金屬頂刊雙語導讀丨Scripta Mater. Vol.194, 15 Mar. 2021(上)
2021-02-01 來源:Goal Science
Vol. 194 目錄
1. Unravelling the deposition mechanism of brittle particles in metal matrix composites fabricated via cold spray additive manufacturing
揭示通過冷噴涂增材制造法制備的金屬基復合材料中脆性顆粒的沉積機理
2. Temperature dependence of martensite variant reorientation in stress-induced martensite aged Ni49Fe18Ga27Co6 single crystals
應力誘導馬氏體時效Ni49Fe18Ga27Co6單晶中馬氏體變體重取向的溫度依賴性
3. Effects of grain size on body-centered-cubic martensitic transformation in metastable Fe46Co30Cr10Mn5Si7V2 high-entropy alloy
晶粒尺寸對亞穩態Fe46Co30Cr10Mn5Si7V2高熵合金體心立方馬氏體相變的影響
4. Functionally graded structures realized based on Fe-Mn-Al-Ni shape memory alloys
基于Fe-Mn-Al-Ni形狀記憶合金的功能梯度結構
5. Subsurface faceted cracking behavior of selective laser melting Ni-based superalloy under very high cycle fatigue
選擇性激光熔化鎳基高溫合金在高周疲勞下的亞表面裂紋行為
6. Diffraction artefacts from twins and stacking faults, and the mirage of hexagonal, polytypes or other superstructures
孿晶和層錯的衍射偽像,以及六方、多型體或其他超結構的幻象
7. Heterogenous columnar-grained high-entropy alloys produce exceptional resistance to intermediate-temperature intergranular embrittlement
異質柱狀晶高熵合金對中溫晶間脆化展現出優異的抵抗能力
8. Interactions of solutes with crystal defects: A new dynamic design parameter for advanced alloys
溶質與晶體缺陷的相互作用:一種新的先進合金動態設計參數
9. Nanograin formation in dimple ridges due to local severe-plastic-deformation during ductile fracture
韌性斷裂過程中由于局部嚴重塑性變形在韌窩脊中形成納米晶
10. Grain-boundary plane orientation dependence of faceting-roughening transition in Au grain boundaries under electron-beam irradiation
電子束輻照下金晶界切面化-粗化轉變的晶界面取向依賴性
SCRIPTA
Vol. 194, 15 Mar. 2021, 113614
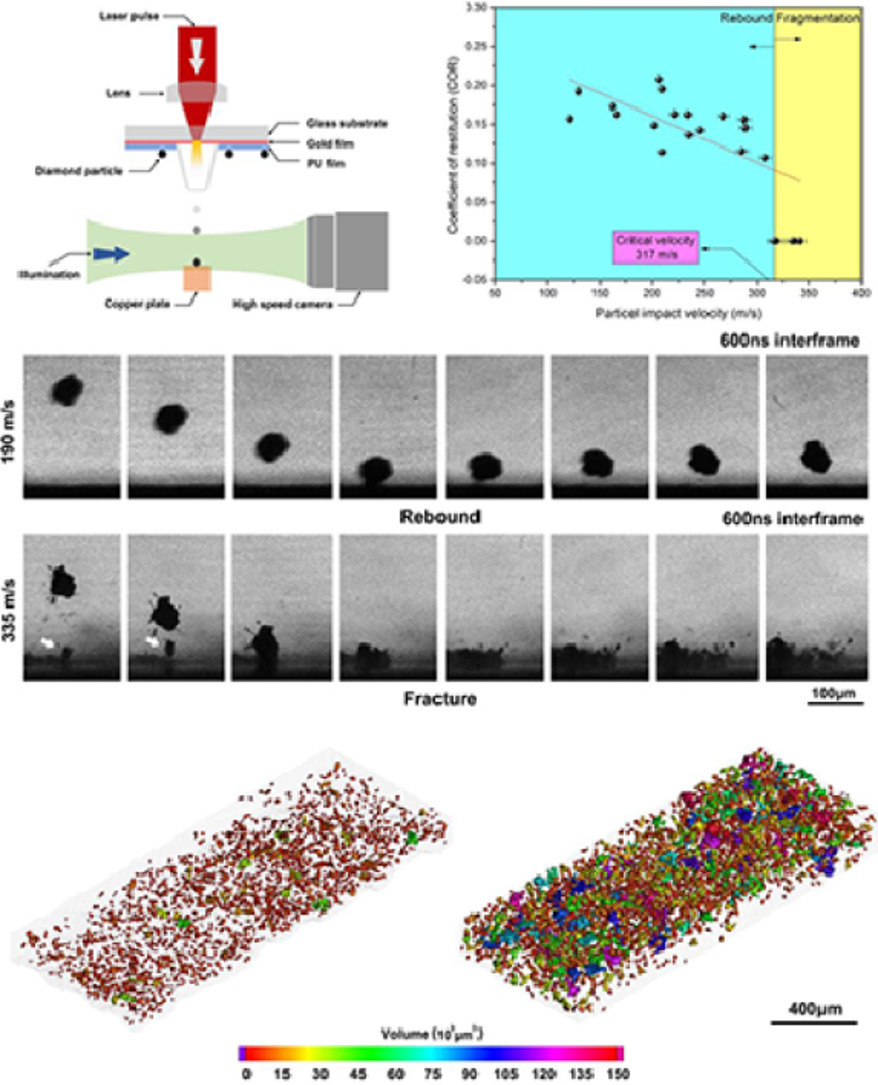
1. Unravelling the deposition mechanism of brittle particles in metal matrix composites fabricated via cold spray additive manufacturing
揭示通過冷噴涂增材制造法制備的金屬基復合材料中脆性顆粒的沉積機理
Shuo Yin?, Mostafa Hassani, Qingge Xie, Rocco Lupoi
Shuo Yin: yins@tcd.ie
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.10.055
摘要
近年來,冷噴涂沉積(CSD)已發展為一種增材制造工藝。在所有金屬增材制造工藝中,它具有最高的效率。本工作研究了金屬基復合材料(MMCs)的CSD過程中脆性增強顆粒的沉積機理。通過原位觀察以微米級的分辨率,在納秒尺度對脆性顆粒的回彈和破碎進行了研究。我們首次確定了從粒子回彈到粒子破碎過渡的速度。在此,我們將該速度定義為“破碎速度”。在CSD沉積臺上進行的X射線計算斷層掃描顯示,沉積臺上的大多數鉆石都是原始顆粒的碎片,其體積分數主要取決于其相對于破碎速度的撞擊速度。基于這些發現以及微觀組織特征,我們提出了MMCs在CSD過程中脆性增強顆粒的沉積機理。

SCRIPTA
Vol. 194, 15 Mar. 2021, 113618
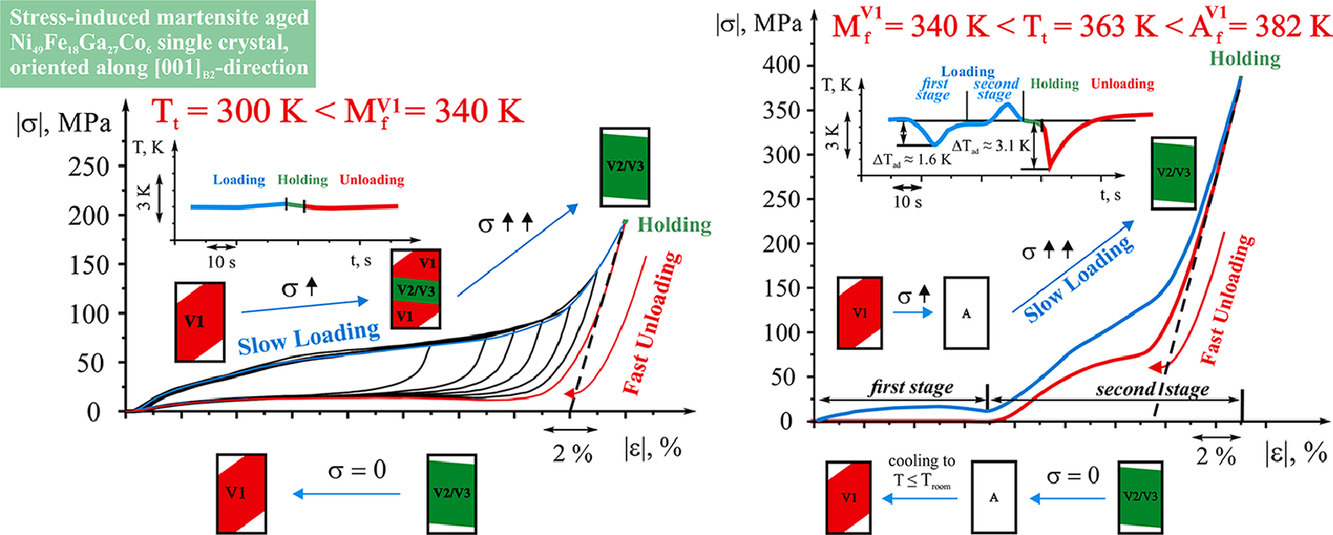
2. Temperature dependence of martensite variant reorientation in stress-induced martensite aged Ni49Fe18Ga27Co6 single crystals
應力誘導馬氏體時效Ni49Fe18Ga27Co6單晶中馬氏體變體重取向的溫度依賴性
E. Panchenko?, A. Tokhmetova, N. Surikov, A. Eftifeeva, A. Tagiltsev, E. Timofeeva, Y. Chumlyakov, G. Gerstein, H.J. Maier
E. Panchenko: panchenko@mail.tsu.ru
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.10.056
摘要
本工作研究了Ni49Fe18Ga27Co6單晶在壓縮過程中,應力誘發的馬氏體沿[110]B2||[100]L10方向馬氏體變體重取向的溫度依賴性。這種馬氏體時效引起了類似橡膠的行為,在248K至344K的溫度范圍內,沿[001]B2方向可逆應變高達-16.0%,這是由L10-馬氏體變體重取向引起的。在從344K到382K的正向和反向轉變之間的較高溫度下,應力誘發馬氏體時效晶體表現出兩階段應力應變的響應,可逆應變高達-13.5%。第一階段的特點是低的臨界應力σcr1≈1-15MPa,且在加載下具有逆彈性效應(吸熱)。在第二階段觀察到超彈性,σcr2≥100MPa。在此溫度范圍內,馬氏體變體的重取向是通過反向然后正向的馬氏體相變發生的。

SCRIPTA
Vol. 194, 15 Mar. 2021, 113620
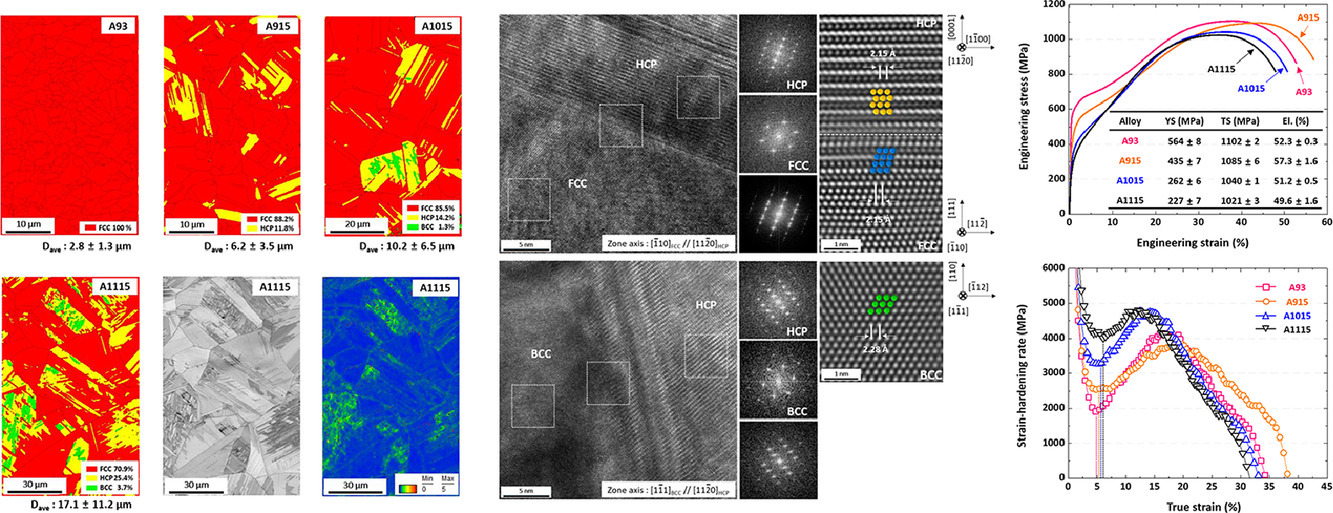
3. Effects of grain size on body-centered-cubic martensitic transformation in metastable Fe46Co30Cr10Mn5Si7V2 high-entropy alloy
晶粒尺寸對亞穩態Fe46Co30Cr10Mn5Si7V2高熵合金體心立方馬氏體相變的影響
Yong Hee Jo, Dae Woong Kim, Hyoung Seop Kim, Sunghak Lee?
Sunghak Lee: shlee@postech.ac.kr
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.11.005
摘要
本工作系統地研究了晶粒尺寸對亞穩態Fe46Co30Cr10Mn5Si7V2高熵合金(HEA)的微觀組織和力學性能的影響。晶粒粗化導致面心立方(FCC)相的穩定性降低,形成了層狀六方密堆積(HCP)和蝶形體心立方(BCC)結構的馬氏體。在拉伸試驗中,通過中間HCP相過渡的FCC到BCC相的轉變,發生了相變誘導塑性(TRIP),且BCC相的加速轉變速率提高了應變硬化率。結果表明,與熱誘導馬氏體相變和應變硬化機制相關的微觀組織演變可以通過理解從FCC到HCP到BCC相的馬氏體相變來很好地解釋。

SCRIPTA
Vol. 194, 15 Mar. 2021, 113619
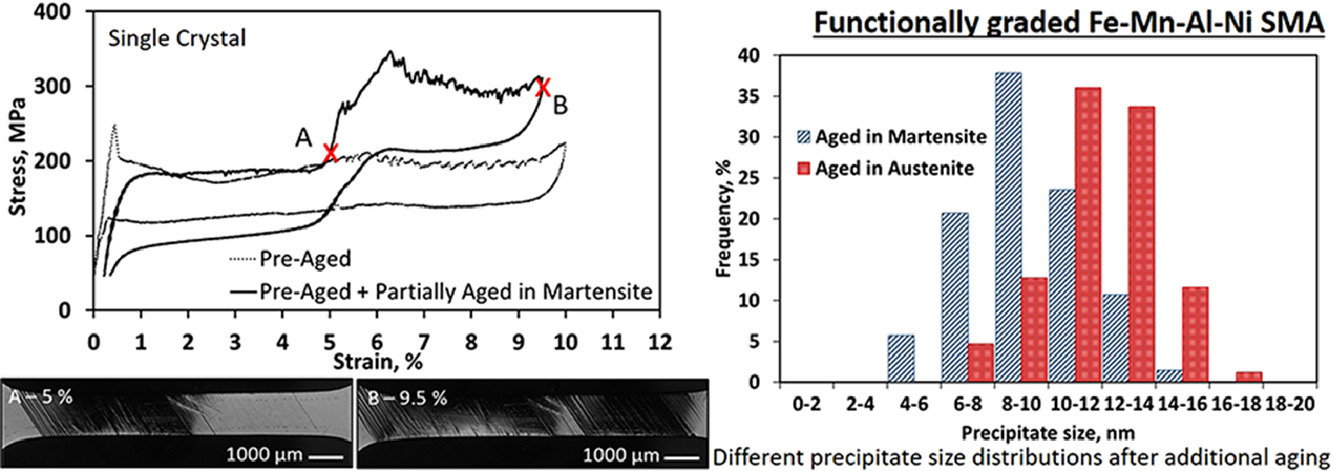
4. Functionally graded structures realized based on Fe-Mn-Al-Ni shape memory alloys
基于Fe-Mn-Al-Ni形狀記憶合金的功能梯度結構
M. Vollmer?, A. Bauer, M.J. Kriegel, M. Motylenko, T. Niendorf
M. Vollmer: vollmer@uni-kassel.de
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.10.057
摘要
本工作介紹了一種在Fe-Mn-Al-Ni形狀記憶合金中獲得功能梯度性能的新方法。表現出超彈性的單晶樣品在部分馬氏體狀態下進行時效處理。結果表明奧氏體時效區的特征是超彈性滯后會發生改變,且具有不同的正/反向相變臨界應力;而馬氏體時效區的性能幾乎保持不變。透射電子顯微鏡研究表明,納米β析出,作為嚴重影響相變溫度并最終影響相變應力的物相,在馬氏體時效區的平均尺寸約為9 nm,在奧氏體時效區的平均尺寸約為12nm。基于這些結果,以某種方式調整Fe-Mn-Al-Ni的成分,使其局部表現不同的功能特性似乎是可行的。

SCRIPTA
Vol. 194, 15 Mar. 2021, 113613
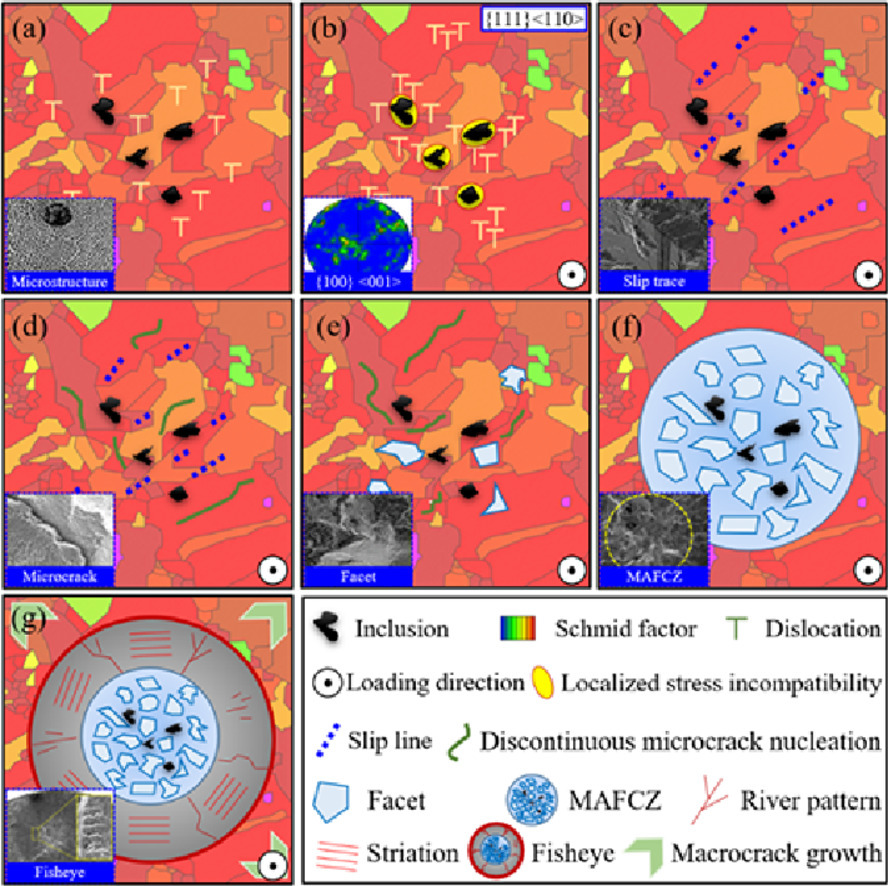
5. Machine learning based surrogate modeling approach for mapping crystal deformation in three dimensions
選擇性激光熔化鎳基高溫合金在高周疲勞下的亞表面裂紋行為
Wei Li?, Rui Sun, Ping Wang?, XiaoLong Li, Yucheng Zhang, Tianyi Hu, Cheng Li, Tatsuo Sakai
Wei Li: lliw@bit.edu.cn,北京理工大學
Ping Wang: ping_wf@163.com,齊魯工業大學
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.11.001
摘要
本文研究了在極高的循環疲勞(VHCF)下通過選擇性激光熔化(SLM)制備的鎳基高溫合金的結構-性能,帶有魚眼圖案的亞表面裂紋成為一種顯著的破壞模式。由于存在亞表面破壞,出現了S-N曲線的下降特性。基于二維和三維的顯微觀察,魚眼內存在一個粗糙的區域,該區域有多個小平面和夾雜物,被稱為“多夾雜物輔助平面裂紋區(MAFCZ)”。結合電子背散射衍射分析,亞表面破壞與晶粒尺寸和取向,微觀織構以及晶體缺陷有關。在夾雜物的幫助下,裂紋從具有最高施密特因子的大晶粒內形核。具有裂紋撓度的粗糙表面形貌揭示了MAFCZ中超慢的裂紋擴展行為。結合失效建模和斷裂力學分析,闡明了VHCF條件下SLM鎳基高溫合金的亞表面破壞機理。

SCRIPTA
Vol. 194, 15 Mar. 2021, 113629
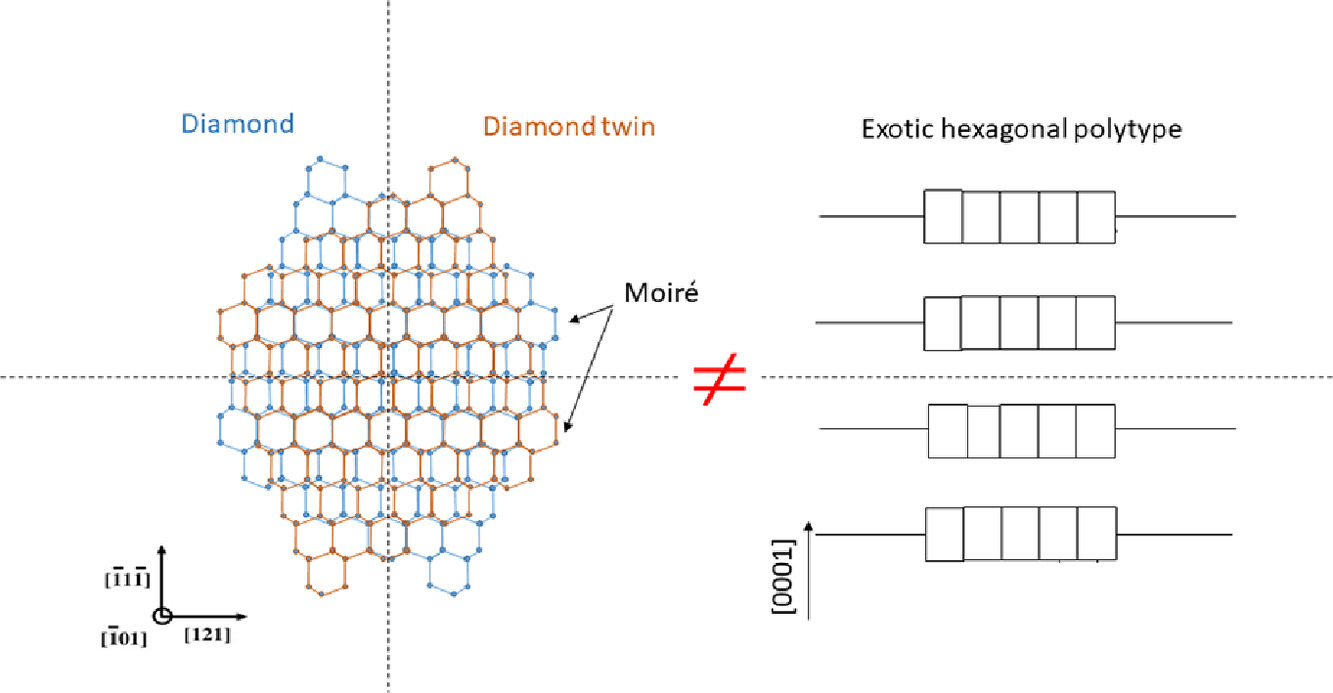
6. Diffraction artefacts from twins and stacking faults, and the mirage of hexagonal, polytypes or other superstructures
孿晶和層錯的衍射偽像,以及六方、多型體或其他超結構的幻象
Cyril Cayron?
Cyril Cayron: cyril.cayron@epfl.ch
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.11.014
摘要
最近,在多項研究中已報道了高碳鋼中的六方相。本工作表明這些研究錯誤地解釋了使用的電子顯微鏡結果。衍射花樣中的額外斑點和高分辨率圖像中的異常襯度不是超結構,而是由于孿晶和層錯的存在引起的雙重衍射和條紋效應所致。我們在報道鋁或銅中存在9R結構或鉆石中存在奇異形式的碳的論文中指出了類似令人遺憾的誤解。

SCRIPTA
Vol. 194, 15 Mar. 2021, 113622
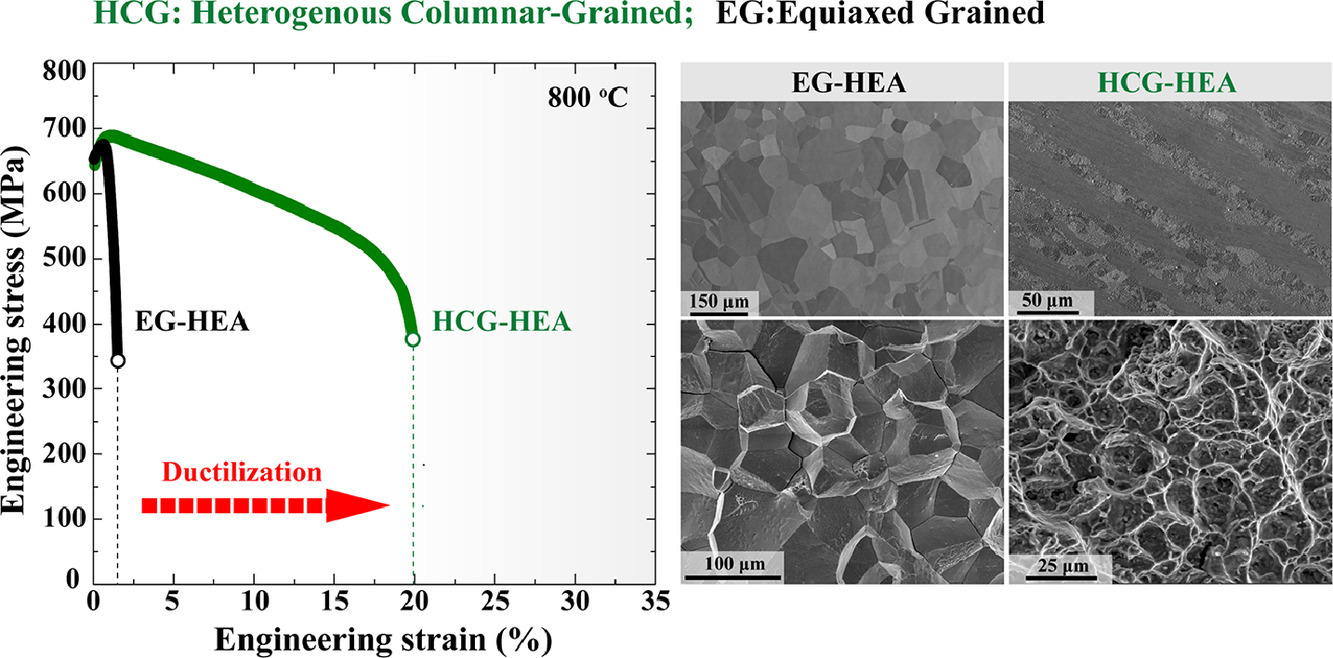
7. Heterogenous columnar-grained high-entropy alloys produce exceptional resistance to intermediate-temperature intergranular embrittlement
異質柱狀晶高熵合金對中溫晶間脆化展現出優異的抵抗能力
B.X. Cao, H.J. Kong, L. Fan, J.H. Luan, Z.B. Jiao, J.J. Kai, T. Yang?, C.T. Liu?
T. Yang: taoyang6-c@my.cityu.edu.hk,香港城市大學
C.T. Liu: chainliu@cityu.edu.hk,香港城市大學
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.11.007
摘要
由共格納米顆粒增強的高熵合金(HEA)在高溫結構應用中顯示出巨大潛力,但是,在中溫下進行測試時,通常會出現嚴重的晶間脆化。本研究中,我們展示了一種新穎的“異質柱狀晶”(HCG)的方法,有效克服了這一棘手的問題。與等軸晶合金在800°C時沿晶界表現出極大的脆性不同,由于獨特的晶界特征和分布,新開發的HCG-HEA展現出對晶間斷裂極高的抵抗力。異質柱狀晶結構的存在極大地抑制了裂紋形核和沿界面的擴展,從而在800°C下獲得了~18.4%的異常拉伸塑性以及~652 MPa的高屈服強度。這一發現為具有優異機械性能的高溫材料的創新設計提供了新的見解。

SCRIPTA
Vol. 194, 15 Mar. 2021, 113626
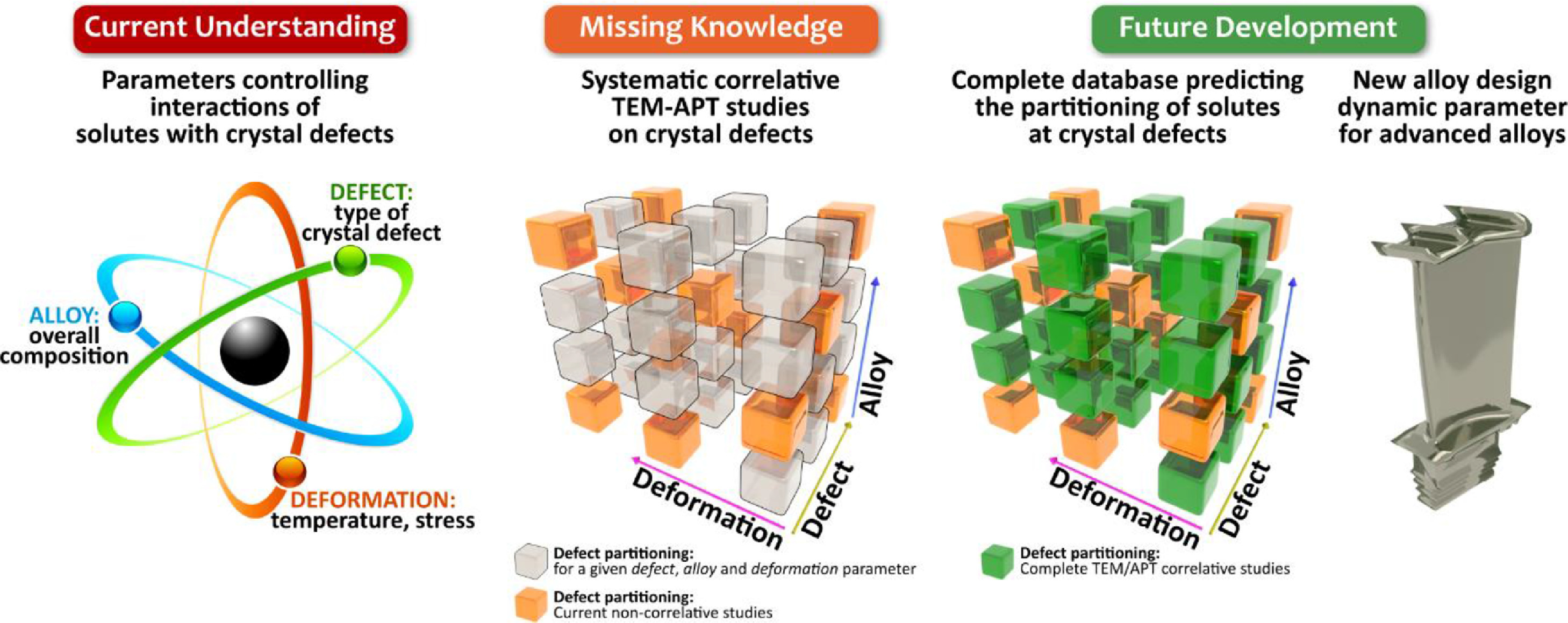
8. Interactions of solutes with crystal defects: A new dynamic design parameter for advanced alloys
溶質與晶體缺陷的相互作用:一種新的先進合金動態設計參數
Paraskevas Kontis?
Paraskevas Kontis: p.kontis@mpie.de
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.11.011
摘要
為了實現可持續發展的未來,提高工程系統的效率和減少排放需要新材料來突破其性能極限。當前的合金設計策略將合金視為靜態系統,但其微觀組織和成分在操作中不斷發生演化。本文關注一種新的合金設計動力學參數,該參數來源于溶質與近原子尺度獲得的晶體缺陷的相互作用相關的信息。最近高分辨表征的技術突破使近原子尺度的結構和成分成像成為可能,從而為此類相互作用提供了新的見解。本文討論了這些相互作用對決定高溫合金(例如鎳基,鈷基合金和鈦合金)失效的組織和成分不斷演變的影響。開發一種能夠考慮這些相互作用的溶質-缺陷數據庫,旨在更準確地預測當前合金和新合金的機械性能,對于更具動態性的合金設計策略是非常必要的。

SCRIPTA
Vol. 194, 15 Mar. 2021, 113631
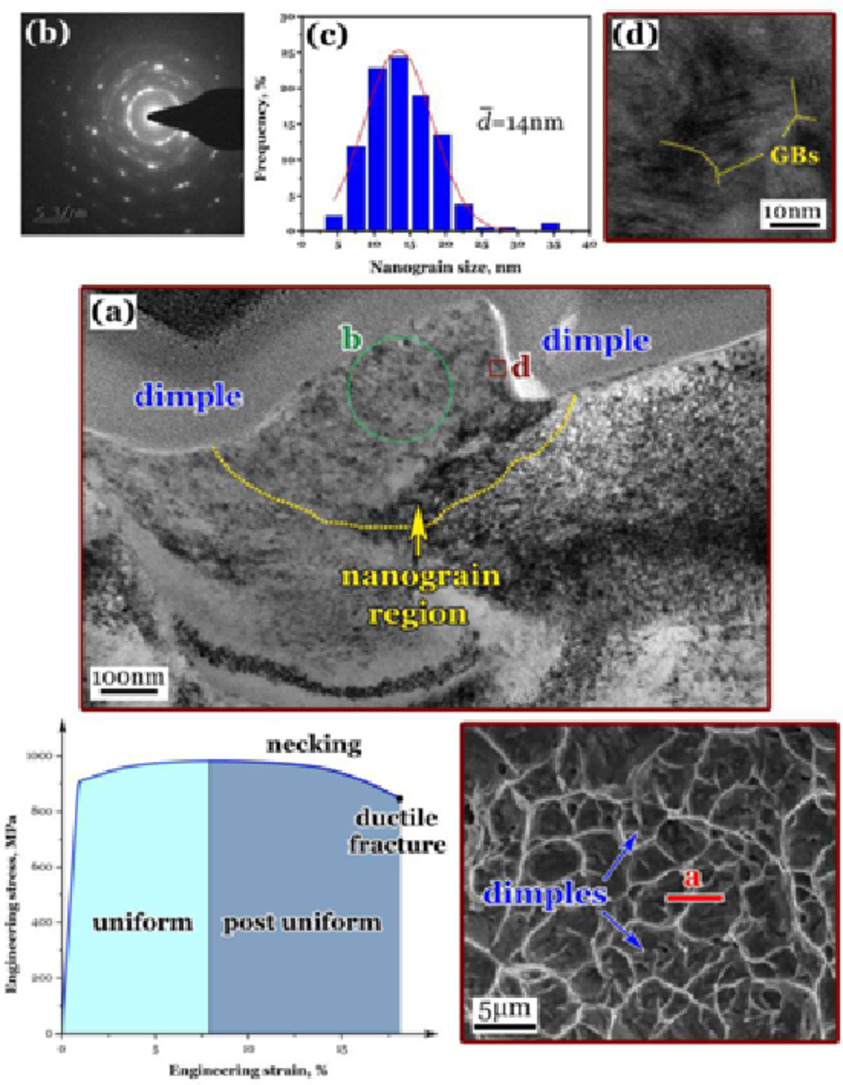
9. Nanograin formation in dimple ridges due to local severe-plastic-deformation during ductile fracture
韌性斷裂過程中由于局部嚴重塑性變形在韌窩脊中形成納米晶
Xiangnan Pan, Guian Qian, Youshi Hong?
Youshi Hong: hongys@imech.ac.cn,中國科學院大學
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.113631
摘要
納米晶材料在力學,物理和化學方面具有卓越的性能。本研究中,我們發現了一種新現象,即鈦合金在韌性斷裂過程中會自發地形成納米晶粒,其主要機制是局部嚴重的塑性變形(LSPD)。我們揭示了在單調拉伸的整個過程中的微觀組織演變,以進一步了解從塑性變形到頸縮以及最終破壞的韌性斷裂行為,尤其是在斷后延伸階段,在該階段,孔洞形核、生長并聯合。LSPD過程可以為高延展性材料的設計和生產提供新的概念和方法,其中納米晶的形成將消耗大量的應變能,從而使試樣在頸縮后的斷后延伸階段獲得較大的伸長率。

SCRIPTA
Vol. 194, 15 Mar. 2021, 113630
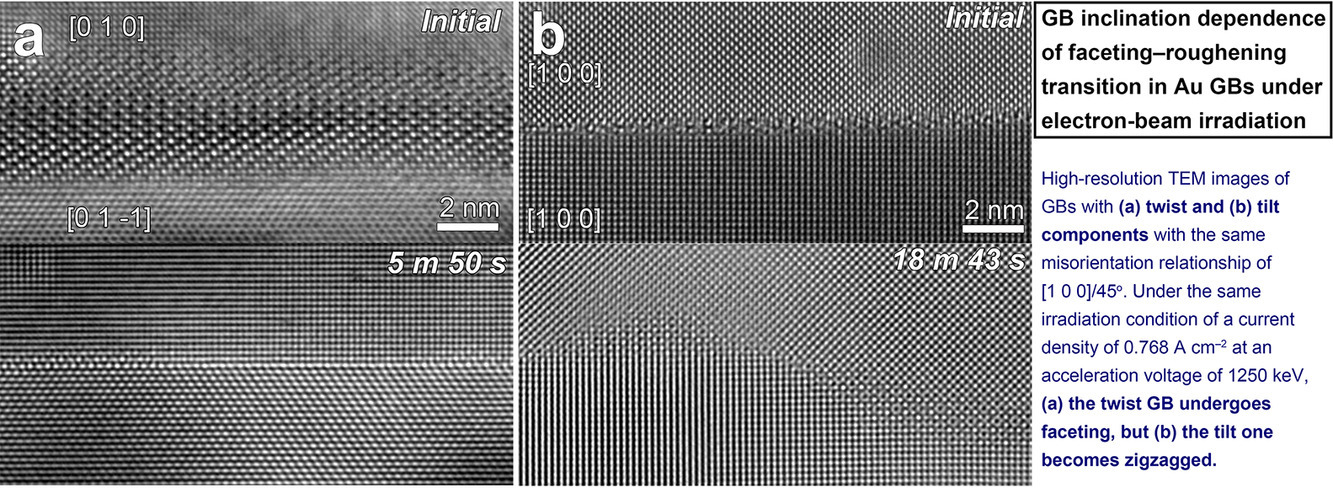
10. Grain-boundary plane orientation dependence of faceting-roughening transition in Au grain boundaries under electron-beam irradiation
電子束輻照下金晶界切面化-粗化轉變的晶界面取向依賴性
Sung Bo Lee?, Seung Jo Yoo, Jinwook Jung, Heung Nam Han
Sung Bo Lee: bolee@snu.ac.kr
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.11.015
摘要
晶界作用是吸收和湮滅多晶核材料中高能粒子產生的點缺陷。因此,了解高能粒子輻照對晶界結構變化的影響是發展具有理想性能核材料的先決條件。可以預料,對于不同的晶界特征,此種影響是不同的。為了探究這種可能性,我們在加速電壓為1250 keV的高壓透射電子顯微鏡下,以金為模型體系,研究了具有相同[1 0 0]/ 45°錯配關系的扭曲和傾斜分量的晶界。我們觀察到,在相同的輻照條件下,傾斜的晶界發生粗化,而扭曲的晶界則發生切面化。