金屬頂刊雙語導(dǎo)讀丨Scripta Mater. Vol.197, 1 May. 2021(上)
2021-03-28 來源:Goal Science

本期包含金屬材料領(lǐng)域論文10篇,涵蓋了單晶、馬氏體鋼、高熵合金、鎂基合金、超強(qiáng)鋼等,國內(nèi)科研單位包括臺灣成功大學(xué)、北京科技大學(xué)等(通訊作者單位)。
Vol. 197 目錄
1. Precise measurement of activation parameters for individual dislocation nucleation during in situ TEM tensile testing of single crystal nickel
鎳單晶原位TEM拉伸測試過程中單個(gè)位錯(cuò)形核的激活參數(shù)的精確測量
2. Tensile behavior and inelastic strain recovery of Cu-Co nanolaminates
Cu-Co納米層狀結(jié)構(gòu)的拉伸行為和非彈性應(yīng)變回復(fù)
3. Ultrafine intralath precipitation of V(C,N) in 12Cr-1MoWV (wt.%) ferritic/martensitic steel
12Cr-1MoWV (wt.%) 鐵素體/馬氏體鋼中V(C,N)的超細(xì)板條內(nèi)析出
4. 3D mapping of orientation variation and local residual stress within individual grains of pearlitic steel using synchrotron dark field X-ray microscopy
使用同步加速暗場X射線顯微鏡對珠光體鋼單個(gè)晶粒內(nèi)的取向變化和局部殘余應(yīng)力進(jìn)行三維成像
5. Unveiling interactions of non-metallic inclusions within advanced ultra-high-strength steel: A spectro-microscopic determination and first-principles elucidation
揭示先進(jìn)超高強(qiáng)度鋼中非金屬夾雜物的相互作用:光譜顯微鏡測定和第一性原理解釋
6. Inhibiting the detrimental Cu protrusion in Cu through-silicon-via by highly (111)-oriented nanotwinned Cu
用高(111)取向的納米孿晶銅抑制銅硅通孔中的有害銅突起
7. Modelling the effect of intrinsic radiation damage on mechanical properties: The crystalline-to-amorphous transition in zircon
本征輻照損傷對力學(xué)性能影響的模擬:鋯石從晶態(tài)到非晶態(tài)的轉(zhuǎn)變
8. Formation mechanism and stability of austenitic islands in carbides in a Ni-Cr-Fe based high-temperature austenitic alloy undergoing carburization
Ni-Cr-Fe基高溫奧氏體合金滲碳過程中碳化物中奧氏體島的形成機(jī)理及穩(wěn)定性
9. Machine learning approach to predict new multiphase high entropy alloys
用機(jī)器學(xué)習(xí)方法預(yù)測新型多相高熵合金
10. Superior dehydrogenation performance of Mg-based alloy under electropulsing
鎂基合金在電脈沖作用下的優(yōu)異脫氫性能
SCRIPTA
Vol. 197, 1 May. 2021, 113764
1. Precise measurement of activation parameters for individual dislocation nucleation during in situ TEM tensile testing of single crystal nickel
鎳單晶原位TEM拉伸測試過程中單個(gè)位錯(cuò)形核的激活參數(shù)的精確測量
Xiaoqing Li?, Andrew M. Minor?
Andrew M. Minor: aminor@berkeley.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113764
摘要
晶體缺陷(如位錯(cuò))的形核是機(jī)械變形的核心。本研究中,我們展示了一種在原位透射電子顯微鏡(TEM)拉伸測試中觀察單個(gè)位錯(cuò)形核的技術(shù),并從單個(gè)事件中測量與塑性相關(guān)的基本參數(shù)。我們的方法依賴于在定向單晶鎳樣品中通過自動圖像分析系統(tǒng)地檢測位錯(cuò)滑移痕跡。利用從原位測試中識別單個(gè)缺陷痕跡,將累積概率函數(shù)應(yīng)用于關(guān)聯(lián)位錯(cuò)形核事件和相應(yīng)的應(yīng)力水平之間的關(guān)系。我們的分析允許使用一個(gè)樣品在一個(gè)拉伸試驗(yàn)中的數(shù)據(jù),對單個(gè)位錯(cuò)形核事件的激活參數(shù)進(jìn)行外推。從原位TEM納米力學(xué)測試中獲得的位錯(cuò)形核激活參數(shù)的精確且定量的關(guān)聯(lián)可以為塑性計(jì)算模型提供直接的定量測量。

SCRIPTA
Vol. 197, 1 May. 2021, 113781
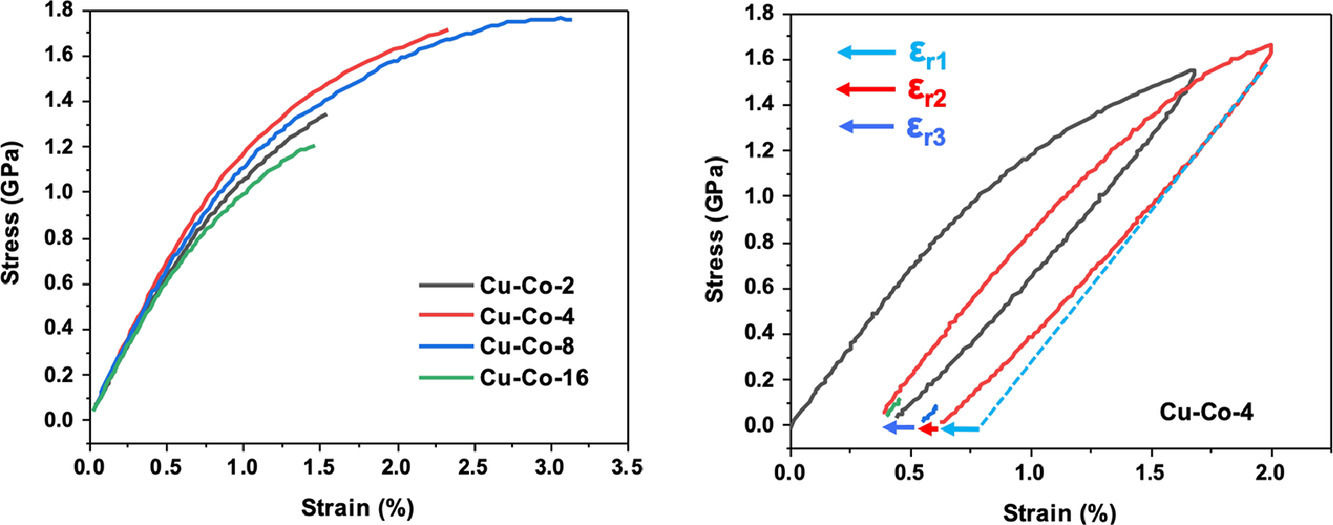
2. Tensile behavior and inelastic strain recovery of Cu-Co nanolaminates
Cu-Co納米層狀結(jié)構(gòu)的拉伸行為和非彈性應(yīng)變回復(fù)
Rohit Berlia, Paul Rasmussen, Shize Yang, Jagannathan Rajagopalan?
Jagannathan Rajagopalan:jrajago1@asu.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113781
摘要
宏觀尺度金屬試樣的力學(xué)響應(yīng)通常是通過單軸拉伸試驗(yàn)確定的,該試驗(yàn)提供了楊氏模量和屈服強(qiáng)度等關(guān)鍵性能的直接測量結(jié)果。然而,由于實(shí)驗(yàn)的挑戰(zhàn),單軸拉伸實(shí)驗(yàn)很少被用于研究金屬納米層板的力學(xué)行為。本文利用定制的微機(jī)電系統(tǒng)(MEMS)設(shè)備研究了四種不同層厚(h = 2,4,8,16 nm)的Cu-Co納米層狀結(jié)構(gòu)的準(zhǔn)靜態(tài)、單軸拉伸行為。實(shí)驗(yàn)顯示,在h = 4 nm處有一個(gè)屈服強(qiáng)度峰值,而楊氏模量與h無關(guān)。令人驚訝的是,納米層狀結(jié)構(gòu)在卸載過程中和卸載后回復(fù)了大量的非彈性變形(> 60%),并且隨著溫度的升高,這種回復(fù)得到了增強(qiáng)。本文討論了這種異常應(yīng)變回復(fù)在Cu-Co納米層狀結(jié)構(gòu)中存在的可能機(jī)制。

SCRIPTA
Vol. 197, 1 May. 2021, 113787
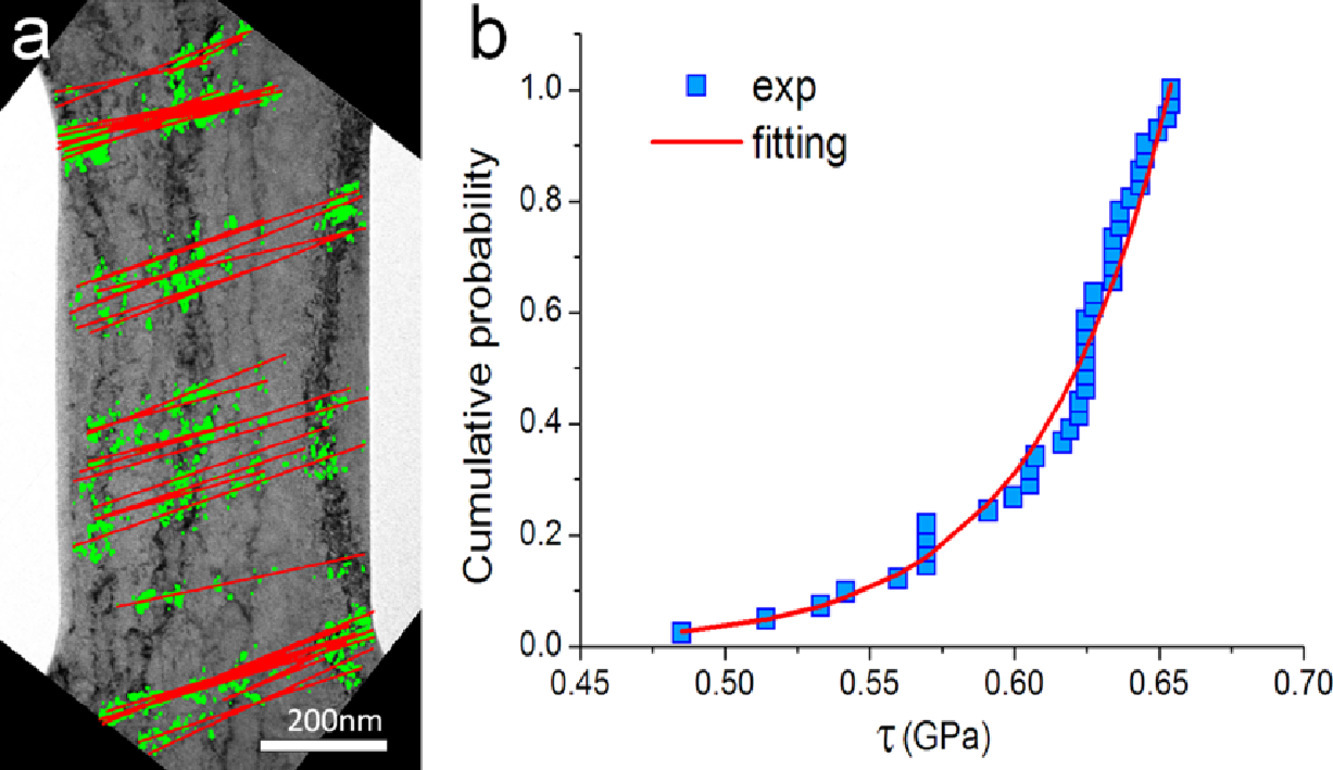
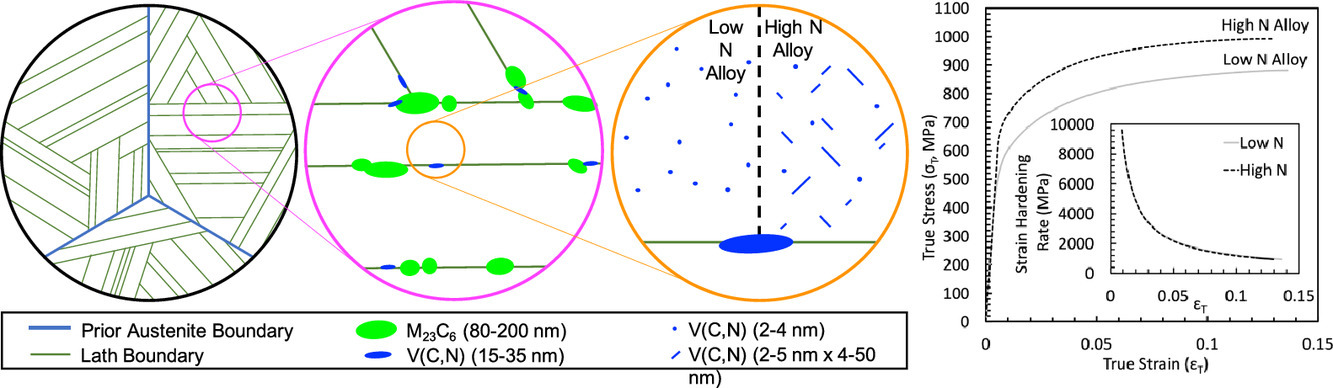
3. Ultrafine intralath precipitation of V(C,N) in 12Cr-1MoWV (wt.%) ferritic/martensitic steel
12Cr-1MoWV (wt.%) 鐵素體/馬氏體鋼中V(C,N)的超細(xì)板條內(nèi)析出
A. J. Rietema?, M.M. Hassan, O. Anderoglu, B.P. Eftink, T.A. Saleh, S.A. Maloy, A.J. Clarke, K.D. Clarke
A. J. Rietema: crietema@mines.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113787
摘要
12Cr-1MoWV鐵素體/馬氏體(F/M)鋼是先進(jìn)核反應(yīng)堆燃料包殼的候選材料。因此,了解這些鋼在輻照環(huán)境下的微觀組織和力學(xué)性能之間的關(guān)系是至關(guān)重要的。本文首次揭示了常規(guī)熱處理12Cr-1MoWV鋼中存在超細(xì)尺度(2-5 nm)的V(C,N)板條內(nèi)析出物。較低的N含量導(dǎo)致更細(xì)的板條內(nèi)析出,而較高的N含量導(dǎo)致更大的,拉長的圓盤或針狀析出。N含量對析出相特性的影響顯著改變了強(qiáng)度,但對應(yīng)變硬化行為沒有影響。更細(xì)的析出可能對輻照行為有影響,特別是它們作為缺陷源的能力。在常規(guī)熱處理的12Cr-1MoWV鋼中,超細(xì)尺度V(C,N)析出物的存在受N含量的控制,為調(diào)整F/M鋼的強(qiáng)度和核輻照響應(yīng)提供了一種新的手段。

SCRIPTA
Vol. 197, 1 May. 2021, 113783
4. 3D mapping of orientation variation and local residual stress within individual grains of pearlitic steel using synchrotron dark field X-ray microscopy
使用同步加速暗場X射線顯微鏡對珠光體鋼單個(gè)晶粒內(nèi)的取向變化和局部殘余應(yīng)力進(jìn)行三維成像
A. Yildirim?, C. Jessop, J. Ahlström, C. Detlefs, Y. Zhang?
A. Yildirim: can.yildirim@esrf.fr
A. Zhang: yubz@dtu.dk
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113783
摘要
以納米分辨率評估嵌入式鋼晶粒中的局部殘余應(yīng)力和取向仍然具有很大挑戰(zhàn)性。在本研究中,我們使用先進(jìn)的同步加速器技術(shù),暗場X射線顯微鏡來繪制珠光體鋼中兩種先共析鐵素體晶粒內(nèi)的3D晶格變化,包括晶體學(xué)取向和晶格應(yīng)變。我們發(fā)現(xiàn)樣品中存在高達(dá)0.5°的取向變化和高達(dá)1.8×10-3的壓縮彈性應(yīng)變。測得的壓縮應(yīng)變與晶格取向之間沒有直接關(guān)系。我們討論了變化的根源及其對制造過程和機(jī)械性能的影響。
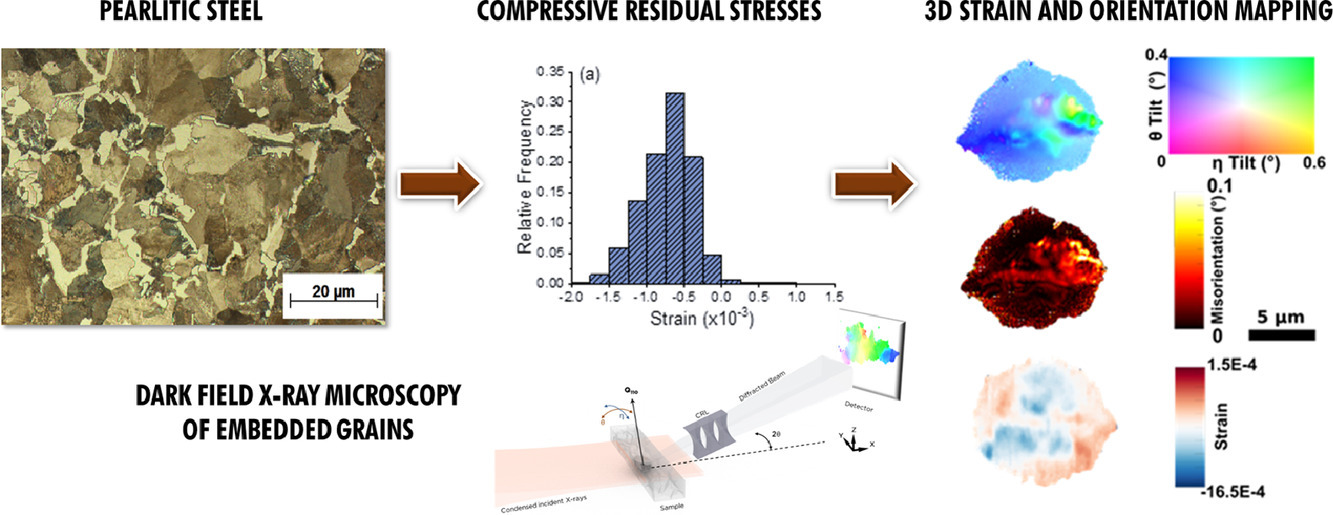

SCRIPTA
Vol. 197, 1 May. 2021, 113791
5. Unveiling interactions of non-metallic inclusions within advanced ultra-high-strength steel: A spectro-microscopic determination and first-principles elucidation
揭示先進(jìn)超高強(qiáng)度鋼中非金屬夾雜物的相互作用:光譜顯微鏡測定和第一性原理解釋
Harishchandra Singh?, Tuomas Alatarvas?, Andrey A Kistanov, S Assa Aravindh, Shubo Wang, Lin Zhu, Brice Sarpi, Yuran Niu, Alexei Zakharov, F.M.F. de Groot, Marko Huttula, Wei Cao?, Timo Fabritius
Harishchandra Singh: harischandra.singh@oulu.fi
Tuomas Alatarvas: tuomas.alatarvas@oulu.fi
Wei Cao: wei.cao@oulu.fi
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113791
摘要
確定非金屬夾雜物(NMIs)對超高強(qiáng)度鋼的設(shè)計(jì)至關(guān)重要,因?yàn)樗鼈儗π阅芷鹬鴽Q定性作用,對于通過常規(guī)技術(shù)進(jìn)行探測至關(guān)重要。本文利用先進(jìn)的同步X射線吸收結(jié)合光電發(fā)射電子顯微鏡和第一性原理計(jì)算,提供了幾種NMI模型體系的結(jié)構(gòu)、局部鍵合結(jié)構(gòu)和電子性質(zhì),以及它們在鋼基體之間的交互作用機(jī)制。B K -, N K -, Ca L2,3-和Ti L2,3-邊緣光譜表明,額外的B傾向于導(dǎo)致h-BN,表現(xiàn)出與Ca2+的強(qiáng)相互作用。這些Ca2+基相也通過TiN趨于穩(wěn)定,揭示了Ca2+的不規(guī)則配位。第一性原理計(jì)算進(jìn)一步支持了觀察到的TiN和BN的非交互作用,其中發(fā)現(xiàn)了TiN和BN的不利組合和更大尺寸的Ca2+基夾雜物的穩(wěn)定性。這些觀察結(jié)果有助于優(yōu)化各種夾雜物和鋼基體之間的交互作用機(jī)制。
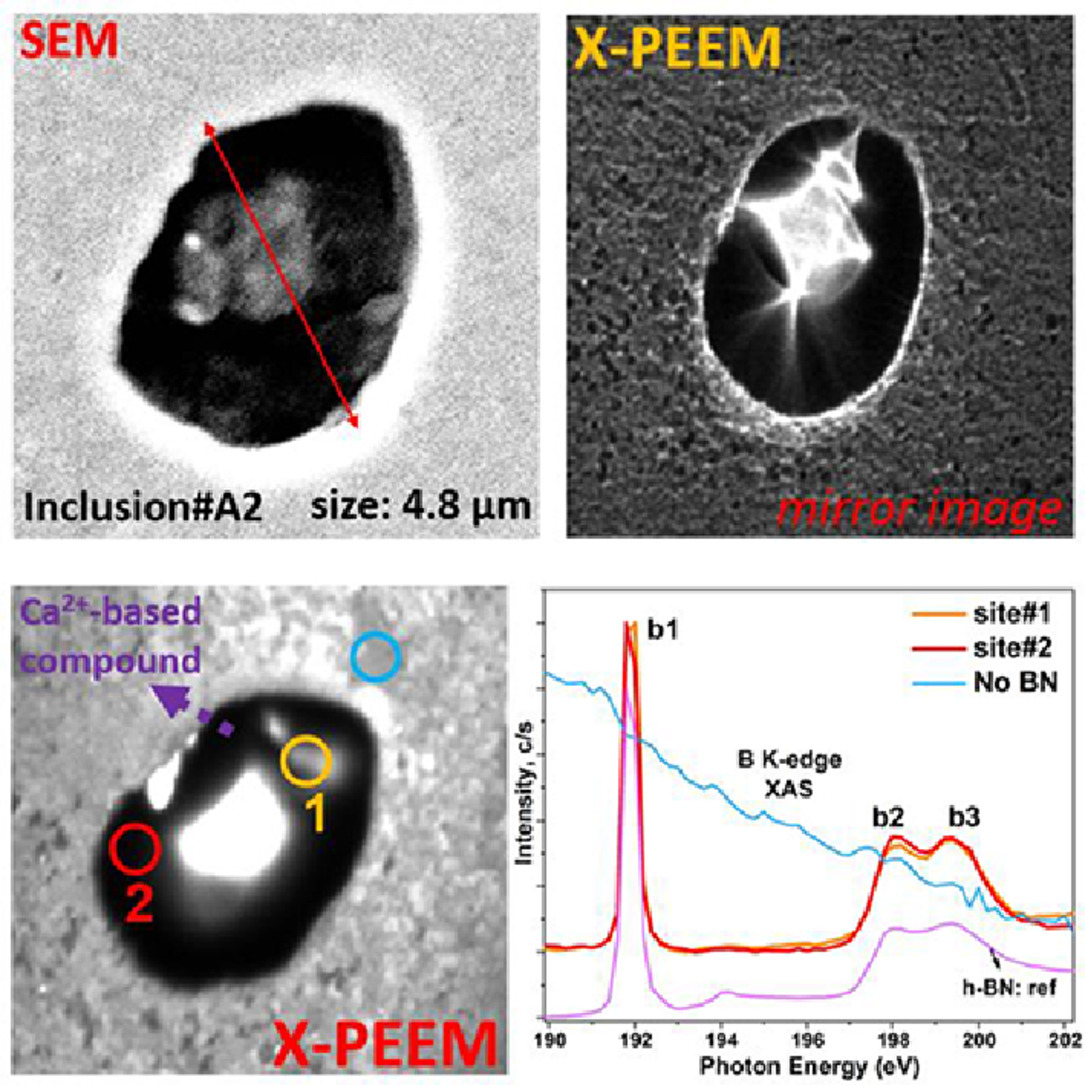

SCRIPTA
Vol. 197, 1 May. 2021, 113782
6. Inhibiting the detrimental Cu protrusion in Cu through-silicon-via by highly (111)-oriented nanotwinned Cu
用高(111)取向的納米孿晶銅抑制銅硅通孔中的有害銅突起
Ting-Chun Lin, Chien-Lung Liang?, Shan-Bo Wang, Yung-Sheng Lin, Chin-Li Kao, David Tarng, Kwang-Lung Lin
Chien-Lung Liang:clliang@gs.ncku.edu.tw 臺灣成功大學(xué)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113782
摘要
銅的突起現(xiàn)象是銅硅通孔(TSV)技術(shù)面臨的最大挑戰(zhàn)之一,其原因是熱退火過程中產(chǎn)生的熱應(yīng)力積累和隨之而來的塑性變形。在此,我們提出了一種有效的方法,通過引入高度(111)取向的納米孿晶銅的TSV結(jié)構(gòu)來抑制有害的銅突起。與普通的Cu結(jié)構(gòu)相比,在250℃的熱退火過程中,納米孿晶結(jié)構(gòu)的突起高度降低了70.3%。突起抑制歸因于高分?jǐn)?shù)共格納米孿晶界與位錯(cuò)的有效相互作用。低能共格孿晶界的存在阻礙了位錯(cuò)滑移,使TSV增強(qiáng),顯著抑制了突起。在250℃熱退火2 h后,電沉積納米孿晶Cu TSV展現(xiàn)出良好的熱穩(wěn)定性;納米硬度分析顯示,顯微硬度損失很小,僅為6.7%。
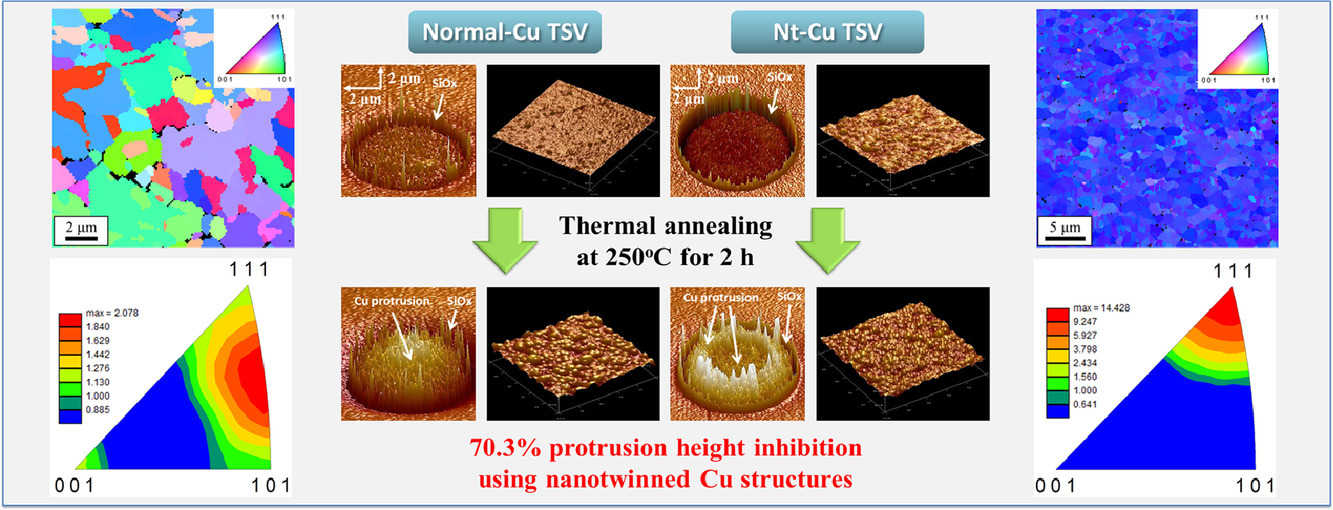

SCRIPTA
Vol. 197, 1 May. 2021, 113789
7. Modelling the effect of intrinsic radiation damage on mechanical properties: The crystalline-to-amorphous transition in zircon
本征輻照損傷對力學(xué)性能影響的模擬:鋯石從晶態(tài)到非晶態(tài)的轉(zhuǎn)變
Norbert Huber?, Tobias Beirau
Norbert Huber: norbert.huber@hzg.de
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113789
摘要
采用水平切高斯隨機(jī)場方法模擬了輻射誘導(dǎo)非晶化對鋯石(ZrSiO4)楊氏模量、泊松比和硬度的影響。模擬結(jié)果與之前的納米壓痕實(shí)驗(yàn)結(jié)果基本一致。在~16%和~84%的非晶態(tài)體積分?jǐn)?shù)下發(fā)生了兩個(gè)滲流轉(zhuǎn)變,導(dǎo)致楊氏模量的演化偏離線性。晶體區(qū)和非晶區(qū)之間的界面區(qū)域穩(wěn)定了相當(dāng)數(shù)量的非晶部分的硬度。該建模方法對預(yù)測與本征輻照損傷相關(guān)的各種材料力學(xué)性能的演化具有重要的應(yīng)用前景。
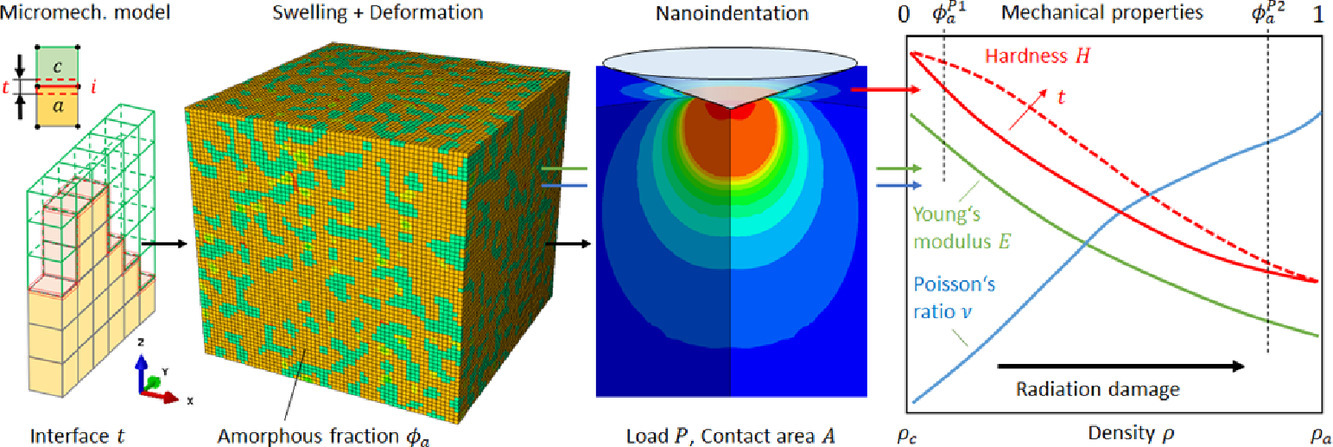

SCRIPTA
Vol. 197, 1 May. 2021, 113792
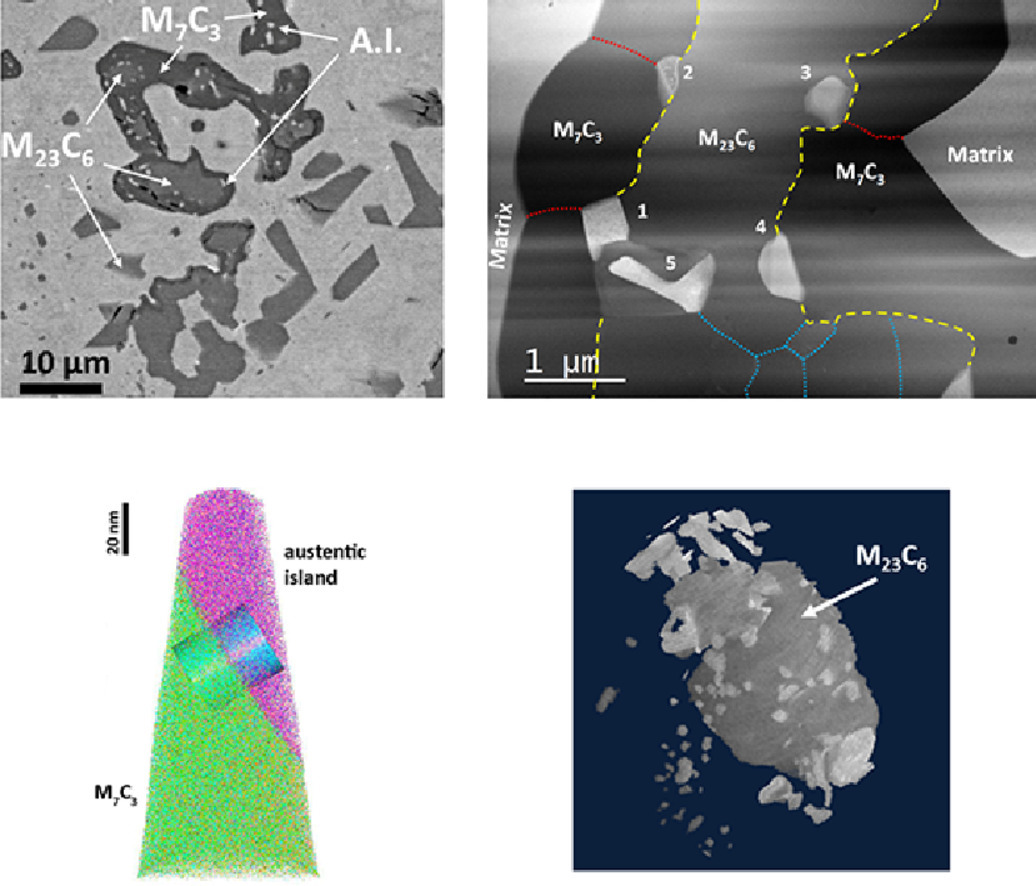
8. Formation mechanism and stability of austenitic islands in carbides in a Ni-Cr-Fe based high-temperature austenitic alloy undergoing carburization
Ni-Cr-Fe基高溫奧氏體合金滲碳過程中碳化物中奧氏體島的形成機(jī)理及穩(wěn)定性
Shipeng Shu?, Xiaobing Hu, Maryam Kazemzadeh-Atoufi, Tao Liu, Anyu Shang, Mark B. Davis, Robin Ziebarth, Sandeep Dhingra, Robert D. Morgan, Yao Du, Peter W.Voorhees, David N. Seidman
Shipeng Shu: spshu@northwestern.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113792
摘要
我們利用多尺度實(shí)驗(yàn)技術(shù)研究了Ni-Cr-Fe基高溫合金在技術(shù)上重要的滲碳過程中的相變。研究了M23C6向M7C3相變過程中碳化物結(jié)構(gòu)中形成的新型奧氏體島的形成及其穩(wěn)定性。結(jié)果表明,隨著M7C3的長大,金屬原子在M23C6-碳化物中過度飽和,奧氏體島形核于M23C6/M7C3相變前沿。奧氏體島形成后,由于其較大的尺寸(直徑幾百納米)和較弱的吉布斯-湯姆遜效應(yīng),奧氏體島與基體的成分暫時(shí)保持平衡,但在碳化物內(nèi)部保持相對穩(wěn)定。

SCRIPTA
Vol. 197, 1 May. 2021, 113804
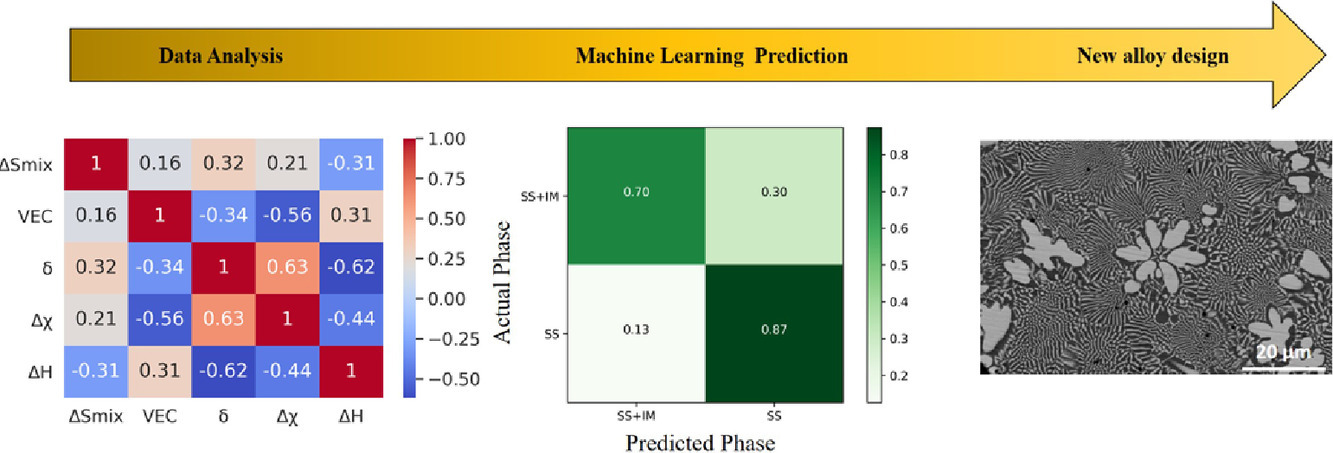
9. Machine learning approach to predict new multiphase high entropy alloys
用機(jī)器學(xué)習(xí)方法預(yù)測新型多相高熵合金
Yegi Vamsi Krishna, Ujjawal Kumar Jaiswal, Rahul M R?
Rahul M R: rahulmr@iitism.ac.in
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113804
摘要
多主元高熵合金因其良好的性能和可調(diào)控的微觀組織而引起了研究界的廣泛關(guān)注。在本研究中,我們使用機(jī)器學(xué)習(xí)方法預(yù)測了含有固溶體和金屬間化合物(SS+IM)的多相合金體系,數(shù)據(jù)集為636種合金。使用的算法有邏輯回歸、決策樹、支持向量機(jī)分類器、隨機(jī)森林、梯度增強(qiáng)分類器和人工神經(jīng)網(wǎng)絡(luò)(ANN)。ANN對試驗(yàn)數(shù)據(jù)的精度達(dá)到了80%以上。通過對新型合金的制備和表征對預(yù)測結(jié)果進(jìn)行了驗(yàn)證,發(fā)現(xiàn)ANN對所研究合金體系的預(yù)測更為準(zhǔn)確。對已建立數(shù)據(jù)集的統(tǒng)計(jì)分析揭示了妨礙成功預(yù)測的設(shè)計(jì)參數(shù)之間的重疊邊界。實(shí)驗(yàn)數(shù)據(jù)證實(shí)了新型多相合金的形成。

SCRIPTA
Vol. 197, 1 May. 2021, 113788
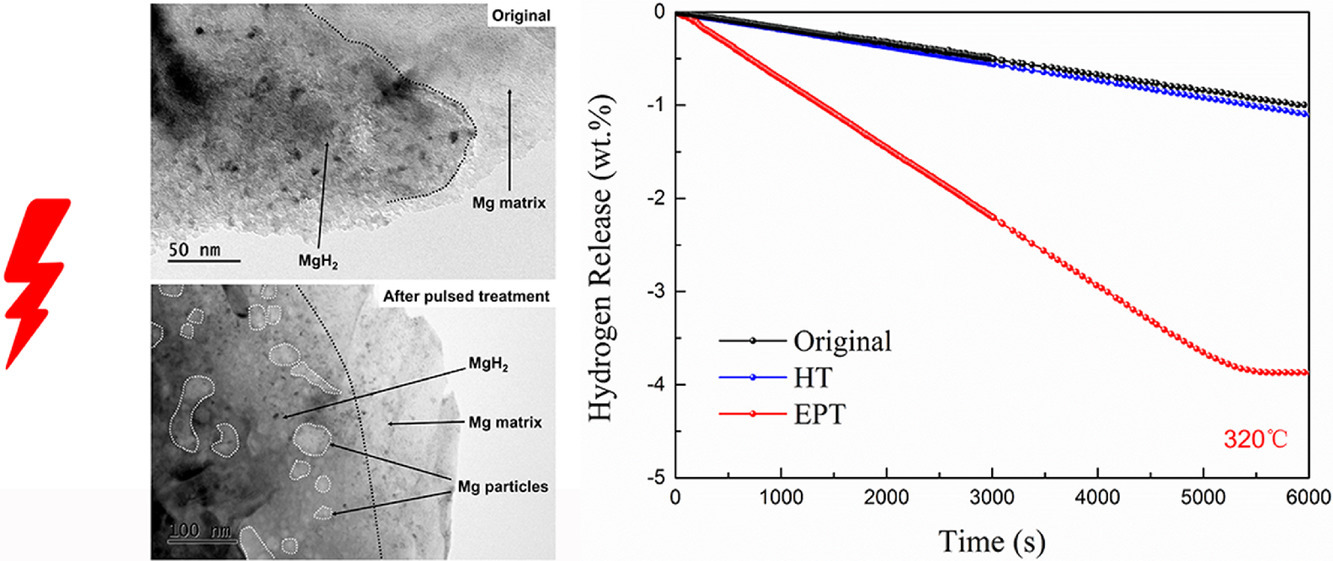
10. Superior dehydrogenation performance of Mg-based alloy under electropulsing
鎂基合金在電脈沖作用下的優(yōu)異脫氫性能
Guozhu Zhang, Shuyang Qin, Longge Yan, Xinfang Zhang?
Xinfang Zhang: xfzhang@ustb.edu.cn 北京科技大學(xué)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113788
摘要
氫能作為促進(jìn)全球能源轉(zhuǎn)型的可行技術(shù)途徑,已逐漸成為世界能源領(lǐng)域的熱點(diǎn)話題。為了解決固體儲氫材料中糟糕的脫氫動力學(xué)性能,本工作通過分析脫氫量、脫氫率、相組成和微觀組織,研究了電脈沖處理對鎂合金脫氫動力學(xué)性能的影響。經(jīng)電脈沖處理后,脫氫起始溫度降低了39℃,最大脫氫速率由7.48 wt.% H2/h提高到了14.36 wt.% H2/h。電脈沖處理為提高儲氫材料的脫氫動力學(xué)性能提供了新的思路和方法。