金屬頂刊雙語導讀丨Scripta Mater. Vol.201, 1 Aug. 2021(下)
2021-06-20 來源:GS_Metals
本期包含金屬材料領域論文5篇,涵蓋了高熵合金、不銹鋼、高溫合金等,國內科研單位包括上海交通大學等(通訊作者單位)。
1. Interfacial phases formed in friction stir lap welding high entropy alloy to Al alloy
高熵合金與鋁合金攪拌摩擦搭接焊接過程中形成的界面相
2. Enhanced resistance to fatigue crack propagation in metastable austenitic stainless steel by nanotwin bundles
納米孿晶束增強亞穩奧氏體不銹鋼的抗疲勞裂紋擴展能力
3. Real-time visualization of particle evolution during reactive flux-assisted processing of aluminum melts
反應助熔劑輔助處理鋁熔體過程中粒子演化的實時可視化
4. Compositionally graded nano-sized borides in a directionally solidified nickel-base superalloy
定向凝固鎳基高溫合金中的成分梯度納米硼化物
5. Origin of twin-like {33-64} tilt boundary and associated solute segregation in a high strain rate deformed Mg-Y alloy
高應變率變形Mg-Y合金中類孿晶{33-64}傾斜邊界的起源及伴隨的溶質偏聚
Vol. 201, 1 Aug. 2021, 113972
1. Interfacial phases formed in friction stir lap welding high entropy alloy to Al alloy
高熵合金與鋁合金攪拌摩擦搭接焊接過程中形成的界面相
Haining Yao, Hongyuan Wen, Ke Chen?, Muyang Jiang, Kolan Madhav Reddy, Katsuyoshi Kondoh, Min Wang, Xueming Hua, Aidang Shan
Ke Chen: chenke83@sjtu.edu.cn 上海交通大學
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113972
摘要
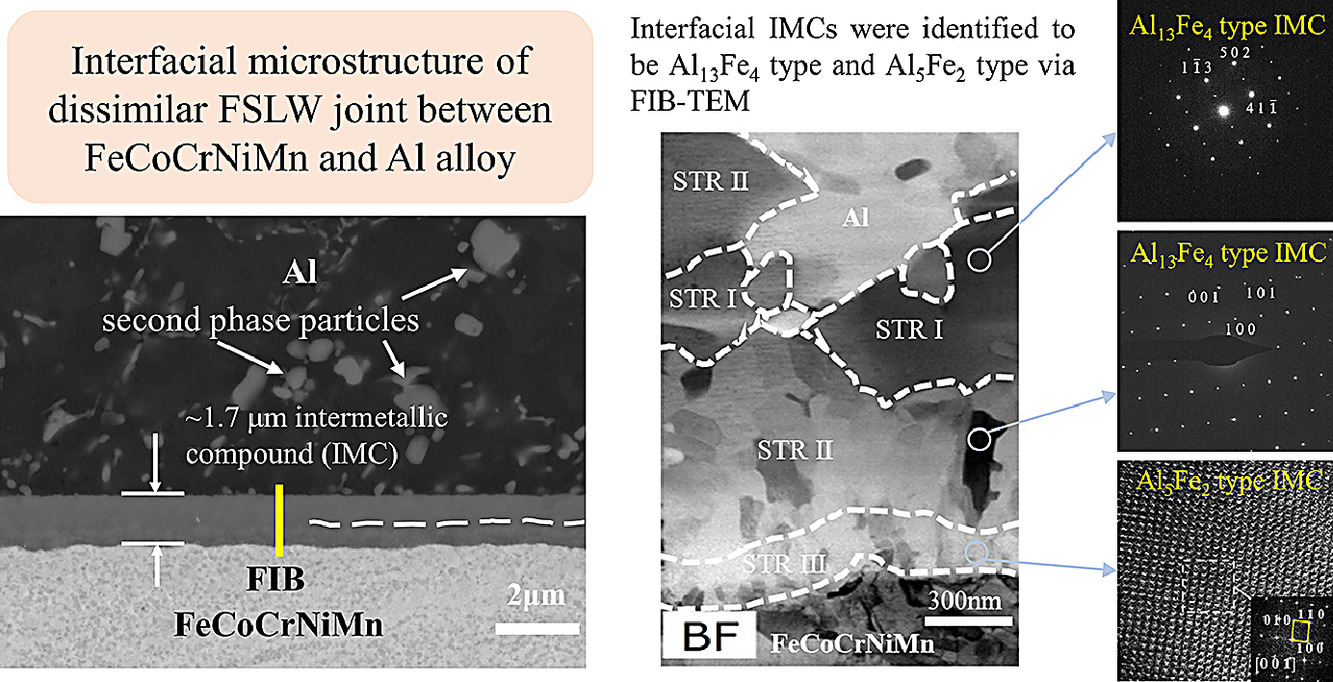
不同金屬結合界面處金屬間化合物(IMCs)的形成是近年來研究的熱點,因為這些界面IMCs在很大程度上決定了接頭的性能。本研究采用攪拌摩擦搭接焊(FSLW)將FeCoCrNiMn高熵合金(HEA)與傳統的1060Al合金連接,以降低HEA過高的成本。微觀組織表征表明,界面層是連續的,但厚度在1.3~1.7 μm之間。界面結構可分為三種類型。靠近Al的是STR I和STR II,確認是相同的單斜Al13Fe4型IMC,但和STR I中Cr和Mn的共損耗以及Co和Ni的共富集展現出強烈的成分差異。靠近HEA側的是STR III,由平行排列的超細柱狀晶粒組成,經鑒定為斜方晶Al5Fe2型IMC。
The formation of intermetallic compounds (IMCs) at the joint interface between dissimilar metals has been the focus of recent research, since joint properties are largely determined by these interfacial IMCs. In this study, FeCoCrNiMn high entropy alloy (HEA) was joined to traditional 1060Al alloy by friction stir lap welding (FSLW) for the purpose of reducing the excessive cost of HEAs. Microstructural characterization shows the interfacial layer is continuous but varies in thickness from 1.3 to 1.7 μm. The interfacial structure can be divided into three types. Close to the Al side are STR I and II, confirmed to be of same monoclinic Al13Fe4 type IMC, but showing sharp difference in composition with simultaneous co-depletion of Cr and Mn and co-enrichment of Co and Ni in STR I. Close to the HEA side is STR III, consisting of parallelly arranged ultra-fine columnar grains, identified to be orthorhombic Al5Fe2 type IMC.
Vol. 201, 1 Aug. 2021, 113976
2. Enhanced resistance to fatigue crack propagation in metastable austenitic stainless steel by nanotwin bundles
納米孿晶束增強亞穩奧氏體不銹鋼的抗疲勞裂紋擴展能力
Aya Matsushita, Yoji Mine?, Kazuki Takashima
Yoji Mine: mine@msre.kumamoto-u.ac.jp
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113976
摘要
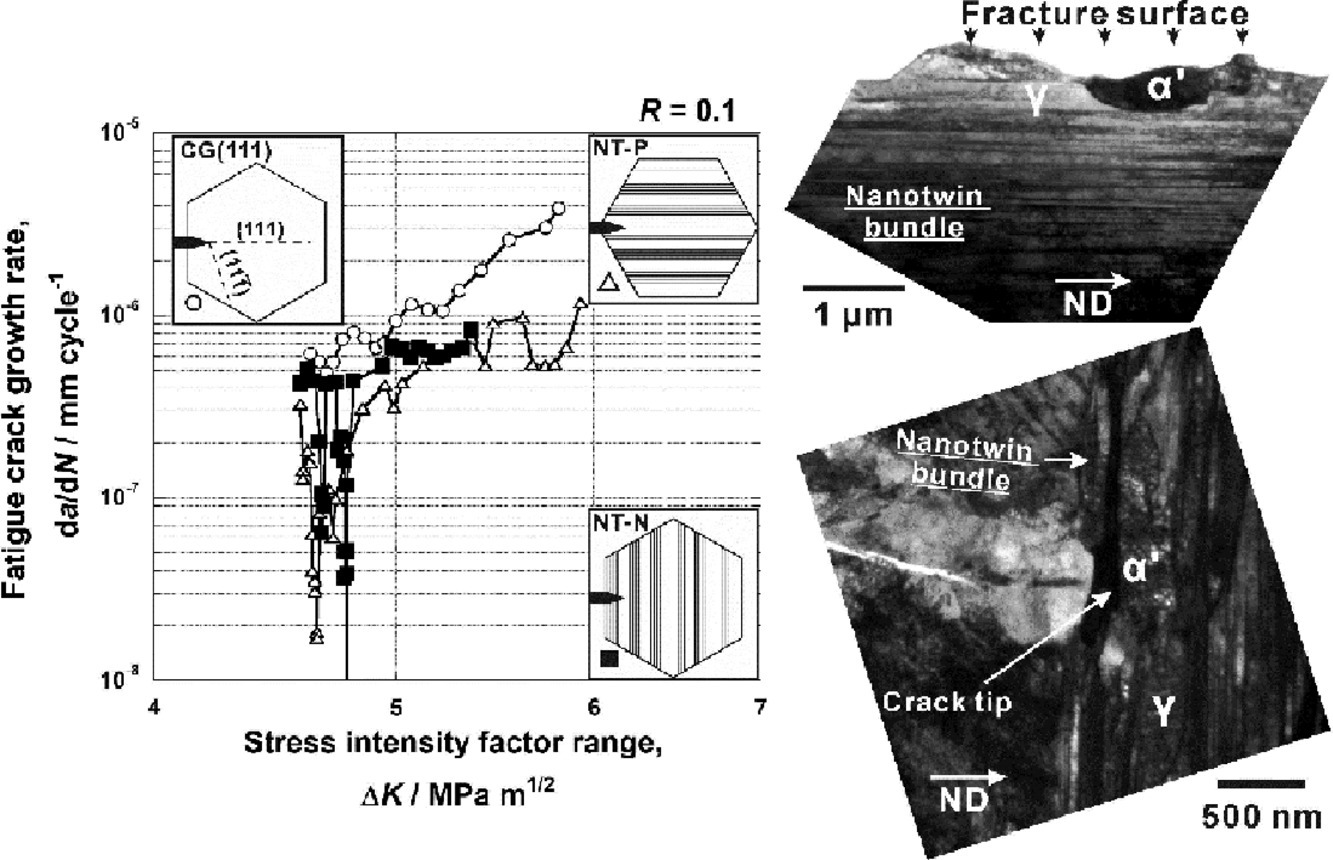
采用微型緊湊拉伸試樣結合疲勞后金相組織觀察,研究了含納米孿晶束的304亞穩奧氏體不銹鋼的組織敏感型疲勞裂紋擴展。與無納米孿晶束的粗晶試樣相比,無論層取向如何,單變體納米孿晶試樣均具有較高的抗裂紋擴展能力。在納米孿晶束中,裂紋擴展過程中馬氏體變體在與孿晶面平行的慣習面上形成。即使裂紋沿孿晶界擴展,它也傾向于通過多個滑移系的激活進入形成的馬氏體相,從而抑制脆性孿晶界的分離。疲勞后透射電鏡的表征顯示去孿晶發生在裂紋尖端之前。因此,在亞穩奧氏體鋼中引入納米孿晶束,通過去孿晶和馬氏體的形成改變了損傷積累過程,提高了抗疲勞裂紋擴展能力。
Microstructure-sensitive fatigue crack growth in 304 metastable austenitic stainless steel containing nanotwin bundles was studied using a miniature compact tension specimen combined with post-fatigue metallographic examinations. The single-variant nanotwinned specimens exhibited high crack growth resistance compared to the coarse-grained specimen without nanotwin bundles, regardless of lamellar orientation. In the nanotwin bundles, martensite variants are formed with the habit plane parallel to the twin plane during crack propagation. Even when the crack propagates along the twin boundary, it tends to proceed by activation of multiple slip systems into the formed martensite phase, which inhibits brittle twin boundary separation. Post-fatigue transmission electron microscopy revealed that detwinning occurred ahead of the crack tip. Therefore, introducing nanotwin bundles into the metastable austenitic steel changes the course of damage accumulation through detwinning and martensite formation, enhancing the fatigue crack growth resistance.
Vol. 201, 1 Aug. 2021, 113978
3. Real-time visualization of particle evolution during reactive flux-assisted processing of aluminum melts
反應助熔劑輔助處理鋁熔體過程中粒子演化的實時可視化
C. W. Reese?, A. Gladstein, P. Shevchenko, X. Xiao, A.J. Shahani, A.I. Taub
C. W. Reese: reesecw@umich.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113978
摘要
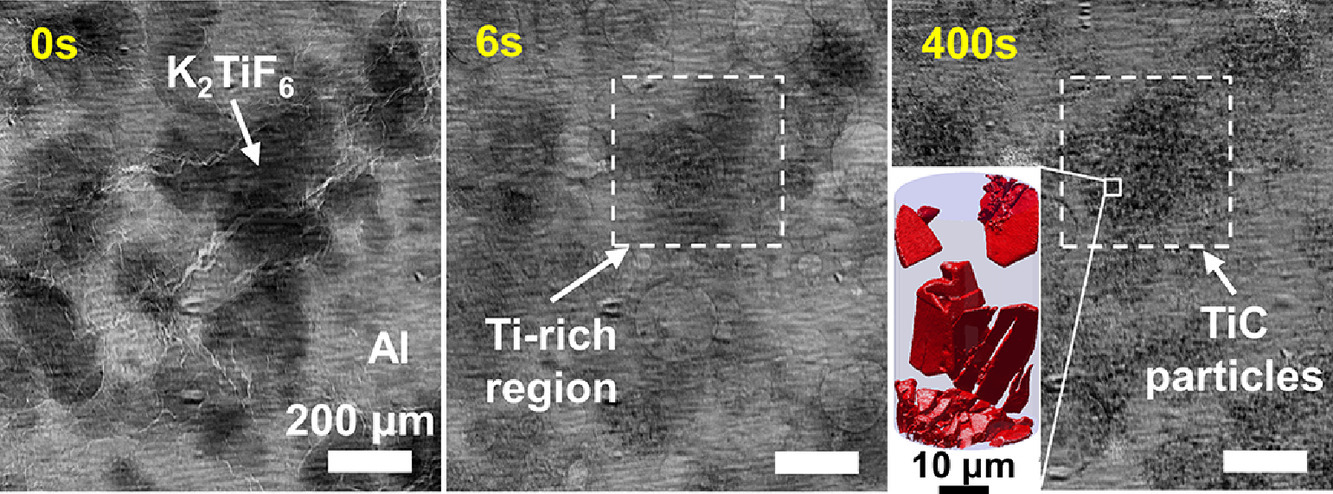
本文報道了用熔劑輔助反應合成的Al-TiC金屬基復合材料的多模態、多尺度相關層析成像研究。同步X射線顯微放射照像術用于實時可視化反應和粒子演化。顆粒直徑和面數密度的變化表明這一過程是形核主導的而不是長大主導的。在950℃時,大部分反應發生在相對較短的時間內,小于600s。在二維(掃描電子顯微鏡)和三維(同步X射線納米層析成像)中,顯微結構以更高的分辨率成像,顯示處了具有六方薄片形貌的碳化物顆粒的形成。我們認為這種形貌的出現是由于實驗中Si雜質的摻入造成的。相關的層析工作流程和分析對未來金屬基復合材料(MMC)的加工策略將具有指導意義。
A multi-modal, multi-scale correlative tomography investigation of Al-TiC metal matrix composites processed via flux-assisted reaction synthesis is reported. Synchrotron X-ray microradiography is utilized to visualize the reaction and particle evolution in real-time. Changes in particle diameter and areal number density suggest that the process is nucleation- rather than growth-dominated. At 950 °C, the bulk of the reaction takes place in a relatively short time span of less than 600 s. The microstructure is imaged at higher resolution in 2D (scanning electron microscopy) and 3D (synchrotron X-ray nanotomography), revealing the formation of carbide particles with a hexagonal platelet morphology. We propose that the morphology arises due to the incorporation of Si impurities during the experiment. It is expected that the correlative tomography workflow and analysis may guide future metal matrix composite (MMC) processing strategies.
Vol. 201, 1 Aug. 2021, 113981
4. Compositionally graded nano-sized borides in a directionally solidified nickel-base superalloy
定向凝固鎳基高溫合金中的成分梯度納米硼化物
Richa Gupta, K.C. Hari Kumar, M.J.N.V. Prasad, Prita Pant?
Prita Pant: pritapant@iitb.ac.in
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113981
摘要
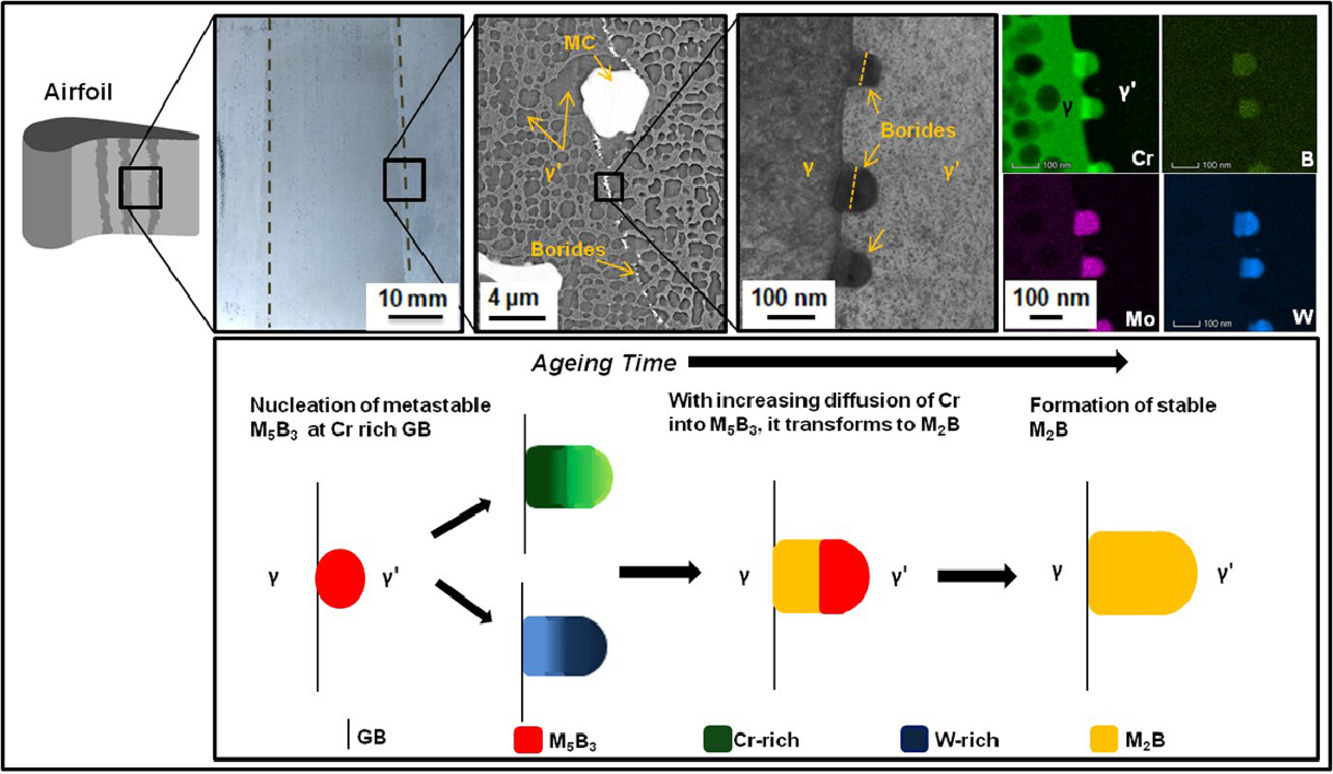
硼可以影響晶界的微區化學成分,從而提高高溫合金的力學性能;然而,硼在晶界的存在形式仍然存在爭議。我們從電子顯微鏡表征表明,在定向凝固的鎳基高溫合金中,硼以近球形的納米金屬硼化物的形式存在。我們還報道了沿晶界分布的納米級硼化物析出相中Cr、W成分梯度的存在。這些硼化物是離散存在的,并抑制了大多數學者報道的M23C6碳化物在柱狀晶界的團聚。這可能是硼改良定向凝固高溫合金橫向蠕變性能改善的原因之一。
Boron is known to influence the grain boundary microchemistry and thereby improve the mechanical performance of superalloys; however, the form in which boron exists at the grain boundary is debatable. We show from electron microscopy characterization that in a directionally solidified Ni-base superalloy boron is present in the form of nearly spherical nano-sized metal borides. We also report the existence of a gradient in composition of Cr, and W within the nano-sized boride precipitates located along the grain boundaries. These borides are present discretely and suppress the agglomeration of mostly reported M23C6 carbides at the columnar grain boundaries. This could be a possible reason for the reported improvement in transverse creep properties of boron modified directionally solidified superalloys.
Vol. 201, 1 Aug. 2021, 113982
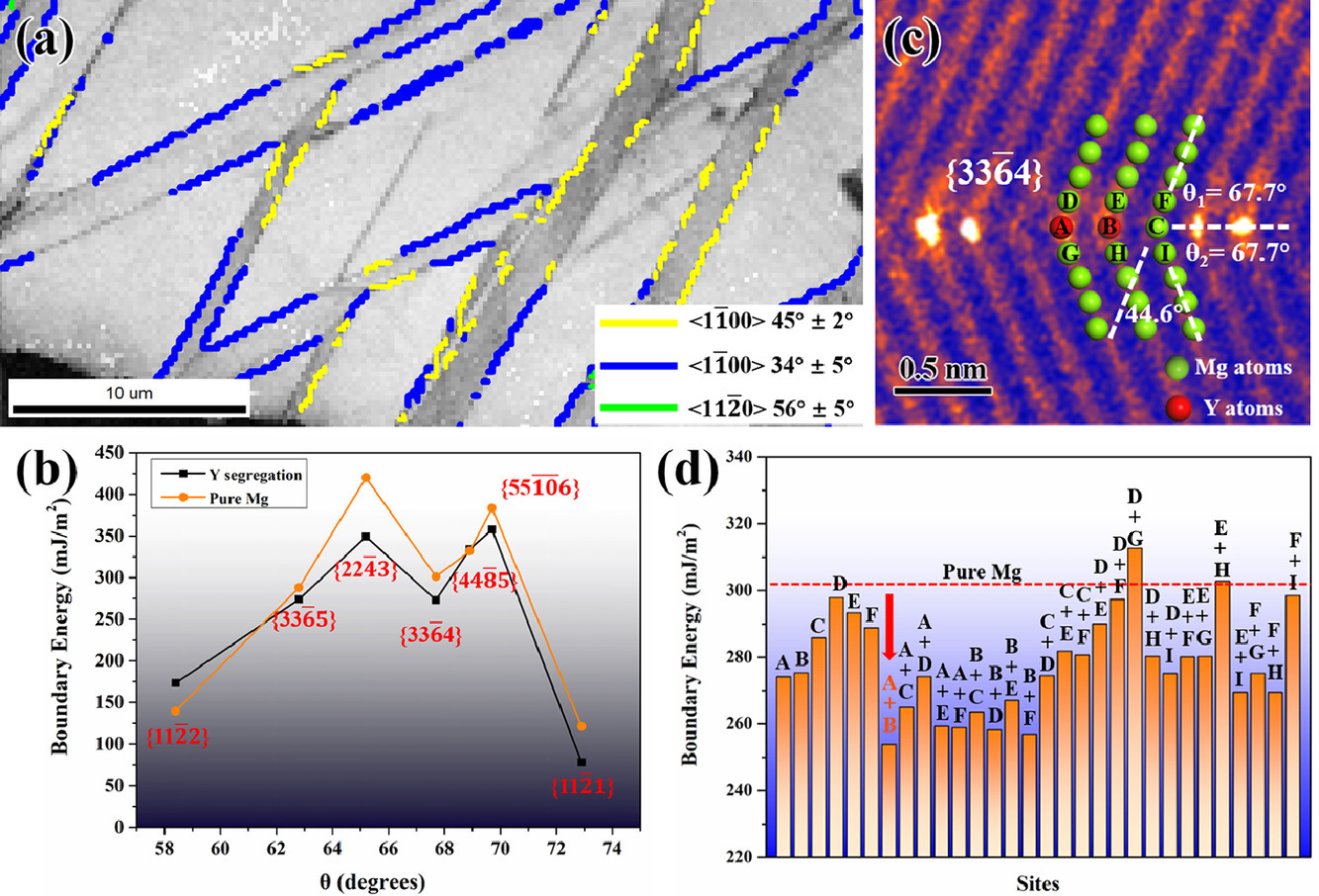
5. Origin of twin-like {33-64} tilt boundary and associated solute segregation in a high strain rate deformed Mg-Y alloy
高應變率變形Mg-Y合金中類孿晶{33-64}傾斜邊界的起源及伴隨的溶質偏聚
Huan Zhang, Yangxin Li?, Zhigang Ding, Tian Xie, Ruixue Liu, Yuliang Li, Dezhi Zhang, Qingchun Zhu, Xiaoqing Shang, Xiaoqin Zeng?
Yangxin Li: astatium@sjtu.edu.cn 上海交通大學
Xiaoqin Zeng: xqzeng@sjtu.edu.cn 上海交通大學
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113982
摘要
為研究<1-100>對稱傾斜晶界,制備了高應變率壓縮的Mg-Y合金。在變形Mg-Y合金中,首次發現了由{11-21}孿晶界演化而形成的類孿晶界{33-64}傾斜晶界。結合高角度環形暗場掃描透射電子顯微鏡和密度泛函理論計算,對{33-64}傾斜晶界的形成和Y原子的相關偏聚進行了合理的解釋。這一發現對孿晶行為提供了新的見解,為新型高性能鎂合金的設計提供了新的思路。
A high strain rate compressed Mg-Y alloy is prepared for the study of <1-100> symmetric tilt grain boundary. A twin-like {33-64} tilt boundary, which is formed via the evolution of {11-21} twin boundary, is commonly found for the first time in the deformed Mg-Y alloy. Via combining high-angle annular dark-field scanning transmission electron microscopy and density functional theory calculations, the formation of {33-64} tilt boundary and the associated segregation of Y atoms are rationalized. Such a finding provides a new vision on twinning behavior for the design of new high-performance Mg alloys.
.