金屬頂刊雙語導讀丨Acta Mater. Vol.200,Nov. 2020(下)
2020-12-21 來源:Goal Science
本期包含金屬材料領域論文15篇,涵蓋了高熵合金、鎳合金、奧氏體不銹鋼、TWIP鋼、增材制造等,國內科研單位包括北京理工大學、北京科技大學、湖南大學、天津大學等(通訊作者單位)。
Vol. 200 目錄
43. A scrap-tolerant alloying concept based on high entropy alloys
基于高熵合金的成分靈活性概念
44. Thermal transport property correlated with microstructural evolution of Fe-based amorphous alloy
鐵基非晶合金的導熱與組織演變的關系
45. Dramatically Enhanced Combination of Ultimate Tensile Strength and Electric Conductivity of Alloys via Machine Learning Screening
通過機器學習方法實現合金抗拉強度和電導率的綜合提高
46. Phase-field model of deformation twin-grain boundary interactions in hexagonal systems
HCP系統中孿晶界相互作用的相場模擬
47. Anomalous texture development induced by grain yielding anisotropy in Ni and Ni-Mo alloys
Ni和Ni-Mo合金中晶粒屈服各向異性引起的異常織構
48. Effect of stress on vacancy formation and diffusion in fcc systems: Comparison between DFT calculations and elasticity theory
FCC體系中應力對空位形成和擴散的影響:第一性原理計算與彈性理論的比較研究
49. Multiscale modeling of cruciform dwell tests with the uncertainty-quantified parametrically homogenized constitutive model
十字樣品靜載實驗的非確定量化參數本構模型多尺度模擬
50. Microstructure evolution and thermal stability of equiatomic CoCrFeNi films on (0001) α-Al2O3
(0001) α-Al2O3上生長的等原子CoCrFeNi薄膜的微觀結構演變和熱穩定性
51. Extensive nanoprecipitate morphology transformation in a nanostructured ferritic alloy due to extreme thermomechanical processing
納米鐵素體合金高溫機械加工過程中的析出形態轉變
52. First principles study of the effect of hydrogen in austenitic stainless steels and high entropy alloys
氫在奧氏體不銹鋼和高熵合金中作用的第一性原理研究
53. Synergistic deformation pathways in a TWIP steel at cryogenic temperatures: In situ neutron diffraction
低溫下TWIP鋼協同變形的原位中子衍射研究
54. Spinodal decomposition versus classical γ’ nucleation in a nickel-base superalloy powder: An in-situ neutron diffraction and atomic-scale analysis
鎳基高溫合金粉末中調幅分解與經典形核的原位中子衍射和原子尺度分析研究
55. Dislocation-based serrated plastic flow of high entropy alloys at cryogenic temperatures
高熵合金在低溫下基于位錯的鋸齒狀塑性流動
56. Deformation faulting in a metastable CoCrNiW complex concentrated alloy: A case of negative intrinsic stacking fault energy?
亞穩CoCrNiW合金的變形:一種負內秉層錯能的例子?
57. Grain refinement mechanisms in additively manufactured nano-functionalized aluminum
增材制造納米功能鋁合金的晶粒細化機制
ACTA Vol. 200, Nov. 2020, P735-744
43. A scrap-tolerant alloying concept based on high entropy alloys
基于高熵合金的成分靈活性概念
M.R. Barnett?, M. Senadeera, D. Fabijanic, K.F. Shamlaye, J. Joseph, S.R. Kada, S. Rana, S. Gupta, S. Venkatesh
M.R. Barnett:barnettm@deakin.edu.au
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.09.027
摘要
本文提出了成分靈活性的概念。目的是在分離混合合金成本極高的現有條件下,促進廢棄合金的商業應用。一種成分靈活的合金應當可以通過將一些廢棄的合金進行混合來生產。雖然不同時段不同批次這樣生產出來的合金可能成分所有不同,但都能滿足某些基本的性能目標。以FeNiCr基高熵合金為例,我們利用貝葉斯優化,可以生成一系列強度在指定的范圍內(150-250 MPa, 200-350 MPa和300-350 MPa)內的復合合金。這一概念的靈感來自于文獻中大量報道的高熵合金,盡管它們的成分分布廣泛,但都表現出了相似的性能。我們基于合金中每種元素允許變化的范圍,提出了一種簡單的成分靈活性測量方法,并制備了68種模型合金來對我們提出的概念和方法進行演示和說明。結果表明,我們的模型合金都可以通過將現有的鎳合金與316不銹鋼進行組合實現生產。我們希望成分靈活性的概念能夠促進合金回收和再利用。
英文摘要
The present article advances the idea of compositional flexibility. The intent is to provide an avenue for value creation from waste alloys in cases where costs of separating co-mingled alloy flows are prohibitively high. A compositionally flexible alloy has the potential to be produced solely from varying and intermingled flows of end-of-life alloys. While the alloy composition may vary from day-to-day or from heat-to-heat, the intent is that it will still satisfy base performance targets. Using FeNiCr based high entropy alloys as inspiration, we exploited Bayesian Optimization to define a number of example compositionally complex alloys that display strengths within specified limits (150-250 MPa, 200-350 MPa and 300-350 MPa). The concept was motivated by the surprising number of high entropy alloys reported in the literature that display a similarity of properties despite their wide dispersion of composition. We propose a simple measure of compositional flexibility by combining the ranges over which each elemental addition is permitted to vary and suggest methods of alloy specification. A series of 68 prototype compositions were produced and characterized to demonstrate the concept and approach. We show that our model alloys could conceivably be produced using multiple different combinations of existing Ni alloys in combination with 316 stainless steel. Our hope is that the concept will find application to facilitate alloy recovery where it might not otherwise be feasible.
ACTA Vol. 200, Nov. 2020, P793-802
44. Thermal transport property correlated with microstructural evolution of Fe-based amorphous alloy
鐵基非晶合金的導熱與組織演變的關系
Haihua Yao, Lu Wang, Zheng Zhou?, Benpeng Wang, Zhen Tan, Dingyong He, Yunfei Xue?
Z. Zhou:zhouzhengbjut@bjut.edu.cn,北京理工大學
Y.Xue:xueyunfei@bit.edu.cn,北京理工大學
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.09.072
摘要
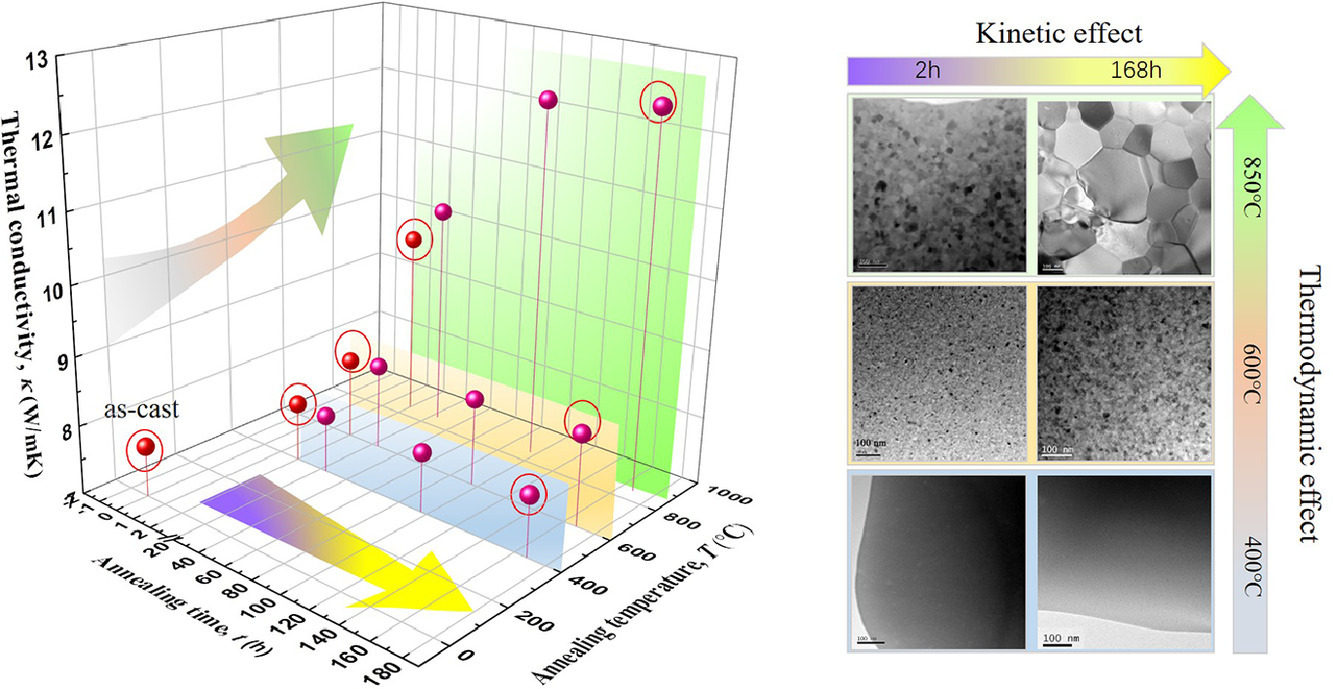
非晶合金熱傳導性能與組織演化之間的關系對其在作為絕熱材料方面的應用至關重要。本文以導熱系數為7.74 W/mK的Fe48Cr15Mo14C15B6Y2非晶合金為對象,對這兩者之間的關系進行了研究。等時退火實驗表明,結晶溫度(Tx1= 620.7°C)以下,當溫度升高時,由于電子和聲子對熱導的貢獻相互矛盾,因此盡管存在結構弛豫或部分結晶,但導熱系數的提高有限。而當退火溫度高于Tx1時,由于兩者的貢獻者協同,因此熱導率顯著增加。另一方面,等溫退火實驗表明,當溫度低于Tx1時,熱導率與退火時間無關。雖然在600°C退火材料可以緩慢發生完全結晶,但導熱系數幾乎保持在8.35 W/mK左右。這是由于新生成相界面的散射導致的。此外,在850°C長時間退火時,晶粒長大會導致導熱系數緩慢增加,并在12.44 W/mK左右達到飽和。以上結果表明了鐵基非晶合金作為熱絕緣體的潛力,為非晶合金的組織演化和相變化動力學遲滯效應的后續研究奠定了基礎。
英文摘要
The correlation between the thermal transport properties and microstructural evolution of amorphous alloys is crucial for their application in thermal insulation. Herein, Fe48Cr15Mo14C15B6Y2 amorphous alloy with low thermal conductivity of 7.74 W/mK was investigated to reveal this relationship. Isochronal annealing experiment demonstrates a limited increase in thermal conductivity at temperatures below the crystallization temperature (Tx1= 620.7°C), despite the occurrence of structural relaxation or partial crystallization, which is ascribed to the conflicting variations of electron and phonon contributions with increasing temperature. At annealing temperature above Tx1, the two contributors start to cooperate, leading to abrupt enhancement of thermal conductivity. On the other hand, isothermal annealing experiments reveal that at temperatures below Tx1, the thermal conductivity is independent of annealing time. Although full crystallization can be induced slowly by annealing at 600 °C, the thermal conductivity keeps nearly constant at 8.35 W/mK, which is attributed to additional scattering by a newly introduced phase interface. Moreover, grain growth upon prolonged annealing at 850 °C results in a slow increase in thermal conductivity, which asymptotically saturates at 12.44 W/mK. The obtained results demonstrate the potential of the Fe-based amorphous alloy as thermal insulator and form a basis for future works aiming to shed further light on the evolution of amorphous alloy and the sluggish effect of transformation kinetics.
ACTA Vol. 200, Nov. 2020, P803-810
45. Dramatically Enhanced Combination of Ultimate Tensile Strength and Electric Conductivity of Alloys via Machine Learning Screening
通過機器學習方法實現合金抗拉強度和電導率的綜合提高
Hongtao Zhang, Huadong Fu, Xingqun He, Changsheng Wang, Lei Jiang, Long-Qing Chen?, Jianxin Xie?
L.-Q. Chen:lqc3@psu.edu
J. Xie:jxxie@mater.ustb.edu.cn,北京科技大學
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.09.068
摘要
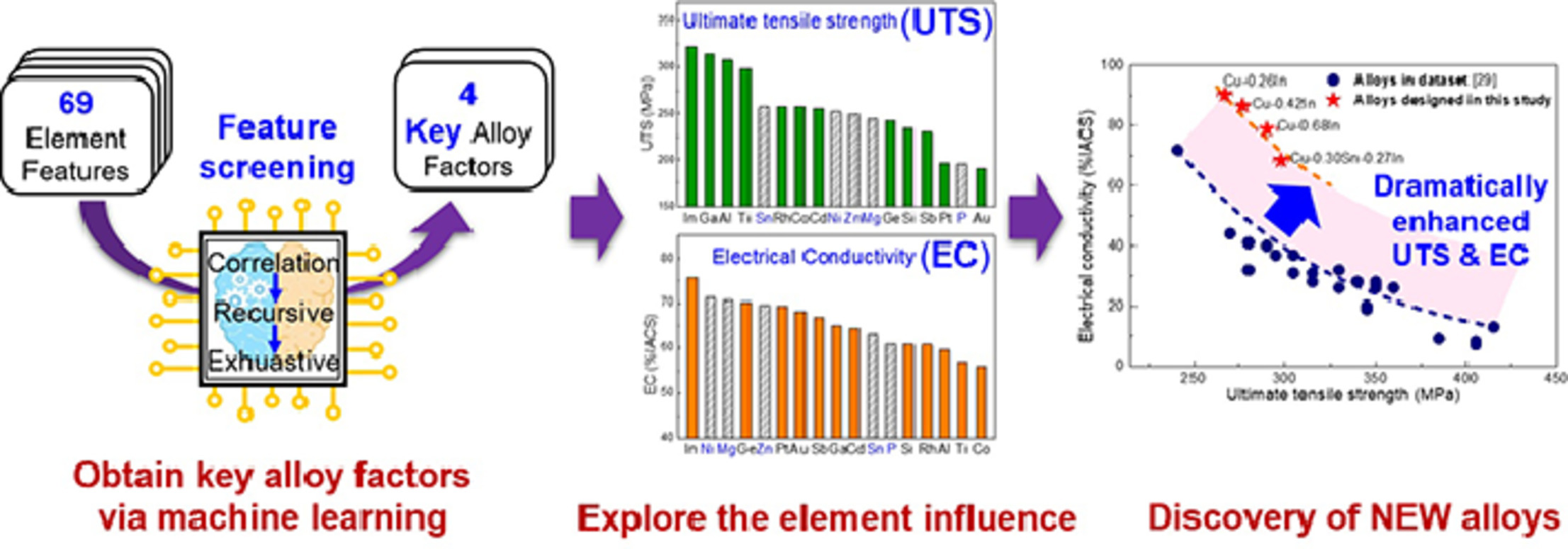
對材料相互沖突的性能(如機械強度和韌性或介電常數和擊穿強度)進行綜合優化一直以來都是一項具有挑戰性的工作。我們提出了一種機器學習方法,通過對現有數據集進行相關性分析、遞歸消除和窮舉識別出一組關鍵特征,從而顯著提高材料綜合抗拉強度(UTS)和電導率(EC)。我們證明了固溶強化導電銅合金的關鍵特征是電負性、核心電子距離和原子半徑,在此基礎上,我們發現了一系列新的合金元素,可以顯著改善抗拉強度和電導率。我們制備了四種新型銅合金對預測進行了驗證。這些銅合金有望取代目前在鐵路線上應用的昂貴Cu-Ag合金。此外,我們發現,相同的一套關鍵特性可普遍用于更廣泛的導電合金設計。
英文摘要
Optimizing two conflicting properties such as mechanical strength and toughness or dielectric constant and breakdown strength of a material has always been a challenge. Here we propose a machine learning approach to dramatically enhancing the combined ultimate tensile strength (UTS) and electric conductivity (EC) of alloys by identifying a set of key features through correlation screening, recursive elimination and exhaustive screening of existing datasets. We demonstrate that the key features responsible for solid solution strengthened conductive Copper alloys are absolute electronegativity, core electron distance, and atomic radius, based on which, we discovered a series of new alloying elements that can significantly improve the combined UTS and EC. The predictions are then validated by experimentally fabricating four new Cu-In alloys which could potentially replace the more expensive Cu-Ag alloys currently used in railway wiring. We show that the same set of key features can be generally applicable to designing a broad range of conductive alloys.
ACTA Vol. 200, Nov. 2020, P821-834
46. Phase-field model of deformation twin-grain boundary interactions in hexagonal systems
HCP系統中孿晶界相互作用的相場模擬
Xin Hua, Yanzhou Ji?, Tae Wook Heo?, Long-Qing Chen, Xiangyang Cui?
Y. Ji:yxj135@psu.edu
T.W. Heo:heo1@llnl.gov
X. Cui:cuixy@hnu.edu.cn,湖南大學
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.09.062
摘要
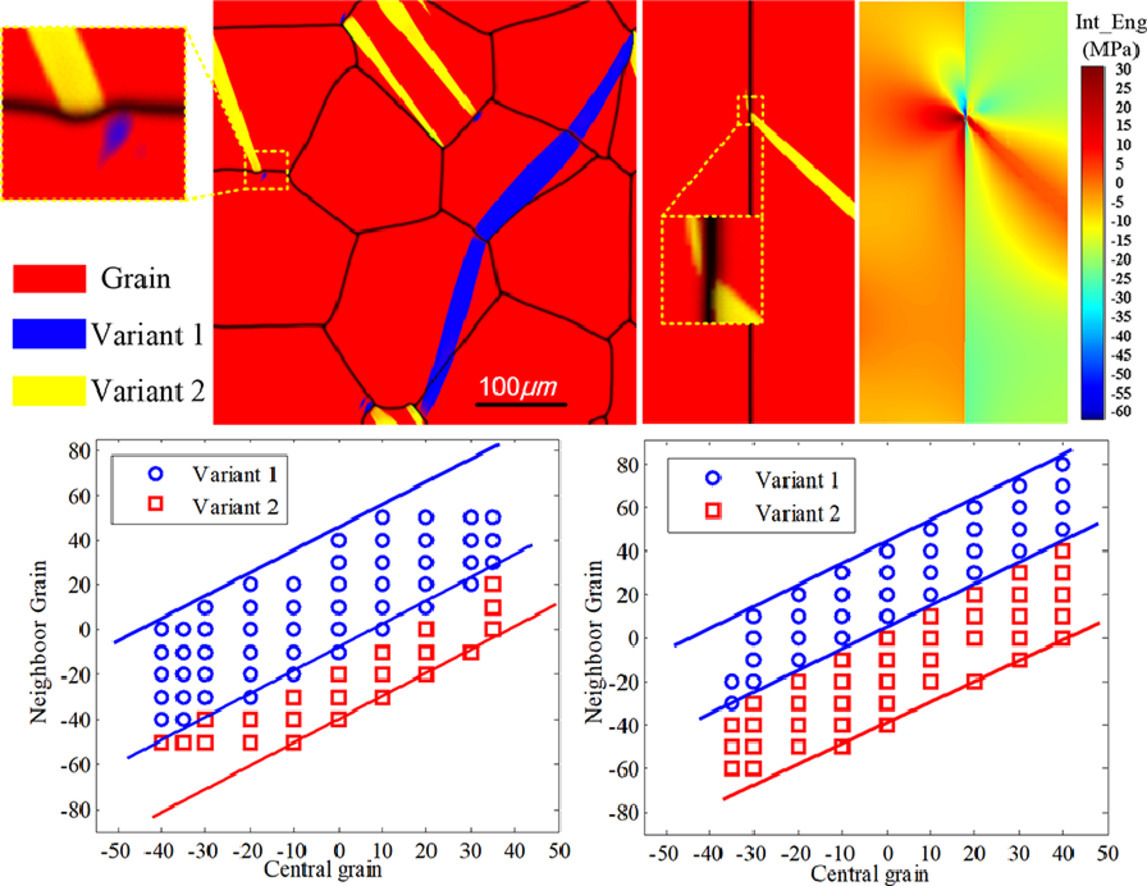
我們建立了一種用于描述六方密排(HCP)金屬中晶界與形變孿晶動態相互作用的相場模型。通過引入變形孿晶的跨晶界傳播,模型可以很好地模擬鎂合金中晶粒與孿晶的耦合演化機制。我們對晶界附近的應變弛豫進行了分析,發現它與相鄰晶粒間取向導致的幾何特性有關。相場模擬表明,孿晶穿過晶界進入相鄰晶粒會使得晶界向相鄰晶粒移動,晶界寬度減小。相鄰晶粒中孿晶變體的優先形核位置與彈性相互作用能分布有關。模型預測的孿晶傳播行為與已有的實驗觀察和分子動力學模擬相吻合。通過對相場模擬結果的系統性分析,我們建立了一套與旋轉角有關的孿晶變體選擇規則,用于分析鎂及鎂合金中變形孿晶的跨晶界傳播。
英文摘要
A phase-field model for describing dynamic interactions between deformation twins and grain boundaries in a hexagonal close packed (HCP) metal is established. It is applied to simulating the coupled evolution mechanisms of grains and twins in magnesium (Mg) by probing the transmission of deformation twins across grain boundaries. We analyze the effect of the strain relaxation near a grain boundary, which is related to the geometric compatibility arising from the misorientation angle between adjoining grains. Phase-field simulations demonstrate that twin transmission across a grain boundary into a neighboring grain leads to grain boundary migration towards the neighboring grain with a reduced grain boundary width. The preferred nucleation site of new twin variant in the neighboring grain is related to the elastic interaction energy distribution. These predicted transmission behaviors agree well with existing experimental observations and molecular dynamics simulations. By analyzing set of systematic phase-field simulation results, we establish a rotation-angle-related twin variant selection rule for analyzing the transmission of deformation twins across grain boundaries in Mg and its alloys.
ACTA Vol. 200, Nov. 2020, P857-858
47. Anomalous texture development induced by grain yielding anisotropy in Ni and Ni-Mo alloys
Ni和Ni-Mo合金中晶粒屈服各向異性引起的異常織構
Lu Han, Lars P.H. Jeurgens, Claudia Cancellieri, Jing Wang, Yifei Xu, Yuan Huang, Yongchang Liu, Zumin Wang?
Z. Wang:z.wang@tju.edu.cn,天津大學
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.09.063
摘要
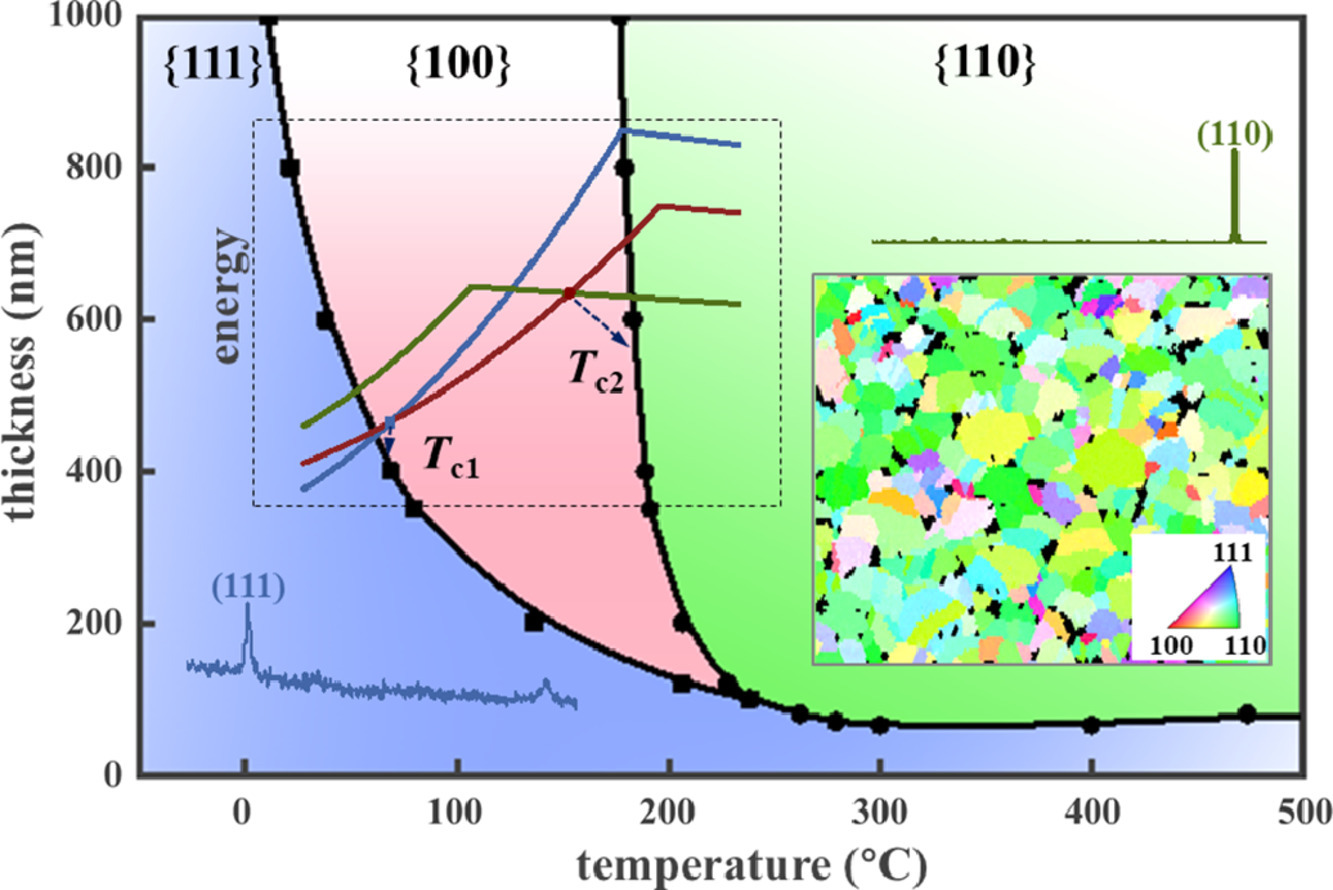
在Ni和Ni-Mo薄膜回火過程中,材料形成了具有高表面能和高應變能的{110}織構。這種織構是由于晶粒各向異性屈服導致的。基于模型計算,我們繪制了{111}, {100}和{110}織構圖,用于預測不同厚度薄膜的織構轉變溫度。我們進一步對織構的演化進行了動態模擬,結果表明織構的演化受晶界處原子的自擴散控制。以上結果對于調控薄膜材料的組織織構具有重要意義。
英文摘要
During the annealing of Ni and Ni-Mo films, a {110} texture, usually considered to be both of high surface energy and high strain energy, was found to develop. Quantitative thermodynamic model calculations showed that the anomalous formation of this {110} texture originates fundamentally from the grain yielding anisotropy of Ni. Based on extensive grain yielding anisotropy model calculations, a “tex- ture map”based on {111}, {100}, and {110} textures was constructed to predict the texture transition temperatures for different film thicknesses. A kinetic analysis of the texture evolution in the films is further presented, revealing that the texture evolution is controlled by the self-diffusion of atoms at grain boundaries. These findings pave the way for the achievement of unusual surface orientations through the quantitative texture design of thin films.
ACTA Vol. 200, Nov. 2020, P869-882
48. Effect of stress on vacancy formation and diffusion in fcc systems: Comparison between DFT calculations and elasticity theory
FCC體系中應力對空位形成和擴散的影響:第一性原理計算與彈性理論的比較研究
Damien Connétable?, Philippe Maugis?
D. Connétable: damien.connetable@ensiacet.fr
P. Maugis: philippe.maugis@im2np.fr
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.09.053
摘要
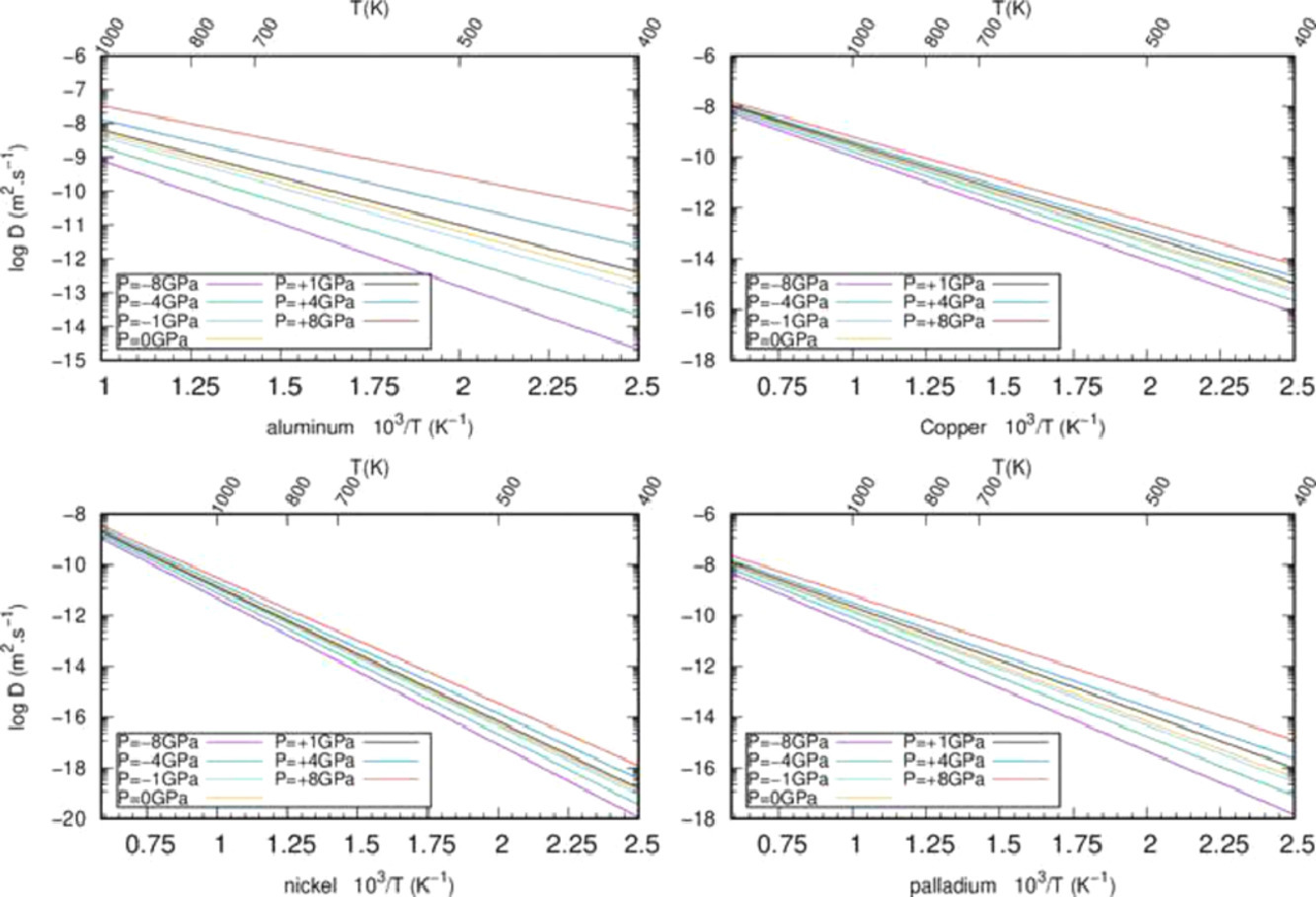
在本文中,我們基于點缺陷的彈性理論討論了應力對空位溶解度和擴散系數的影響。我們使用第一性原理計算對模型進行了驗證。特別地,我們分別對使用第一性原理計算Al系統和使用彈性模型計算Ni, Cu,Pd等BCC系統的結果進行了討論。我們考慮了靜水壓力、多軸應力和剪應力等不同類型載荷。在單軸加載的情況下,我們對晶體學主軸方向[001]和垂直密排面(111)這兩個不同方向進行了研究。為了量化應力對擴散系數的影響,我們給出了各種情形下擴散系數的表達式供進一步計算。通過分析加載過程中的對稱斷裂,我們可以對非等價原子躍遷進行識別,從而導出擴散方程。通過結合第一性原理計算,我們實現了多尺度的物理模型構建。結果表明,彈性能能夠準確地反映應力對空位擴散和溶解度的影響。
英文摘要
This paper discusses the effect of stress on the solubility and diffusivity of vacancies using the elasticity theory of point defects. To support the discussion, results are compared with DFT calculations to verify model accuracy. The particular case of vacancies in aluminum is discussed in detail (DFT-elasticity), while three other metallic fcc systems – Ni, Cu and Pd – are discussed through the elasticity approach only. Different types of loading were considered: hydrostatic, multi-axial and shear stresses. In the case of a uni-axial loading, two different directions were investigated: the first along a main crystallographic direction, i.e. [001], and the second perpendicular to the dense plane (111). In order to quantify the effect of stress on diffusivity, the diffusion coefficient of each configuration was expressed for further calculations. By analyzing the symmetry break during the loading process, non-equivalent atomic jumps were identified and diffusion equations obtained. A multi-physic approach was carried out by combining first-principles calculations, to study atomic-scale processes, and a multi-state formalism, to obtain exact diffusion equations. Results show that elasticity accurately captures the effects of stress on vacancy diffusion and solubility and an application method is presented.
ACTA Vol. 200, Nov. 2020, P893-907
49. Multiscale modeling of cruciform dwell tests with the uncertainty-quantified parametrically homogenized constitutive model
十字樣品靜載實驗的非確定量化參數本構模型多尺度模擬
Thirupathi Maloth, Deniz Ozturk, Garrison M. Hommer, Adam L. Pilchak, Aaron P. Stebner, Somnath Ghosh?
S. Ghosh: sghosh20@jhu.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.09.037
摘要
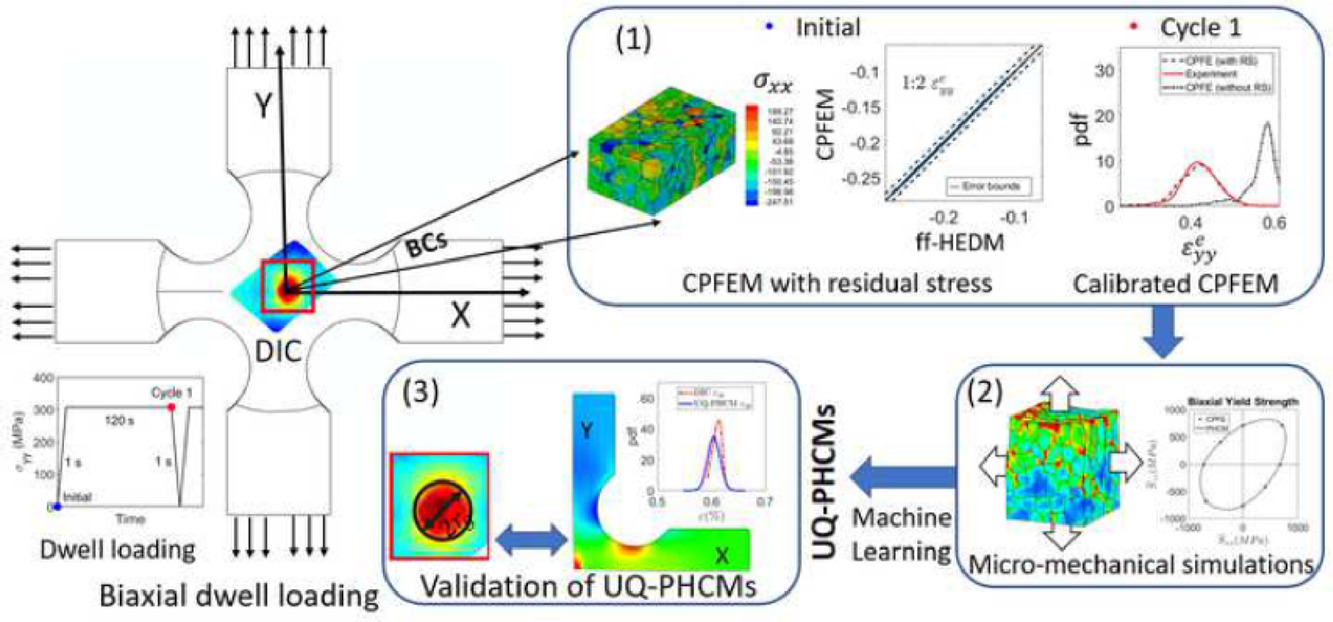
本文提出了一種新的多尺度方法,對靜載下Ti-7Al試樣的多軸應力-應變演化進行了分析。通過機器學習和非確定性量化方法對嚴格的晶體塑性有限元模型(CPFEM)進行擴展,我們建立了具有熱力學一致性的非確定性量化參數本構模型(UQ-PHCM)。該模型通過典型微觀結構參數(RAMPs)對材料的組織信息進行了整合。我們通過非確定性量化方法來處理模型簡化、數據稀疏和組織特征選擇中的不確定性問題。通過將多軸多尺度實驗與多尺度模擬相結合,使UQ-PHCM成為一種彌補實驗樣品宏觀觀測結果與有限元模擬微觀應力應變之間差距的一種有效工具。通過使用數字圖像(DIC)測量樣品表面應變和使用原位遠場高能衍射(ff-HEDM)測量晶格應變,對CPFEM進行了校準和驗證。我們在CPFEM中的框架下提出了一種計算方法,將初始殘余應力與測量的晶格應變進行了對應。在Ti-7Al試樣的雙向拉伸實驗結果驗證了UQ-PHCM的有效性,模型準確預測了DIC測得的應變演化。此外,由微觀結構變化引起的應變場不確定性也通過DIC測量得到了證實。
英文摘要
This paper presents a novel multiscale approach for analyzing multi-axial stress-strain evolution in Ti-7Al cruciform specimens under dwell loading, through the use of an uncertainty-quantified, parametrically homogenized constitutive model (UQ-PHCM). The thermodynamically-consistent UQ-PHCM is built from rigorous upscaling of crystal plasticity FE models (CPFEM) using machine learning and uncertainty quantification. They explicitly incorporate microstructural information in the form of representative aggregated microstructural parameters (RAMPs). Uncertainty quantification accounts for uncertainty in model reduction, data sparsity and microstructural descriptors. This paper integrates advanced multiscale, multi-axial experiments with computational modeling at multiple scales to establish the UQ-PHCM as an effective tool for bridging the gap between laboratory specimen-scale experimental observations and micro-scale stresses and strains using CPFEM. The CPFEM is calibrated and validated by experimental data from surface strain measurements using digital image correlation (DIC) and grain-by-grain lattice strain measurements with in-situ far field high energy diffraction microscopy (ff-HEDM). A computational method is developed in CPFEM, to incorporate initial residual stresses consistent with measured lattice strains. The UQ-PHCM is validated with biaxial tensile dwell test results performed on the cruciform specimen with satisfactory prediction of gauge strain evolution in DIC measurements. Uncertainty in the strain field due to microstructural variability is also corroborated by the DIC measurements.
ACTA Vol. 200, Nov. 2020, P908-921
50. Microstructure evolution and thermal stability of equiatomic CoCrFeNi films on (0001) α-Al2O3
(0001) α-Al2O3上生長的等原子CoCrFeNi薄膜的微觀結構演變和熱穩定性
Younès Addab, Maya K. Kini, Blandine Courtois, Alan Savan, Alfred Ludwig, Nathalie Bozzolo, Christina Scheu, Gerhard Dehm, Dominique Chatain?
D. Chatain: chatain@cinam.univ-mrs.fr
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.09.064
摘要
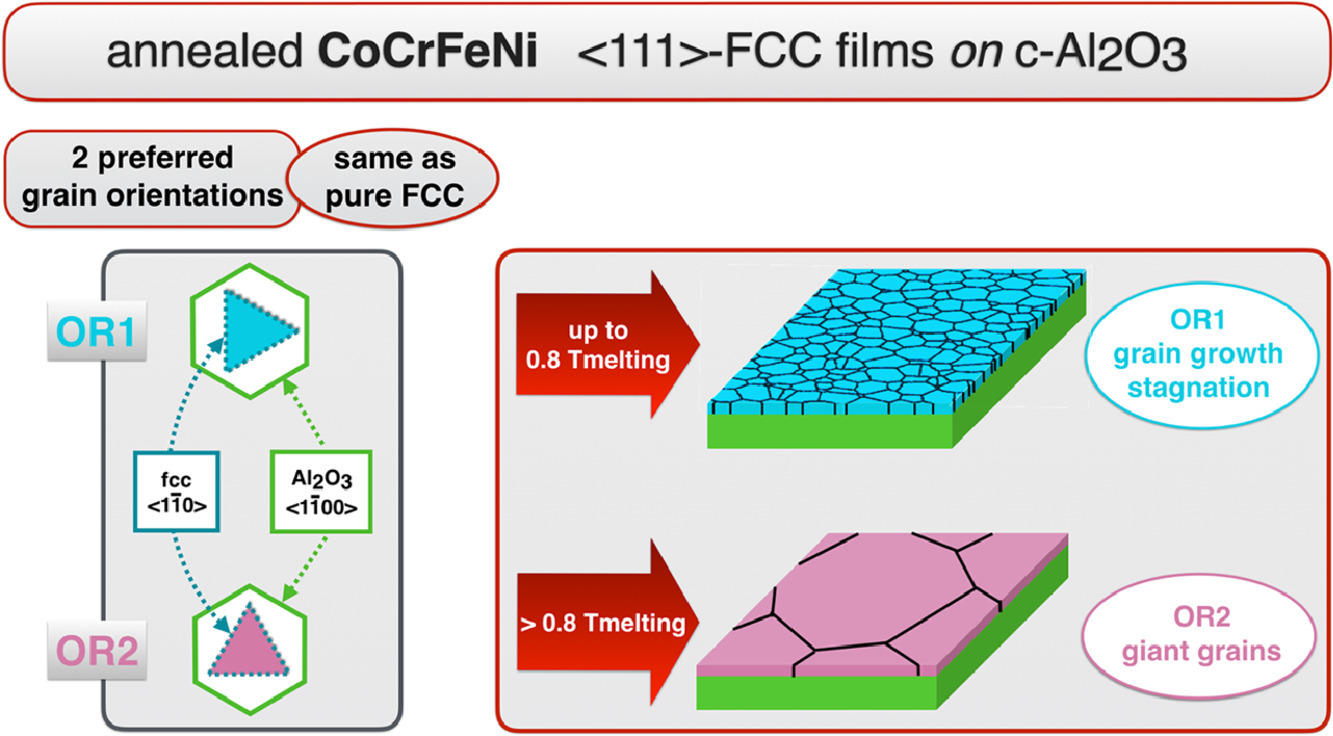
我們在室溫下在(0001) α-Al2O3基體上沉積了均勻的FCC多晶CoCrFeNi薄膜并研究了200 ~ 670 nm厚薄膜在973 ~ 1423 K之間相穩定性和形貌穩定性。研究表明,在30-100 nm柱狀晶經退火演變為約10 或1000μm尺寸晶粒的過程中,FCC相能夠穩定存在。只有基體具有兩種特定取向關系的晶粒發生長大。這兩種取向分別為OR1: (M(111)[110]//α-Al2O3(0001)[1-100])和OR2: (M(111)[110]//α-Al2O3(0001)[11-20])及其孿晶變體(OR1t和OR2t)。這些結果與已報道的幾種FCC純金屬膜一致。因此,這些體系中的取向似乎不受FCC相化學成分或晶格參數控制。退火后,薄膜可能保持完整,也可能開裂。這取決于晶粒生長和晶界裂紋擴展的動力學競爭。我們對影響薄膜穩定性的主要因素——三叉晶界進行了進一步研究。結果表明,較薄的厚度和較高的溫度更容易導致薄膜破裂。1000 K以下,無論薄膜厚度,薄膜穩定組織均為約10μm的OR1 和 OR1t晶粒。1000k以上,OR2和OR2t晶粒迅速長大,引起材料破裂。此外,我們發現在相同退火溫度下,CoCrFeNi合金中OR2和OR2t晶粒的生長速度比純FCC金屬要快。
英文摘要
Homogeneous face-centered cubic (fcc) polycrystalline CoCrFeNi films were deposited at room temperature on (0001) α-Al2O3 (c-sapphire). Phase and morphological stability of 200 to 670 nm thick films were investigated between 973 K and 1423 K.The fcc-phase persists while the original texture of 30-100 nm wide columnar grains evolves into ~10 or ~1000 μm wide grains upon annealing. Only the metallic M grains having two specific orientation relationships (ORs) to the c-sapphire grow. These ORs are OR1 (M(111)[110]//α-Al2O3(0001)[1-100]) and OR2 (M(111)[110]//α-Al2O3(0001)[11-20]) and their twin-related variants (OR1t and OR2t). They are identical to those reported for several pure fcc metal (M) films. Thus, the ORs in these fcc/c-sapphire systems appear not to be controlled by the fcc phase chemistry or its lattice parameter as usually assumed in literature. Upon annealing, the films either retain their integrity or break-up depending on the competing kinetics of grain growth and grain boundary grooving. Triple junctions of the grain boundaries, the major actors in film stability, were tracked. Thinner films and higher temperatures favor film break-up by dewetting from the holes grooved at the triple junctions down to the substrate. Below 1000 K, the film microstructure stabilizes into 10 μm wide OR1 and OR1t twin grains independent of film thickness. Above 1000 K, the OR2 and OR2t grains expand to sizes exceeding more than a 1000 times the film thickness. The grain boundaries of the OR2 and OR2t grains migrate fast enough to overcome the nucleation of holes from which break-up could initiate. The growth of the OR2 and OR2t grains in this complex alloy is faster than in pure fcc metals at equivalent homologous annealing temperatures.
ACTA Vol. 200, Nov. 2020, P922-931
51. Extensive nanoprecipitate morphology transformation in a nanostructured ferritic alloy due to extreme thermomechanical processing
納米鐵素體合金高溫機械加工過程中的析出形態轉變
Caleb P. Massey?, David T. Hoelzer, Kinga A. Unocic, Yury N. Osetskiy, Philip D. Edmondson, Baptiste Gault, Steven J. Zinkle, Kurt A. Terrani
C.P. Massey: masseycp@ornl.gov
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.09.020
摘要
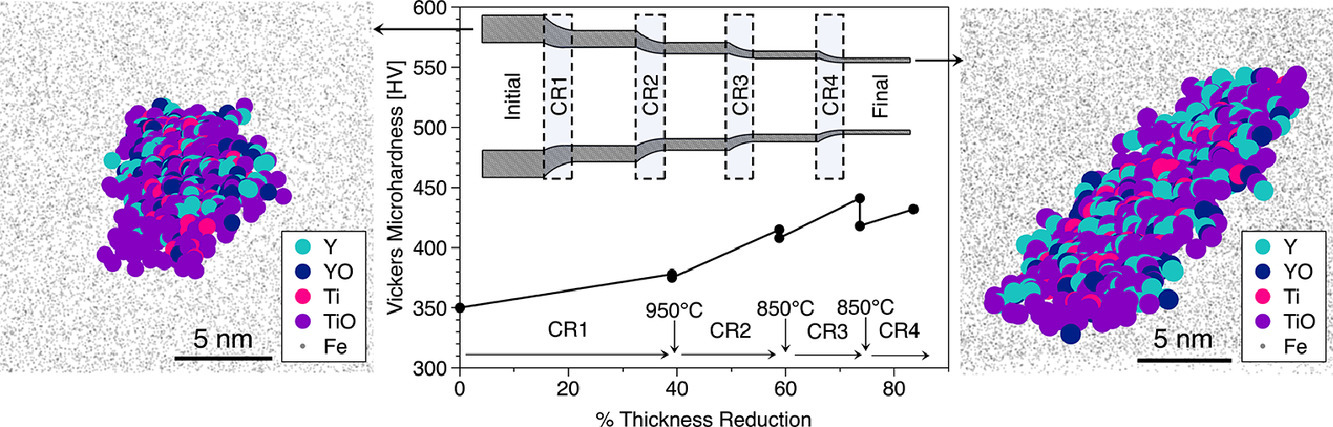
我們研究了經高溫機械加工成薄壁管的鐵素體鋼中的納米析出相。結果發現,析出相的體積分數(0.3%)和數密度(>1023m−3)沒有顯著變化,但析出相的形貌由球形變為棒狀,長寬比達到了9。高分辨率電子顯微鏡顯示,析出相與鐵基體基體共格,且原子探針掃描結果表明析出相成分無明顯變化。析出形貌上的變化是由于Y-Ti-O析出的剪切性質,它們是位錯運動過程的“軟”障礙。析出長寬比的變化在5 nm以上的析出物中較為明顯,這可能是由于在熱處理導致的回復過程中,小析出(1-3 nm)優先溶解,大析出隨后長大造成的。
英文摘要
Nano-oxide precipitates in a modern nanostructured ferritic alloy were investigated after extreme thermomechanical processing into a thin-walled tube geometry. It was found that the morphology of the precipitates changed from spherical to rod-shaped, with some increasing to aspect ratios of up to 9, despite the precipitate volume fraction (0.3%) and number density (>1023m−3) of precipitates remaining unchanged. High-resolution electron microscopy showed that the precipitates likely remained coherent with the Fe-matrix, while atom probe tomography confirmed that the precipitate compositions remained unaffected by the transformation. The morphological change was attributed to the shearable nature of the (Y,Ti,O)-rich precipitates, indicating they should be considered as “soft” obstacles to dislocation motion. The elongation was most pronounced in larger (>5 nm) precipitates, which may be caused by preferential dissolution of the smallest (1–3 nm) precipitates followed by the competition between re-precipitation and solute diffusion to larger precipitates during recovery heat treatments.
ACTA Vol. 200, Nov. 2020, P932-942
52. First principles study of the effect of hydrogen in austenitic stainless steels and high entropy alloys
氫在奧氏體不銹鋼和高熵合金中作用的第一性原理研究
Xiao Zhou?, William A. Curtin
X. Zhou: x.zhou@epfl.ch
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.09.070
摘要
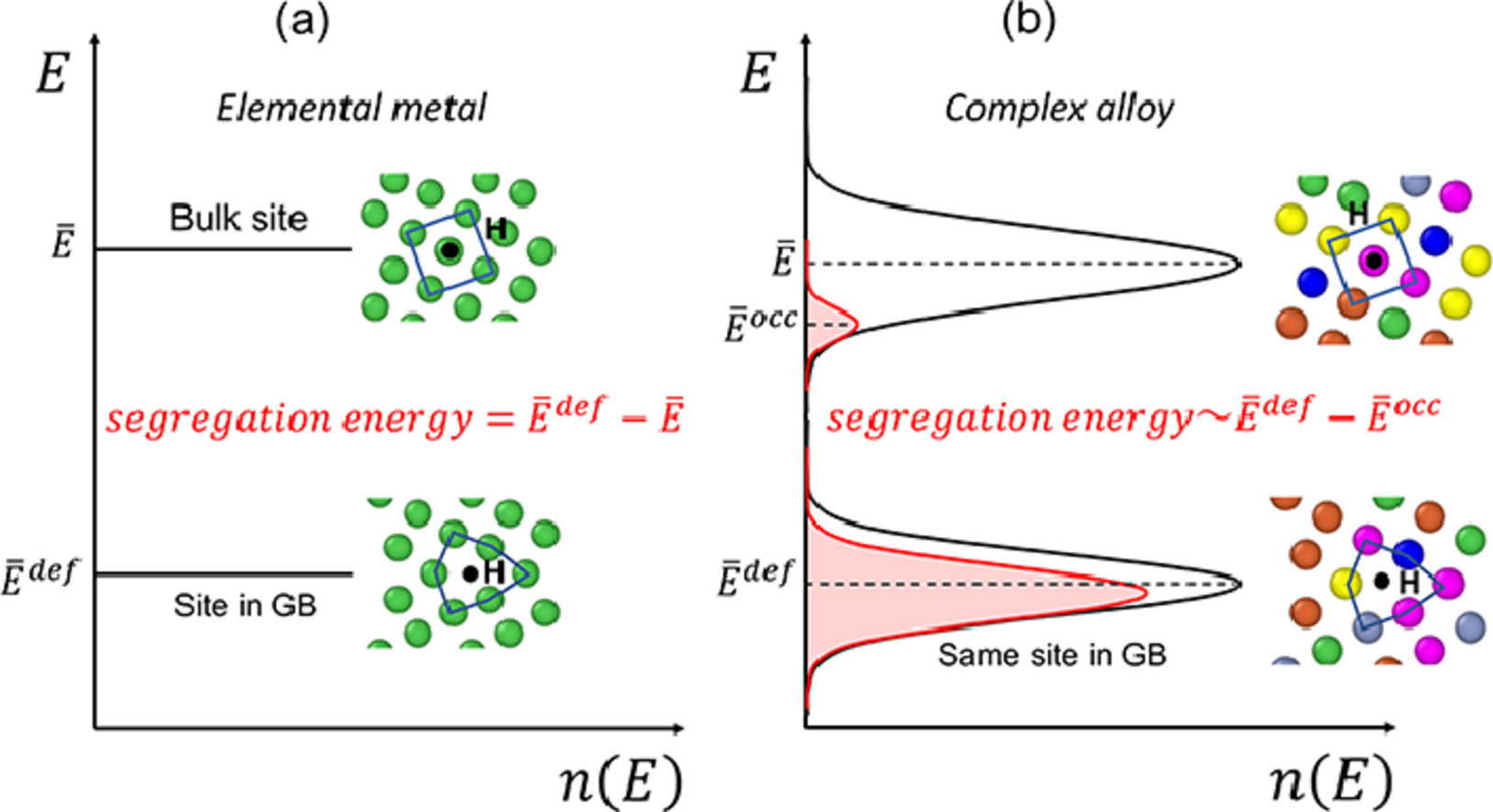
多組分奧氏體合金中的氫脆問題嚴重限制其應用。最近的實驗表明,高熵合金CoCrFeMnNi比304不銹鋼能吸收更多H,更不容易發生脆化。而在相同條件下,CoCrFeNi合金則不發生脆化。為了更好地理解氫脆,我們對304不銹鋼、316不銹鋼、CoCrFeNi和CoCrFeMnNi的H吸收、表面能和斷裂能進行了全面的第一原理模擬研究。我們采用了更為符合實際的共線順磁態模型。所有合金的H吸收位點都有統計分布。在H濃度較低的條件下,H被有效地束縛在晶格中,使得H難以擴散到缺陷或界面。通過對平均H吸收能進行擬合,可以得到與實驗H溶解度一致的結果。在所有合金中,0、50和100% H覆蓋率的(111)表面能非常相似。在此基礎之上,我們確定了兩種典型熱力學條件下的斷裂能。模擬結果表明,SS304和CoCrFeNi合金的斷裂能最低,而實驗中兩種合金卻表現出了與之不相符的脆化趨勢。這些結果表明,奧氏體合金的氫脆性能差異不僅僅是由于H吸收或斷裂能的差異導致,需要進一步研究。
英文摘要
Hydrogen (H) embrittlement in multicomponent austenitic alloys is a serious limitation to their application in many environments. Recent experiments show that the High-Entropy Alloy (HEA) CoCrFeMnNi absorbs more H than 304 Stainless Steel but is less prone to embrittlement while the HEA CoCrFeNi is not embrittled under comparable conditions. As a first step toward understanding H embrittlement, here a comprehensive first-principles study of H absorption, surface, and fracture energies in the presence of H is presented for 304 Stainless Steel, 316 Stainless Steel, CoCrFeNi, and CoCrFeMnNi. A collinear paramagnetic model of the magnetic state is used, which is likely more realistic than previous proposed magnetic states. All alloys have a statistical distribution of H absorption sites. Hence, at low concentrations, H is effectively trapped in the lattice making it more difficult for H to segregate to defects or interfaces. Agreement with experimental H solubilities across a range of chemical potentials can be achieved with minor fitting of the average H absorption energy. The (111) surface energies for 0, 50, and 100% H surface coverage are very similar across all alloys. The fracture energies for two representative thermodynamic conditions are then determined. SS304 and CoCrFeNi are found to have the lowest fracture energies, but experiments suggest rather different embrittlement tendencies. These results indicate that differences in H embrittlement across these austenitic alloys are not due solely to differences in H absorption or H-reduced fracture energy, thus requiring more sophisticated concepts than those recently found successful for fcc Ni.
ACTA Vol. 200, Nov. 2020, P943-958
53. Synergistic deformation pathways in a TWIP steel at cryogenic temperatures: In situ neutron diffraction
低溫下TWIP鋼協同變形的原位中子衍射研究
Lei Tang, Li Wang, Minshi Wang, Huibin Liu, Saurabh Kabra, Yulung Chi, Biao Cai?
B. Cai:b.cai@bham.ac.uk
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.09.075
摘要
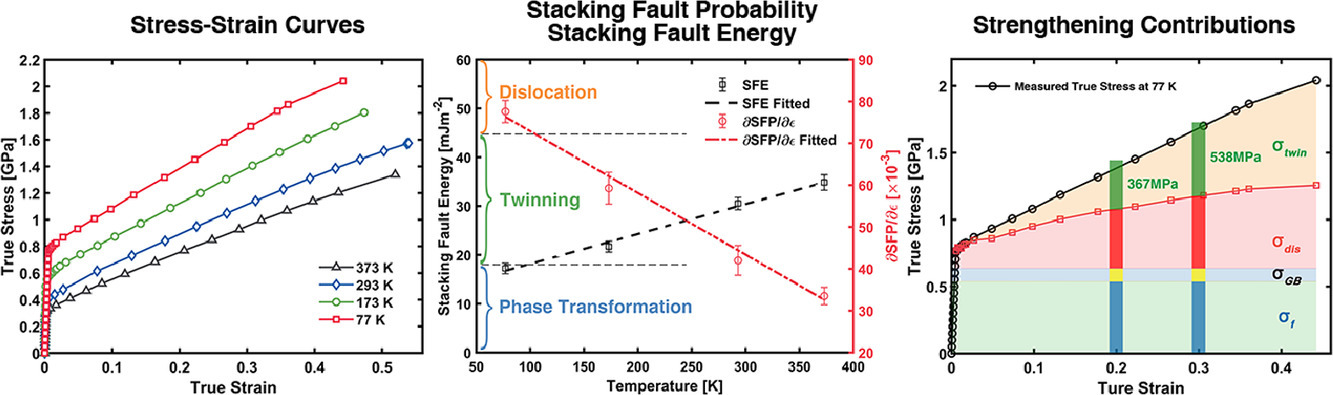
高錳鋼在低溫環境中具有廣闊的應用前景。在本研究中,我們通過原位中子衍射和顯微鏡表征,研究了低溫(373 – 77K)下高錳孿晶誘導塑性鋼的力學響應和微觀結構演化。實驗結果表明,在塑性變形過程中,溫度越低,層錯和位錯密度增加的速度越快,因此組織中有更高的位錯密度和更致密的孿晶結構。我們對層錯能進行了估計,373 K時約為34.8 mJm−2,77 K時線性下降到17.2 mJm−2。77K形變時,少量奧氏體轉變為馬氏體。我們研究了不同溫度下溶質原子、晶界、位錯和孿晶對流變應力的貢獻,發現TWIP鋼的高應變硬化能力來自于位錯和孿晶網絡的協同強化。以上研究結果揭示了低溫下層錯能、微觀組織演變和變形機理之間的關系,為設計具有優異低溫力學性能的TWIP鋼奠定了基礎。
英文摘要
High manganese steels are promising candidates for applications in cryogenic environments. In this study, we investigate the mechanical and microstructural responses of a high manganese twinning induced plasticity (TWIP) steel at a low-temperature range (from 373 to 77 K) via in situ neutron diffraction qualification and correlative microscopy characterization. During plastic deformation, stacking fault probability and dislocation density increased at a faster rate at a lower temperature, hence, higher dislocation density and denser mechanical twins were observed, confirmed by microscopic observation. Stacking fault energy was estimated, dropping linearly from 34.8 mJm−2 at 373 K to 17.2 mJm −2 at 77 K. A small amount of austenite transferred to martensite when deforming at 77 K. The contributions to flow stress from solutes, grain boundary, dislocation, and twinning were determined at different temperatures, which shows that the high work strain hardening capacity of the TWIP steel originates from the synergetic strengthening effects of dislocations and twin-twin networks. These findings reveal the relationship among stacking fault energy, microstructure, and deformation mechanisms at the low-temperature range, paving a way in designing TWIP steels with the superb mechanical performance for cryogenic applications.
ACTA Vol. 200, Nov. 2020, P959-970
54. Spinodal decomposition versus classical γ’ nucleation in a nickel-base superalloy powder: An in-situ neutron diffraction and atomic-scale analysis
鎳基高溫合金粉末中調幅分解與經典形核的原位中子衍射和原子尺度分析研究
David M. Collins?, Neil D’Souza, Chinnapat Panwisawas, Chrysanthi Papadaki, Geoff D. West, Aleksander Kostka, Paraskevas Kontis?
D.M. Collins: d.m.collins@bham.ac.uk
P.Kontis: p.kontis@mpie.de
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.09.055
摘要
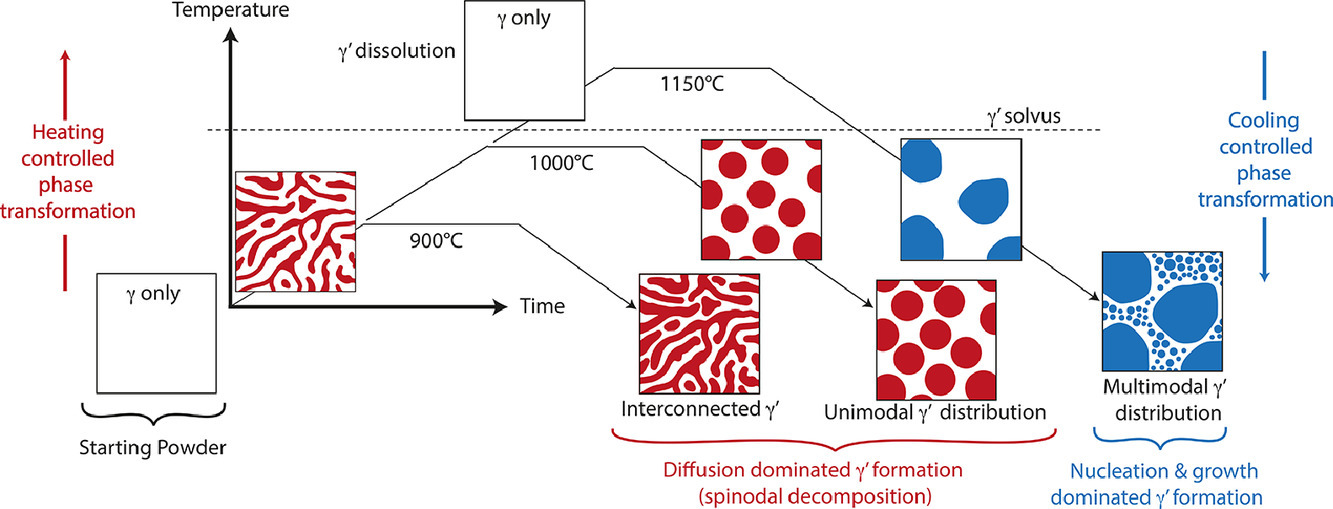
粉末成型多晶鎳基高溫合金的微觀結構和性能很大程度上取決于加工過程中的熱機械處理。本研究中,我們通過原子探針和原位中子衍射,研究了高溫對合金粉末的的影響,以闡明強化析出物的控制形成機制。最初的合金粉末為單相過飽和γ相;隨后,我們對γ’相體積分數和晶格錯配的演化進行了分析。初始粉末具有明顯的Cr、Co元素偏析,且Ni、Al、Ti與Cr存在明顯排斥。因此我們認為存在一個γ - γ’ 相變的前驅體。亞熔點熱處理導致γ’相形成單峰分布,有證據表明γ’相是通過調幅分解形成。高于熔點的熱處理會導致材料在加熱過程中形成相同的γ’相,但隨溫度進一步升高而溶解。在冷卻過程中,γ’相通過經典形核長大發生多模態析出。原子探針實驗表明,加熱和冷卻過程中形成的析出在化學成分和微觀結構上存在明顯差異。
英文摘要
Contemporary powder-based polycrystalline nickel-base superalloys inherit microstructures and properties that are heavily determined by their thermo-mechanical treatments during processing. Here, the influence of a thermal exposure to an alloy powder is studied to elucidate the controlling formation mechanisms of the strengthening precipitates using a combination of atom probe tomography and insitu neutron diffraction. The initial powder comprised a single-phase supersaturated γ only; from this, the evolution of γ’ volume fraction and lattice misfit was assessed. The initial powder notably possessed elemental segregation of Cr and Co and elemental repulsion between Ni, Al and Ti with Cr; here proposed to be a precursor for subsequent γ to γ’ phase transformations. Subsolvus heat treatments yielded a unimodal γ’ distribution, formed during heating, with evidence supporting its formation to be via spinodal decomposition. A supersolvus heat treatment led to the formation of this same γ’ population during heating, but dissolves as the temperature increases further. The γ’ then reprecipitates as a multimodal population during cooling, here forming by classical nucleation and growth. Atom probe characterisation provided intriguing precipitate characteristics, including clear differences in chemistry and microstructure, depending on whether the γ’ formed during heating or cooling.
ACTA Vol. 200, Nov. 2020, P980-991
55. Dislocation-based serrated plastic flow of high entropy alloys at cryogenic temperatures
高熵合金在低溫下基于位錯的鋸齒狀塑性流動
A.S. Tirunilai, T. Hanemann, K.-P. Weiss, J. Freudenberger, M. Heilmaier, A. Kauffmann
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.09.052
摘要
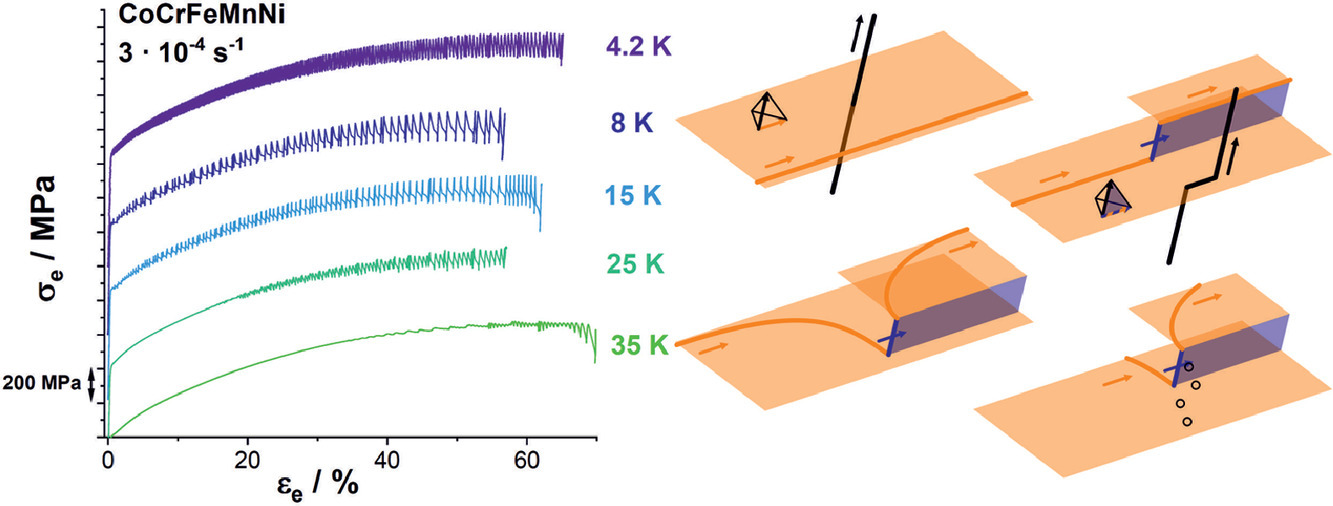
已有文獻表明,一些金屬或合金在0 K附近會發生鋸齒狀塑性變形,這可能與它材料的熱不穩定性或機械不穩定性有關。近來的一些研究結果表明,這些鋸齒是一種與位錯有關的機械現象,但目前還沒有一個完整的模型對其進行解釋。CoCrFeMnNi是一種理想的研究材料,它具有明顯的鋸齒狀塑性變形,且應力波動較大,超過100MPa。此外,其發生低溫鋸齒狀塑性變形溫度(35 K)遠高于其他合金。因此,我們提出以下以下推論:(1)溫度和位錯密度是低溫鋸齒狀塑性的重要控制參數,且這兩者不可相互替代 (2)隨著溫度降低,交滑移難度增加,導致了位錯最終發生大規模的突然擴展 (3) 以上模型通過交滑移,建立了由完全無鋸齒變形到完全鋸齒變形的漸進過渡,這與傳統模型提出的離散過渡有很大不同 (4)變形過程中溶質-位錯的相互作用和層錯能(SFE)對是控制位錯形成和交滑移的重要因素,對鋸齒狀塑性變形起關鍵作用 (5)否定了變形孿晶、形變誘導塑性和熱力學因素對鋸齒形塑性變形的直接影響。我們通過CoCrFeMnNi與CoCrNi和CoNi的對比,對其中的一些觀點進行了進一步闡述。
英文摘要
Serrated plastic deformation at temperatures close to 0 K has been previously reported in some metals and alloys, and is associated with two possible origins: (i) thermomechanical instability or (ii) mechanical instability. While some recent results indicate that serrations are a mechanical dislocation-based phenomenon, a comprehensive model does not exist. CoCrFeMnNi, an expectedly ideal candidate, exhibits severe serrated plastic deformation with large stress drops in excess of 100 MPa. Furthermore, it also shows cryogenic serrated plastic deformation at a higher temperature (35 K) than previously reported for any other alloy. The exacerbated nature of serrated plastic deformation in CoCrFeMnNi led to the following inferences: (i) temperature and dislocation density are indisputable controlling parameters for cryogenic serrated plastic deformation and they cannot supersede each another; (ii) a phenomenological model is elucidated based on the increasing difficulty for cross-slip with decreasing temperature, leading to sudden massive dislocation proliferation event; (iii) the model establishes a gradual transition from completely non-serrated to completely serrated deformation, mediated by cross-slip, as opposed to the conventional model which proposed a discrete transition; (iv) solute dislocation interaction and associated Stacking Fault Energy (SFE) during deformation plays a key role in controlling dislocation constriction and cross-slip and correspondingly serrated plastic deformation; (v) the need/direct influence of deformation twinning, transformation induced plasticity and especially thermomechanical factors on serrated plastic deformation is invalidated. Some of these points were further clarified through comparisons with CoCrNi and CoNi, also presented in the present article.
ACTA Vol. 200, Nov. 2020, P992-1007
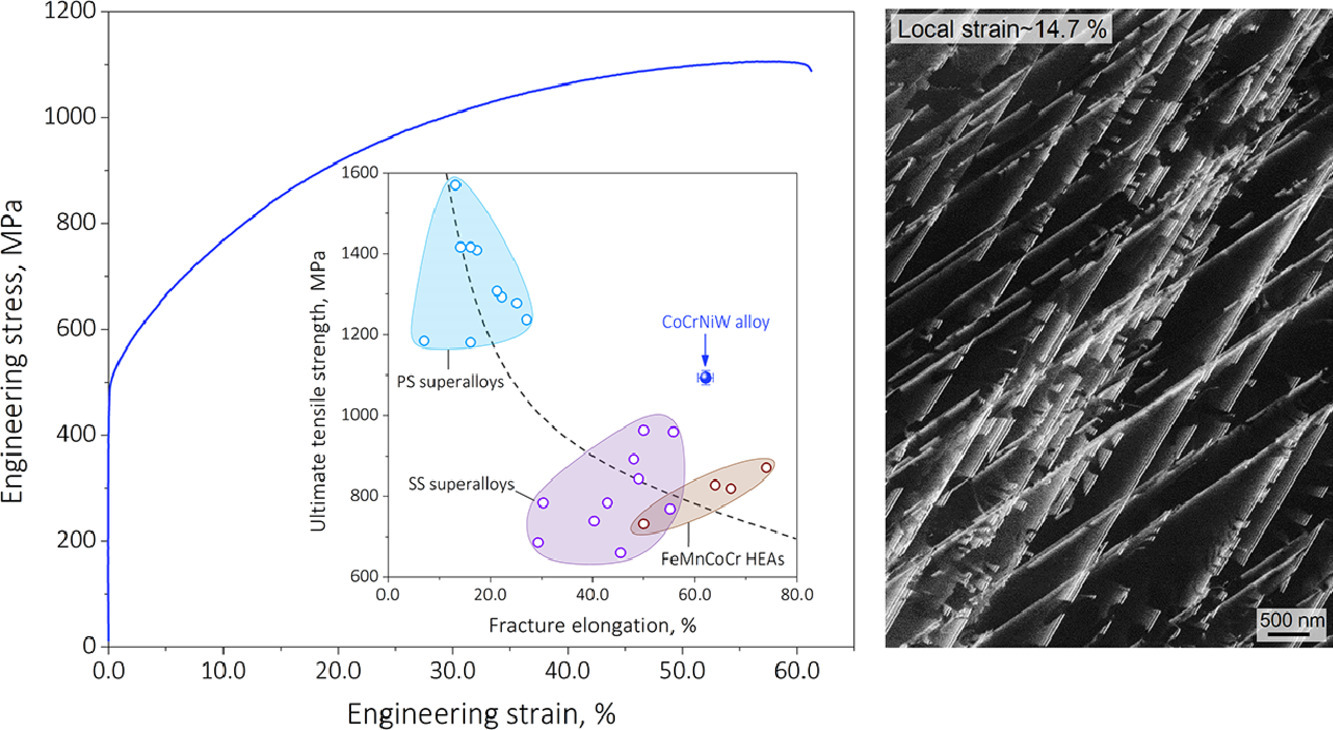
56. Deformation faulting in a metastable CoCrNiW complex concentrated alloy: A case of negative intrinsic stacking fault energy?
亞穩CoCrNiW合金的變形:一種負內秉層錯能的例子?
Shaolou Wei, Cemal Cem Tasan?
C.C. Tasan:tasan@mit.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.09.056 1359-645
摘要
晶體的微觀缺陷對于闡明合金塑性變形響應,調控宏觀力學性能具有重要意義。特別是在復雜合金(CCAs)的亞穩態組織調控中,學界大量研究了相界/孿晶界與可動位錯之間的相互作用,卻很少研究層錯與位錯的相互作用。在本研究中,我們通過原位同步輻射X射線衍射和電子隧穿比對成像(ECCI)結合的方式對CoCrNiW合金進行了研究。結果表明,層錯也可以成為材料的主要微觀變形機制,在宏觀應變硬化的同時協調微觀塑性應變。我們對相穩定性進行了熱力學模擬,揭示了這種變形斷裂響應與材料的負內秉層錯能有關。我們基于熱力學、材料組織和力學響應對實驗結果進行了詳細討論,并對層錯行為進行了原位實驗驗證。
英文摘要
Microscopic crystalline defects are of fundamental importance in unraveling the plastic deformation response and thereby tailoring the macroscopic load-bearing performances of metallic alloys. Especially in the microstructural metastability engineering context of complex concentrated alloys (CCAs), while profuse interest has been focused on phase and twin boundaries as well as their interactions with glissile dislocations, stacking faults, as another essential planar defects, have remained comparatively lessexplored and unutilized. In the present work, by investigating a metastable CoCrNiW CCA via the combination of in-situ synchrotron X-ray diffraction and in-situ electron channeling contrast imaging (ECCI), we show that stacking faults formation can also operate as the predominant deformation micro-mechanism, accommodating plastic strain while enabling macroscopic strain hardening. Through the examination of relative phase stability by thermodynamic modeling, we reveal that this sort of deformation faulting response is largely correlated with a negative intrinsic stacking fault energy. The corresponding physical revelation is explored in greater details regarding thermodynamics, structure, and mechanics, followed by in-situ experimental verification of the stacking fault activities.
ACTA Vol. 200, Nov. 2020, P1022-1037
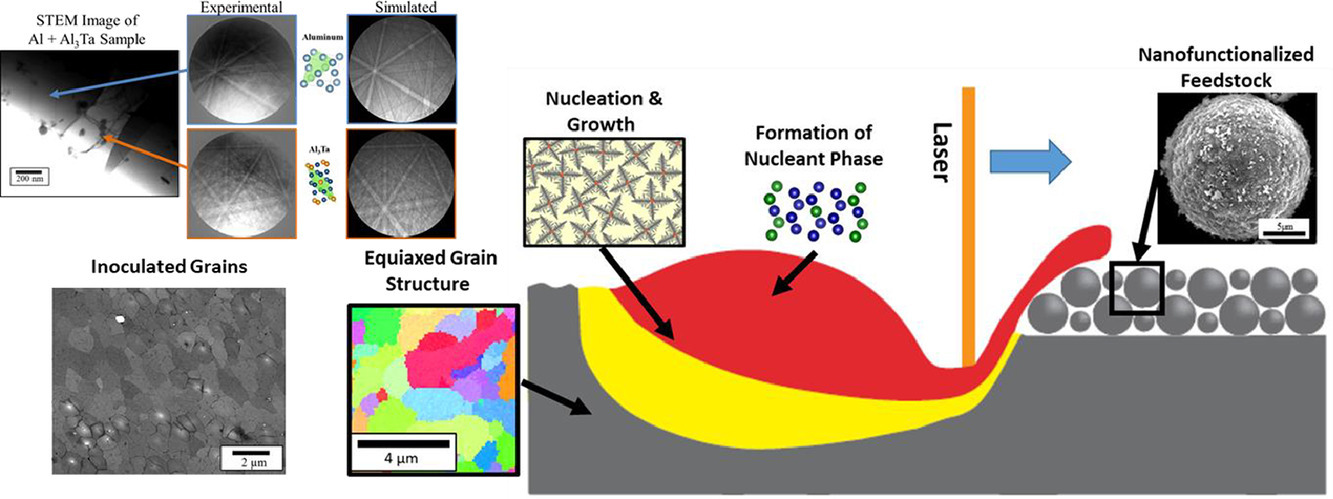
57. Grain refinement mechanisms in additively manufactured nano-functionalized aluminum
增材制造納米功能鋁合金的晶粒細化機制
J. Hunter Martin?, Brennan Yahata, Justin Mayer, Robert Mone, Ekaterina Stonkevitch, Julie Miller, Mark R. O’Masta, Tobias Schaedler, Jacob Hundley, Patrick Callahan, Tresa Pollock
J.H. Martin:jhmartin@hrl.com
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.09.043
摘要
增材制造(AM)是一種有廣闊前景的材料制備方法,能夠生產復雜的幾何形狀,實現構件的結構和性能優化。通過增材制方法制備的材料性能與組織密切相關,對晶粒各向異性尤其敏感。這就需要我們對加工過程中的材料組織的熱動力學演化有更深的理解。本研究探討了納米功能鋁合金增材制造過程中的熱力學條件和晶粒細化。Al-Ta體系是本研究的重點,Al3Ta金屬間化合物被證明具有可觀的晶粒細化能力。當加入1vol % Ta后,材料的晶粒尺寸相對純鋁細化了近1000倍。進一步研究表明,晶體學條件和孕育劑對Al3Ta的晶粒細化作用有重要影響。
英文摘要
Additive manufacturing (AM) is a new and promising production methodology adept at producing complex geometries, which can be optimized for lower weight and enhanced capabilities. The material properties of these additive components are dictated by the microstructures developed during processing, with a high sensitivity to grain structure and associated anisotropy. With this new processing modality comes the added difficulty of understanding the thermodynamics and kinetic mechanisms that dictate the evolution of microstructure. This research addresses the unique thermal conditions present in AM and the pathways for grain refinement in nanofunctionalized aluminum alloys. The Al-Ta system, in which Al3Ta intermetallic compounds are demonstrated to have substantial grain refining capacity, are the focus of this study. The grain size is shown to be reduced relative to pure aluminum by 1000X when tantalum is added at 1 vol%. The effectiveness of the Al3Ta intermetallic is dictated by the crystallography and availability of the inoculant phase under AM conditions.
微信公眾號:Goal Science
投稿郵箱:wechat@gs-metals.com
投稿微信:GSmaterial
