金屬頂刊雙語導讀丨Scripta Mater. Vol.202, 1 Sep. 2021(上)
2021-07-04 來源:GS_Metals

本期包含金屬材料領域論文8篇,涵蓋了高熵合金、增材制造、高溫合金等,國內科研單位包括北京科技大學等(通訊作者單位)。
Vol. 202 目錄
1. Design of a new cobalt base nano-lamellar eutectic high entropy alloy
一種新型鈷基納米層狀共晶高熵合金的設計
2. Hierarchical structure in Al-Cu alloys to promote strength/ductility synergy
Al-Cu合金中的層次結構促進強度/塑性的協同作用
3. Role of deformation twinning in fatigue of CrCoNi medium-entropy alloy at room temperature
變形孿晶在CrCoNi中熵合金室溫疲勞中的作用
4. High strength NiMnFeCrAlCu multi-principal-element alloys with marine application perspective
高強度NiMnFeCrAlCu多主元素合金在海洋中的應用前景
5. Vacancy surface migration mechanisms in dilute nickel-chromium alloys
稀Ni-Cr合金中的空位表面遷移機制
6. Effect of alloying elements on the coarsening rate of γ? precipitates in multi-component CoNi-based superalloys with high Cr content
合金元素對高Cr多組分CoNi基高溫合金γ?析出相粗化速率的影響
7. Dual plateau stress of C15-type topologically close-packed lattice structures additive-manufactured by laser powder bed fusion
通過激光粉末床熔合技術增材制造的C15型拓撲密排晶格結構的雙平臺應力
8. Simultaneous deformation twinning and martensitic transformation in CoCrFeMnNi high entropy alloy at high temperatures
CoCrFeMnNi高熵合金在高溫下同時產生變形孿晶和馬氏體相變
SCRIPTA
Vol. 202, 1 Sep. 2021, 113993
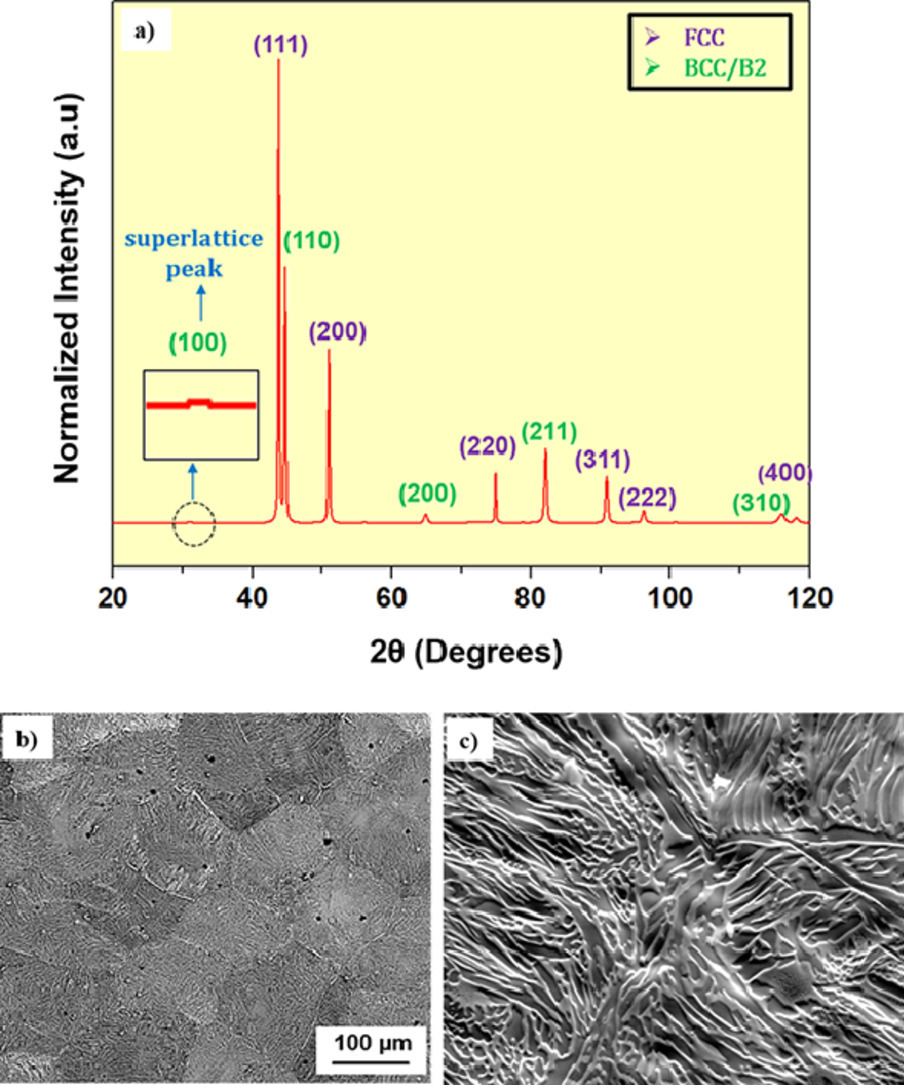
1. Design of a new cobalt base nano-lamellar eutectic high entropy alloy
一種新型鈷基納米層狀共晶高熵合金的設計
R. J. Vikram, Kushagra Gupta, Satyam Suwas?
Satyam Suwas: satyamsuwas@iisc.ac.in
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113993
摘要
受鈷基高溫合金優異性能的啟發,以價電子濃度(VEC)為基礎開發了鈷基高溫高熵合金(HEA)。新開發的鈷基高熵合金具有納米層狀共晶形貌的兩相組織。通過相圖計算(CALPHAD)驗證了組成相為面心立方(FCC)和有序立方(B2)結構。新開發的HEA在室溫下表現出顯著的應變硬化行為,并在500-800℃的溫度范圍內表現出熱穩定性。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 202, 1 Sep. 2021, 113996
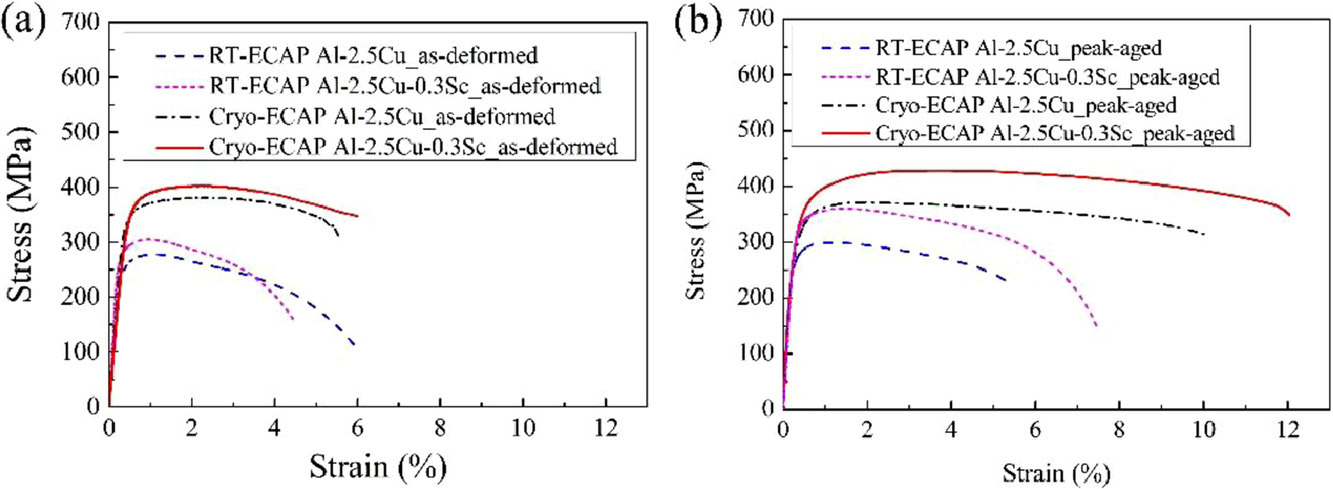
2. Hierarchical structure in Al-Cu alloys to promote strength/ductility synergy
Al-Cu合金中的層次結構促進強度/塑性的協同作用
S. H. Wu, H. Xue, C. Yang, J. Kuang, P. Zhang, J.Y. Zhang, Y.J. Li, Hans J. Roven?, G. Liu?, J. Sun?
Hans J. Roven: hans.j.roven@ntnu.no
G. Liu: lgsammer@mail.xjtu.edu.cn 西安交通大學
J.Sun: junsun@mail.xjtu.edu.cn 西安交通大學
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113996
摘要
實驗結果表明,與室溫下的等通道轉角擠壓(ECAP)相比,低溫下的ECAP能促進Al-2.5wt.%Cu的強度-塑性協同作用。兩者的同時改善與多峰晶粒的組織層次、低角度晶界和晶間/晶內的析出相有關,這可以通過時效處理配合低溫ECAP來調節。人工時效可以保持多峰晶粒尺寸分布,引入大量低角度晶界,產生晶內析出相,從而提高合金的強度/塑性。0.3 wt.% Sc的添加可有效優化合金的析出,進一步提高合金的強度/塑性組合。低溫ECAP對強度和塑性提高的潛在機制是合理的。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 202, 1 Sep. 2021, 113985
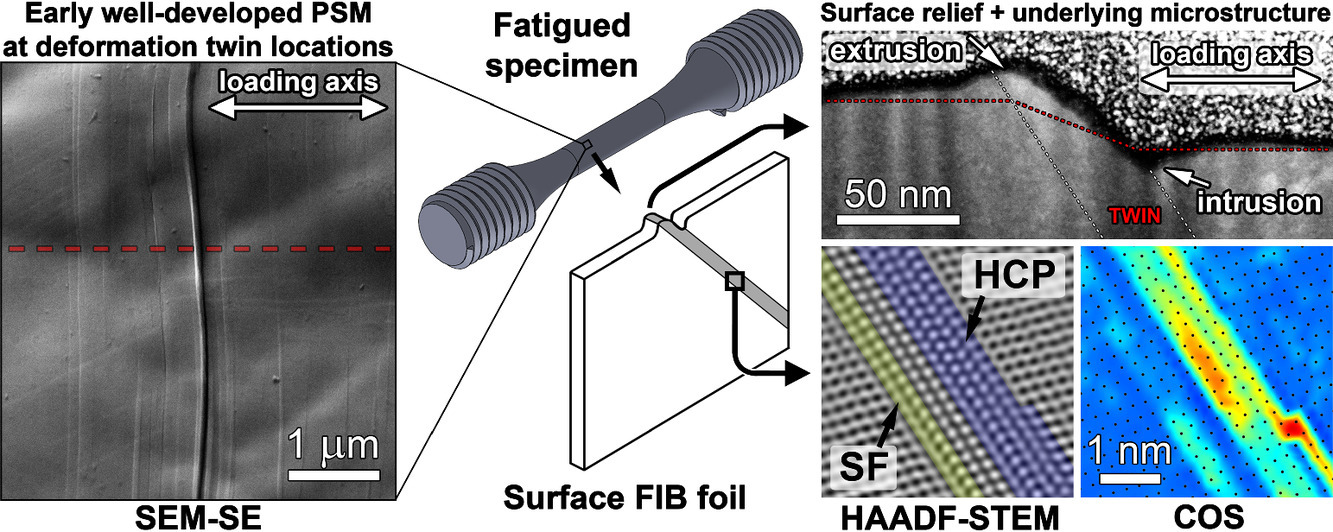
3. Role of deformation twinning in fatigue of CrCoNi medium-entropy alloy at room temperature
變形孿晶在CrCoNi中熵合金室溫疲勞中的作用
Milan Heczko?, Veronika Mazánová, Connor E. Slone, Mulaine Shih, Easo P. George, Maryam Ghazisaeidi, Jaroslav Polák, Michael J. Mills
Milan Heczko: heczko.2@osu.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113985
摘要
對表面電解拋光CrCoNi合金的圓柱形試樣進行了恒總應變幅低周疲勞試驗。合金呈現出先循環硬化后循環軟化直至失效的過程。在循環應力峰值硬化階段結束時,由擠壓物和侵入物組成的持久滑移標記(PSMs)建立了起來,這與薄的變形孿晶有關。本文設計了一個復雜的實驗流程,從被測材料的表面和塊體中提取信息。采用SEM、EBSD、ECCI、FIB和HR-STEM技術相結合,研究了循環加載初期變形孿晶的內部結構和表面形貌。此外,變形孿晶附近的局部循環塑性應變和應力集中不僅導致了早期的、發育良好的PSMs,而且導致了即使在低宏觀應力幅度下TWIP和TRIP塑性的激活。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 202, 1 Sep. 2021, 113992
4. High strength NiMnFeCrAlCu multi-principal-element alloys with marine application perspective
高強度NiMnFeCrAlCu多主元素合金在海洋中的應用前景
Yidong Wu, Yuluo Li, Xuli Liu, Qinjia Wang, Xiaoming Chen, Xidong Hui?
Xidong Hui: xdhui@ustb.edu.cn 北京科技大學
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113992
摘要
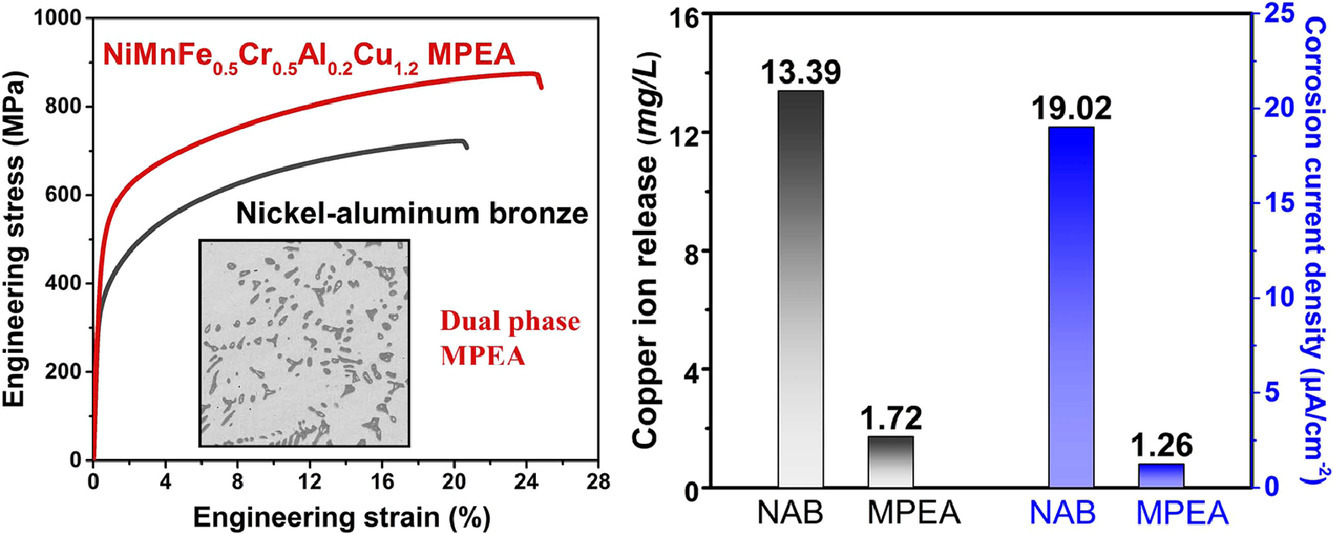
鎳鋁青銅(NAB)合金是傳統的海洋材料,使用了幾十年,但面臨著強度和腐蝕性能不足的問題。在本研究中,我們開發了新型NiMnFeCrAlCu多主元素合金(MPEA),由于其具有很強的固溶強化、耐腐蝕和抗生物結垢能力,該合金具有良好的力學性能和耐腐蝕性能。結果表明,與NBA相比,NiMnFe0.5Cr0.5Al0.2Cu1.2 MPEA具有較高的屈服強度和抗拉強度,腐蝕電流密度低1個數量級,且具有較好的銅離子釋放濃度。這些優點主要歸因于FCC+BCC雙相組織,以及Cu在FCC基體中富集和Cr在BCC晶粒中富集。這項工作對發展先進海洋材料的新戰略具有重要意義。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 202, 1 Sep. 2021, 113998
5. Vacancy surface migration mechanisms in dilute nickel-chromium alloys
稀Ni-Cr合金中的空位表面遷移機制
Jacob Startt, Chaitanya Deo, Rémi Dingreville?
Rémi Dingreville: rdingre@sandia.gov
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113998
摘要
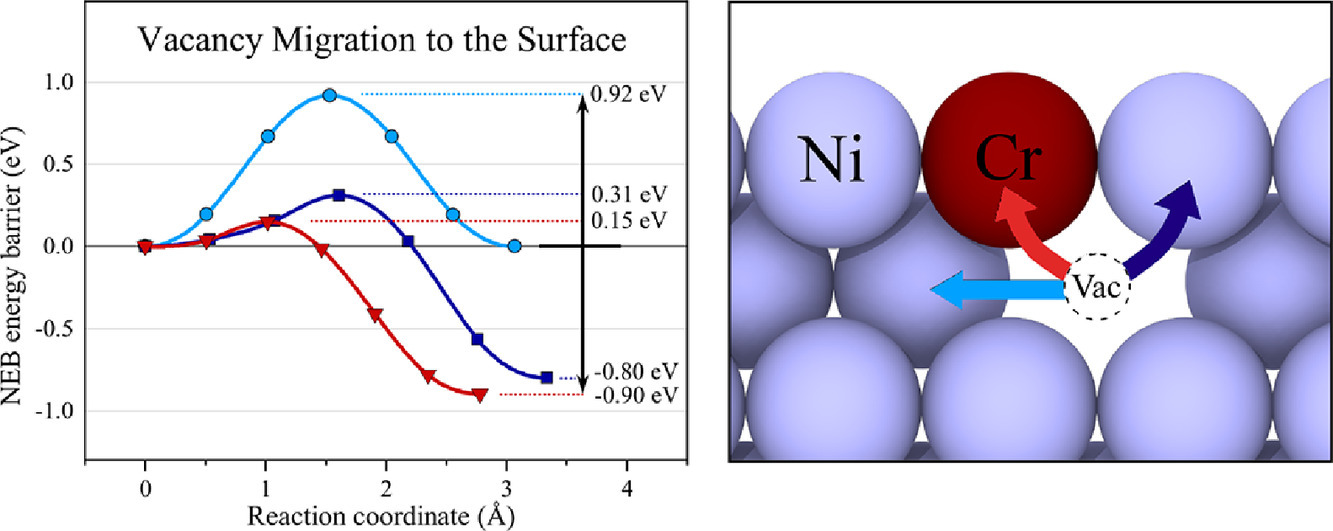
我們用第一性原理計算研究了稀Ni-Cr合金中與表面空位遷移有關的單一機制。我們調查了一套完整表面和(100)自由表面附近空位的亞表面遷移路徑,并計算了相應的遷移勢壘。結果表明,向自由表面遷移的空位會面臨較低的能壘,其通過與鄰近的Cr原子交換而不是與Ni原子交換來進行遷移。一旦一個空位到達自由表面,它就會被困在那里。結果還表明,當一個Cr原子位于自由表面下方的原子面時,導致亞表面Cr原子上方的空位的任何面內空位躍遷在能量上都是不利的。綜上所述,這些基本的單一表面遷移機制為Ni-Cr基合金表面偏析和空位遷移現象之間的復雜交互作用提供了見解。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 202, 1 Sep. 2021, 114004
6. Effect of alloying elements on the coarsening rate of γ? precipitates in multi-component CoNi-based superalloys with high Cr content
合金元素對高Cr多組分CoNi基高溫合金γ?析出相粗化速率的影響
Xiaoli Zhuang, Stoichko Antonov, Longfei Li?, Qiang Feng
Longfei Li: lilf@skl.ustb.edu.cn 北京科技大學
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114004
摘要
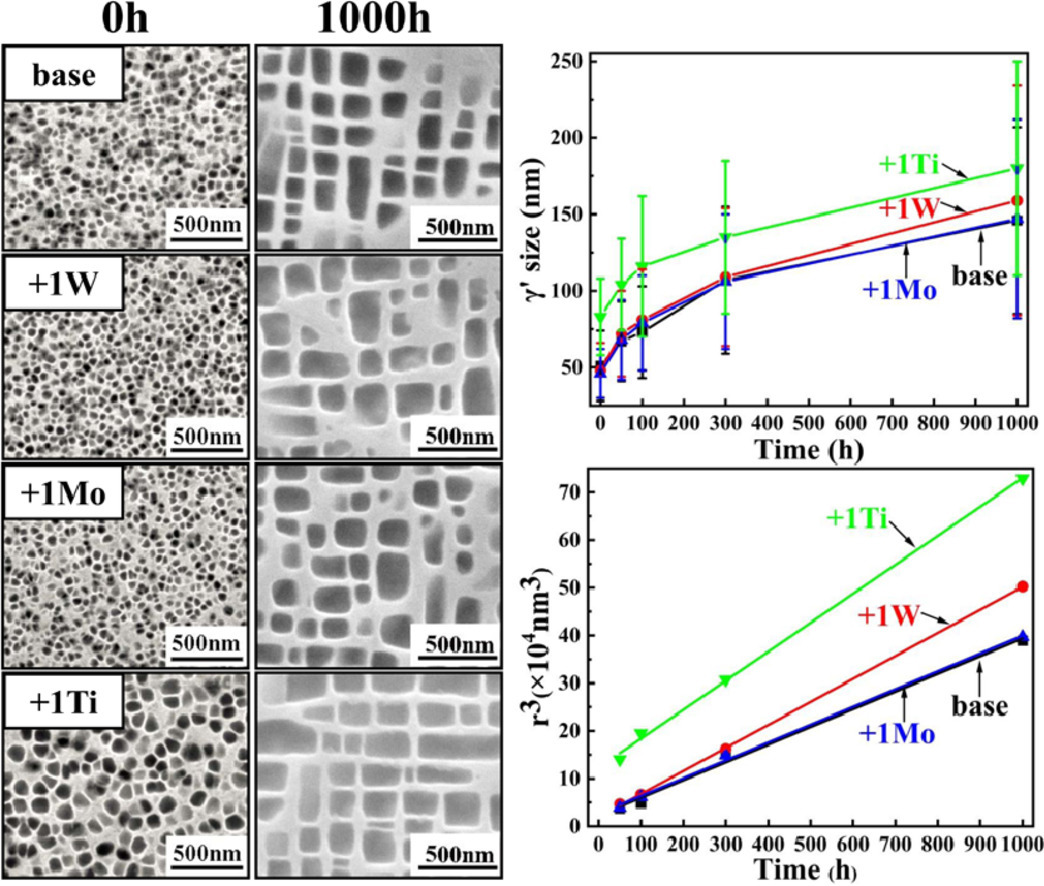
研究了高(14 at.%) Cr含量的多組分CoNi基高溫合金在850℃的長期時效過程中γ'的粗化行為,以及W,Mo或Ti(1 at.%)的添加對于γ/γ?微觀組織的變化、晶格錯配和元素配分行為的影響。γ'析出相的粗化行為遵循經典的Lifshitz-Slyozov-Wagner(LSW)模型,其尺寸與t1/3成比例關系。添加W,Mo或Ti(1at%)改變γ/γ'元素分配行為,從而改變γ/γ'的晶格錯配度和界面能,導致γ'析出相的粗化速率相當不同,其中Ti具有最顯著的影響。結果發現Cr是γ'粗化的速率限制元素,而不是其他合金元素。該研究可以為具有較低γ'粗化速率的CoNi基高溫合金的設計和優化提供指導。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 202, 1 Sep. 2021, 114003
7. Dual plateau stress of C15-type topologically close-packed lattice structures additive-manufactured by laser powder bed fusion
通過激光粉末床熔合技術增材制造的C15型拓撲密排晶格結構的雙平臺應力
Xiaoyang Liu?, Asuka Suzuki, Naoki Takata, Makoto Kobashi, Masaki Kato
Xiaoyang Liu: liu.xiaoyang@e.mbox.nagoya-u.ac.jp
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114003
摘要
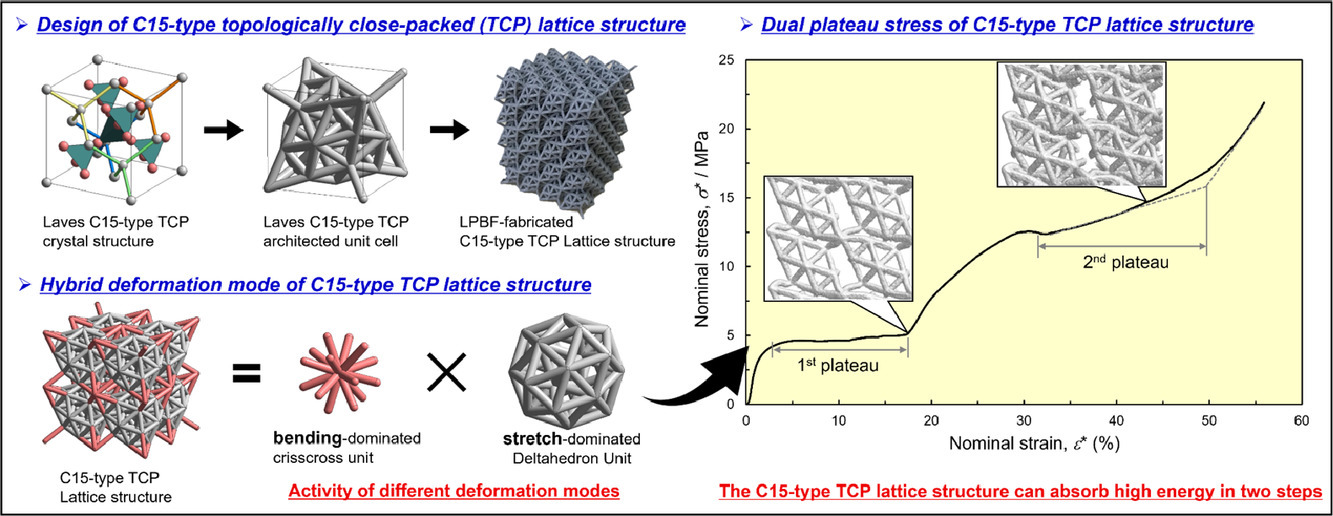
模擬晶體結構為設計由節點(充當原子)和支柱(充當原子鍵)的元胞構成的晶格結構提供了新的途徑。我們通過激光粉末床熔合制備了C15 Laves相(AB2型金屬間化合物)的拓撲致密(TCP)結構,在晶格結構的應力-應變曲線中發現了獨特的雙平臺區。壓縮變形晶格結構的X射線斷層掃描和有限元分析表明,兩種相對密度不同的單元的存在導致了雙平臺區。此外,C15晶格結構表現出彎曲和拉伸主導的混合變形模式,在兩種應力水平下均能吸收較高的總能量(5.0 MJ·m-3)。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 202, 1 Sep. 2021, 113995
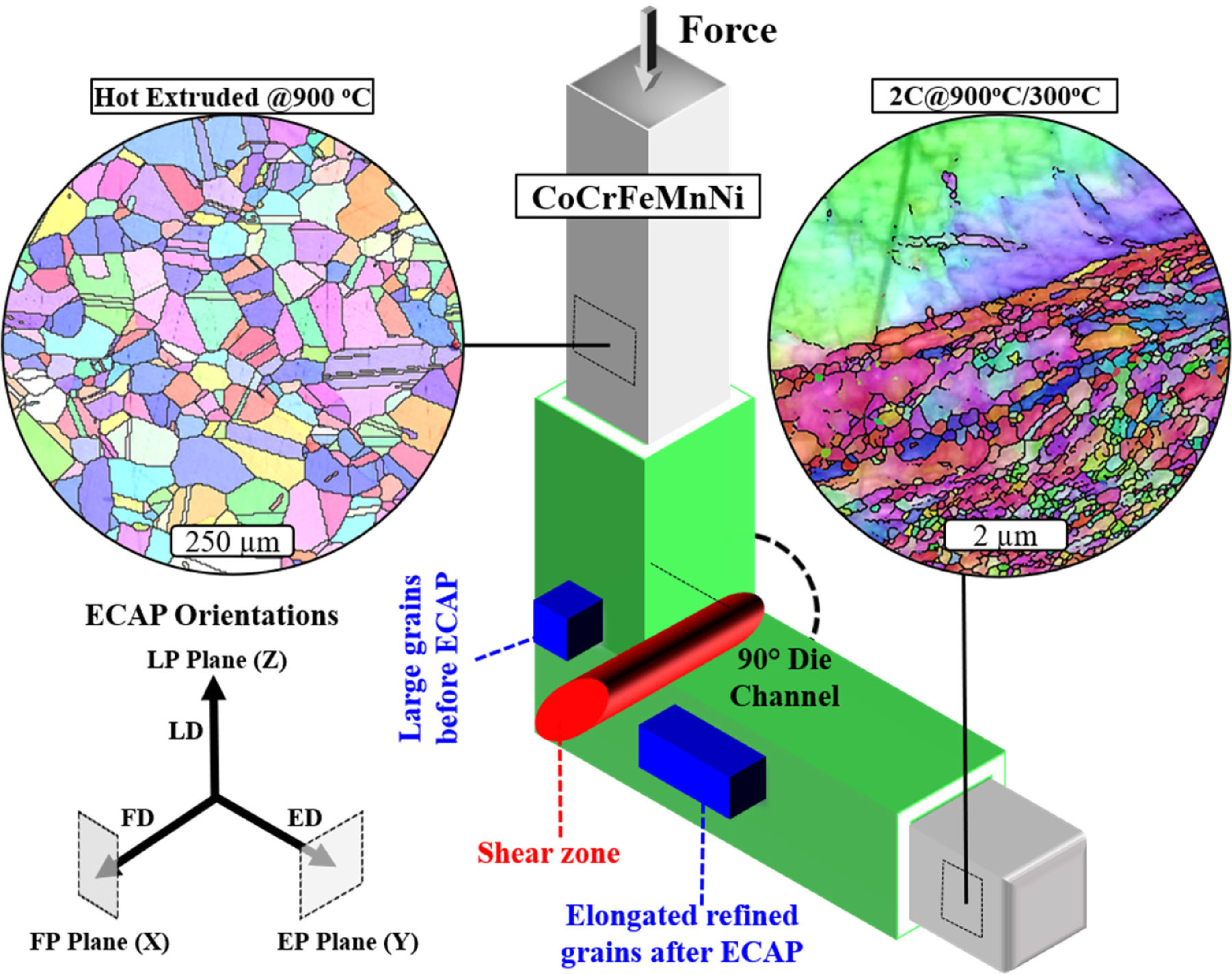
8. Simultaneous deformation twinning and martensitic transformation in CoCrFeMnNi high entropy alloy at high temperatures
CoCrFeMnNi高熵合金在高溫下同時產生變形孿晶和馬氏體相變
S. Picak, H.C. Yilmaz, I. Karaman?
I. Karaman: ikaraman@tamu.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113995
摘要
劇烈塑性變形(SPD)可以通過晶粒細化引起材料的顯著強化,然而使用已知的SPD技術制備的材料由于低的應變硬化能力而缺乏均勻的塑性變形。本研究利用等通道轉角擠壓(ECAP)處理在高溫下同時激活CoCrFeMnNi高熵合金(HEA)的孿晶誘導(TWIP)和相變誘導塑性(TRIP),這是首次報道的高溫異常現象。透射電鏡和電子背散射衍射分析揭示了顯微結構特征。在室溫拉伸實驗中,相變區和孿晶區以及晶粒細化產生了高強度(~1 GPa)和均勻的塑性變形能力。TWIP/TRIP的出現歸因于ECAP處理過程中的高強度水平和目前HEA相對較低的層錯能。