金屬頂刊雙語導讀丨Scripta Mater. Vol.201, 1 Aug. 2021(上)
2021-06-06 來源:GS_Metals

本期包含金屬材料領域論文14篇,涵蓋了高熵合金、奧氏體鋼等,國內科研單位包括西北工業大學、清華大學等(通訊作者單位)。
Vol. 201 目錄
1. Martensitic transformation induced dislocation walls in Fe42Mn38Co10Cr10 high-entropy alloy
Fe42Mn38Co10Cr10高熵合金中馬氏體相變誘發位錯墻的形成
2. Investigation of the orientation relationship between nano-sized G-phase precipitates and austenite with scanning nano-beam electron diffraction using a pixelated detector
采用具有像素化檢測器的掃描納米束電子衍射研究G相納米析出與奧氏體的取向關系
3. Remelting induced fully-equiaxed microstructures with anomalous eutectics in the additive manufactured Ni32Co30Cr10Fe10Al18 eutectic high-entropy alloy
增材制造Ni32Co30Cr10Fe10Al18共晶高熵合金中具有異常共晶的重熔誘導全等軸微觀組織
4. Effect of alloying elements on the hydrogen diffusion and trapping in high entropy alloys
合金元素對高熵合金中氫擴散和捕獲的影響
5. Nanoparticle enabled high performance high modulus steels
納米顆粒使高性能高模量鋼成為可能
6. A statistical model of irradiation hardening induced by non-periodic irradiation defects
非周期輻照缺陷誘導輻照硬化的統計模型
7. Lattice distortion in selective laser melting (SLM)-manufactured unstable β-type Ti-15Mo-5Zr-3Al alloy analyzed by high-precision X-ray diffractometry
用高精度X射線衍射儀分析選擇性激光熔化(SLM)制造的不穩定β型Ti-15Mo-5Zr-3Al合金的晶格畸變
8. Towards controlling intrinsic heat treatment of maraging steel during laser directed energy deposition
在激光直接能量沉積過程中控制馬氏體時效鋼的本征熱處理
9. Work hardening discrepancy designing to strengthening gradient nanotwinned Cu
加工硬化差異化設計強化梯度納米孿晶Cu
10. The detrimental effect of elemental contaminants when using B additions to improve the creep properties of a Ni-based superalloy
B添加改善Ni基高溫合金蠕變性能時,元素污染物的有害影響
11. A universal configurational entropy metric for high-entropy materials
高熵材料的通用構型熵度量
12. Reducing functional fatigue, transition stress and hysteresis of NiTi micropillars by one-step overstressed plastic deformation
通過一步超應力塑性變形降低NiTi微柱的功能性疲勞、相變應力和滯后
13. Bulk nanostructured Al-Si alloy with remarkable improvement in strength and ductility
強度和塑性顯著提高的塊體納米結構Al-Si合金
14. Enhanced ductility of as-quenched martensite by highly stable nano-sized austenite
高穩定納米奧氏體提高淬火態馬氏體的塑性
SCRIPTA
Vol. 201, 1 Aug. 2021, 113929
1. Martensitic transformation induced dislocation walls in Fe42Mn38Co10Cr10 high-entropy alloy
Fe42Mn38Co10Cr10高熵合金中馬氏體相變誘發位錯墻的形成
L. Qi, X.D. Huang, A.P. Zhang, H.W. Chen?, J.F. Nie?
H. W. Chen: hwchen@cqu.edu.cn 重慶大學
J. F. Nie: jianfeng.nie@monash.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113929
摘要
利用像差校正掃描透射電鏡在原子尺度上對Fe42Mn38Co10Cr10 (at.%)冷變形高熵合金中兩種迄今未被報道的位錯墻進行了表征。兩種位錯墻均位于兩個平行并置的馬氏體片層間的界面上,盡管它們分別由全30°混合或全90°刃型肖克利部分位錯構成。在這兩種位錯墻內,兩組不同的肖克利部分位錯具有大小相同但符號相反的伯氏矢量,并在六角晶格的連續基面上交替排列。包含這種致密位錯墻的界面通過各種位錯-界面的相互作用,可以改善應變硬化和塑性協調。

SCRIPTA
Vol. 201, 1 Aug. 2021, 113930
2. Investigation of the orientation relationship between nano-sized G-phase precipitates and austenite with scanning nano-beam electron diffraction using a pixelated detector
采用具有像素化檢測器的掃描納米束電子衍射研究G相納米析出與奧氏體的取向關系
Niels Cautaerts?, Edgar F. Rauch, Jiwon Jeong, Gerhard Dehm, Christian H. Liebscher
Niels Cautaerts: n.cautaerts@mpie.de
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113930
摘要
采用具有像素化探測器的掃描納米束電子衍射,研究了輻照誘導的納米G相(M6Ni16Si7)與奧氏體基體的取向關系。利用該探測器,由細小G相粒子產生的微弱衍射斑可以同時分解為強矩陣反射。采用兩階段模板匹配方案對衍射圖形進行分析,即先對基體進行索引,然后在減去基體對衍射圖形的貢獻后對析出相進行索引。結果表明,G相與奧氏體呈一定的取向關系,這是面心立方(FCC)到體心立方(BCC)轉變的特征。本研究表明,具有像素化探測器的納米束電子衍射技術可以相對輕松地研究其他材料體系中具有復雜晶體結構的納米析出相的取向關系。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 201, 1 Aug. 2021, 113952
3. Remelting induced fully-equiaxed microstructures with anomalous eutectics in the additive manufactured Ni32Co30Cr10Fe10Al18 eutectic high-entropy alloy
增材制造Ni32Co30Cr10Fe10Al18共晶高熵合金中具有異常共晶的重熔誘導全等軸微觀組織
Kexuan Zhou, Junjie Li?, Qingfeng Wu, Zhilin Zhang, Zhijun Wang?, Jincheng Wang
Junjie Li: lijunjie@nwpu.edu.cn 西北工業大學
Zhijun Wang: zhjwang@nwpu.edu.cn 西北工業大學
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113952
摘要
在合金的增材制造中,通常會獲得外延生長的粗大柱狀晶粒,從而造成各向異性的力學性能甚至熱撕裂裂紋的形成。在本研究中,我們提出了一種新的方法,即在增材制造Ni32Co30Cr10Fe10Al18共晶高熵合金中,通過重熔誘導柱狀晶向等軸晶轉變,從而促進全等軸晶微觀組織的形成。與傳統鑄態和其他打印態的共晶高熵合金相比,我們的工作展示了具有優異的強度和塑性組合的各向同性力學性能。這一新發現可應用于其他共晶體系的增材制造,以調控等軸組織并優化性能。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 201, 1 Aug. 2021, 113957
4. Effect of alloying elements on the hydrogen diffusion and trapping in high entropy alloys
合金元素對高熵合金中氫擴散和捕獲的影響
Sara Correa Marques, Amanda Ventura Castilho, Dilson S. dos Santos?
Dilson S. dos Santos: dilson@metalmat.ufrj.br
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113957
摘要
研究了合金元素濃度對Fe20Mn20Ni20Co20Cr20和Fe22Mn40Ni30Co6Cr2兩種高熵合金中氫擴散率和捕獲率的影響。從兩種合金的氣體滲透試驗中得到,氫擴散率為溫度的函數(300-550°C)。在兩種面心立方合金中均觀察到S型行為,遵循菲克第二定律。等原子和非等原子合金的擴散系數分別為D=4.3χ10-7exp()和D=2.8χ10-8exp()。第一性原理模擬結果表明,擴散系數的差異主要是由于Cr含量的降低,Cr在固溶狀態下會與氫產生強烈的交互作用。通過對高熵合金和傳統鋼在Cr含量上的比較,進一步加強了這一分析。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 201, 1 Aug. 2021, 113954
5. Nanoparticle enabled high performance high modulus steels
納米顆粒使高性能高模量鋼成為可能
Shiqi Zheng, Rosalía Rementeria, Wenbin Kan, Mingjie Xu, Jin Huang, Yu Huang, Xiaoqing Pan, Diran Apelian, Yongfeng Liang, Junpin Lin, Marcos Perez, Xiaochun Li?
Xiaochun Li: xcli@seas.ucla.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113954
摘要
在此,我們提出了一種新的概念,使用低體積分數的納米顆粒對Fe-Ti-B熔體進行納米化處理,用于制備新型高性能高模量鋼(HMS)。研究了納米處理后的Fe-Ti-B HMS的微觀組織。納米處理的HMS由細小的TiB2顆粒和出乎意料的超細Fe2B片層組成。由于固有的脆性效應,傳統上認為Fe2B相在煉鋼過程中是有害的,但本研究表明,有害的Fe2B相可以成功地轉變為有利相。納米處理后的HMS的抗拉強度明顯高于常規制備的HMS(950 MPa vs. 510 MPa),同時保持了高的楊氏模量、低的密度和高的塑性。這一新概念有效地證明了在不改變凝固速率的情況下,使用納米粒子成功地細化了Fe-Ti-B體系的結構。這克服了實現提高機械性能與主流應用制造之間的兩難困境,并使剛性HMS能夠用于實際應用的輕量化。本文提出了一種在合金熔體中納米顆粒誘導納米級溶質富集的新機制,為金屬制備提供了新的途徑。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 201, 1 Aug. 2021, 113959
6. A statistical model of irradiation hardening induced by non-periodic irradiation defects
非周期輻照缺陷誘導輻照硬化的統計模型
Wei Cui, Yinan Cui?, Wei Liu?
Yinan Cui: cyn@mail.tsinghua.edu.cn 清華大學
Wei Liu: liuw@mail.tsinghua.edu.cn 清華大學
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113959
摘要
由于輻照硬化模型在核反應堆設計和服役壽命預測中的重要作用,人們為發展輻照硬化模型付出了大量的努力。大多數模型都是基于位錯線張力近似,假設有周期性的輻照缺陷排列。隨機分布效應通常也從完全確定性的角度考慮,如著名的Bacon-Kocks-Scattergood模型。與以往的研究不同,本研究旨在通過系統地粗化位錯與非周期輻照缺陷之間的交互作用機制,建立統計輻照硬化模型。通過解析推導得到了克服輻照缺陷勢壘的臨界切應力的累積分布函數,并將其集中到二維蒙特卡羅模型中,用于預測輻照材料的力學響應。預測結果與三維離散位錯動力學結果和實驗數據吻合得很好。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 201, 1 Aug. 2021, 113953
7. Lattice distortion in selective laser melting (SLM)-manufactured unstable β-type Ti-15Mo-5Zr-3Al alloy analyzed by high-precision X-ray diffractometry
用高精度X射線衍射儀分析選擇性激光熔化(SLM)制造的不穩定β型Ti-15Mo-5Zr-3Al合金的晶格畸變
Aya Takase?, Takuya Ishimoto, Ryoya Suganuma, Takayoshi Nakano?
Aya Takase: aya.takase@mat.eng.osaka-u.ac.jp
Takayoshi Nakano: nakano@mat.eng.osaka-u.ac.jp
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113953
摘要
通過高精度X射線衍射(XRD)分析,首次觀察到選擇性激光熔化(SLM)制備的不穩定β型Ti-15Mo-5Zr-3Al中的特殊晶格畸變。經SLM處理后,Ti-15Mo-5Zr-3Al由體心立方結構轉變為體心四方結構;c軸比a軸短0.63%。XRD分析表明,試樣表面的拉伸殘余應力為210±12 MPa。數值模擬表明,SLM過程中存在快速冷卻,這可能導致殘余應力的產生。通過對部分釋放應力的SLM試樣和殘余應力可忽略的電子束熔鑄試樣進行比較,發現SLM中快速冷卻引起的殘余應力導致了晶格畸變。這一發現與之前認為殘余應力改變晶格參數而不產生晶格畸變的認識不一樣。這項研究為SLM特有的超快冷速和不穩定相共同產生的晶格畸變提供了新的見解。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 201, 1 Aug. 2021, 113973
8. Towards controlling intrinsic heat treatment of maraging steel during laser directed energy deposition
在激光直接能量沉積過程中控制馬氏體時效鋼的本征熱處理
Sasan Amirabdollahian, Faraz Deirmina?, Luke Harris, Raveendra Siriki, Massimo Pellizzari, Paolo Bosetti, Alberto Molinari?
Faraz Deirmina: Faraz.deirmina@sandvik.com
Alberto Molinari: Alberto.molinari@unitn.it
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113973
摘要
研究了馬氏體時效鋼粉末在激光直接能量沉積(L-DED)過程中的本征熱處理(IHT)。模擬了構筑過程中每一層的熱歷史,以評估層間暫停對材料經歷的最高和最低溫度的影響。最低溫度隨層間停頓而降低,增強了奧氏體向馬氏體的轉變,從而觸發了在隨后的層間沉積過程中金屬間化合物的析出。隨后,制備不同層間停頓的試樣,研究了沿構筑方向的硬度分布、抗壓強度和微觀組織,并與時效曲線進行比較。結果與模擬結果一致,并表明本征熱處理可以避免構筑后熱處理。

SCRIPTA
Vol. 201, 1 Aug. 2021, 113975
9. Work hardening discrepancy designing to strengthening gradient nanotwinned Cu
加工硬化差異化設計強化梯度納米孿晶Cu
Tao Wan, Zhao Cheng, Linfeng Bu, Lei Lu?
Lei Lu: llu@imr.ac.cn 沈陽材料科學國家(聯合)實驗室
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113975
摘要
本研究通過固定表面硬組分,改變中心層的軟組分,以研究夾層梯度納米孿晶(GNT)銅的力學行為。我們發現,隨著構件加工硬化差值的增加,GNT Cu的強度和加工硬化同時增加,與獨立構件相比會產生更好的強度-塑性協同效應。力學性能的優化是應變離域化、彈塑性轉變時間延長和應變梯度增大的結果,這些因素在界面處誘發了更多的幾何必須位錯(GNDs)。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 201, 1 Aug. 2021, 113971
10. The detrimental effect of elemental contaminants when using B additions to improve the creep properties of a Ni-based superalloy
B添加改善Ni基高溫合金蠕變性能時,元素污染物的有害影響
Martin Detrois?, Zongrui Pei, Tao Liu, Jonathan D. Poplawsky, Michael C. Gao, Paul D. Jablonski, Jeffrey A. Hawk
Martin Detrois: martin.detrois@netl.doe.gov
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113971
摘要
利用先進的表征技術和第一性原理模擬方法,研究了在不同Si含量下使用B改善Ni基高溫合金蠕變性能時Si污染的影響。Si的存在緩解了B沿晶界偏析對蠕變性能的積極影響,Si也表現出類似的偏析傾向。采用密度泛函理論,通過計算晶界解理能進行了驗證。Si降低了晶界結合力,抵消了B的積極作用。
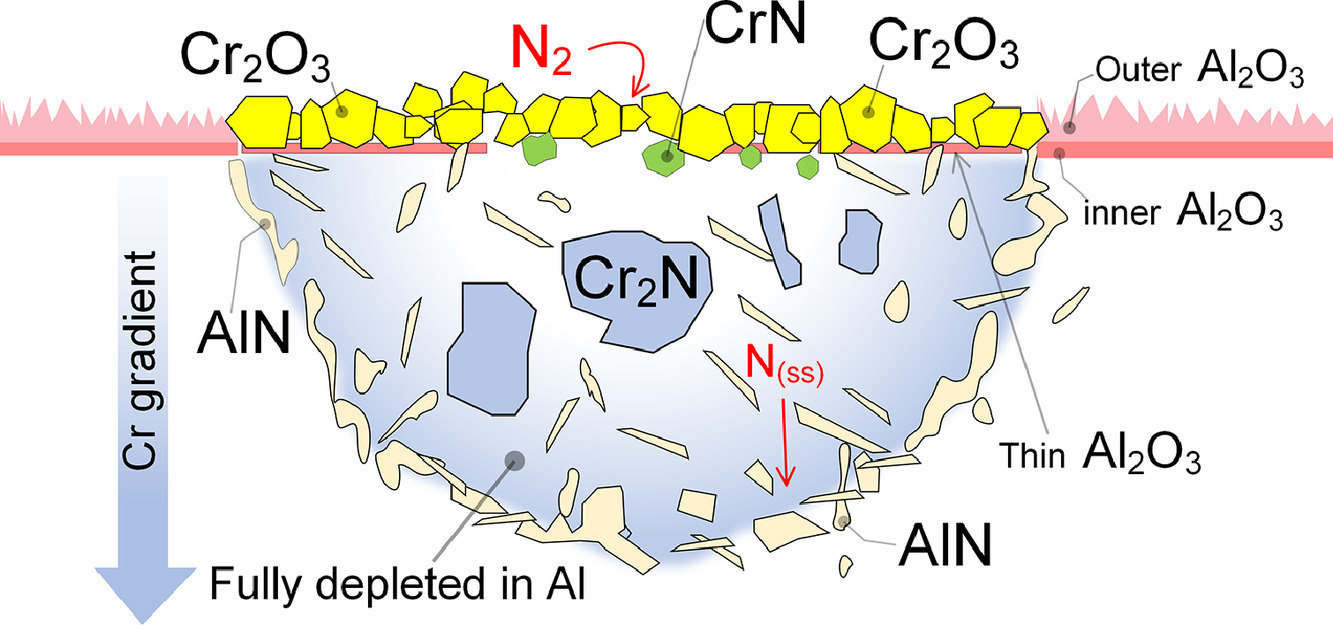
SCRIPTA
Vol. 201, 1 Aug. 2021, 113974
11. A universal configurational entropy metric for high-entropy materials
高熵材料的通用構型熵度量
Olivia F. Dippo, Kenneth S. Vecchio?
Kenneth S. Vecchio: kvecchio@eng.ucsd.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113974
摘要
近年來,高熵材料變得越來越復雜,超越了基于構型熵計算的簡單固溶體,也超越了先前建立的對于高、中和低熵的度量。先前的度量標準是基于特定金屬的熔化熵和單原子氣體的內能的近似,因此不適用于其他材料。本文提出了一種普遍適用于晶體材料的新型熵度量,從簡單的固溶高熵合金到具有復雜晶體結構和多個亞晶格的高熵材料。此外,本文還討論了復雜晶體結構中構型熵的計算方法。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 201, 1 Aug. 2021, 113958
12. Reducing functional fatigue, transition stress and hysteresis of NiTi micropillars by one-step overstressed plastic deformation
通過一步超應力塑性變形降低NiTi微柱的功能性疲勞、相變應力和滯后
Kangjie Chu, Qingping Sun?
Qingping Sun: meqpsun@ust.hk 香港科技大學
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113958
摘要
研究了一次超應力壓縮塑性變形對多晶NiTi功能性疲勞的影響。立方形的微柱在1.8 GPa條件下進行一次塑性變形,殘余應變為3.5%,然后在1 GPa條件下進行106次循環壓縮。與初始微柱相比,塑性變形微柱的總殘余應變、相變應力和滯后回線面積分別減小了74%、52%和67%。顯微組織分析表明,在一次塑性變形過程中,所觀察到的變化來源于飽和位錯結構和殘余納米馬氏體。前者抑制了后續循環相變中位錯的進一步形成,從而提高了循環穩定性,而后者通過產生的殘余應力和直接的馬氏體生長降低了整體相變應力和滯后損耗。該方法簡單有效地降低了用于彈熱制冷機的NiTi合金的功能性疲勞,提高了NiTi的冷卻性能。
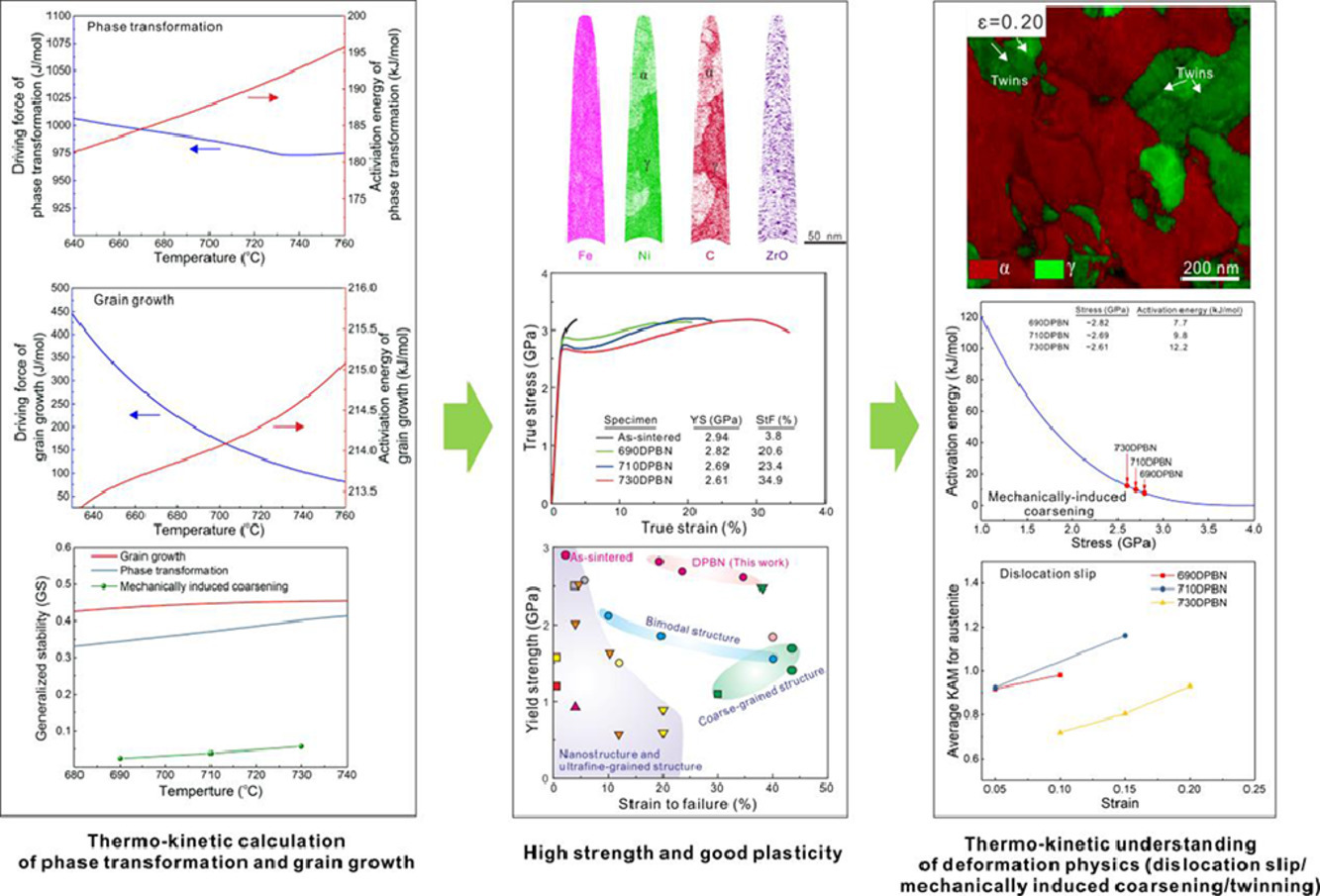
SCRIPTA
Vol. 201, 1 Aug. 2021, 113970
13. Bulk nanostructured Al-Si alloy with remarkable improvement in strength and ductility
強度和塑性顯著提高的塊體納米結構Al-Si合金
Maowen Liu, Ruixiao Zheng?, Wenlong Xiao?, Jin Li, Guodong Li, Qiuming Peng, Chaoli Ma
Ruixiao Zheng: zhengruixiao@buaa.edu.cn 北京航空航天大學
Wenlong Xiao: wlxiao@buaa.edu.cn 北京航空航天大學
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113970
摘要
對具有低溶合金元素的金屬材料進行微觀組織細化一直是一項艱巨的任務。我們提出了一種新的兩步法來實現這一目標,該方法已成功地應用于亞共晶Al-Si合金。首先在超高等靜壓下通過固溶處理制備Al-Si單相合金,然后進行高壓扭轉,首次獲得塊體納米結構亞共晶Al-Si合金。超細的Al晶粒、Si納米顆粒、濃縮的Si溶質和位錯對屈服強度有很大的貢獻。同時,通過將Si細化到納米尺度,避免了普通Al-Si合金中微米級Si相的脆性斷裂,顯著提高了合金的塑性。因此,納米結構Al-Si合金表現出403 MPa的高屈服強度和32%的總延伸率。這項工作為實現具有低溶組分的塊體納米結構合金提供了一個有效的途徑。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 201, 1 Aug. 2021, 113955
14. Enhanced ductility of as-quenched martensite by highly stable nano-sized austenite
高穩定納米奧氏體提高淬火態馬氏體的塑性
Ji Hoon Kim?, Guiyoung Gu, Minseo Koo, Eun-Young Kim, Jae-Sang Lee, Dong-Woo Suh
Ji Hoon Kim: kjh8027@postech.ac.kr
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113955
摘要
奧氏體是提高先進高強鋼拉伸性能的關鍵。在本研究中,利用包括富Mn滲碳體和鐵素體基體的化學非均質初始組織,在淬火馬氏體中形成了納米尺寸的奧氏體顆粒。富Mn滲碳體在奧氏體化過程中轉變為納米奧氏體,冷卻至室溫后仍有相當數量的奧氏體保留。奧氏體顆粒具有特殊的穩定性,這不能完全解釋為Mn的富集。壓應力和配分到奧氏體中的C元素也可能提高奧氏體的穩定性。高穩定性的奧氏體提供了持久的TRIP效應,顯著提高了延伸率,而不影響淬火態馬氏體的抗拉強度。