金屬頂刊雙語導讀丨Scripta Mater. Vol.199, 1 July. 2021(上)
2021-06-03 來源:GS_Metals

本期包含金屬材料領域論文8篇,涵蓋了高熵合金、奧氏體、形狀記憶合金等,國內科研單位包括重慶大學、天津大學、香港城市大學等(通訊作者單位)。
Vol. 199 目錄
1. Influence of parent Nb-alloy grain morphology on the layer formation of Nb3Sn and its flux pinning characteristics
母相Nb合金晶粒形貌對Nb3Sn層形成及其釘扎特性的影響
2. Oxidation mechanisms of an intermetallic alloy at high temperatures
金屬間化合物在高溫下的氧化機理
3. In situ monitoring nanoscale solid-state phase transformation of Ag nanowire during electrochemical reaction
電化學反應中銀納米線在納米尺度固態相變的原位監測
4. A novel L12-strengthened multicomponent Co-rich high-entropy alloy with both high γ′-solvus temperature and superior high-temperature strength
具有高γ'固溶溫度和優異高溫強度的新型L12強化多組分富鈷高熵合金
5. Revisiting the formation mechanism of intragranular κ-carbide in austenite of a Fe-Mn-Al-Cr-C low-density steel
重論Fe-Mn-Al-Cr-C低密度鋼奧氏體中晶內κ-碳化物的形成機制
6. Nucleation of coupled body-centered-cubic and closed-packed structures in liquid Ni-Cr alloys
液態Ni-Cr合金中體心立方和密堆積結構的耦合形核
7. Martensite phase structure of Mg-Sc lightweight shape memory alloy and the effect of rare earth elements doping
Mg-Sc輕質形狀記憶合金的馬氏體相結構及稀土元素摻雜的影響
8. Influence of element distribution on mechanical properties in the bonding zone of explosively welded steels
爆炸焊接鋼結合區元素分布對力學性能的影響
SCRIPTA
Vol. 199, 1 July. 2021, 113822
1. Influence of parent Nb-alloy grain morphology on the layer formation of Nb3Sn and its flux pinning characteristics
母相Nb合金晶粒形貌對Nb3Sn層形成及其釘扎特性的影響
Nobuya Banno?, Taro Morita, Tsuyoshi Yagai, Shigeki Nimori
Nobuya Banno: banno.nobuya@nims.go.jp
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113822
摘要
用基礎方法闡明了母相Nb合金晶粒形貌對Nb3Sn層的形成及其釘扎特性的影響。本文采用Nb-Ta-Hf,其回復溫度超過700℃,高于Nb3Sn相的形成溫度。首先,制備了Cu/ Nb-4at % Ta-1at %Hf單芯復合導線(外部為Cu)。隨后,切下兩片,其中一片在再結晶溫度下進行中間退火。然后,通過電鍍將Sn吸附在兩個樣品的表面,并對樣品進行熱處理,形成Nb3Sn層。顯然,冷拔后的Nb合金層晶粒明顯細化,具有更好的釘扎力性能。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 199, 1 July. 2021, 113852
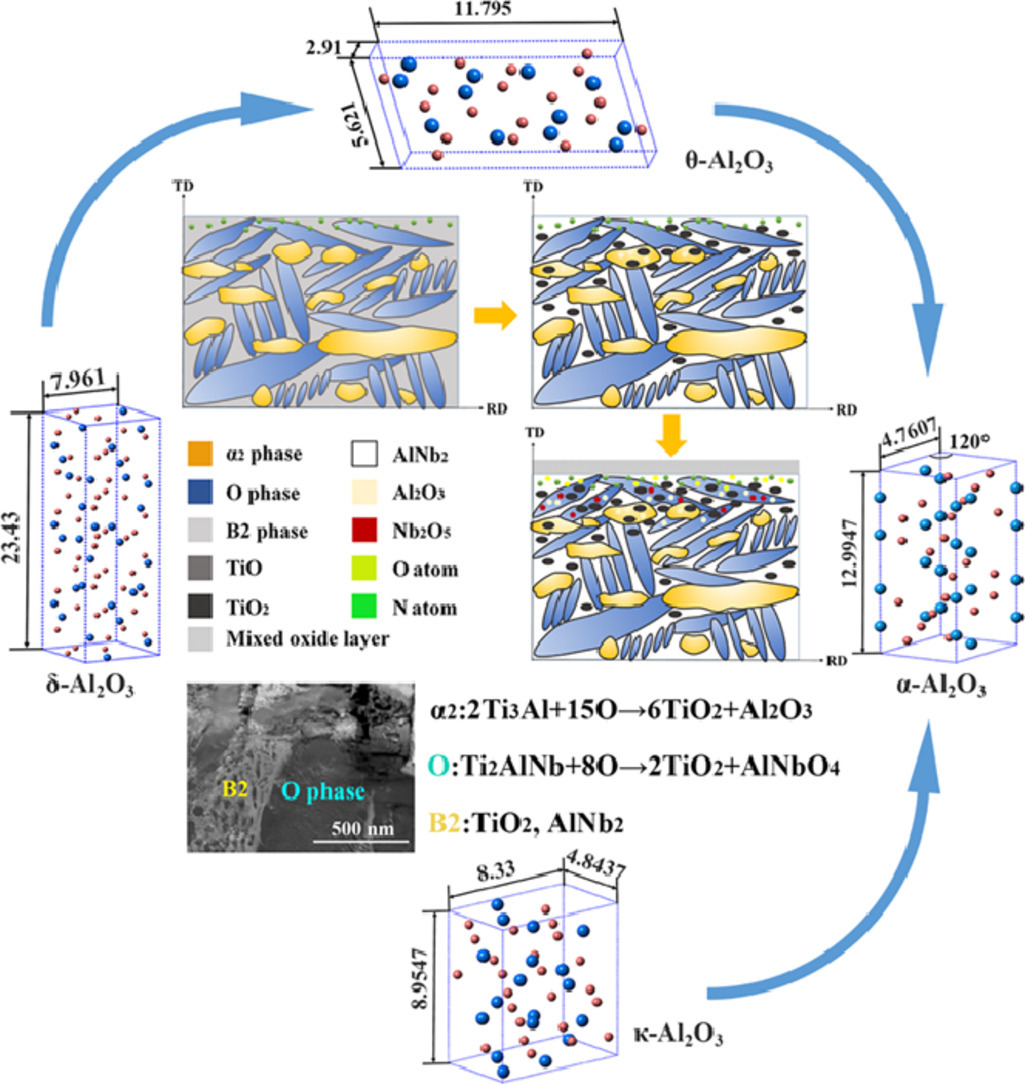
2. Oxidation mechanisms of an intermetallic alloy at high temperatures
金屬間化合物在高溫下的氧化機理
A. Chen, Q. Chen, S.J. Qu?, H.P. Xiang, C. Wang, J.B. Gao, A.H. Feng, D.L. Chen?
A. J. Qu: qushoujiang@tongji.edu.cn 同濟大學
A. L. Chen: dchen@ryerson.ca
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113852
摘要
本研究的目的是通過透射電子顯微鏡、X射線衍射和熱力學計算對氧化層/基體界面進行詳細分析,確定Ti2AlNb基合金的高溫氧化機理。氧首先吸附在合金表面,與B2相反應生成TiO2。B2相中鈦的耗竭促使剩余的鋁和鈮形成AlNb2,從而阻止了B2相的進一步氧化反應。α2相易被氧化形成TiO2和Al2O3。O相的氧化產物為TiO2和AlNbO4,它們是由Nb2O5和Al2O3進一步反應形成的。通過基于密度泛函理論的第一性原理計算,證實了反應的可能性,建立了Al2O3由亞穩態向穩態轉變的兩條路徑:δ-Al2O3→θ-Al2O3→α-Al2O3和κ-Al2O3→α-Al2O3。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 199, 1 July. 2021, 113835
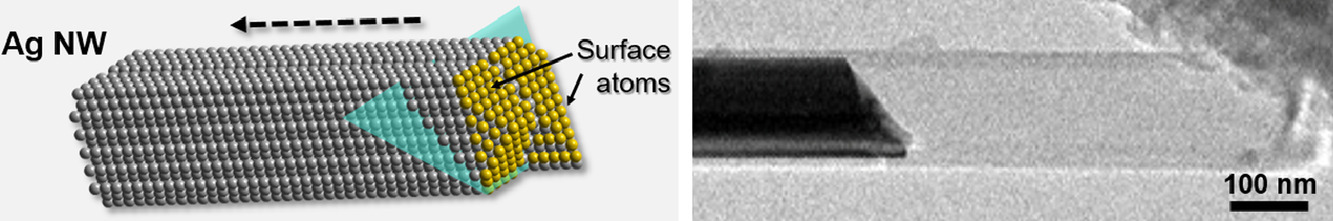
3. In situ monitoring nanoscale solid-state phase transformation of Ag nanowire during electrochemical reaction
電化學反應中銀納米線在納米尺度固態相變的原位監測
Lei Xu, Youran Hong, Jiangwei Wang?, Langli Luo?
Jiangwei Wang: jiangwei_wang@zju.edu.cn 浙江大學
Langli Luo: luolangli@tju.edu.cn 天津大學
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113835
摘要
金屬和合金在電化學過程中納米尺度的固態相變對于腐蝕、電化學加工和堿金屬電池等應用是至關重要的。然而,傳統表征技術缺少具有高空間分辨率的位點特定信息,無法檢測到金屬表面和界面處納米尺度的相和化學轉變。在這里,我們使用原位透射電子顯微鏡來驗證Ag納米線與Li在電化學合金化時的一種獨特相變。它的特點是Ag的電化學鋰化的表面反應,然后Ag快速重新分配到嵌入Li2O的小納米顆粒中。Ag-Li合金化反應通過表面反應模式進行,且與表面切面有很強的依賴性。AgLi和TEM柱中殘存的O2之間的弱鍵合使形成的Ag-Li合金立即轉變為一種分散良好的Ag納米粒子的Li2O殼層。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 199, 1 July. 2021, 113826
4. A novel L12-strengthened multicomponent Co-rich high-entropy alloy with both high γ′-solvus temperature and superior high-temperature strength
具有高γ'固溶溫度和優異高溫強度的新型L12強化多組分富鈷高熵合金
A. X. Cao, H.J. Kong, Z.Y. Ding, S.W. Wu, J.H. Luan, Z.B. Jiao, J. Lu, C.T. Liu?, T. Yang?
A. T. Liu: chainliu@cityu.edu.hk 香港城市大學
A. Yang: taoyang6-c@my.cityu.edu.hk 香港城市大學
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113826
摘要
本文開發了一種具有良好組織穩定性的L12強化多組分富鈷高熵合金。在800~1100℃等溫時效后,合金基體中形成了高密度的立方γ′顆粒;長期熱暴露后,在晶界和晶內均未形成脆性金屬間化合物相。原子探針分析表明,Ta和Nb元素優先配分到γ′金屬間化合物中,這對L12有序晶體結構的穩定具有重要作用。更重要的是,該合金具有較高的γ′-固溶溫度(1125°C)和較低的質量密度(8.28 g cm-3),并具有優異的高溫抗拉強度(800°C時為755 MPa, 900°C時為664 MPa)。該研究結果為設計基于Co的具有更廣泛溫度性能的先進L12強化高溫合金提供了基本范式。
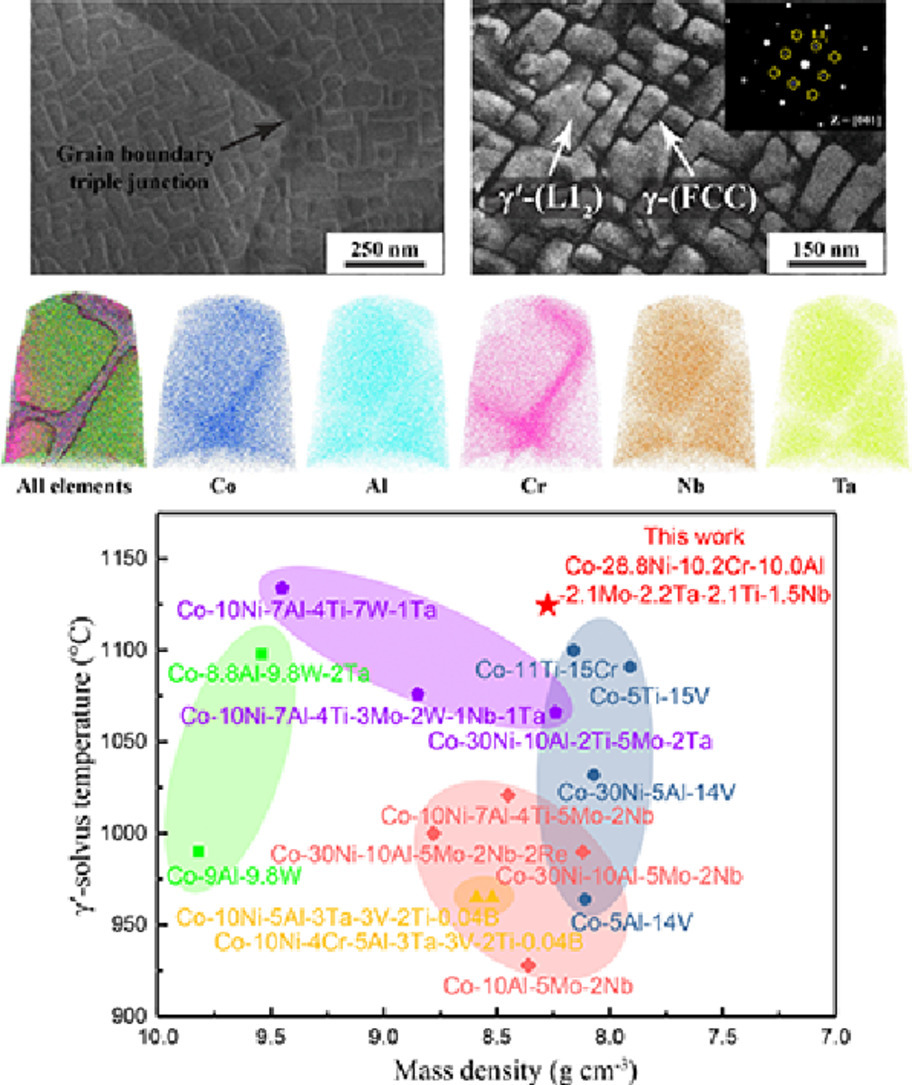
SCRIPTA
Vol. 199, 1 July. 2021, 113836
5. Revisiting the formation mechanism of intragranular κ-carbide in austenite of a Fe-Mn-Al-Cr-C low-density steel
重論Fe-Mn-Al-Cr-C低密度鋼奧氏體中晶內κ-碳化物的形成機制
Jianlei Zhang, Yueshan Jiang, Weisen Zheng, Yuxiang Liu, Ahmed Addad, Gang Ji?, Changjiang Song?, Qijie Zhai
Gang Ji: gang.ji@univ-lille.fr
Changjiang Song: riversong@shu.edu.cn 上海大學
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113836
摘要
通常認為γ-奧氏體中晶內κ-碳化物的形成是由于調幅分解和隨后的有序反應。在本工作中,我們用高分辨透射掃描顯微鏡和原子探針斷層掃描對奧氏體基Fe-20Mn-9Al-3Cr-1.2C(wt.%)低密度鋼進行了近原子尺度的表征,結果表明初步形成的κ碳化物(顆粒尺寸為2-3nm)為有序的L′12結構,但是沒有檢測到元素的配分。在400 ~ 800℃溫度范圍內,熱力學計算表明FCC相的吉布斯能隨Al和C含量的變化始終呈現出正曲率(即(d2G/dx2)< 0)。這兩個結果都表明,有序的κ-碳化物核心可以直接在無序的γ-奧氏體中形成,而不是由于眾所周知的調幅分解有序機制。γ-奧氏體基體與κ-碳化物具有相似的晶格結構、相同的成分和完全的共格性,這導致了極低的形核勢壘。
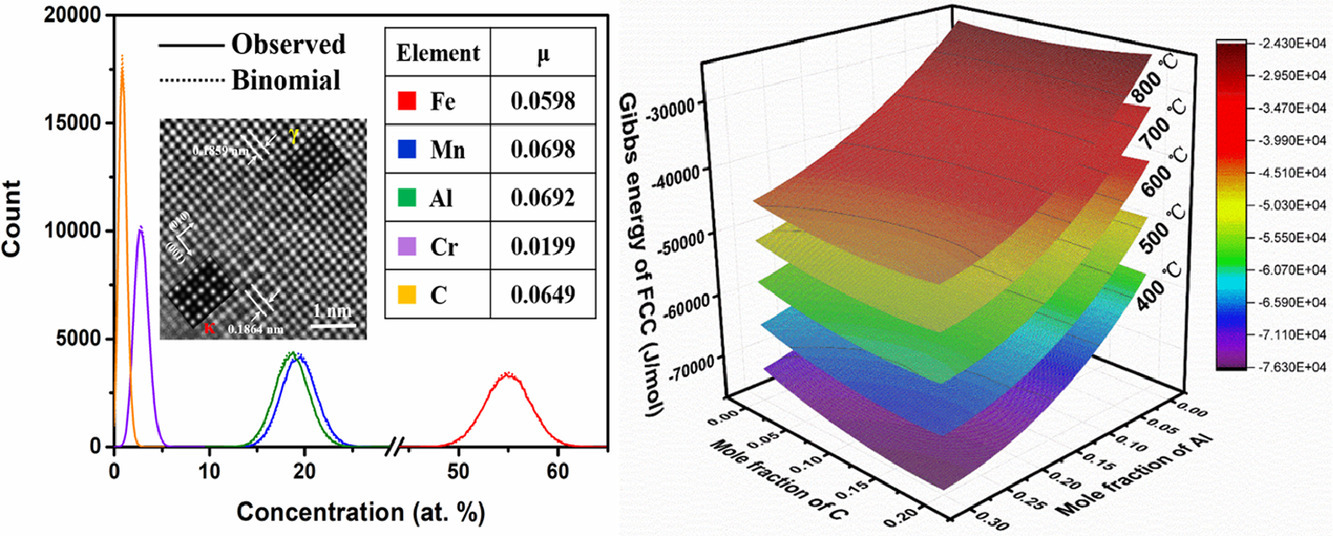
SCRIPTA
Vol. 199, 1 July. 2021, 113857
6. Nucleation of coupled body-centered-cubic and closed-packed structures in liquid Ni-Cr alloys
液態Ni-Cr合金中體心立方和密堆積結構的耦合形核
Deep Choudhuri?, Skyler Matteson, Reilly Knox
Deep Choudhuri: deep.choudhuri@nmt.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113857
摘要
在過去的四十年中,對單組分面心立方(FCC)材料液相內的預臨界固態核心的結構進行了廣泛的研究。這些研究表明,平衡FCC的形成是由亞穩態體心立方(BCC)結構的預臨界核心介導的。然而,目前未知這種形核機理是否適用于以FCC和BCC結構作為平衡相的多組分結構合金。我們通過分子動力學模擬,以Ni-35at.%Cr和Ni-50at.%Cr二元合金為對象對此問題進行了研究。結果表明,預臨界和臨界晶核由富Cr的BCC和富Ni的密堆積(FCC和六方密堆積)結構組成。通過將合金熔體預先分離成富Cr和富Ni的液袋,可以促進這種多結構預臨界晶核的形成。晶核內的BCC和密排區域由隨時間演變的非平衡成分組成。因此,濃縮Ni-Cr合金中的非傳統形核機理使其能夠凝固成FCC-BCC微觀結構。
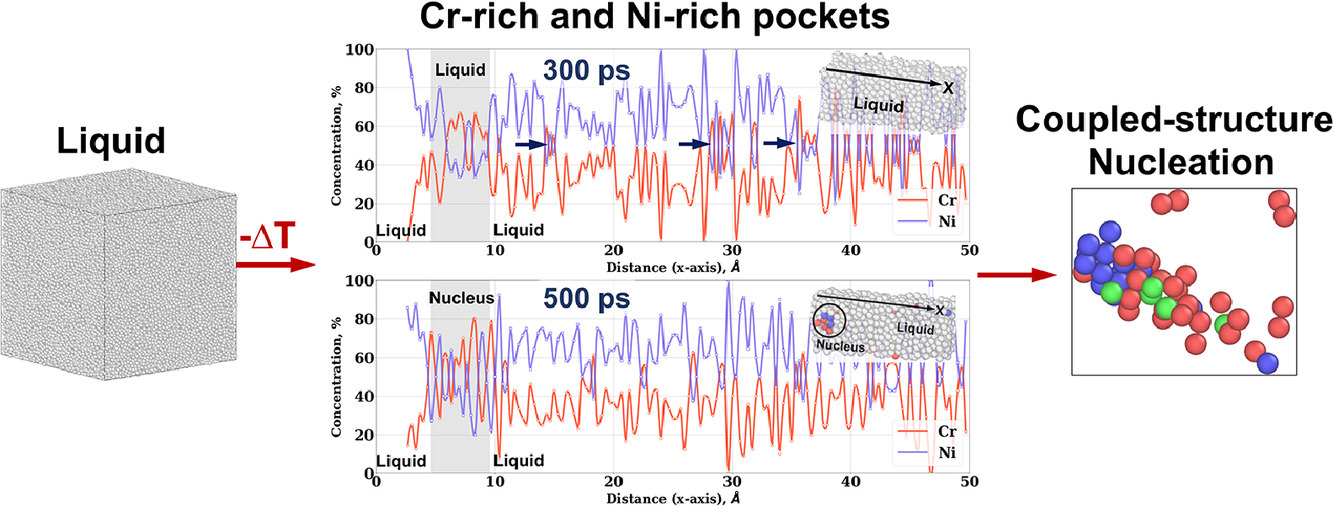
SCRIPTA
Vol. 199, 1 July. 2021, 113863
7. Martensite phase structure of Mg-Sc lightweight shape memory alloy and the effect of rare earth elements doping
Mg-Sc輕質形狀記憶合金的馬氏體相結構及稀土元素摻雜的影響
Wenbin Zhao, Erjun Guo, Kun Zhang?, Xiaohua Tian, Changlong Tan
Kun Zhang: kunzhang@hrbust.edu.cn 哈爾濱理工大學
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113863
摘要
隨著輕量化形狀記憶合金(SMAs)應用需求的不斷增加,Mg-Sc合金作為一種新型形狀記憶合金受到了人們的廣泛關注。然而,Mg-Sc合金不明確的馬氏體組織,不明確的相變路徑以及低的馬氏體相變溫度(Tm)等問題仍然存在。本文系統研究了Mg-Sc合金的馬氏體組織和相變路徑。通過形成能確定了馬氏體相為正交晶相。此外,為了改善Tm,研究了稀土元素的摻雜對Tm的影響;在1.25 at.% Gd摻雜下,Tm提高了28.2 K。總態密度表明,相穩定性決定了Tm的增加。此外,偏態密度表明,d軌道電子在Sc和Gd原子之間的耦合導致了Tm的變化。我們的研究結果為設計新型Mg-Sc基輕量化SMAs提供了堅實的基礎。
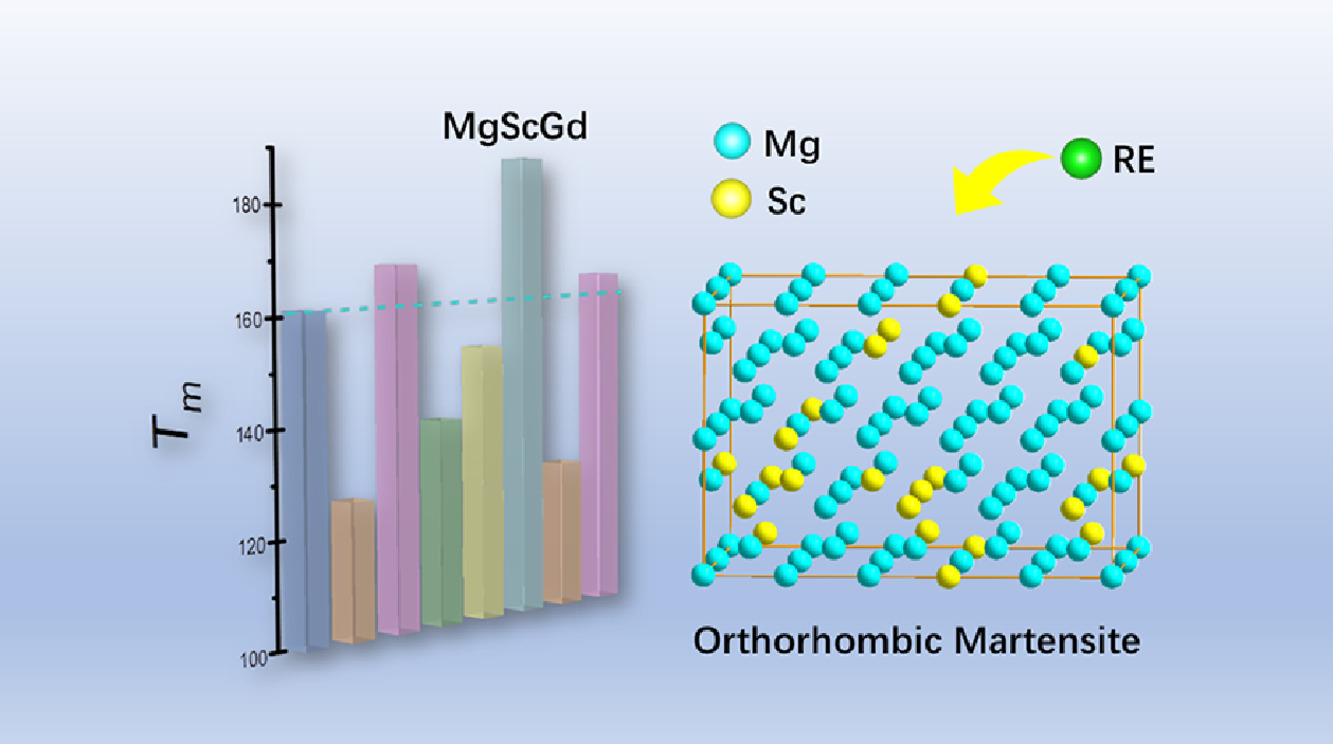
SCRIPTA
Vol. 199, 1 July. 2021, 113860
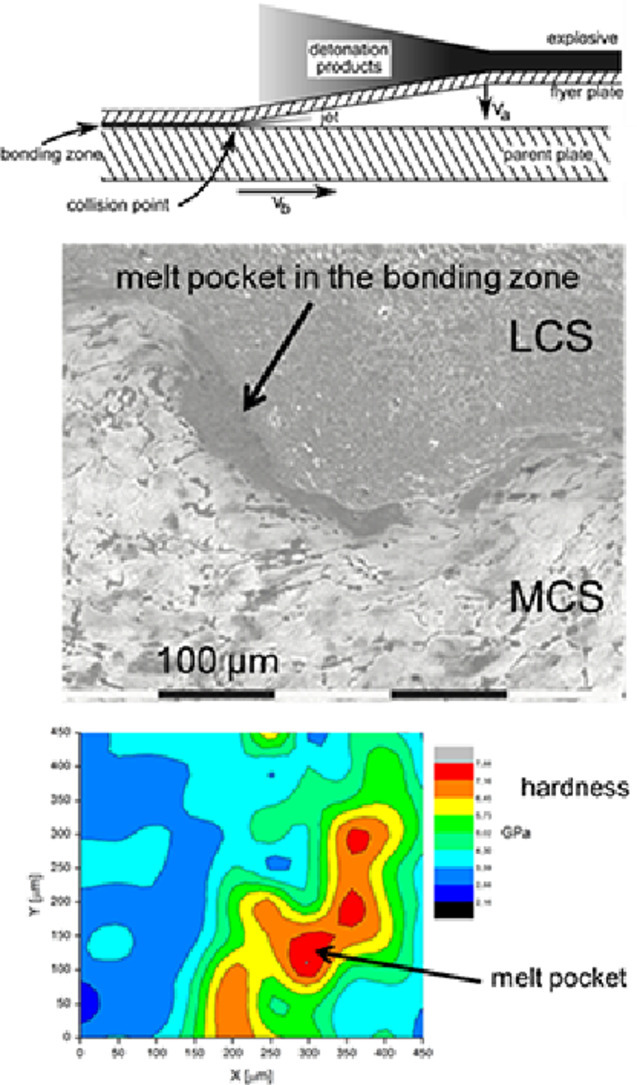
8. Influence of element distribution on mechanical properties in the bonding zone of explosively welded steels
爆炸焊接鋼結合區元素分布對力學性能的影響
A. Borchers?, J. Arlt, C. Nowak, F. Gärtner, M. Hammerschmidt, H. Kreye, C.A. Volkert, R. Kirchheim
A. Borchers: cborche@uni-goettingen.de
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113860
摘要
利用激光輔助原子探針層析技術研究了中碳鋼與低碳鋼爆炸焊接結合過程中結合區的熔袋特征。結果表明,該區域具有納米晶結構,亞晶界富含碳元素。熔袋中的高硬度值歸因于(亞)晶粒尺寸和碳分布的共同作用。