deformation bands and stacking faults induced by the high strain rate of swaging. Our work advances the industrial-scale production of bulk NC Mg alloys by exploring a simple and low-cost fabrication technique.
ACTA Vol. 200, Nov. 2020, P287-296
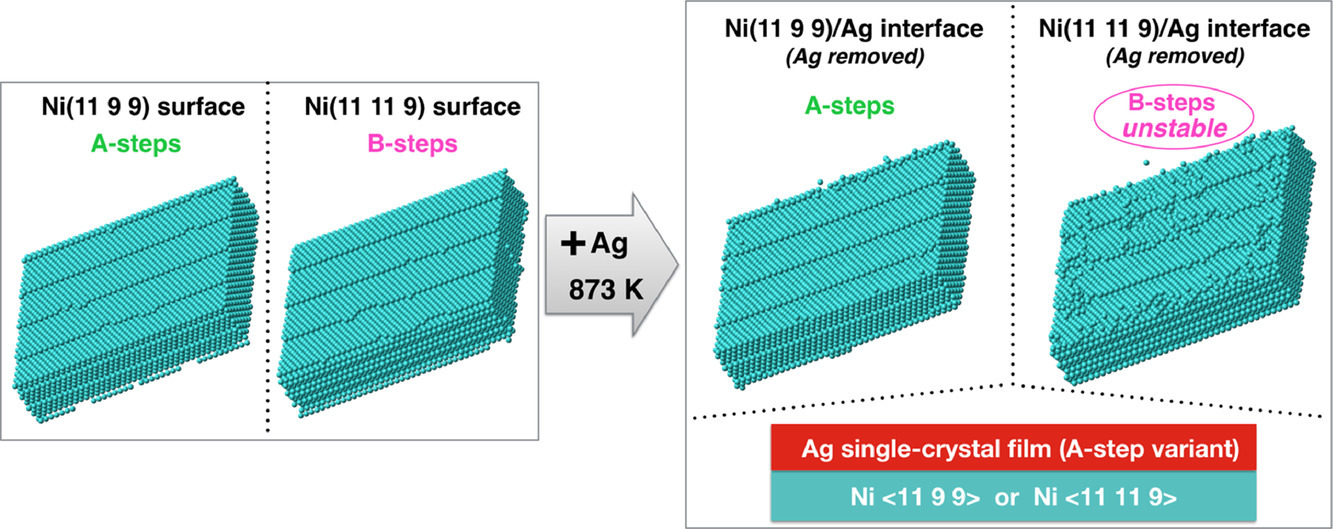
20. Influence of step structure on preferred orientation relationships of Ag deposited on Ni(111)
臺階結構對Ni(111)上銀沉積擇優取向關系的影響
Dominique Chatain?, Saransh Singh, Blandine Courtois, Jérémie Silvent, Elodie Verzeroli,Gregory S.Rohrer,MarcDe Graef,Paul Wynblatt
Dominique Chatain:chatain@cinam.univ-mrs.fr
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.08.082
摘要
先前的研究表明,異質外延中形成的取向關系強烈受到沉積層中的臺階與原前存在基體中臺階的排列方式的影響。本文采用實驗與計算機模擬相結合的方法,研究了基體臺階結構對沉積層最終取向關系的重要影響。我們利用沉積在鎳上的銀作為異質外延研究的模型系統。該系統顯示出16%的大晶格失配。結果表明,在與Ni(111)相鄰的任何表面上,具有兩種可能的〈110〉臺階(A臺階帶{100}臺階)和B臺階(帶{111}臺階),由于Ag的存在下,只有A-臺階在保持穩定,所以銀鍍層采用了單取向關系。
英文摘要
Previous studies have shown that the orientation relationships which develop in hetero-epitaxy are strongly influenced by the alignment of steps in the deposit with the pre-existing steps of the substrate. In this paper we use a combination of experiments with computer simulations to identify the important influence of substrate step structure on the eventual orientation relationships that develop in the deposit. We have made use of Ag deposited on Ni as it has been used extensively as a model system for the study of hetero-epitaxy. This system displays a large lattice mismatch of 16%. It is shown that on any surface vicinal to Ni(111), which has two possible kinds of 〈110〉 steps (A-steps with {100} ledges and B-steps with {111} ledges), a Ag deposit adopts a single orientation relationship because only A-steps remain stable in the presence of Ag.
ACTA Vol. 200, Nov. 2020, P297-304
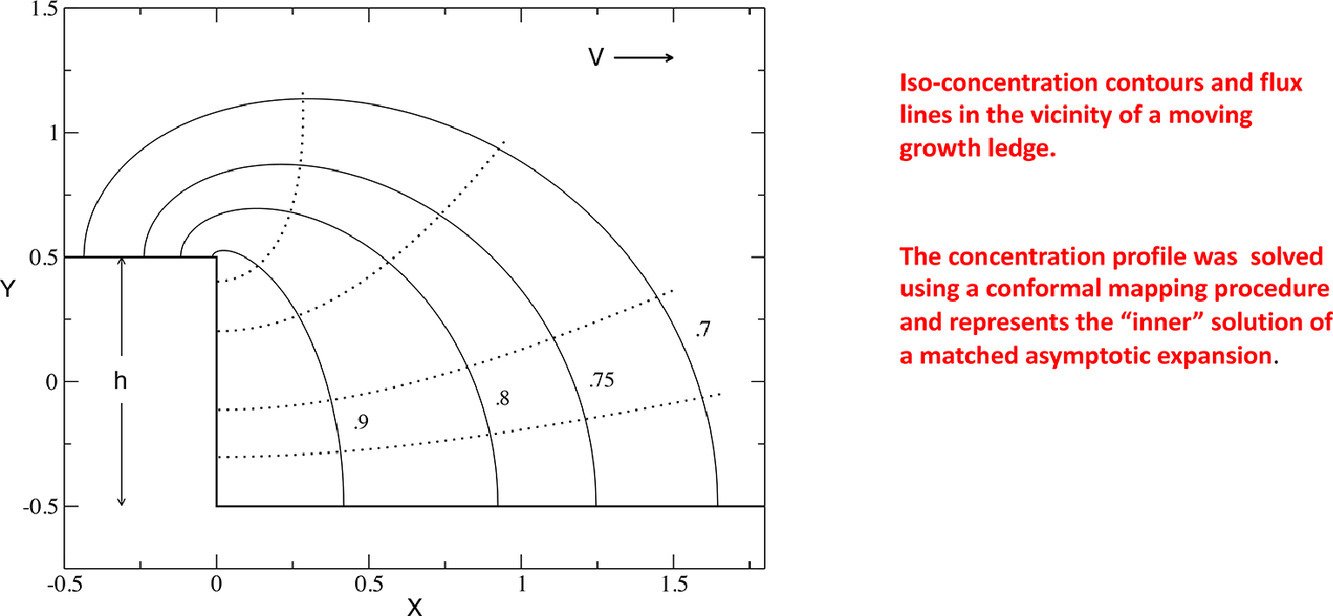
21. The diffusion controlled growth rate of solid-solid interphase boundaries containing ledges
通過擴散控制含臺階的固-固界面生長速率
J.J. Hoyt?
J.J. Hoyt:hoytj@mcmaster.ca
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.09.011
摘要
本文用匹配漸近展開法求解界面上孤立生長壁的速度,其中“內”解由保角映射程序獲得。相比之前的工作,在求解過程中,沿臺階面的所有點都保持恒定通量和局部平衡。匹配過程得到問題的可解性條件,進而得到Peclet數作為過飽和度函數的解析解。將理論處理以近似的方式推廣到多步的情況。將匹配漸近展開公式的預測結果與Ni-Cr系統中BCC沉淀生長的實驗結果進行了比較。
英文摘要
In this work the velocity of an isolated growth ledge located on an interphase boundary is solved by the method of matched asymptotic expansion where the “inner” solution is obtained by a conformal mapping procedure. In contrast to previous work, both a constant flux and local equilibrium is maintained at all points along the step face when formulating the solution. The matching procedure leads to a solvability condition for the problem, which in turn yields an analytic solution for the Peclet number as a function of supersaturation. The theoretical treatment is extended, in an approximate way, to the case of multiple steps. Predictions from the matched asymptotic expansion formulation are compared to experimental results for BCC precipitate growth in the Ni–Cr system.
ACTA Vol. 200, Nov. 2020, P315-327
22. High-energy synchrotron x-ray study of deformation-induced martensitic transformation in a neutron-irradiated Type 316 stainless steel
中子輻照316不銹鋼形變誘發馬氏體相變的高能同步輻射x射線研究
Xuan Zhang?,Chi Xu?,Yiren Chen?,Wei-Ying Chen?,Jun-Sang Park?,Peter Kenesei?,Jonathan Almer?,Jatuporn Burns?,Yaqiao Wu?,Meimei Li?
Xuan Zhang:xuanzhang@anl.gov
Chi Xu:xuchi@bnu.edu.cn
Yiren Chen:yiren_chen@anl.gov
Wei-Ying Chen:wychen@anl.gov
Jun-Sang Park:parkjs@anl.gov
Peter Kenesei:kenesei@anl.gov
Jonathan Almer:almer@anl.gov
Jatuporn Burns:Jatuporn.Burns@inl.gov
Yaqiao Wu:YaqiaoWu@boisestate.edu
Meimei Li:mli@anl.gov
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.08.057
摘要
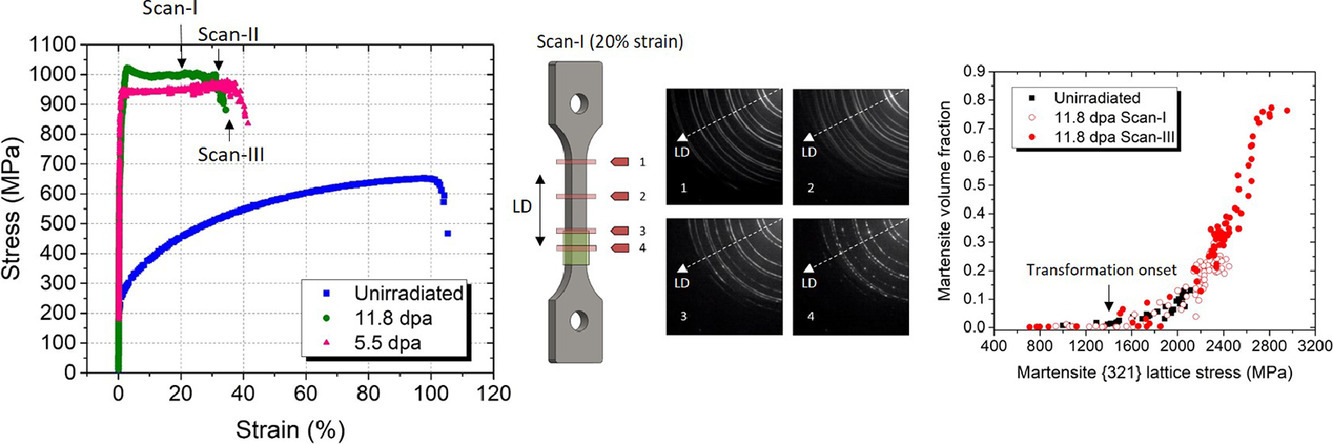
在室溫試驗期間,觀察到兩個中子輻照316不銹鋼樣品沿試樣厚度以擴展帶形式出現的異常拉伸變形行為,導致了高強度和高延展性。這些擴展帶在未經輻照的對應物中沒有觀察到。利用原位高能同步輻射x射線衍射技術,跟蹤了每個樣品在不同的變形水平下特定晶體相信息。用電子顯微鏡觀察輻照后和變形后樣品,以表征各種微觀結構特征。所有樣品均表現出形變誘發馬氏體相變,這是伴隨位錯硬化的第二應變硬化機制。通過施加應力對有效馬氏體起始溫度的影響,使形變誘發馬氏體相變合理化。結果表明,輻照并沒有改變位錯硬化和馬氏體相變機制,但輻照材料屈服強度的提高促進了塑性變形開始時的局部化相變,而未輻照材料需要預應變。馬氏體相變的硬化效應減少了頸縮的趨勢,并通過以擴展帶的形式進行變形來減輕輻照材料的延展性損失。盡管馬氏體相變產生了有益的影響,但這項研究表明,在核反應堆的典型工作溫度下,這一機制不能被激活。
英文摘要
An unusual tensile deformation behaviour in the form of a propagating band along the sample gauge was observed in two neutron-irradiated 316 stainless steel samples during room-temperature tests, leading to a combination of high strength and high ductility. These bands were not observed in an unirradiated counterpart. With the help of in situ high-energy synchrotron x-ray diffraction, the phase-specific crystal information was tracked at different deformation levels in each sample. Post-irradiation and post-deformation samples were examined using electron microscopy to characterize various microstructural features. All samples displayed a deformation-induced martensitic phase transformation, which was identified as a second strain-hardening mechanism accompanying the dislocation hardening. The deformation-induced martensitic transformation was rationalized by the effect of applied stress on the effective martensite start temperature. The results showed that the irradiation did not alter the dislocation hardening and the martensitic transformation mechanisms, but the increased yield strength in irradiated materials facilitated the localized phase transformation at the onset of plastic deformation, in contrast to the unirradiated material which required pre-straining. The hardening effect of the martensitic transformation reduced the tendency towards necking and mitigated the loss of ductility in the irradiated material by carrying the deformation in the form of a propagating band. Despite the beneficial effect from the martensitic transformation, this study indicates that this mechanism cannot not be activated at typical operating temperatures of nuclear reactors.
ACTA Vol. 200, Nov. 2020, P328-337
23. Mapping the kinetic evolution of metastable grain boundaries under non-equilibrium processing
非平衡加工條件下亞穩晶界的動力學演化圖
Zhitong Bai, Glenn H. Balbus, Daniel S. Gianola, Yue Fan?
Yue Fan:fanyue@umich.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.09.013
摘要
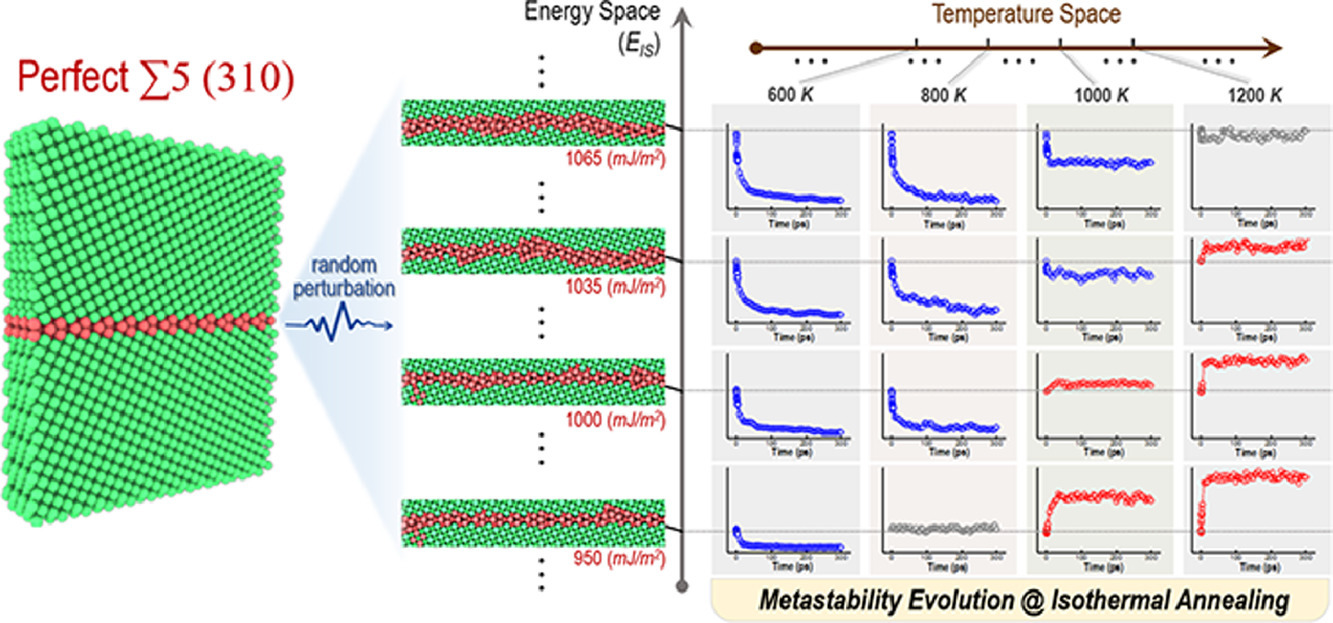
用原子模型研究了快速驅動條件下多亞穩晶界(GBs)的動力學演化。在增強統計分析的輔助下,繪制了寬亞穩態溫度空間上的GBs的能量演化圖,其中兩個不同的區域——老化區域和再生區域——被高保真地恢復。通過比較不同條件下(如隨機擾動、等溫退火和快速加熱/冷卻)的結果,表明這種老化/再生機制圖是通用的,而與用于引發亞穩態GBs的實際刺激無關。老化/再生現象被證明是源于系統勢能線的連續轉變過程中上坡攀爬和下坡下降的能量不平衡引起的。該模型不需要引入自由參數,可以調和經受飛秒激光照射的納米晶金屬的實驗測量的硬度變化,從而為實現多種界面狀態和促進以前無法獲得的性能狀態提供了一個新的視角。
英文摘要
The kinetic evolution of a multiplicity of metastable grain boundaries (GBs) under fast driving conditions are studied by atomistic modeling. Assisted with an enhanced statistical analysis, the energetic evolution of GBs over a broad metastability-temperature space is mapped out, wherein two distinct regimes—an ageing regime and a rejuvenating regime—are retrieved with high fidelity. By comparing the results under various conditions (e.g. random perturbations, isothermal annealing, and fast heating/cooling), it is shown that such ageing/rejuvenating mechanism map is universal, irrespective of the actual stimuli used to elicit the metastable GBs. The ageing/rejuvenating phenomena are demonstrated to stem from the energy imbalance of uphill climbing and downhill dropping during sequential transitions in the system's potential energy landscape. Without the necessity of introducing free parameters, such model can reconcile experimentally measured hardness variation of nanocrystalline metals subjected to femto-second laser irradiation, and it therefore provides a novel perspective on achieving a plurality of interfacial states and facilitating previously inaccessible property regimes.
ACTA Vol. 200, Nov. 2020, P351-365
24. Effects of cryogenic temperature and grain size on fatigue-crack propagation in the medium-entropy CrCoNi alloy
低溫溫度和晶粒尺寸對CrCoNi中熵合金疲勞裂紋擴展的影響
Julian Rackwitz, Qin Yu, Yang Yang, Guillaume Laplanche, Easo P. George,Andrew M. Minor,Robert O. Ritchie?
Robert O. Ritchie:roritchie@lbl.gov
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.09.021
摘要
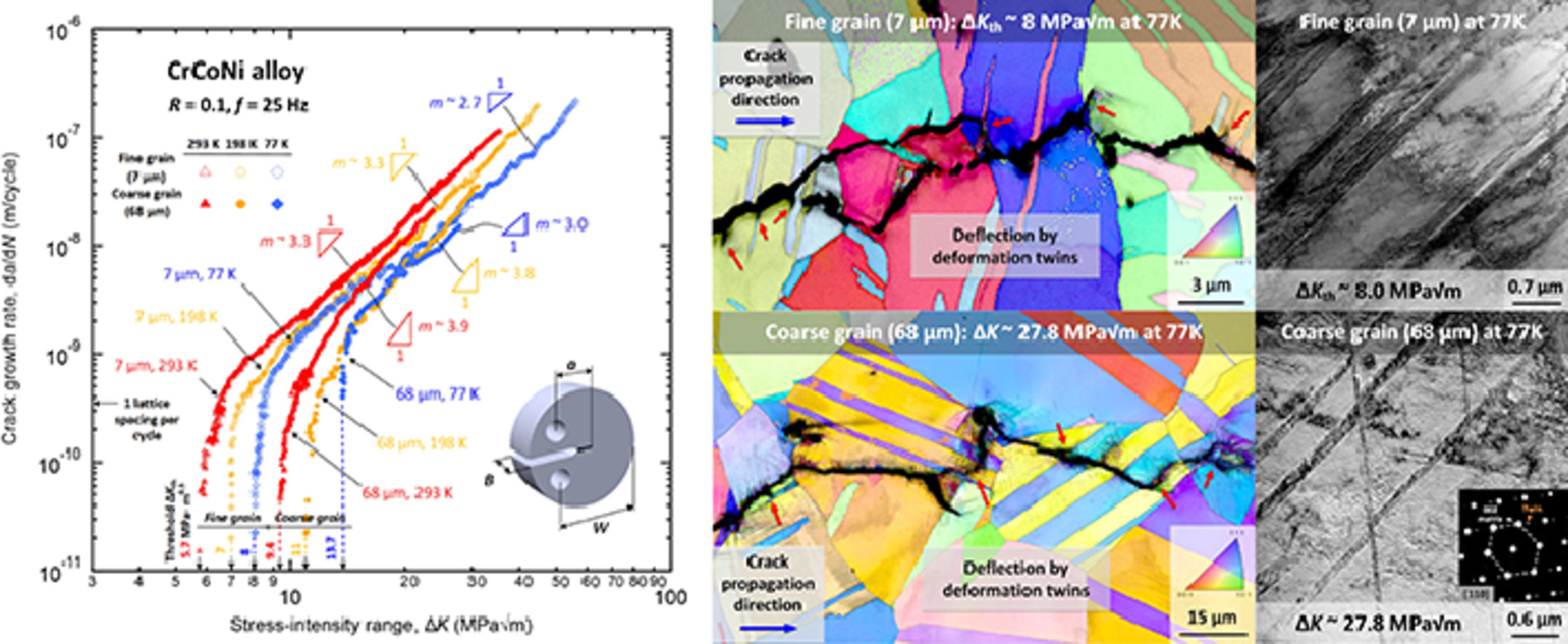
CrCoNi基高熵合金具有優異的力學性能,特別是在低溫下。本文研究了等原子、單相、面心立方、中熵合金CrCoNi的疲勞裂紋擴展特性,該合金具有優異的強度、塑性和韌性,在低溫下都得到了增強。在室溫(293 K)和低溫(198 K,77 K)溫度下,以0.1的載荷比,在不同的生長速率范圍內(從~10−11到>10−7 m/周期),對兩種晶粒尺寸(~7和68µm)的疲勞裂紋擴展進行了檢查,尤其是近閾值行為。我們發現,隨著溫度的降低和晶粒尺寸的增加,疲勞門檻值ΔKth增加:細晶合金從293k時的5.7MPa√m增加到77k時的8MPa√m,粗晶合金從293k時的9.4MPa√m提高到77k時的13.7MPa√m。從機理上講,293K溫度下的穿晶斷裂在低溫下轉變為晶界和穿晶的混合物,其中納米孿晶的增加傾向似乎通過偏轉裂紋路徑來抑制生長速率。然而,影響近閾值行為的主要因素是粗糙誘導的裂紋閉合,這是由裂紋側面之間的干涉引起的,低溫下粗糙的斷裂表面,尤其是在粗晶粒微觀結構中,會增強這種干涉。CrCoNi的疲勞裂紋擴展行為與鎳基高溫合金相當,但優于高熵CrMnFeCoNi(Cantor)合金和許多高強度鋼,這使得CrCoNi合金成為安全關鍵應用的一種極好的候選材料(尤其在低溫條件下)。
英文摘要
CrCoNi-based high-entropy alloys have demonstrated outstanding mechanical properties, particularly at cryogenic temperatures. Here we investigate the fatigue-crack propagation properties of the equiatomic, single-phase, face-centered cubic, medium-entropy alloy (MEA), CrCoNi, that displays exceptional strength, ductility and toughness, all of which are enhanced at cryogenic temperatures. Fatigue-crack growth is examined, at a load ratio of 0.1 over a wide range of growth rates, from ~10−11 to >10−7 m/cycle, at room (293 K) and cryogenic (198 K, 77 K) temperatures for two grain sizes (~7 and 68 µm), with emphasis on near-threshold behavior. We find that the ΔKth fatigue thresholds are increased with decreasing temperature and increasing grain size: from 5.7 MPa√m at 293 K to 8 MPa√m at 77 K in the fine-grained alloy, and from 9.4 MPa√m at 293 K to 13.7 MPa√m at 77 K in the coarse-grained alloy. Mechanistically, transgranular cracking at 293 K transitions to a mixture of intergranular and transgranular at cryogenic temperatures, where the increased propensity of nano-twins appears to inhibit growth rates by deflecting the crack path. However, the main factor affecting near-threshold behavior is roughness-induced crack closure from interference between the crack flanks, which is enhanced by the rougher fracture surfaces at low temperatures, particularly in the coarser-grained microstructure. Fatigue-crack propagation behavior in CrCoNi is comparable to nickel-based superalloys but is superior to that of the high-entropy CrMnFeCoNi (Cantor) alloy and many high-strength steels, making the CrCoNi alloy an excellent candidate material for safety-critical applications, particularly involving low temperatures.
ACTA Vol. 200, Nov. 2020, P366-377
25. Recrystallization-based grain boundary engineering of 316L stainless steel produced via selective laser melting
基于316L不銹鋼選區激光熔化的再結晶晶界工程
Shubo Gao, Zhiheng Hu, Martial Duchamp, P.S. Sankara Rama Krishnan, Sravya Tekumalla,Xu Song,Matteo Seita?
Matteo Seita:mseita@ntu.edu.sg
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.09.015
摘要
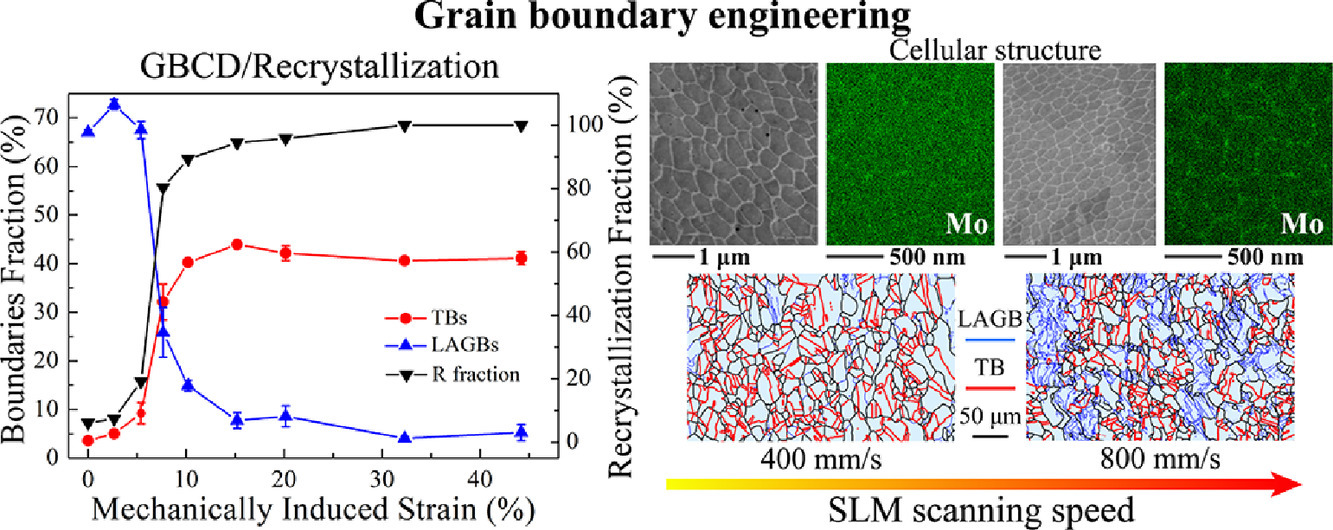
晶界工程(GBE)是一種熱機械加工策略,旨在通過在微觀結構中引入特殊類型的晶界,如孿晶界(TB),來提高多晶金屬的物理和機械性能。由于涉及多個應變退火周期,傳統的GBE不直接適用于近凈形狀零件,例如通過增材制造(AM)技術生產的零件。在這項研究中,我們探索了一種不同的GBE工藝路線,利用選區激光熔化(SLM)生產的奧氏體316L不銹鋼再結晶過程中的TB倍增。我們發現再結晶需要最小程度的機械變形,這與SLM過程中激光掃描速度有關。我們將這一關系歸因于快速凝固過程中晶胞尺寸和在晶胞邊界溶質偏析的數量,它們分別與激光掃描速度成反比和成正比。晶胞結構越粗糙,化學成分越均勻,再結晶晶粒越容易形核和長大。研究結果為設計AM兼容GBE策略提供了基礎,以生產具有復雜幾何形狀的高性能零件。
英文摘要
Grain boundary engineering (GBE) is a thermomechanical processing strategy to enhance the physical and mechanical properties of polycrystalline metals by purposely incorporating special types of grain boundaries—such as twin boundaries (TB)—in the microstructure. Because of the multiple strain-annealing cycles involved, conventional GBE is not directly applicable to near-net-shape parts, such as those produced via additive manufacturing (AM) technology. In this study, we explore a different GBE processing route that leverages TB multiplication during recrystallization of austenitic 316L stainless steel produced via selective laser melting (SLM). We find that recrystallization requires a minimum level of mechanical deformation, which scales with the laser scanning speed employed during SLM. We ascribe this relationship to the cell size and the amount of solute segregating at cell boundaries during rapid solidification, which are inversely and directly proportional to the laser scanning speed, respectively. The coarser the cell structure and the more uniform the chemical composition, the easier the nucleation and growth of recrystallized grains. Our results provide the groundwork for devising AM-compatible GBE strategies to produce high-performance parts with complex geometry.
微信公眾號:Goal Science
投稿郵箱:wechat@gs-metals.com
投稿微信:GSmaterial
