金屬頂刊雙語導讀丨Acta Mater. Vol.211,1 Jun. 2021(上)
2021-07-04 來源:GS_Metals

本期包含金屬材料領域論文9篇,涵蓋了馬氏體、鎂合金、增材制造等,國內科研單位包括上海交通大學等(通訊作者單位)。
Vol. 211 目錄
1. A generally reliable model for composition-dependent lattice constants of substitutional solid solutions
置換型固溶體晶格常數隨組分變化的普適模型
2. Accurate prediction of vacancy cluster structures and energetics in bcc transition metals
BCC過渡族金屬中空位團簇結構與能量的精確預測
3. Frequency-dependent fatigue damage in polycrystalline copper analyzed by FIB tomography
多晶銅疲勞損傷隨頻率變化的FIB斷層掃描研究
4. Factors controlling segregation tendency of solute Ti, Ag and Ta into different symmetrical tilt grain boundaries of tungsten: First-principles and experimental study
Ti、Ag、Ta等溶質元素在對稱傾側晶界偏聚的第一性原理計算與實驗研究
5. Universal prediction of strain footprints via simulation, statistics, and machine learning: low-Σ grain boundaries
基于模擬、統計和機器學習方法識別低Σ晶界
6. Stacking-fault mediated plasticity and strengthening in lean, rare-earth free magnesium alloys
無稀土元素摻雜低合金化鎂合金中層錯介導的強塑性協同提高
7. The development of grain structure during additive manufacturing
增材制造過程中的晶粒結構演化研究
8. Fracture resistance of AlSi10Mg fabricated by laser powder bed fusion
激光粉末熔煉AlSi10Mg的抗斷裂性能研究
9. Ultrafine-grained dual-phase maraging steel with high strength and excellent cryogenic toughness
高強度、高低溫韌性超細晶雙相馬氏體時效鋼研究
ACTA
Vol. 211,1 Jun. 2021, 116865
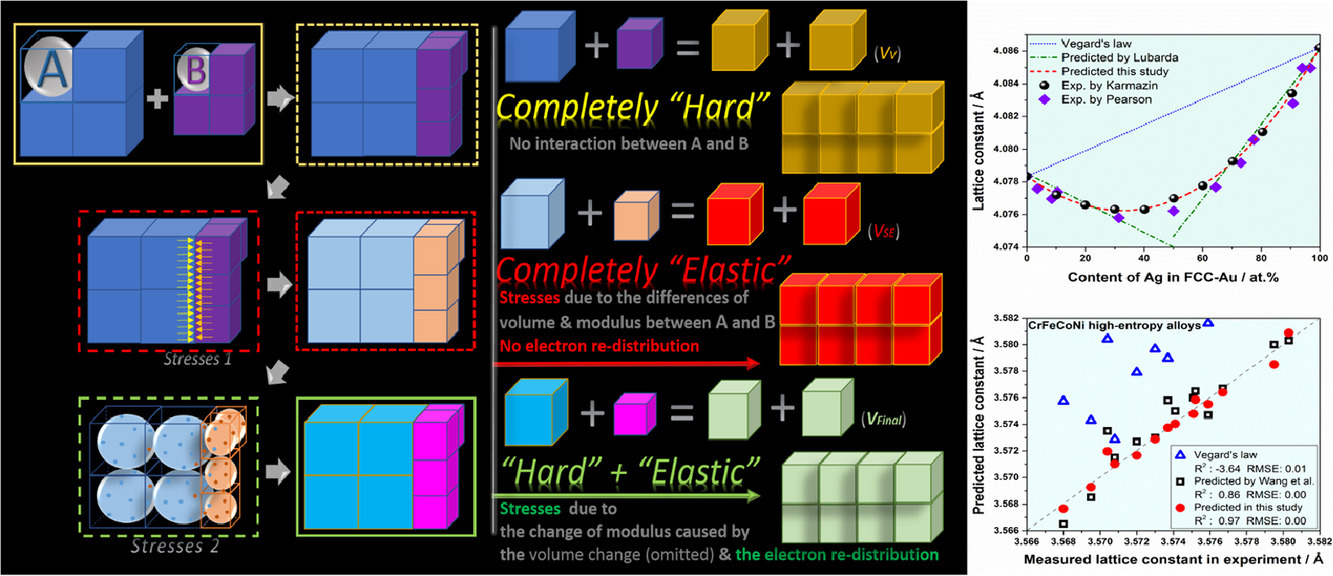
1. A generally reliable model for composition-dependent lattice constants of substitutional solid solutions
置換型固溶體晶格常數隨組分變化的普適模型
Mingxu Wang, Hong Zhu, Gongji Yang, Jinfu Li, Lingti Kong?
L. Kong:konglt@sjtu.edu.cn(上海交通大學)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116865
摘要
固溶強化是一種提高材料性能的有效手段,其效果通常與晶格畸變密切相關,因此,準確描述晶格常數與固溶成分的關系對材料設計具有重要意義。而現有模型很難描述成分和晶格常數之間的非線性關系。本研究中,我們通過同時考慮尺寸效應和電子效應,提出了一個在虛擬晶體近似框架下的新模型。對于n元系統,模型以n元元素和基本性質參數作為輸入,即可預測體系中任何成分固溶體的晶格常數。我們通過高通量第一性原理計算和實驗數據對模型進行了驗證,證明了我們的模型具有高可靠性和泛用性。此外,我們對模型的相關應用和局限性進行了討論。該模型能夠大大加深我們對材料“成分-性能”關系的理解。
ACTA
Vol. 211,1 Jun. 2021, 116860
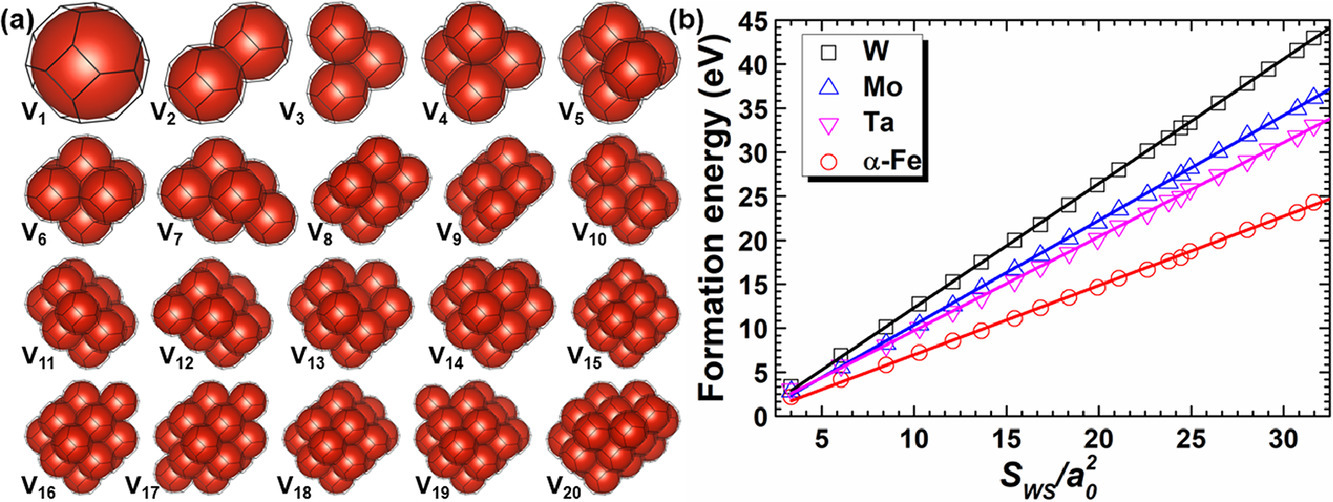
2. Accurate prediction of vacancy cluster structures and energetics in bcc transition metals
BCC過渡族金屬中空位團簇結構與能量的精確預測
Jie Hou, Yu-Wei You, Xiang-Shan Kong?, Jun Song?, C.S. Liu
X.-S. Kong:xskong@sdu.edu.cn(中科院固體物理研究所/山東大學)
J. Song:jun.song2@mcgill.ca
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116860
摘要
空位團簇的結構和能量是金屬缺陷演化中最重要的參數之一。然而,目前還沒有可以準確確定空位團簇精細結構和能量的可靠方法。本研究中,我們采用第一性原理對BCC金屬中空位團簇的穩定結構和能量進行了計算,證明了空位團簇的穩定結構可以通過最小化Wigner-Seitz區域來精確預測,并揭示了形成能與空位團簇Wigner-Seitz區域之間的線性關系。我們進一步建立了一個新物理模型來準確預測任意大小空位簇的穩定結構和能量學。模型得到了第一性原理計算和空位團簇退火實驗的驗證,且相比廣泛使用的球面近似模型具有明顯優勢。本研究為空位團簇的形成演化提供了見解,對原子間作用勢的分析具有重要意義,在預測和調控金屬中的空位相關損傷方面邁出了關鍵一步。
ACTA
Vol. 211,1 Jun. 2021, 116859
3. Frequency-dependent fatigue damage in polycrystalline copper analyzed by FIB tomography
多晶銅疲勞損傷隨頻率變化的FIB斷層掃描研究
S. Fintová?, I. Kuběna, A. Chlupová, M. Jambor, I. Šulák, Z. Chlup, J. Polák
S. Fintová:fintova@ipm.cz
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116859
摘要
我們研究了多晶純銅在4Hz-20kHz頻率循環荷載下的疲勞性能。研究表明,隨著頻率增加,斷裂循環周期增加。我們通過準靜態和動態拉伸試驗,從應變率敏感性的角度對以上現象進行了解釋。我們首先使用SEM研究了不同應力幅度和頻率下樣品表面起伏的演化,發現表面形成了特征滑移帶。在所有樣品中,滑動帶下方的主滑動平面周圍都形成了孔洞。隨后通過對FIB樣品進行三維重構,獲得了孔洞的分布形貌。我們發現孔洞分布和表面浮凸之間存在密切聯系。粗糙的表面和表面下滑移平面附近的孔洞共同導致了疲勞裂紋的產生。我們從滑移帶內空位聚集形成孔洞的角度,對循環應變下的應變率進行了分析。
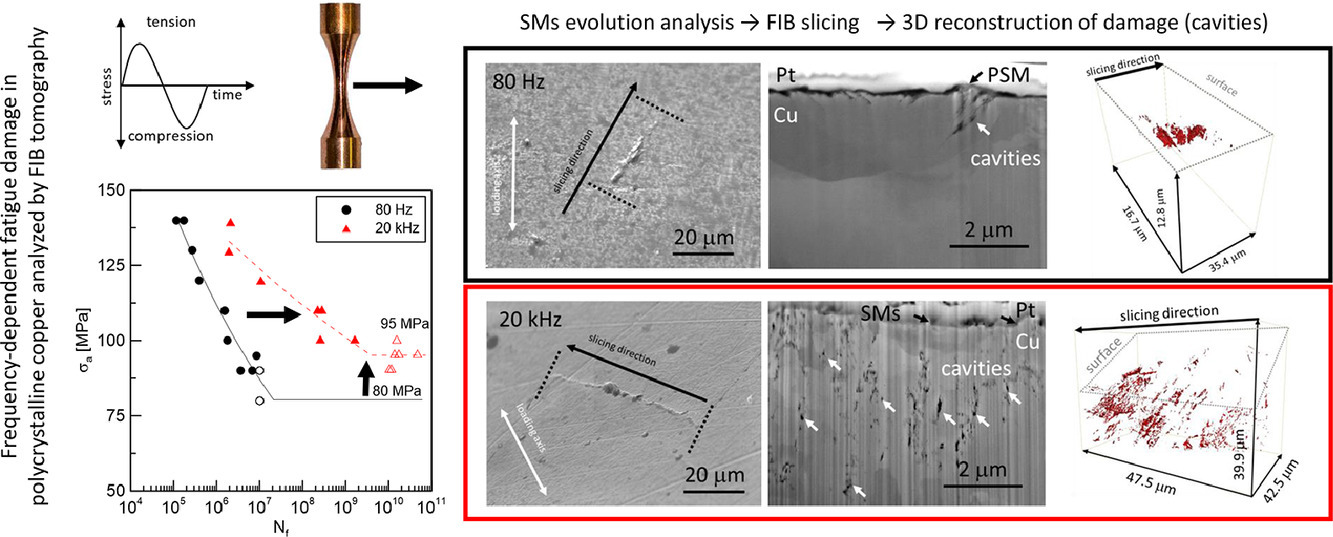

ACTA
Vol. 211,1 Jun. 2021, 116868
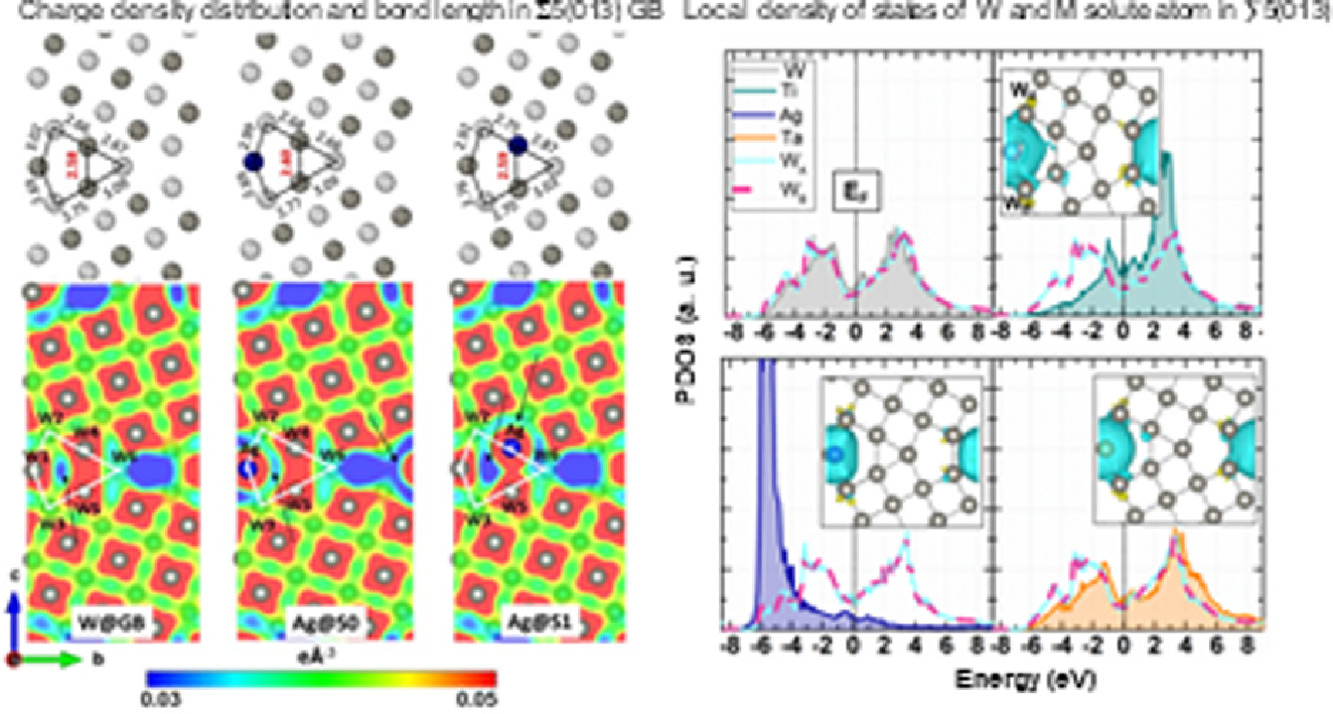
4. Factors controlling segregation tendency of solute Ti, Ag and Ta into different symmetrical tilt grain boundaries of tungsten: First-principles and experimental study
Ti、Ag、Ta等溶質元素在對稱傾側晶界偏聚的第一性原理計算與實驗研究
Ahmed Tamer AlMotasem?, Teodor Huminiuc, Tomas Polcar
A.T. AlMotasem:a.almotasem@aun.edu.eg, ahmed.alasqalani@soton.ac.uk
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116868
摘要
實驗研究表明,晶界(GB)偏聚對晶體材料的熱穩定性和強度具有重要影響。本研究中,我們利用密度泛函理論(DFT)計算了W的小/大角度對稱傾斜晶界(STGBs)處Ti、Ag、Ta等溶質原子的偏聚,并用TEM實驗進行了驗證。我們發現在小角度對稱傾側晶界處,不發生Ti或Ta元素的偏聚;而這兩種元素在大角度對稱傾側晶界核心處則表現出一定的偏聚傾向。相比之下,Ag更容易在晶界平面內及其周圍偏聚。我們計算了力學效應和電子效應對固溶元素能量的貢獻,發現電子的影響占主導地位。此外,我們利用局域態密度函數(PDOS)分析了溶質原子和W原子d軌道電子的作用。發現,在Ta固溶的情況下,大量d軌道電子發生雜化,對W-Ta鍵的穩定起重要作用。另一方面,W-Ti鍵各向異性的特點也有助于周圍W原子的穩定。電荷轉移分析表明,電子從Ti和Ta原子轉移至W原子。與電負性規則相反,Ag原子從鄰近的W原子獲得電子,顯著的s-s雜化可以有效解釋Ag原子在晶界處的偏聚。
ACTA
Vol. 211,1 Jun. 2021, 116850
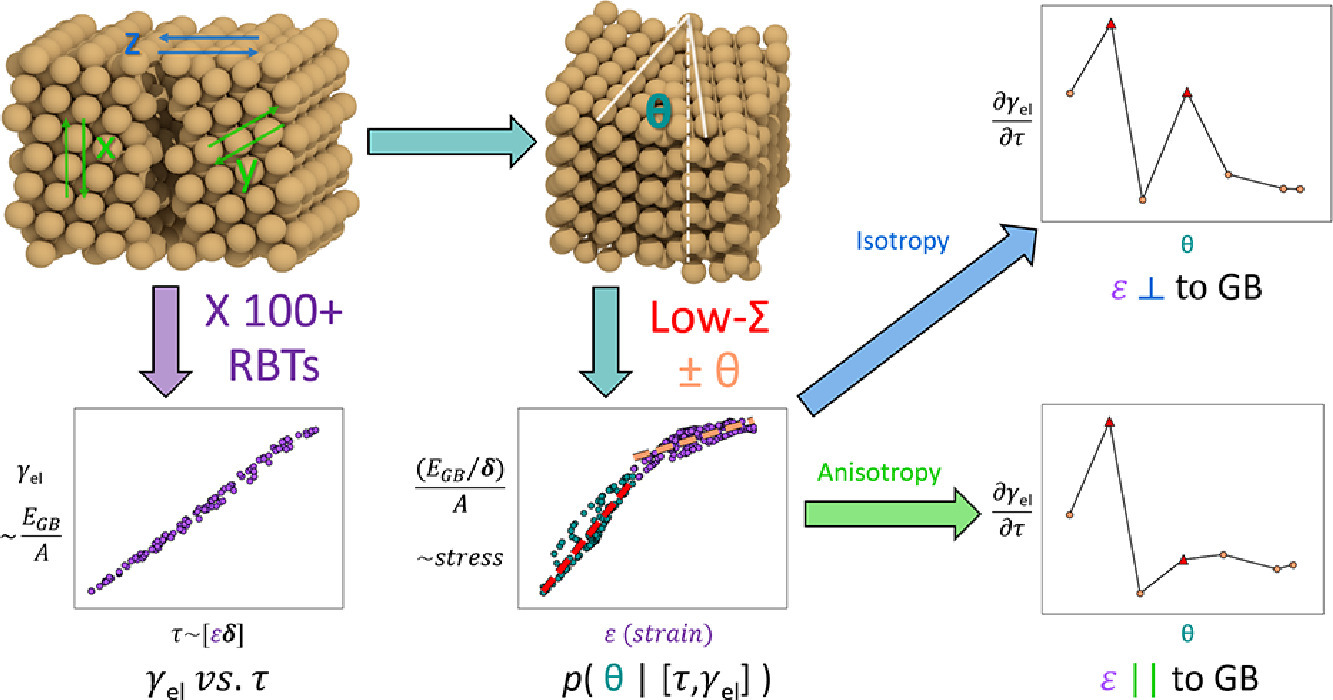
5. Universal prediction of strain footprints via simulation, statistics, and machine learning: low-Σ grain boundaries
基于模擬、統計和機器學習方法識別低Σ晶界
Matthew T. Curnan, Wissam A. Saidi, Judith C. Yang, Jeong Woo Han?
J.W. Han:jwhan@postech.ac.kr
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116850
摘要
人們常常通過界面對材料的催化性能進行綜合調控。由于金屬晶界(GBs)呈無序結構,因此具有巨大的調控潛力。雖然實驗表明晶界的催化路徑取決于位錯的彈性應變,但晶界的原子結構和催化能力的能量起源尚不清楚。在以往通過宏觀自由度定義亞穩態晶界的模型中,我們往往無法對重晶格點位模型預測的低Σ晶界進行準確識別。因此在本研究中,我們發展出了一種結構-能量關系,能夠將原子性質變化與物理模型聯系起來,從而從常規大角晶界中區分出異常晶界。這項工作基于三個微觀自由度構建晶界的彈性響應,通過直接統計方法對晶界進行區分。這一方法可以成功地從大角晶界中區分出低Σ晶界。我們基于亞穩態晶界和相應的彈性響應,構建了機器學習分類算法。驗證表明,其性能優于以往的分類模型。
ACTA
Vol. 211,1 Jun. 2021, 116877
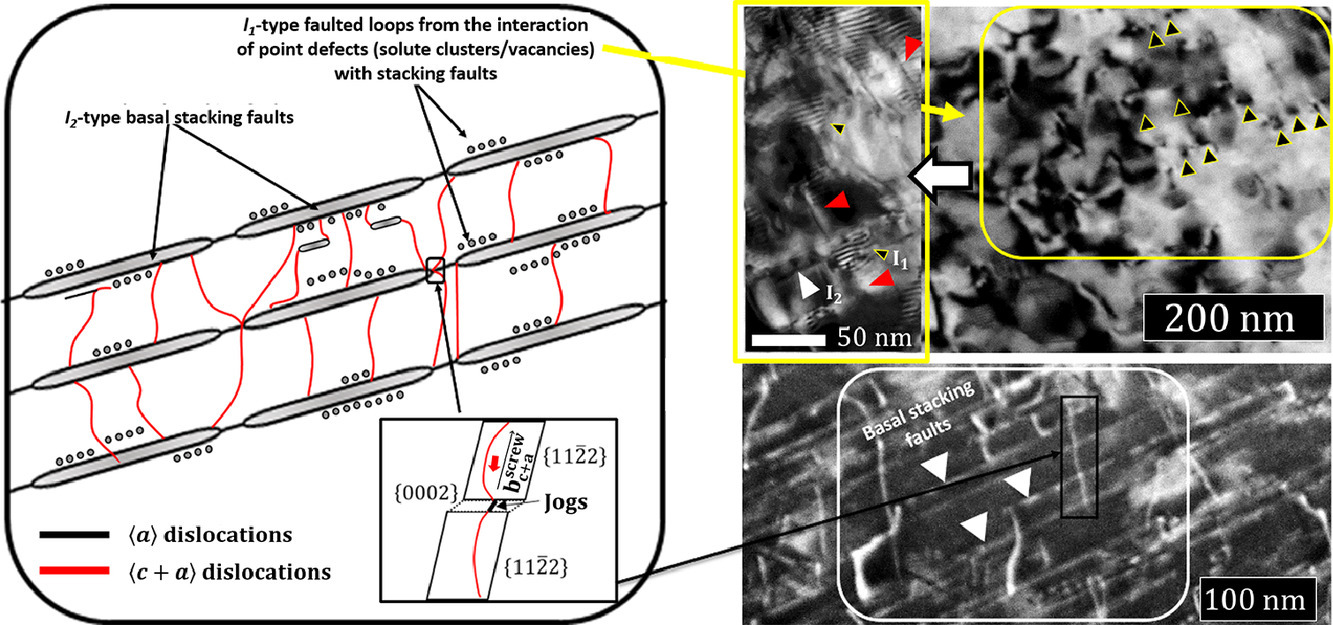
6. Stacking-fault mediated plasticity and strengthening in lean, rare-earth free magnesium alloys
無稀土元素摻雜低合金化鎂合金中層錯介導的強塑性協同提高
I. Basu?, M. Chen, J. Wheeler, R.E. Schäublin, J.F. Löffler?
I. Basu:indranil.basu@mat.ethz.ch
J.F. Löffler:joerg.loeffler@mat.ethz.ch
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116877
摘要
我們在室溫下,對ZX10合金(即少量添加了1wt.%Zn和0.3wt.%Ca的鎂合金)和純鎂進行了微柱壓痕試驗。我們制備了兩種不同取向的單晶微柱,分別用于激活c軸方向的拉伸和壓縮。在兩種加載條件下,與純Mg相比,ZX10的強度增加了2到2.5倍,且塑性也增強。背散電子和透射電子表征表明,拉伸條件下,ZX10變形是通過孿晶發生的,在較高的應力水平下,基底滑移和非基滑移被均勻激活。而純鎂則通過拉伸孿晶和基底滑動發生變形。壓縮條件下,純Mg通過基底位錯介導的大規模滑移發生變形,而ZX10中則發生〈a〉位錯和〈c+a〉位錯的雙重激活。鋅和鈣的添加改變了層錯能,從而導致材料了材料強度和塑性的協同增強。研究證明了少量添加鋅和鈣對激活Mg合金變形機制有益,對無稀土元素添加的高強高塑鎂合金結構材料和生物材料的設計具有重要意義。
ACTA
Vol. 211,1 Jun. 2021, 116862
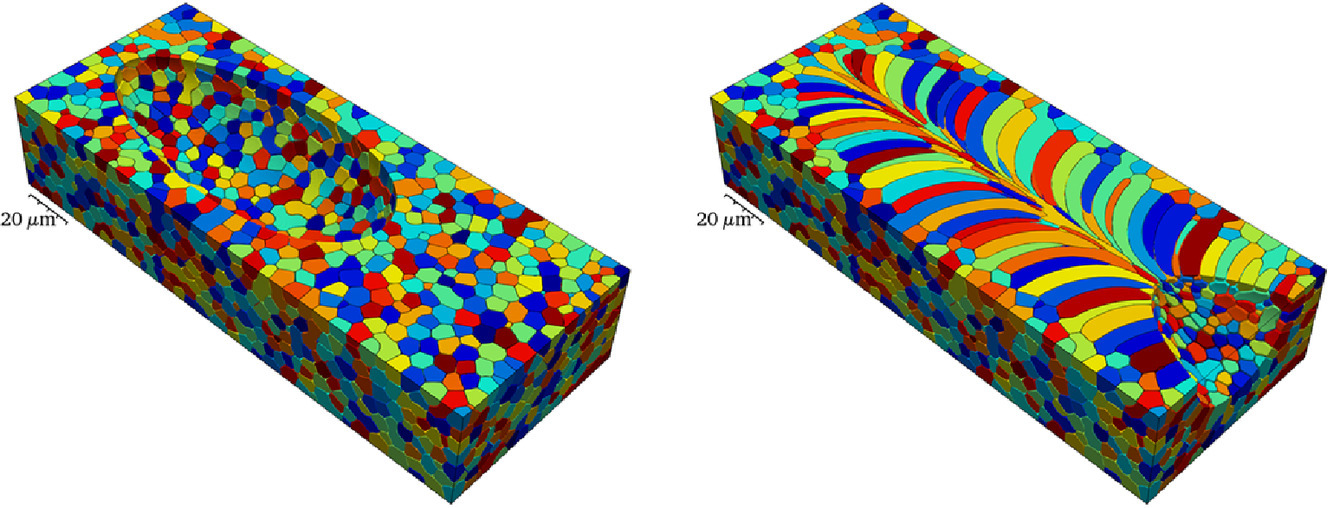
7. The development of grain structure during additive manufacturing
增材制造過程中的晶粒結構演化研究
Alexander F. Chadwick, Peter W. Voorhees?
P.W. Voorhees:p-voorhees@northwestern.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116862
摘要
合金增材制造過程中往往會形成復雜的顯微組織,通常包括由現有晶粒外延生長得到的長柱狀晶粒。在本研究中,我們建立了一個相場模型,模擬固液界面移動足夠快,成分變化可忽略不計的情況下,316L不銹鋼的凝固過程。通過與運動的激光源熱場耦合,模型模擬得到了晶粒在熔池周圍凝固的軌跡。我們通過三維模擬研究了界面動力學各向異性對凝固組織影響。通過定性和定量分析,我們發現沿激光移動軌跡中心處,動力學各向異性的影響最大。凝固早期晶粒的形貌主要受熔池形狀控制。
ACTA
Vol. 211,1 Jun. 2021, 116869
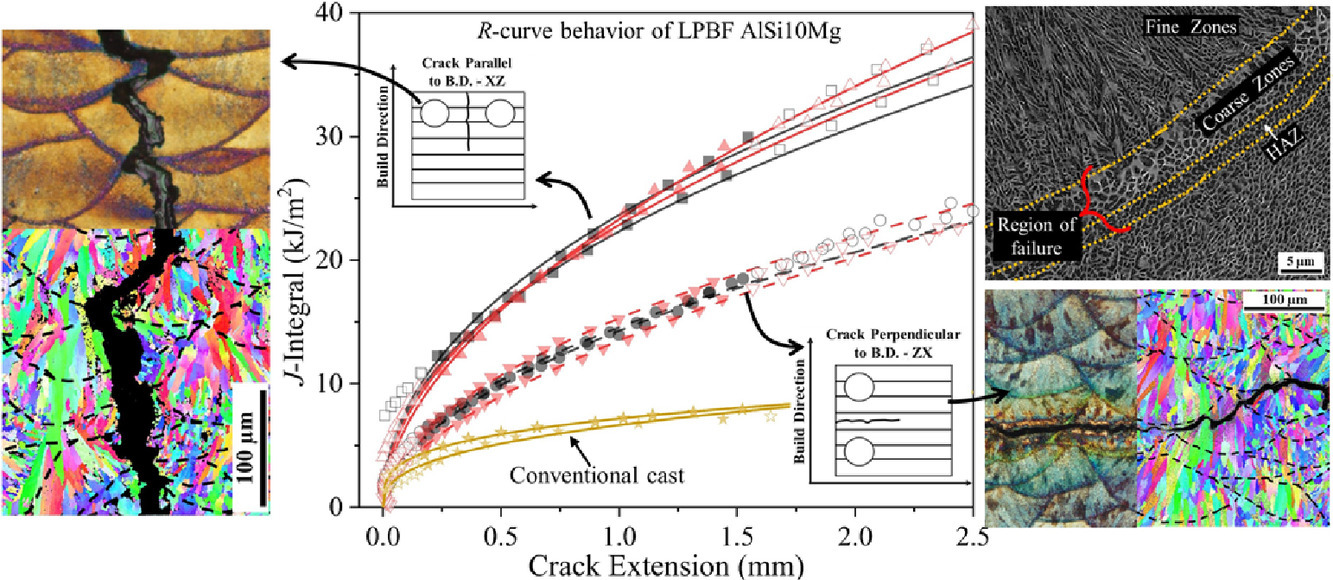
8. Fracture resistance of AlSi10Mg fabricated by laser powder bed fusion
激光粉末熔煉AlSi10Mg的抗斷裂性能研究
Moses J. Paul, Qian Liu, James P. Best, Xiaopeng Li, Jamie J. Kruzic, Upadrasta Ramamurty, Bernd Gludovatz?
B. Gludovatz:b.gludovatz@unsw.edu.au
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116869
摘要
激光粉末熔煉(LPBF)制備的AlSi10Mg中,快速冷卻導致的組織細化和和熔池誘導形成介觀組織使得材料具有優異的強度和斷裂韌性。深入了解加工條件對組織的影響能夠更好地幫助我們調控材料性能,特別是斷裂抗性。為此,我們對以不同層厚、窗口間距和掃描策略加工的AlSi10Mg合金的不同取向抗裂曲線(R曲線)進行了分析,并將其與晶粒尺寸、取向、織構、胞結構形貌、熔池分布等組織特征建立了聯系。結果表明,材料的拉伸性能和斷裂韌性都具有較強的各向異性,其中,強度主要受層厚和窗口間調控,而斷裂韌性主要受掃描策調控。就拉伸性能而言,熔池邊界與加載方向相對關系的不同導致了延伸率的各向異性,而強度主要有晶粒尺寸和胞結構控制。而就斷裂韌性而言,熔池形貌是影響材料失效的主要因素,因此斷裂韌性主要受掃描策調控。進一步研究表明,盡管R曲線具有明顯各向異性,但LPBF制備AlSi10Mg中獨特的組織還是使得這種材料的耐損傷性能優于鑄造合金。
ACTA
Vol. 211,1 Jun. 2021, 116878
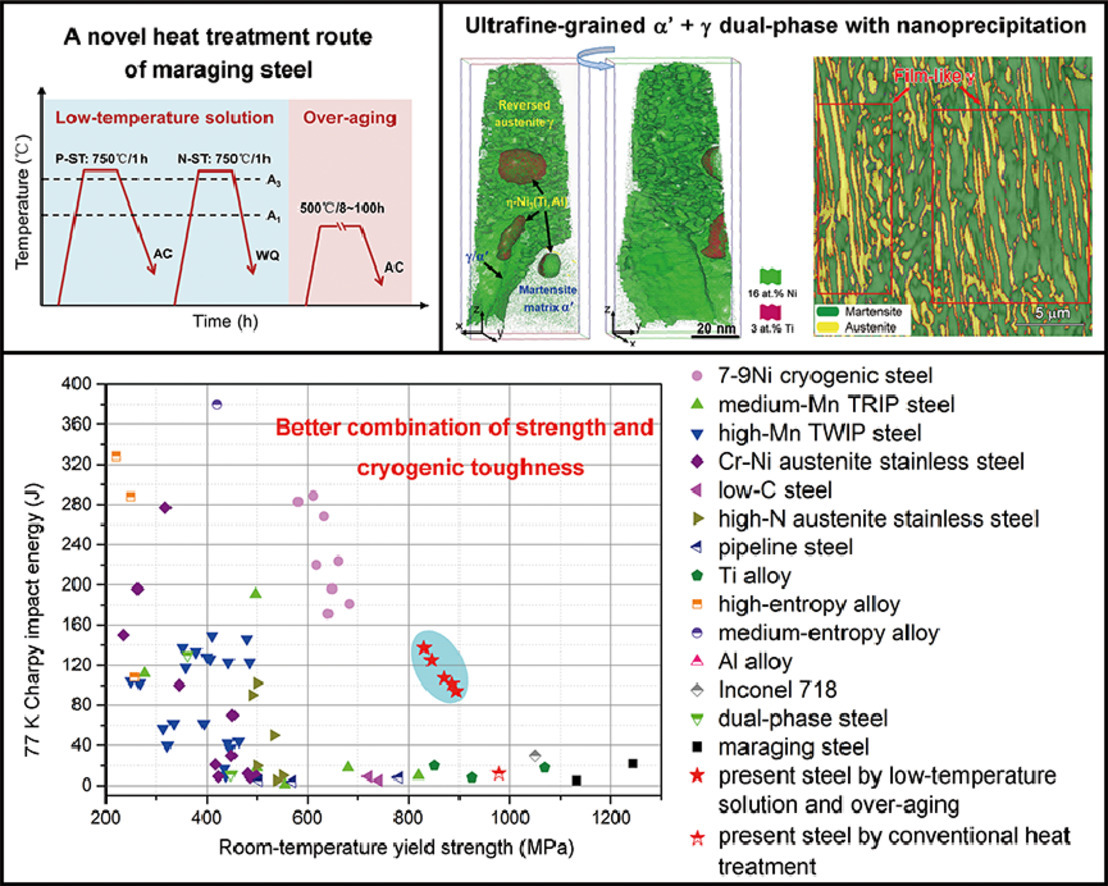
9. Ultrafine-grained dual-phase maraging steel with high strength and excellent cryogenic toughness
高強度、高低溫韌性超細晶雙相馬氏體時效鋼研究
Honglin Zhang, Mingyue Sun?, Yuxuan Liu, Dongping Ma, Bin Xu, Mingxin Huang?, Dianzhong Li, Yiyi Li
M. Sun:mysun@imr.ac.cn(沈陽金屬所)
M. Huang:mxhuang@hku.hk(香港大學)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116878
摘要
我們提出了一種新的熱處理工藝,即低溫固溶和500°C過時效處理,制備得到了具有超細馬氏體(α′)和奧氏體(γ)雙相組織的高強、高低溫韌性鋼鐵材料。與傳統工藝制備得到的的全馬氏體時效鋼相比,材料的低溫沖擊功增加了12倍(77K時~140J),而屈服強度沒有明顯降低。在500°C過時效過程中,馬氏體逆轉變形成大量超細晶奧氏體(體積分數~50%)。令人驚訝的是,在擁有如此高比例奧氏體的情況下,材料的屈服強度能夠與傳統馬氏體時效鋼相當。在馬氏體和奧氏體兩相中都存在高密度納米析出,因此兩相都具有很高的強度,納米壓痕試驗證實了這一點。兩相中高密度的納米析出確保了材料的高強度。而材料優異的低溫韌性主要源于:(i)大量FCC結構的奧氏體本身的韌性較高;(ii)沖擊過程中奧氏體發生TRIP效應;(iii)馬氏體和奧氏體的晶粒細化。這一熱處理工藝為低溫應用的大型工程部件制備提供了一種有效的解決方案。需要注意的是,為保證部件性能均勻,需要較長的熱處理時間。