金屬頂刊雙語導(dǎo)讀丨Scripta Mater. Vol.193, 1 Mar. 2021(全)
2021-01-27 來源:Goal Science
Vol. 193 目錄
1. Machine learning based surrogate modeling approach for mapping crystal deformation in three dimensions
基于機(jī)器學(xué)習(xí)的替代建模方法,用于繪制三維晶體變形
2. Hydride formation in Ti6Al4V: An in situ synchrotron X-ray diffraction study
Ti6Al4V中氫化物的形成:原位同步X射線衍射研究
3. Atomic configurations of planar defects in μ phase in Ni-based superalloys
鎳基高溫合金μ相中平面缺陷的原子構(gòu)型
4. Race against the Machine: can deep learning recognize microstructures as well as the trained human eye?
和機(jī)器賽跑:深度學(xué)習(xí)能像訓(xùn)練有素的人眼那樣識(shí)別微觀組織嗎?
5. Revisiting ω phase embrittlement in metastable β titanium alloys: Role of elemental partitioning
回顧亞穩(wěn)β鈦合金中的ω相脆化:元素配分的作用
6. Bimorphic microstructure in Ti-6Al-4V alloy manipulated by spark plasma sintering and in-situ press forging
火花等離子體燒結(jié)和原位鍛造處理的Ti-6Al-4V合金的雙晶組織
7. Deformation-induced ultrafine grains near fatigue crack tip and correlative fatigue damage in Al matrix composite
鋁基復(fù)合材料疲勞裂紋尖端附近變形誘導(dǎo)的超細(xì)晶粒及其相關(guān)的疲勞損傷
8. Multiscale characterization of the 3D network structure of metal carbides in a Ni superalloy by synchrotron X-ray microtomography and ptychography
用同步加速X射線顯微層析術(shù)和疊層成像術(shù)對(duì)鎳基超合金中金屬碳化物的3D網(wǎng)絡(luò)結(jié)構(gòu)進(jìn)行多尺度表征
9. Ensuring the strength and ductility synergy in an austenitic stainless steel: single- or multi-phase hetero-structures design
確保奧氏體不銹鋼強(qiáng)度和塑性的協(xié)同提升:?jiǎn)蜗嗷蚨嘞喈愘|(zhì)結(jié)構(gòu)設(shè)計(jì)
10. High-throughput mapping method for mechanical properties, oxidation resistance, and phase stability in Ni-based superalloys using composition-graded unidirectional solidified alloys
基于成分梯度單向凝固的鎳基高溫合金力學(xué)性能、抗氧化性和相穩(wěn)定性的高通量映射方法
11. Stable high-entropy TiZrHfNbVCrMoMnFeCoNiAl Laves phase
穩(wěn)定的高熵TiZrHfNbVCrMoMnFeCoNiAl Laves相
12. Formation of core-shell type structure in Duplex Martensitic Steel
雙相馬氏體鋼中核殼型結(jié)構(gòu)的形成
13. Achieving exceptionally high strength in binary Mg-13Gd alloy by strong texture and substantial precipitates
通過強(qiáng)烈的織構(gòu)和大量析出,在二元Mg-13Gd合金中實(shí)現(xiàn)極高的強(qiáng)度
14. Modeling the precipitation processes and the formation of hierarchical microstructures in a single crystal high entropy superalloy
模擬單晶高熵高溫合金中的析出過程和分層微觀組織的形成
15. Properties and influence of microstructure and crystal defects in Fe2VAl modified by laser surface remelting
激光表面重熔改性Fe2VAl的性能及其微觀組織和晶體缺陷的影響
SCRIPTA
Vol. 193, 1 Mar. 2021, P1-5
1. Machine learning based surrogate modeling approach for mapping crystal deformation in three dimensions
基于機(jī)器學(xué)習(xí)的替代建模方法,用于繪制三維晶體變形
Anup Pandey?, Reeju Pokharel
Anup Pandey: anup@lanl.gov
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.10.025
摘要
我們提出了一種基于機(jī)器學(xué)習(xí)的替代建模方法,用于預(yù)測(cè)多晶材料在單軸拉伸載荷下空間分辨的三維晶體學(xué)取向演化。我們的方法比現(xiàn)有的晶體塑性方法快了一個(gè)數(shù)量級(jí),可以用來模擬其他計(jì)算方法無法實(shí)現(xiàn)的大體積體系。這項(xiàng)工作是對(duì)現(xiàn)有基于機(jī)器學(xué)習(xí)模型的重大突破,現(xiàn)有的模型要么局限于2D結(jié)構(gòu),要么只能提供平均的,而非局部的三維全場(chǎng)預(yù)測(cè)結(jié)果。我們展示了替代模型方法在搜集面心立方銅試樣拉伸變形實(shí)驗(yàn)數(shù)據(jù)的速度和準(zhǔn)確性。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 193, 1 Mar. 2021, P12-16
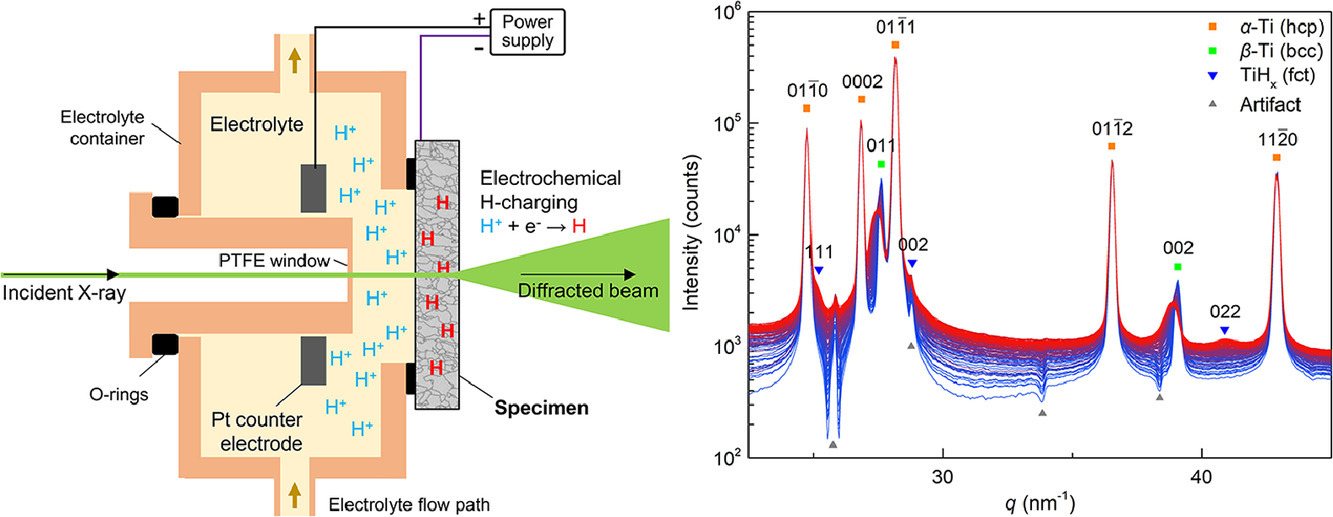
2. Hydride formation in Ti6Al4V: An in situ synchrotron X-ray diffraction study
Ti6Al4V中氫化物的形成:原位同步X射線衍射研究
Jinwoo Kim, Jiyun Kang, C. Cem Tasan?
C. Cem Tasan: tasan@mit.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.10.025
摘要
吸氫會(huì)導(dǎo)致Ti6Al4V中氫化物形成、晶格應(yīng)變和其他晶體學(xué)變化。為了更好地監(jiān)測(cè)和了解這些變化,我們開發(fā)了一種用于透射X射線衍射的原位充氫裝置,并將其用于高能同步X射線源。我們觀察到兩相中氫進(jìn)入引起的各向異性晶格膨脹以及氫化物形成導(dǎo)致的微應(yīng)變的演化。我們利用電子背散射衍射分析,對(duì)氫化物相進(jìn)行了晶體學(xué)表征,包括其與相鄰相的取向關(guān)系。本文還進(jìn)一步討論了該方法在研究氫與微觀結(jié)構(gòu)交互作用方面的應(yīng)用。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 193, 1 Mar. 2021, P27-32
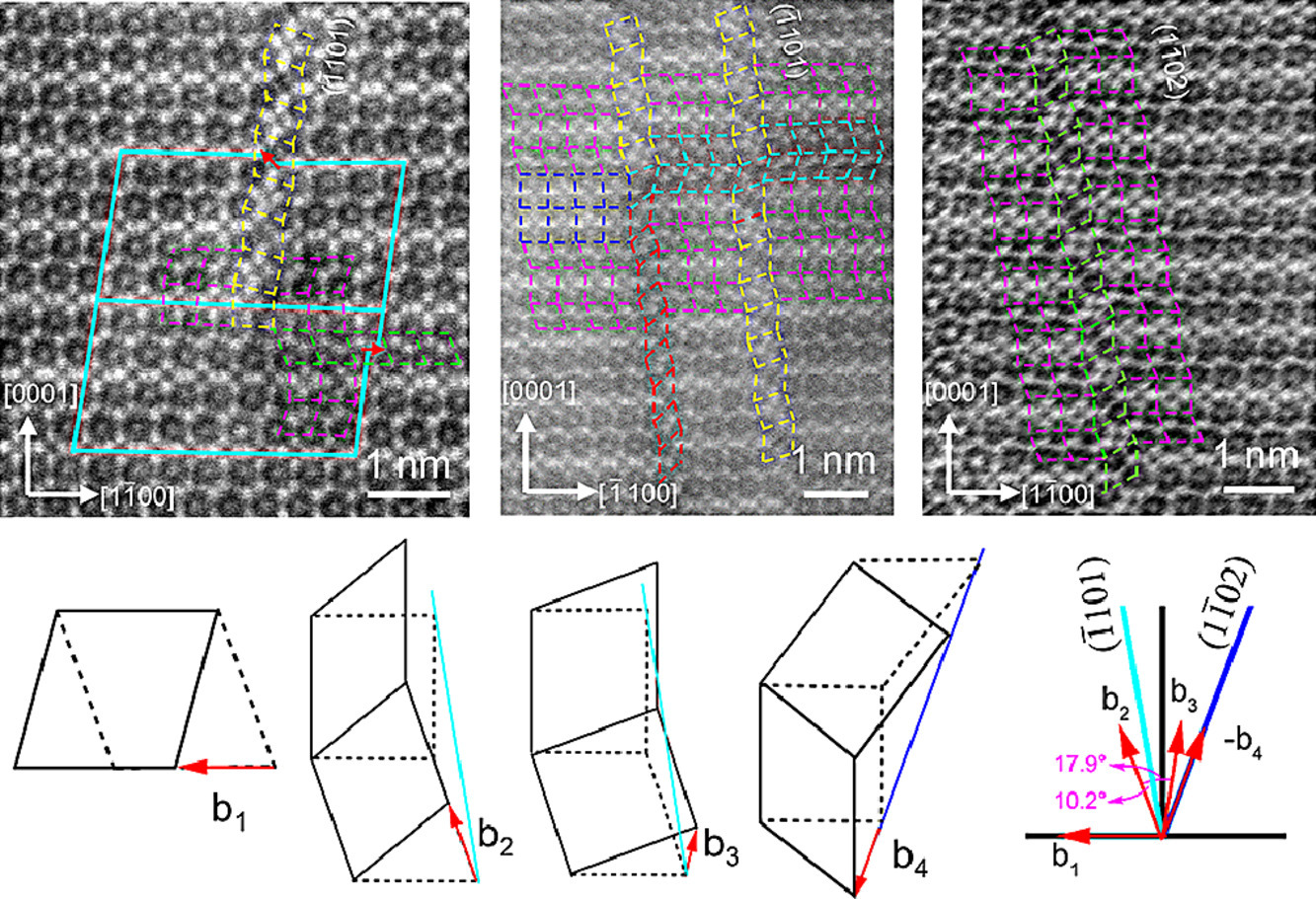
3. Atomic configurations of planar defects in μ phase in Ni-based superalloys
鎳基高溫合金μ相中平面缺陷的原子構(gòu)型
Yongxin Cheng, Guanglei Wang, Jide Liu, Lianlong He?
Lianlong He: llhe@imr.ac.cn,中科院沈陽金屬所
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.09.045
摘要
高溫合金中普遍存在μ拓?fù)渲旅芟啵浔菊髯冃螌?duì)其性能至關(guān)重要。通過像差校正掃描透射電鏡和幾何結(jié)構(gòu)分析,研究了μ相平面缺陷的原子構(gòu)型。研究發(fā)現(xiàn),μ相基面滑移是由Laves內(nèi)三層同步剪切完成的,而非基面的剪切變形則與長(zhǎng)程擴(kuò)散或局部原子重排有關(guān)。與(1-102)金字塔平面不同,(-1101)金字塔平面上的平面錯(cuò)位位移向量偏離滑移平面,導(dǎo)致錯(cuò)位區(qū)域收縮或膨脹。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 193, 1 Mar. 2021, P33-37
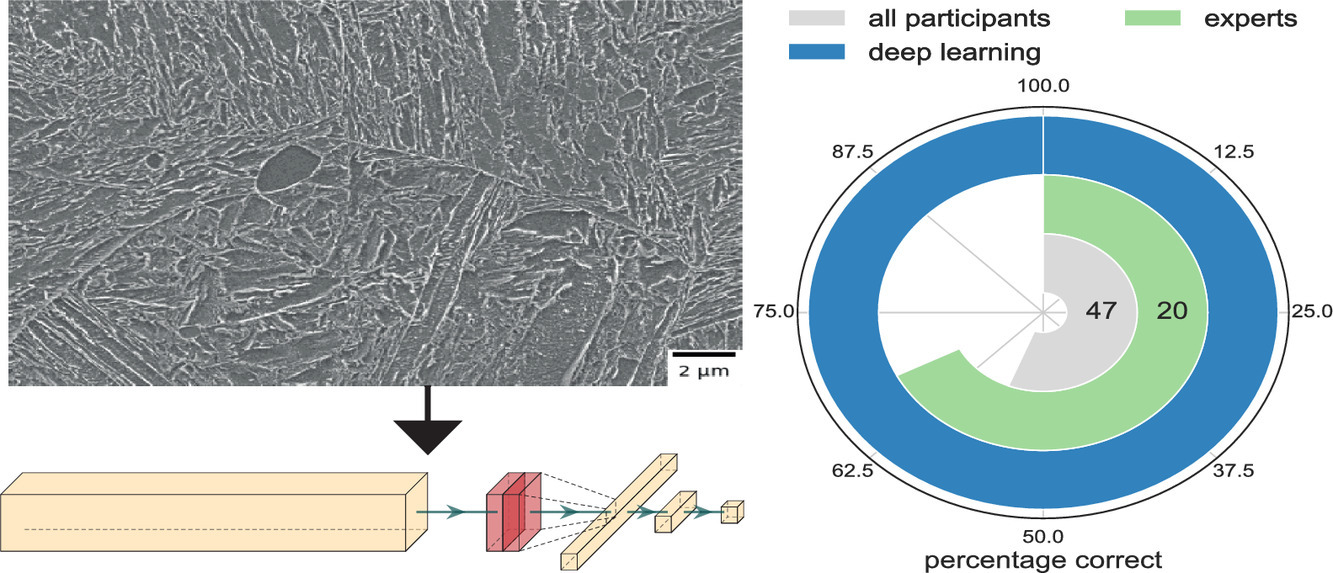
4. Race against the Machine: can deep learning recognize microstructures as well as the trained human eye?
和機(jī)器賽跑:深度學(xué)習(xí)能像訓(xùn)練有素的人眼那樣識(shí)別微觀組織嗎?
Michiel Larmuseau?, Michael Sluydts, Koenraad Theuwissen, Lode Duprez, TomDhaene, Stefaan Cottenier
Michiel Larmuseau: michiel.larmuseau@ugent.be
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.10.026
摘要
圖像識(shí)別中深度學(xué)習(xí)的前景表明了材料科學(xué)中微觀分析的巨大潛力。在材料研究中采用這種方法的一個(gè)主要挑戰(zhàn)是可供訓(xùn)練模型使用的圖像數(shù)量有限。在此,我們提出了一種方法,以創(chuàng)建準(zhǔn)確的圖像識(shí)別模型與小數(shù)據(jù)集。通過明確地考慮到放大率和引入適當(dāng)?shù)霓D(zhuǎn)換,我們?cè)谀P椭薪Y(jié)合了材料科學(xué)盡可能多的見解。這需要對(duì)復(fù)雜的深度學(xué)習(xí)模型進(jìn)行高數(shù)據(jù)效率的訓(xùn)練。我們的結(jié)果表明,用本方法訓(xùn)練的模型能夠超過人類專家。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 193, 1 Mar. 2021, P38-42
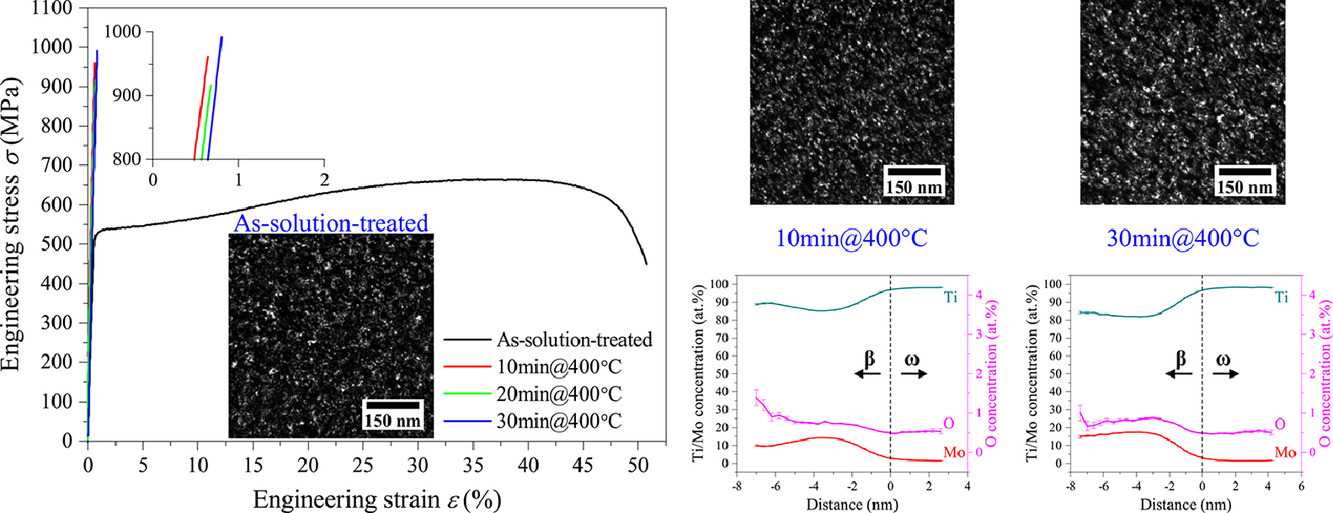
5. Revisiting ω phase embrittlement in metastable β titanium alloys: Role of elemental partitioning
回顧亞穩(wěn)β鈦合金中的ω相脆化:元素配分的作用
M.J. Lai?, T. Li, F.K. Yan, J.S. Li?, D. Raabe
M.J. Lai: lai@nwpu.edu.cn
J.S. Li: ljsh@nwpu.edu.cn,西北工業(yè)大學(xué)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.10.031
摘要
我們用透射電鏡和原子探針斷層掃描技術(shù)研究了最初包含韌性ω相的Ti-12Mo (wt. %)模型合金中,β和ω相之間元素配分對(duì)合金脆化的影響。結(jié)果表明在400°C時(shí)效短短10min,合金就已經(jīng)發(fā)生了脆化,而這時(shí)ω顆粒的尺寸、顆粒間距以及體積分?jǐn)?shù)幾乎沒有發(fā)生變化。時(shí)效誘導(dǎo)脆化的根源是在時(shí)效過程中ω顆粒對(duì)Mo元素(>5 at.%)的強(qiáng)烈排斥,這會(huì)導(dǎo)致ω顆粒剪切模量(>30GPa)的急劇增加,使得在宏觀屈服前就發(fā)生強(qiáng)烈的塑性流變應(yīng)力集中,引起裂紋的萌生。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 193, 1 Mar. 2021, P43-48
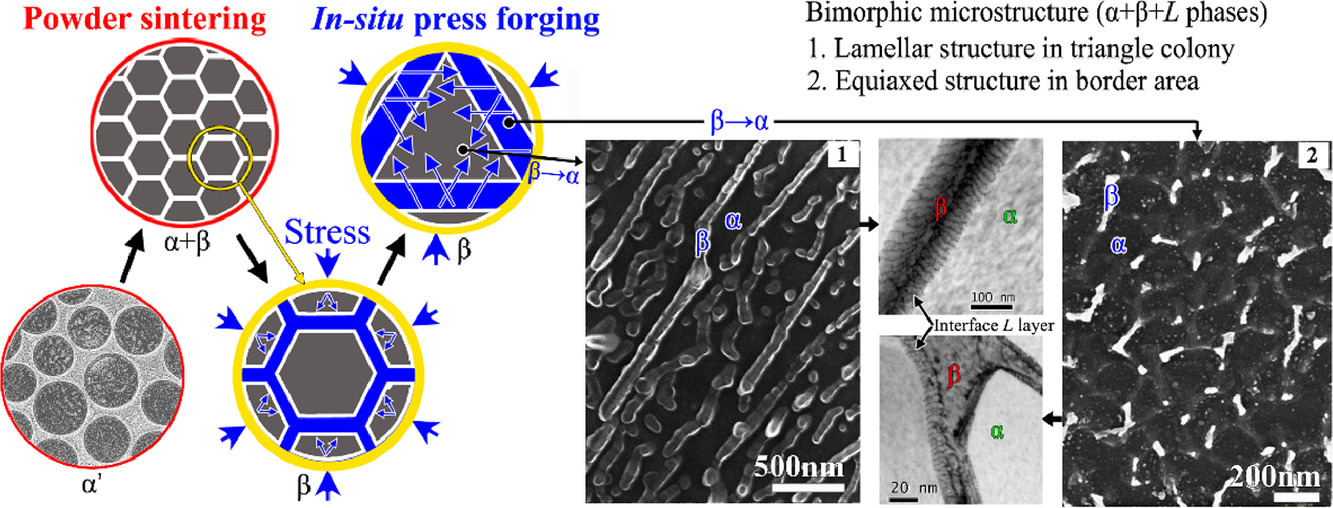
6. Bimorphic microstructure in Ti-6Al-4V alloy manipulated by spark plasma sintering and in-situ press forging
火花等離子體燒結(jié)和原位鍛造處理的Ti-6Al-4V合金的雙晶組織
L.M. Kang, Y.J. Cai, X.C. Luo, Z.J. Li, X.B. Liu, Z. Wang, Y.Y. Li, C. Yang?
C. Yang: cyang@scut.edu.cn,華南理工大學(xué)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.10.035
摘要
本文報(bào)道了一種粉末燒結(jié)和原位壓鍛的方法,用于控制Ti-6Al-4V合金中一種新的雙晶組織。微觀組織包括具有超細(xì)α/β層狀結(jié)構(gòu)的典型三角區(qū)域,具有超細(xì)等軸α晶和分散的納米/超細(xì)β晶的邊界區(qū)域以及α/β界面L層。令人驚訝的是,該雙晶合金在拉伸和壓縮條件下均表現(xiàn)出優(yōu)異的力學(xué)性能,遠(yuǎn)優(yōu)于目前報(bào)道的其他Ti-6Al-4V合金及其復(fù)合材料。因此,本研究為制備高性能金屬合金提供了一種簡(jiǎn)單而經(jīng)濟(jì)的方法。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 193, 1 Mar. 2021, P49-54
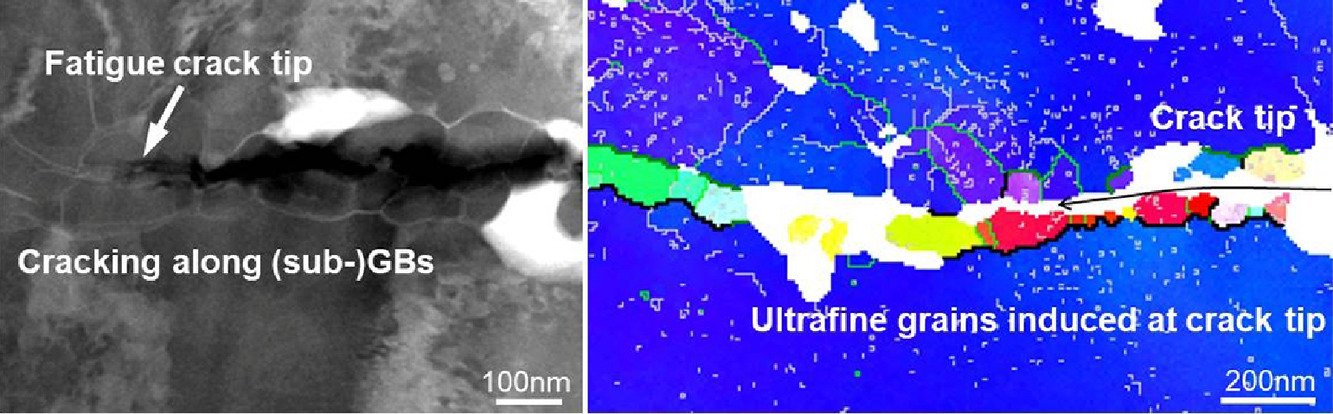
7. Deformation-induced ultrafine grains near fatigue crack tip and correlative fatigue damage in Al matrix composite
鋁基復(fù)合材料疲勞裂紋尖端附近變形誘導(dǎo)的超細(xì)晶粒及其相關(guān)的疲勞損傷
Jiwei Geng, Yugang Li, Hongyu Xiao, Zhiping Wang, Mingliang Wang, Dong Chen?, Haowei Wang
Dong Chen: chend@sjtu.edu.cn,上海交通大學(xué)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.10.040
摘要
我們通過透射菊池衍射和透射電子顯微鏡對(duì)TiB2/Al復(fù)合材料疲勞裂紋尖端附近的組織演變和相關(guān)的損傷機(jī)理進(jìn)行了新的認(rèn)識(shí)。我們發(fā)現(xiàn)微形變帶從裂紋尖端形成,沿著滑移面延伸。超細(xì)晶是在形變帶中產(chǎn)生的,疲勞裂紋傾向于沿著這些形變誘導(dǎo)的邊界擴(kuò)展。此過程被首次證明是裂紋跨越母相晶粒和晶界的基本過程。在裂紋尖端前部,TiB2顆粒可通過阻止變形帶的連續(xù)擴(kuò)展來影響裂紋生長(zhǎng)。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 193, 1 Mar. 2021, P71-76
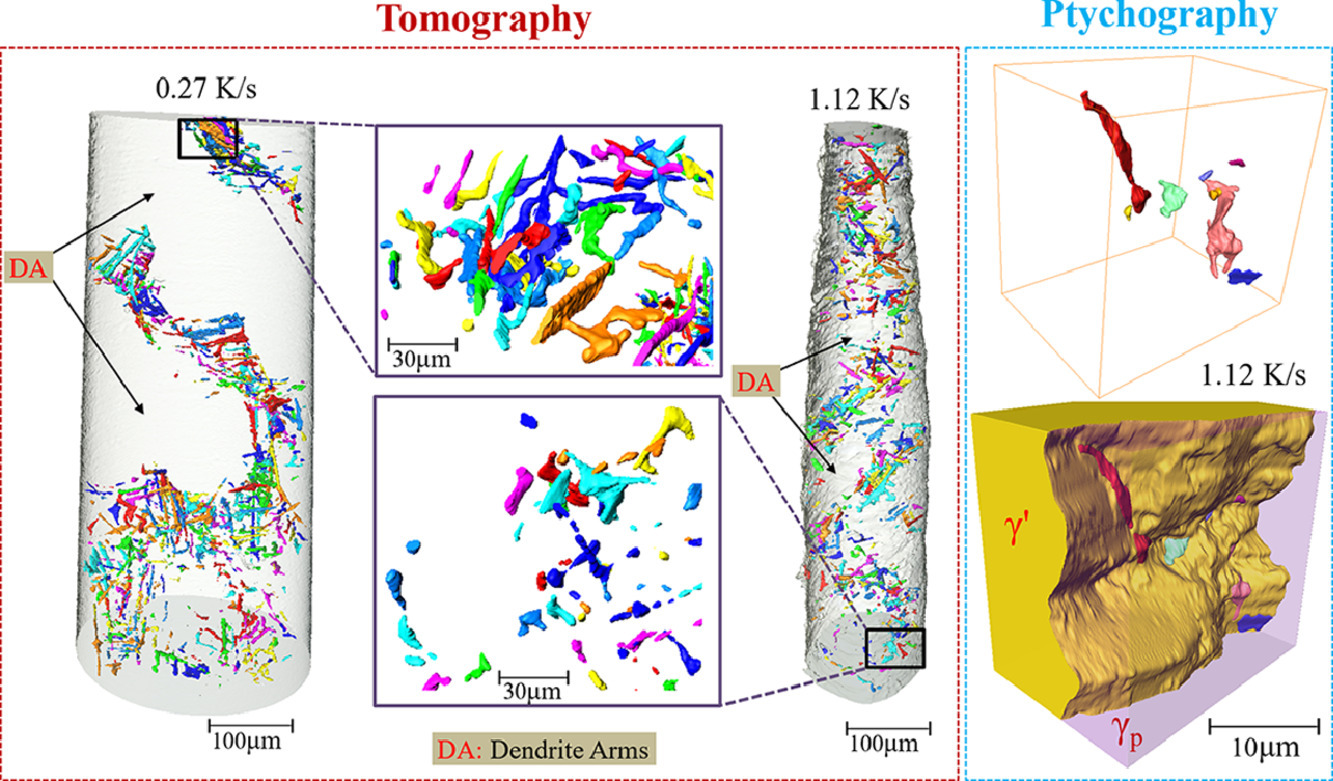
8. Multiscale characterization of the 3D network structure of metal carbides in a Ni superalloy by synchrotron X-ray microtomography and ptychography
用同步加速X射線顯微層析術(shù)和疊層成像術(shù)對(duì)鎳基超合金中金屬碳化物的3D網(wǎng)絡(luò)結(jié)構(gòu)進(jìn)行多尺度表征
Zhiguo Zhang, Jia Chuan Khong, Billy Koe, Shifeng Luo, Shi Huang, Ling Qin, Silvia Cipiccia, Darren Batey, Andrew J.Bodey, Christoph Rau, Yu Lung Chiu, Zhu Zhang, Jean-Christophe Gebelin, Nick Green, Jiawei Mi?
Jiawei Mi: J.Mi@hull.ac.uk
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.10.032
摘要
采用同步X射線顯微層析術(shù)和疊層成像術(shù)對(duì)鑄態(tài)IN713LC鎳基高溫合金中金屬碳化物的三維網(wǎng)絡(luò)結(jié)構(gòu)、形貌和分布進(jìn)行了表征。MC型碳化物主要分布在基體γ和γ'相的晶界。凝固冷速的差異對(duì)MC型碳化物的體積分?jǐn)?shù)影響不大,但是會(huì)強(qiáng)烈影響碳化物的尺寸、分布和網(wǎng)絡(luò)形貌。根據(jù)殘余液相的局部成分和幾何約束,碳化物可以形成球形、條狀或網(wǎng)狀形貌。研究結(jié)果表明,兩種互補(bǔ)層析技術(shù)協(xié)同應(yīng)用于三維空間非破壞性復(fù)雜多相結(jié)構(gòu)的研究具有一定的優(yōu)勢(shì)和技術(shù)潛力,空間分辨率可達(dá)~30 nm。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 193, 1 Mar. 2021, P81-85
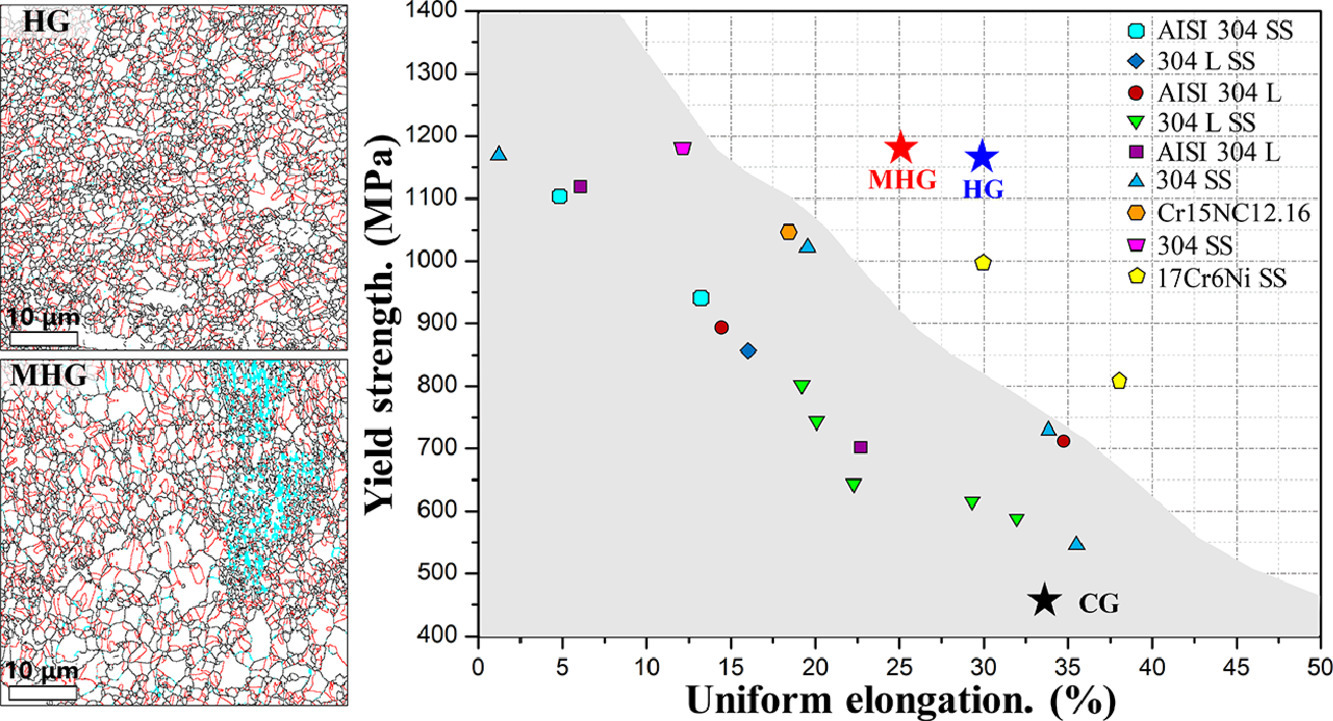
9. Ensuring the strength and ductility synergy in an austenitic stainless steel: single- or multi-phase hetero-structures design
確保奧氏體不銹鋼強(qiáng)度和塑性的協(xié)同提升:?jiǎn)蜗嗷蚨嘞喈愘|(zhì)結(jié)構(gòu)設(shè)計(jì)
Yong Li, Wei Li?, Shilei Li, Na Min, Laizhu Jiang, Qinglong Zhou, Xuejun Jin
Wei Li: weilee@sjtu.edu.cn,上海交通大學(xué)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.10.041
摘要
在許多合金體系中,異質(zhì)微觀組織被提出用來優(yōu)化力學(xué)性能,以協(xié)同提高強(qiáng)度和塑性。本研究通過調(diào)整熱機(jī)械加工參數(shù),獲得了包含細(xì)晶和粗晶的多相異質(zhì)結(jié)構(gòu),其中鐵素體分布在納米晶粒周圍。結(jié)果表明,多相異質(zhì)結(jié)構(gòu)鋼的屈服強(qiáng)度達(dá)到1.2 GPa,是粗晶組織樣品屈服強(qiáng)度的2倍以上,且均勻延伸率損失較小。我們用同步X射線衍射研究了這種復(fù)雜組織中的微觀載荷轉(zhuǎn)移。樣品的持續(xù)加工硬化歸功于異質(zhì)變形誘導(dǎo)應(yīng)力,以及相變誘導(dǎo)塑性(TRIP)效應(yīng)和孿晶誘導(dǎo)塑性(TWIP)效應(yīng)的共同激活。對(duì)比之下,單相異質(zhì)結(jié)構(gòu)鋼的強(qiáng)度較低,但均勻延伸率較高。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 193, 1 Mar. 2021, P91-96
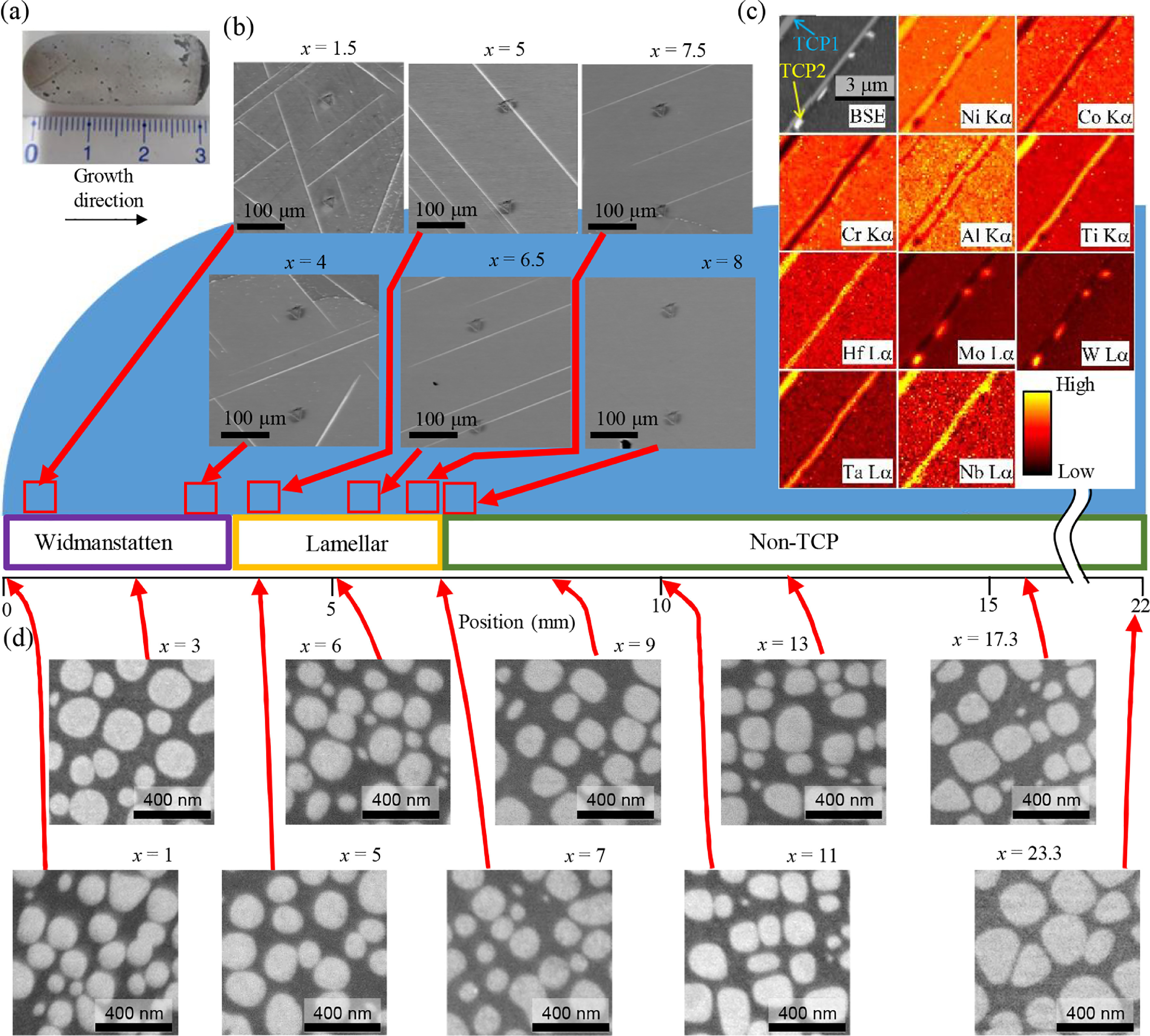
10. High-throughput mapping method for mechanical properties, oxidation resistance, and phase stability in Ni-based superalloys using composition-graded unidirectional solidified alloys
基于成分梯度單向凝固的鎳基高溫合金力學(xué)性能、抗氧化性和相穩(wěn)定性的高通量映射方法
Ayako Ikeda?, Kenta Goto, Toshio Osada, Ikumu Watanabe, Kyoko Kawagishi
Ayako Ikeda: IKEDA.Ayako@nims.go.jp
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.10.043
摘要
本文提出了一種新的高通量實(shí)驗(yàn)評(píng)估方法,用來評(píng)價(jià)鎳基高溫合金的相穩(wěn)定性、力學(xué)性能和氧化性能。利用Bridgman法,研究了一個(gè)樣品中9種元素在長(zhǎng)距離內(nèi)(~24 mm)的漸變特征以及η、μ和γ′相體積分?jǐn)?shù)等寬范圍的微觀組織特征。我們利用納米壓痕法和微觀組織觀察提取了γ-γ′兩相結(jié)構(gòu)的彈性模量/硬度,并評(píng)價(jià)了氧化樣品中的氧化層。我們的方法使得獲得大量與高溫合金成分和微觀組織相關(guān)的數(shù)據(jù)集成為可能。

SCRIPTA
Vol. 193, 1 Mar. 2021, P108-111
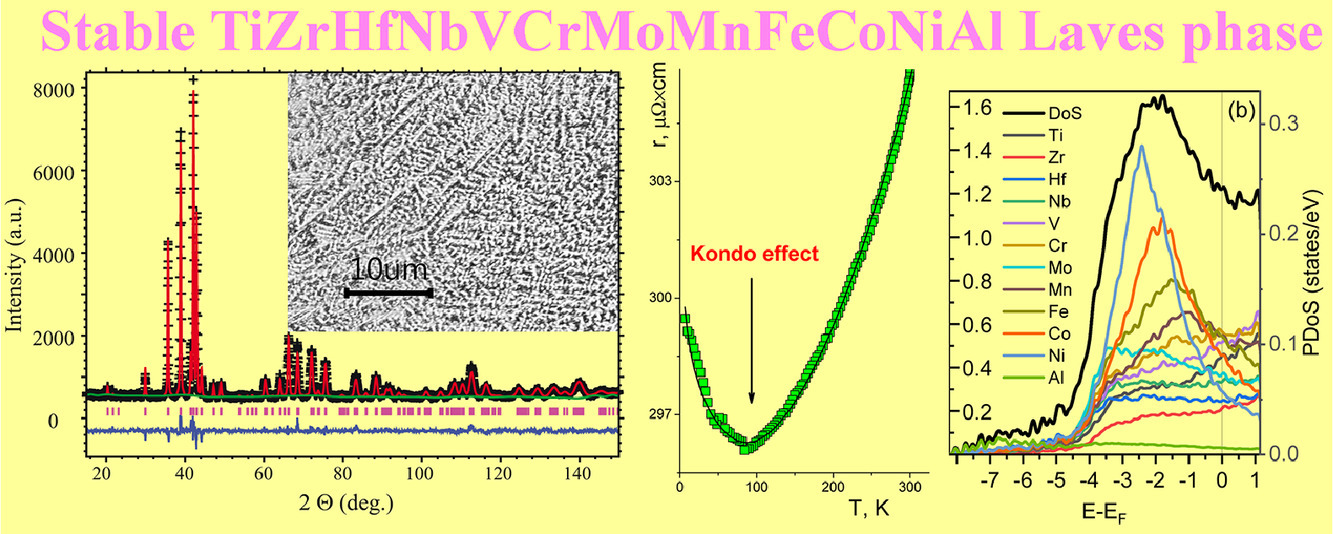
11. Stable high-entropy TiZrHfNbVCrMoMnFeCoNiAl Laves phase
穩(wěn)定的高熵TiZrHfNbVCrMoMnFeCoNiAl Laves相
S.A. Uporov?, R.E. Ryltsev, S.Kh. Estemirova, E.V. Sterkhov, N.M. Chtchelkatchev
S.A. Uporov: segga@bk.ru
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.10.049
摘要
近年來在高熵材料領(lǐng)域的研究發(fā)現(xiàn)了一個(gè)有趣的結(jié)果:具有不同價(jià)態(tài)和半徑的化學(xué)元素組成的多組分體系可以形成具有金屬間Laves相結(jié)構(gòu)的單相固溶體。本文報(bào)道了在TiZrHfNbVCrMoMnFeCoNiAl合金中制備六方Laves相(C14,原型MgZn2)的過程。在973 K熱處理50 h后,相很穩(wěn)定。為了表征這種材料,我們驗(yàn)證了它的導(dǎo)電性和磁性能。測(cè)量結(jié)果表明,Laves相為Curie-Weiss順磁體,在80 K時(shí)表現(xiàn)出金屬導(dǎo)電性和明顯的類Kondo異常。對(duì)實(shí)驗(yàn)數(shù)據(jù)的分析和從頭計(jì)算表明,化學(xué)復(fù)雜性和成分無序性導(dǎo)致了強(qiáng)烈的s-d帶散射,從而導(dǎo)致了導(dǎo)帶中相當(dāng)高密度的d態(tài)。

SCRIPTA
Vol. 193, 1 Mar. 2021, P112-116
12. Formation of core-shell type structure in Duplex Martensitic Steel
雙相馬氏體鋼中核殼型結(jié)構(gòu)的形成
Kenji Kaneko?, Takuya Maeda, Yasuhito Kawahara, Kazuhiro Ichino, Takuro Masumura, Toshihiro Tsuchiyama, Hiroyuki Shirahata, Ryuji Uemori
Kenji Kaneko: kaneko@zaiko.kyushu-u.ac.jp
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.10.044
摘要
通過透射電子顯微鏡研究了淬火和臨界退火中錳鋼的微觀組織,以更好地理解γ-?和γ-α'馬氏體相變。各相之間的取向關(guān)系為(-110)α′//(0001)ε,[111]α′//[11-20]ε(淬火樣品),和(-110)α′//(-111)γ//(0001)ε,[111]α′//[110]γ//[11-20]ε(臨界退火樣品)。另外,我們證實(shí)了具有Mn濃度梯度的核殼型微觀組織的存在,其為殘余奧氏體包圍著?-馬氏體。我們發(fā)現(xiàn)各相的Mn濃度取決于臨界退火過程中Mn擴(kuò)散控制的逆轉(zhuǎn)變奧氏體的長(zhǎng)大。結(jié)果強(qiáng)烈表明在臨界退火過程中形成的Mn濃度梯度會(huì)影響相穩(wěn)定性,從而導(dǎo)致ε/γ核殼微觀結(jié)構(gòu)的形成。
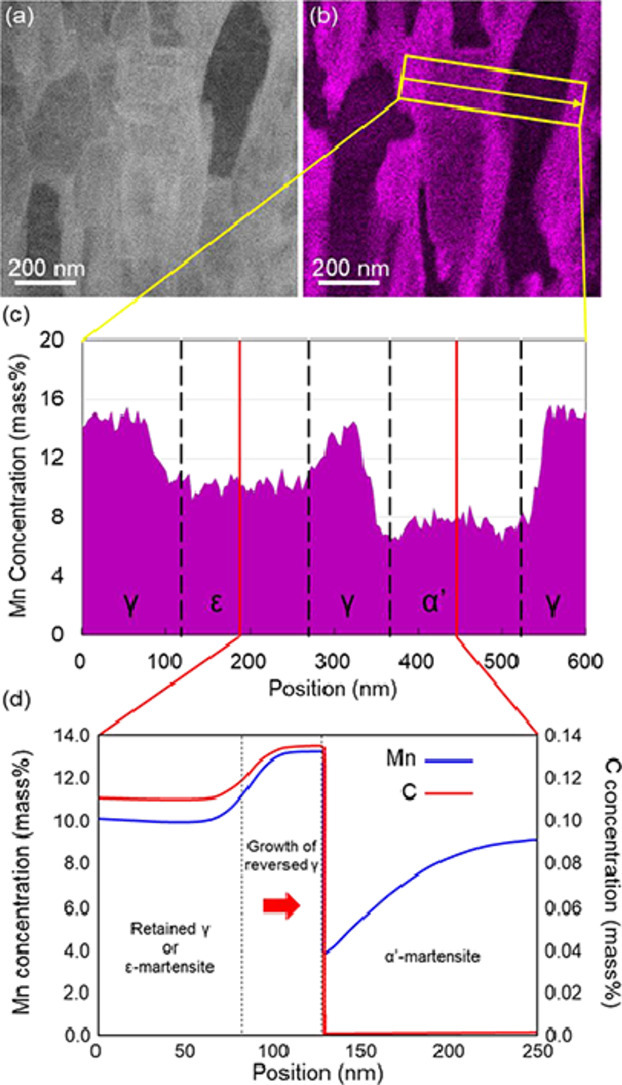

SCRIPTA
Vol. 193, 1 Mar. 2021, P142-146
13. Achieving exceptionally high strength in binary Mg-13Gd alloy by strong texture and substantial precipitates
通過強(qiáng)烈的織構(gòu)和大量析出,在二元Mg-13Gd合金中實(shí)現(xiàn)極高的強(qiáng)度
R.G. Li, H.R. Li, H.C. Pan?, D.S. Xie, J.H. Zhang?, D.Q. Fang?, Y.Q. Dai, D.Y. Zhao, H. Zhang
H.C. Pan: panhc@atm.neu.edu.cn,中國(guó)東北大學(xué)
J.H. Zhang: jinghuaizhang@gmail.com,哈爾濱工程大學(xué)
D.Q. Fang: fangdaqing@xjtu.edu.cn,西安交通大學(xué)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.10.052
摘要
在簡(jiǎn)單的二元Mg-Gd合金中,僅以很小的擠壓比即可獲得超高強(qiáng)度,其主要的強(qiáng)化機(jī)制與以前的報(bào)道有所不同。Mg-13Gd合金的熱擠壓比為4時(shí),其拉伸屈服強(qiáng)度(TYS)可以達(dá)到350 MPa。占大比例的非動(dòng)態(tài)再結(jié)晶區(qū)域內(nèi)的強(qiáng)織構(gòu)和內(nèi)部的位錯(cuò)釘扎對(duì)擠壓態(tài)合金的強(qiáng)度有很大貢獻(xiàn)。我們首次發(fā)現(xiàn)了時(shí)效沉淀僅在大的未再結(jié)晶晶粒中形成,而不會(huì)在細(xì)小的再結(jié)晶晶粒中形成。擠壓+峰時(shí)效合金的TYS增加到了470 MPa。超高的強(qiáng)度主要與織構(gòu)強(qiáng)化和析出強(qiáng)化有關(guān),和具有大塑性變形的傳統(tǒng)Mg合金中的細(xì)晶強(qiáng)化和析出強(qiáng)化不同。
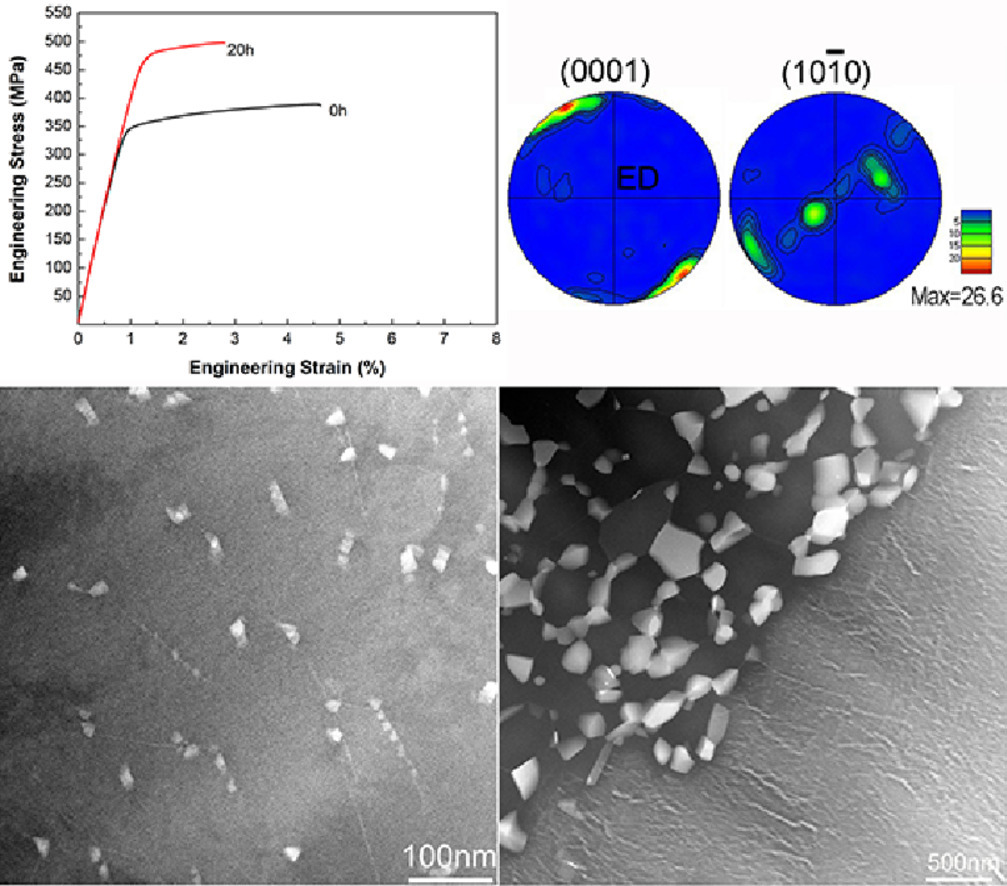

SCRIPTA
Vol. 193, 1 Mar. 2021, P147-152
14. Modeling the precipitation processes and the formation of hierarchical microstructures in a single crystal high entropy superalloy
模擬單晶高熵高溫合金中的析出過程和分層微觀組織的形成
Stéphane Gorsse?, Yung-Ta Chen, Wei-Che Hsu, Hideyuki Murakami, An-Chou Yeh?
Stéphane Gorsse: stephane.gorsse@icmcb.cnrs.fr,國(guó)立清華大學(xué)
An-Chou Yeh: yehac@mx.nthu.edu.tw,國(guó)立清華大學(xué)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.11.002
摘要
盡管高熵高溫合金(HESAs)優(yōu)異的高溫拉伸屈服強(qiáng)度得益于其分層微觀組織,但驅(qū)動(dòng)其形成的析出過程仍不明確。在本研究中,我們使用常規(guī)的計(jì)算熱力學(xué)和動(dòng)力學(xué)工具,分析了γ'和γ析出的動(dòng)力學(xué)、長(zhǎng)大和粗化過程,以模擬熱處理過程中HESA的微觀組織發(fā)生和演化過程。我們?cè)u(píng)估了模擬再現(xiàn)實(shí)驗(yàn)觀察到的微觀組織參數(shù)的能力。我們計(jì)算了溫度-時(shí)間-轉(zhuǎn)變(TTT)圖,為進(jìn)一步優(yōu)化HESA的分層微觀組織提供指導(dǎo)。
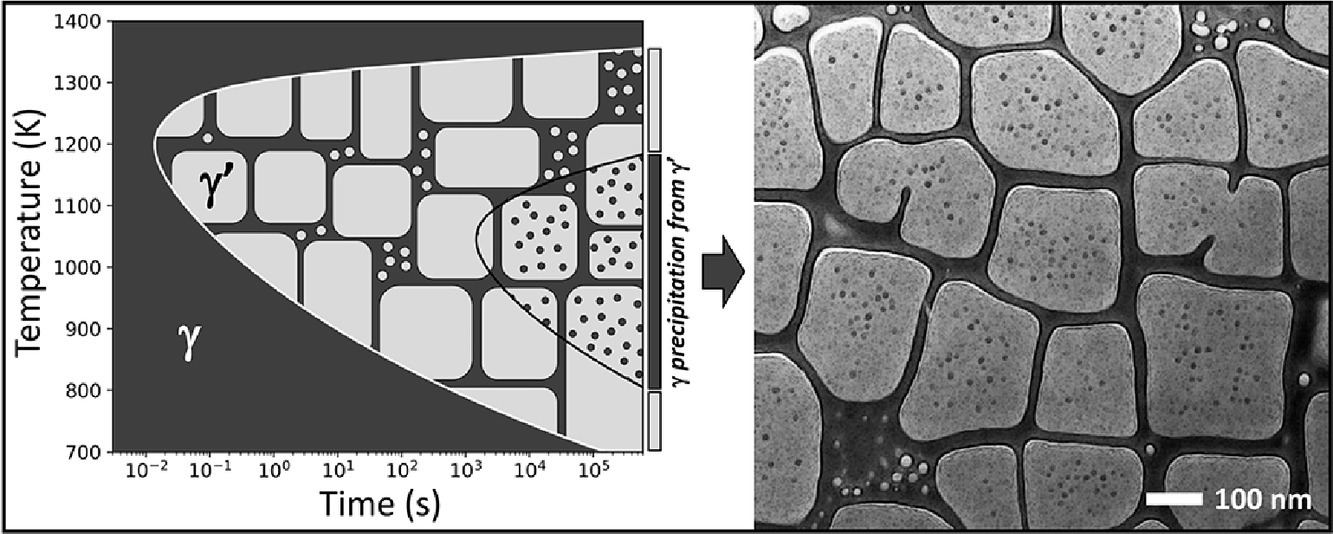

SCRIPTA
Vol. 193, 1 Mar. 2021, P153-157
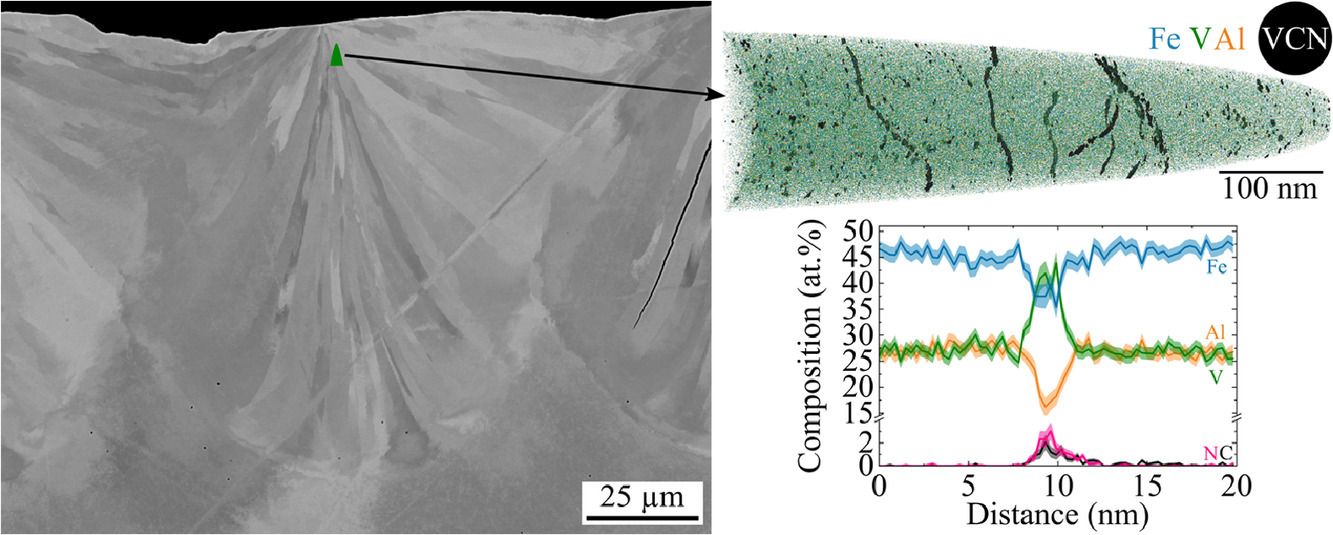
15. Properties and influence of microstructure and crystal defects in Fe2VAl modified by laser surface remelting
激光表面重熔改性Fe2VAl的性能及其微觀組織和晶體缺陷的影響
Leonie Gomell?, Moritz Roscher, Hanna Bishara, Eric A. Jägle, Christina Scheu, Baptiste Gault?
Leonie Gomell: l.gomell@mpie.de
Baptiste Gault: b.gault@mpie.de
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.10.050
摘要
激光表面重熔可用于調(diào)控鑄造材料的微觀組織。本工作對(duì)激光表面重熔后的Fe2VAl進(jìn)行詳細(xì)分析。在熔池中,拉長(zhǎng)的晶粒幾乎沿著熱影響區(qū)外延生長(zhǎng)。這些晶粒通過取向差為1°-5°的小角度晶界分開。我們使用原子探針層析成像技術(shù)觀察到釩、碳和氮在晶界和位錯(cuò)處的偏析,通過原位四點(diǎn)探針技術(shù)測(cè)量局部的電阻率。與鑄造樣品中的大角度晶界相比,在這些小角度晶界處觀察到了較小的電阻率增加。這表明晶界工程在調(diào)控?zé)犭娦阅芊矫嬗泻艽鬂摿Α?/span>