金屬頂刊雙語導讀丨Scripta Mater. Vol.202, 1 Sep. 2021(下)
2021-08-08 來源:Goal Science
本期包含金屬材料領域論文8篇,涵蓋了高熵合金、不銹鋼、中熵合金等,國內科研單位包括四川大學等(通訊作者單位)。
Vol. 202 目錄
1. Fracture toughness of 304L austenitic stainless steel produced by laser powder bed fusion
激光粉末床熔合法制備的304L奧氏體不銹鋼的斷裂韌性
2. Unveiling the thermodynamic driving forces for high entropy alloys formation through big data ab initio analysis
通過大數據從頭計算分析揭示高熵合金形成的熱力學驅動力
3. Cu precipitation-mediated formation of reverted austenite during ageing of a 15-5 PH stainless steel
15-5 PH不銹鋼時效過程中Cu析出介導的逆轉變奧氏體的形成
4. Low-temperature oxy-nitriding of 316 L austenitic stainless steel for improved corrosion resistance in liquid lead-bismuth eutectic
316L奧氏體不銹鋼的低溫氧氮化提高其在液態鉛鉍共晶中的耐蝕性
5. Simultaneous effects of deformation-induced plasticity and precipitation hardening in metastable non-equiatomic FeNiCoMnTiSi ferrous medium-entropy alloy at room and liquid nitrogen temperatures
在室溫和液氮溫度下亞穩態非等原子FeNiCoMnTiSi鐵基中熵合金的變形誘導塑性和沉淀硬化的同步效應
6. A new insight into annealing parameters in tailoring the mechanical properties of a medium Mn steel
調控中錳鋼力學性能的退火參數的新見解
7. Understanding ferrite deformation caused by austenite to martensite transformation in dual phase steels
理解雙相鋼中奧氏體向馬氏體轉變引起的鐵素體變形
8. The effects of interstitial hydrogen and carbon atoms and aging temperature on annihilation behavior of hydrogen-enhanced strain-induced vacancies in iron
間隙氫和碳原子以及時效溫度對鐵中氫增強應變誘導空位的湮沒行為的影響
SCRIPTA
Vol. 202, 1 Sep. 2021, 114002
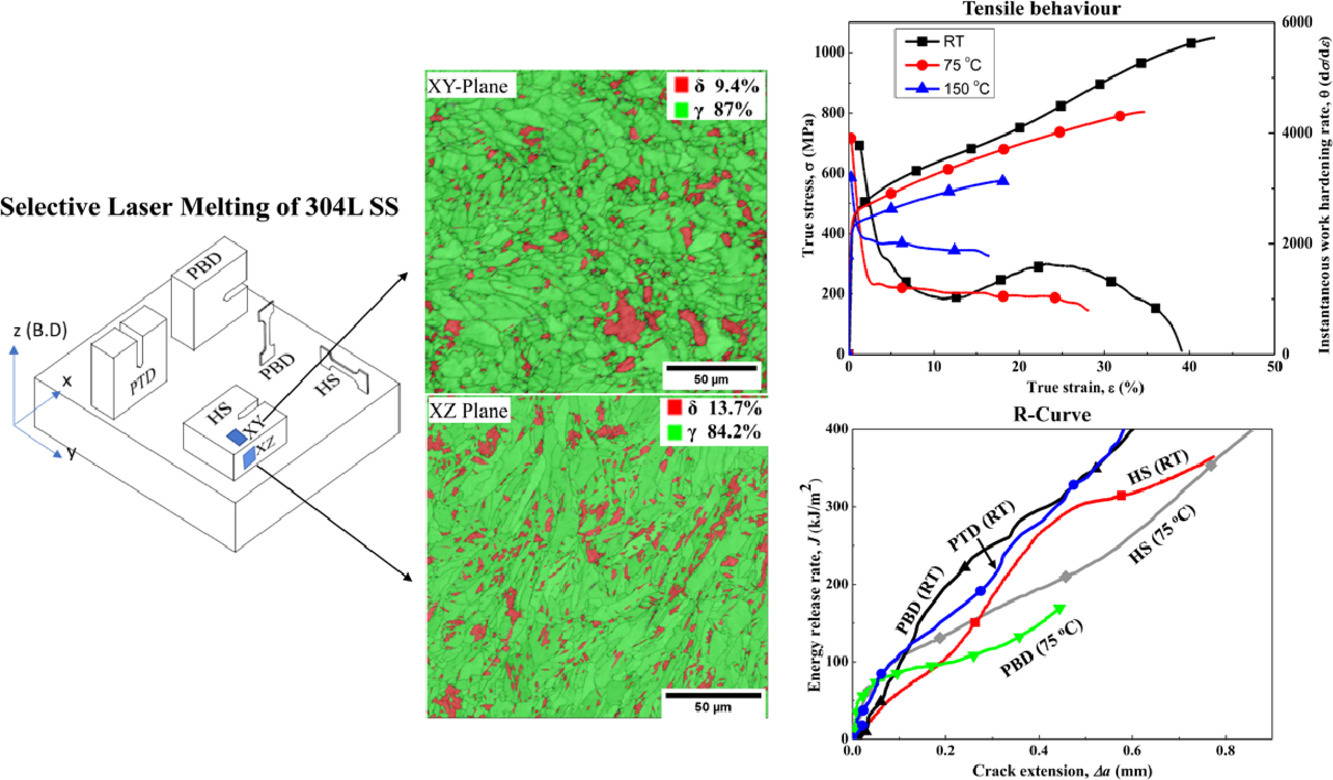
1. Fracture toughness of 304L austenitic stainless steel produced by laser powder bed fusion
激光粉末床熔合法制備的304L奧氏體不銹鋼的斷裂韌性
Punit Kumar?, Zhiguang Zhu, Sharon M.L. Nai, R.L. Narayan, U. Ramamurty
Punit Kumar: punit.kumar@ntu.edu.sg
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114002
摘要
研究了激光粉末床熔合法(LPBF)制備的304L奧氏體不銹鋼的單軸拉伸響應和J積分阻力行為。鋼在室溫下經歷相變誘導塑性(TRIP),產生高的斷裂韌性(JQ)值以及高的強度(σY)和塑性。當溫度升高到75℃時,TRIP變得不活躍,變形機制以位錯滑移和孿晶為主。這導致了JQ的大幅降低和明顯的各向異性,而σY則保持不變。本文討論了這些結果在LPBF工藝制備的鋼的斷裂性能方面的意義。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 202, 1 Sep. 2021, 114000
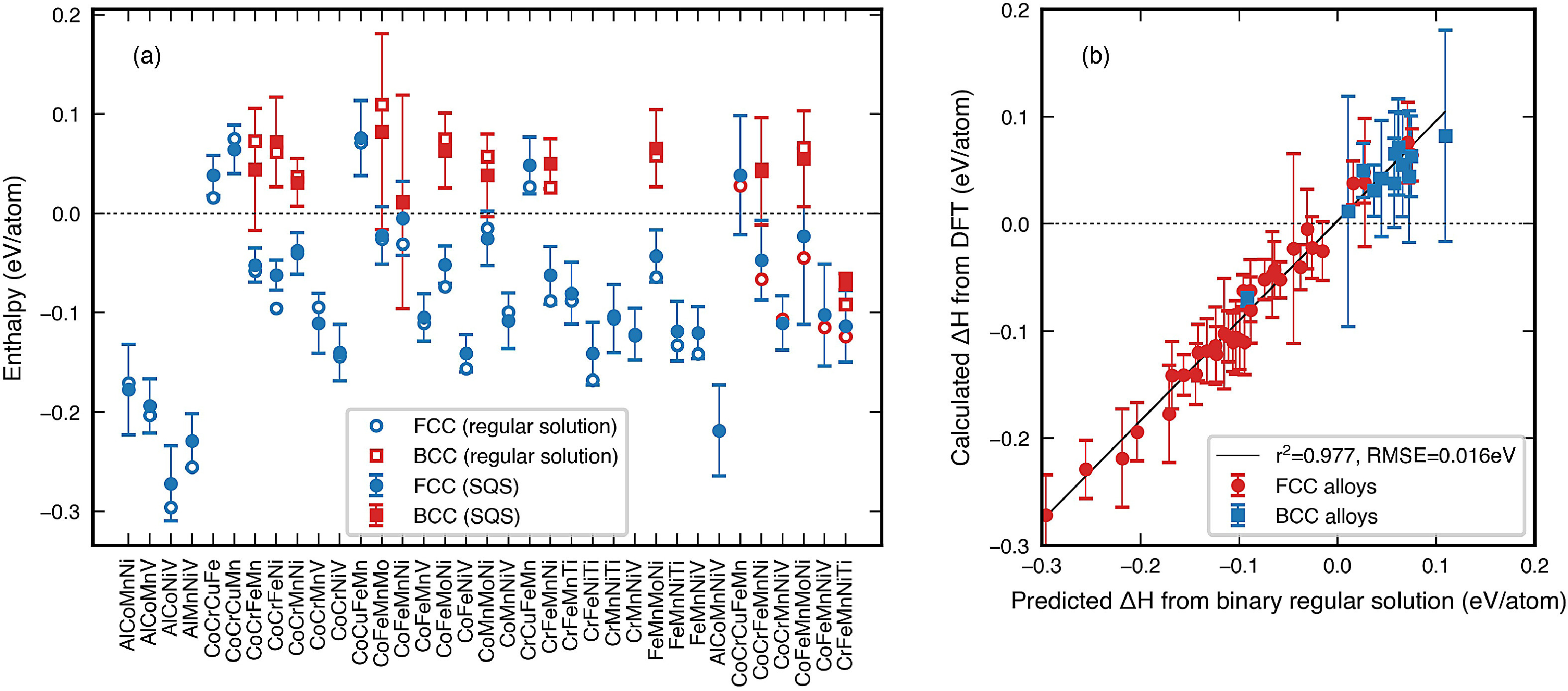
2. Unveiling the thermodynamic driving forces for high entropy alloys formation through big data ab initio analysis
通過大數據從頭計算分析揭示高熵合金形成的熱力學驅動力
G. B. Bokas, W. Chen, A. Hilhorst, P.J. Jacques, S. Gorsse, G. Hautier?
G. Hautier: geoffroy.hautier@dartmouth.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114000
摘要
目前對于高熵合金(HEAs)存在之外的基本熱力學驅動力仍然沒有充分的了解。本文利用熱力學模型結合從頭計算和正規溶液模型,建立了一個超過10萬、由27種常見元素形成的BCC和FCC等摩爾合金的數據庫。我們用統計的方法研究了隨機固溶體中焓和熵的貢獻隨著元素數目的變化是如何演變的。由于隨著元素數目的增加熵的重要性也在增加,普遍認為的HEAs穩定的合理化是有些矛盾的。熵和焓的貢獻有利于混合,但隨著合金中元素數目的增加,這兩種驅動力都減弱。通過將二元金屬間化合物添加到我們的分析中,可以得出結論,容易形成單相HEAs的特定化學成分需要在給定晶格上結合有利焓的元素混合,而不存在強競爭的金屬間化合物。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 202, 1 Sep. 2021, 114007
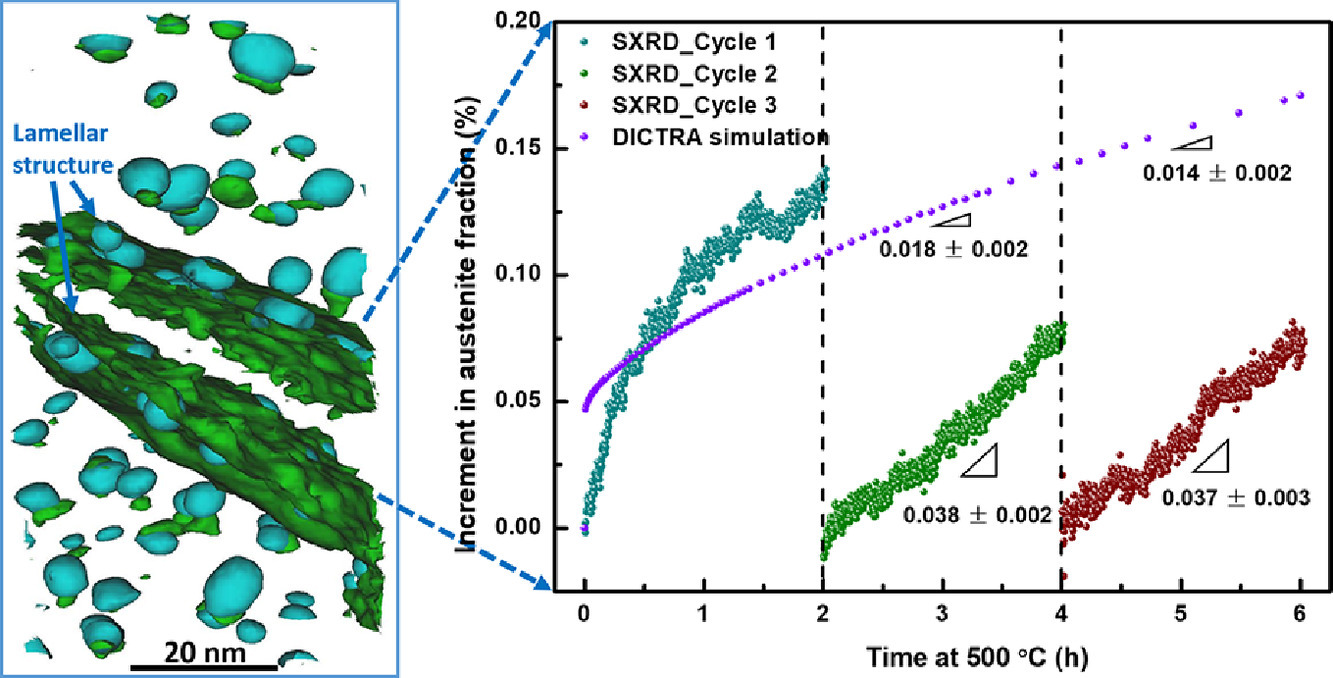
3. Cu precipitation-mediated formation of reverted austenite during ageing of a 15-5 PH stainless steel
15-5 PH不銹鋼時效過程中Cu析出介導的逆轉變奧氏體的形成
Tao Zhou?, Benjamin Neding, Sen Lin, Jo-Chi Tseng, Peter Hedström
Tao Zhou: taozhou@kth.se
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114007
摘要
通過原子探針斷層掃描、原位同步X射線衍射和計算熱力學和動力學,揭示了15-5 PH不銹鋼時效處理過程中Cu沉淀介導的奧氏體相變。奧氏體轉變是通過以下路徑發生的:Cu在馬氏體/殘余奧氏體界面或馬氏體板條界面析出→奧氏體穩定元素向Cu析出界面配分→逆轉變奧氏體形成。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 202, 1 Sep. 2021, 114014
4. Low-temperature oxy-nitriding of 316 L austenitic stainless steel for improved corrosion resistance in liquid lead-bismuth eutectic
316L奧氏體不銹鋼的低溫氧氮化提高其在液態鉛鉍共晶中的耐蝕性
Guang Chen, Jun Wang?, Hongtao Zhang, Longyi Li, Hongyuan Fan
Jun Wang: srwangjun@scu.edu.cn 四川大學
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114014
摘要
研究了316L ASS在823K真空滯留液鉛鉍共晶中低溫氧氮化(LTON)處理對LBE腐蝕行為的影響。結果表明,未處理樣品在液態LBE接觸下存在嚴重的選擇性浸出。LTON處理在試樣表面形成了一層Fe-Cr尖晶石多孔外膜和一層S相內膜,在LBE溶液腐蝕后形成了一層較厚的含有γlow-N的尖晶石膜和分布有CrN析出的區域。這主要是由于S相是亞穩態相,在高溫下比基體更容易被氧化,導致S相的氧化和分解以及間隙原子的向內擴散。這啟發我們,提高材料形成保護性氧化膜的能力可能是緩解液態LBE腐蝕的一個好方法。
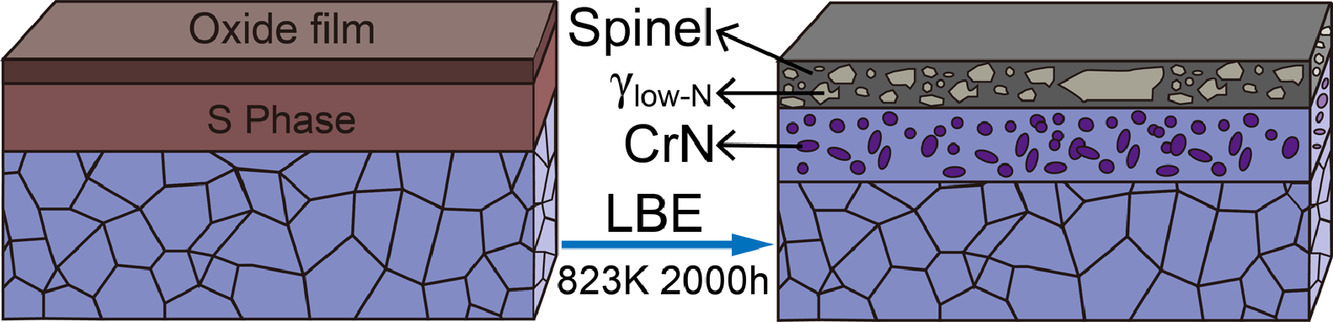
SCRIPTA
Vol. 202, 1 Sep. 2021, 114013
5. Simultaneous effects of deformation-induced plasticity and precipitation hardening in metastable non-equiatomic FeNiCoMnTiSi ferrous medium-entropy alloy at room and liquid nitrogen temperatures
在室溫和液氮溫度下亞穩態非等原子FeNiCoMnTiSi鐵基中熵合金的變形誘導塑性和沉淀硬化的同步效應
Farahnaz Haftlang, Peyman Asghari-Rad, Jongun Moon, Alireza Zargaran, Kee-Ahn Lee, Soon-Jik Hong, Hyoung Seop Kim?
Hyoung Seop Kim: hskim@postech.ac.kr
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114013
摘要
本文研究了一種新型亞穩態65Fe-15Ni-8Co-8Mn-3Ti-Si (at%)鐵基中熵合金在298 K和77 K下的力學性能。采用短時間退火后的時效處理,獲得了由納米析出相裝飾的細晶粒和粗晶粒組成的非均質組織。時效處理后,合金的屈服強度從298K和77K時的0.9 GPa和1.3 GPa顯著提高到1.1 GPa和1.5 GPa,而總延伸率保持在20%以上。這種顯著的改善是由于時效合金在拉伸變形過程中異質變形誘導強化、力學納米孿晶、馬氏體相變以及均勻分布的納米級Fe2SiTi和Ni3Ti析出強化的協同效應。因此,相應的鐵基MEA可以被認為是在極端服役條件下超高強度部件的一種有前途的候選材料。
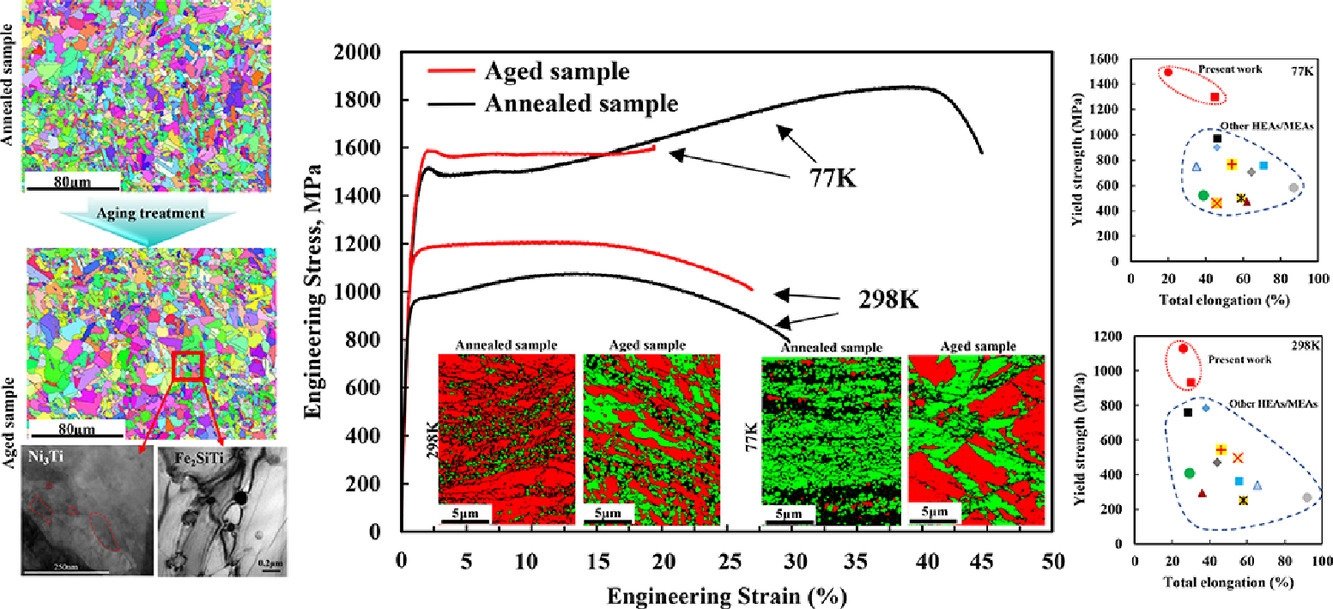
SCRIPTA
Vol. 202, 1 Sep. 2021, 114019
6. A new insight into annealing parameters in tailoring the mechanical properties of a medium Mn steel
調控中錳鋼力學性能的退火參數的新見解
Songyang Jing, Hua Ding?, Yuping Ren, Zhihui Cai
Hua Ding: dingh@smm.neu.edu.cn 東北大學
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114019
摘要
中錳鋼的力學性能一般是通過調節臨界退火(IA)溫度和退火時間來實現的。然而,在本研究中,我們發現IA中的升溫過程對所研究中錳鋼的力學性能也有顯著的控制作用。不同溫度下,升溫周期越長,越有利于奧氏體晶粒的形成,從而使得在單個奧氏體晶粒內和不同奧氏體晶粒間的Mn元素分布更加不均勻。這種非均質組織導致了奧氏體板條之間屈服強度的差異和較慢的應變誘導馬氏體相變動力學。最終,在保持高的極限抗拉強度的同時,所研究的中錳鋼的屈服強度和總延伸率顯著提高。本研究為全面理解退火參數的影響提供了新的見解,以提高中錳鋼的力學性能。
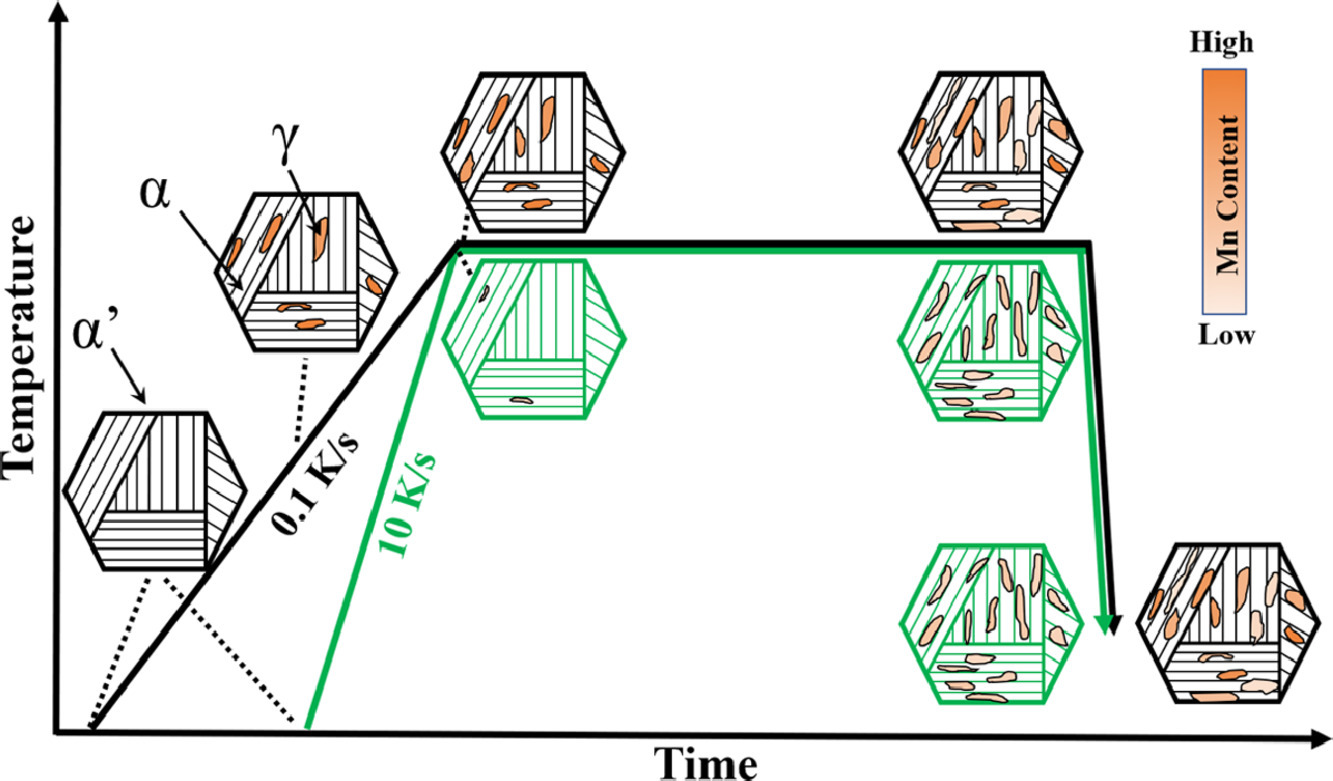
SCRIPTA
Vol. 202, 1 Sep. 2021, 114032
7. Understanding ferrite deformation caused by austenite to martensite transformation in dual phase steels
理解雙相鋼中奧氏體向馬氏體轉變引起的鐵素體變形
Vibhor Atreya?, Cornelis Bos, Maria J. Santofimia
Vibhor Atreya: V.Atreya@tudelft.nl
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114032
摘要
在DP鋼生產過程中,奧氏體向馬氏體轉變時伴隨的體積膨脹和形狀變化可以被周圍鐵素體晶粒的變形所適應。鐵素體晶粒的變形程度最終影響DP鋼的力學性能。利用電子背散射衍射,本研究確定了控制相變誘導鐵素體晶粒變形程度的馬氏體特征。研究發現,小奧氏體晶粒易于轉變為與相鄰鐵素體晶粒成密排平面平行關系的馬氏體變體,從而實現相對容易的滑移傳遞,導致鐵素體晶粒的長程變形。鐵素體晶粒也表現出限制于鐵素體/馬氏體界面附近的短程變形,這主要受馬氏體碳含量的影響。
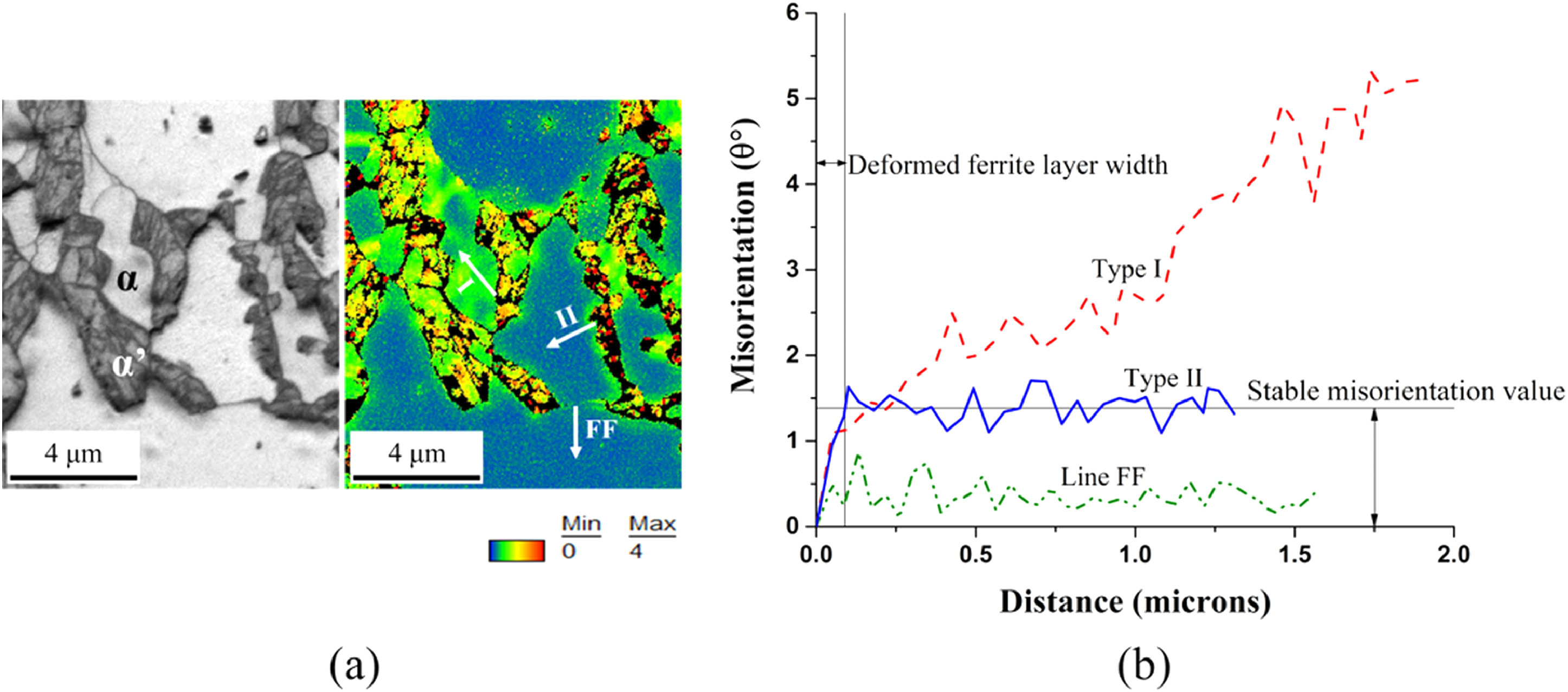
SCRIPTA
Vol. 202, 1 Sep. 2021, 114031
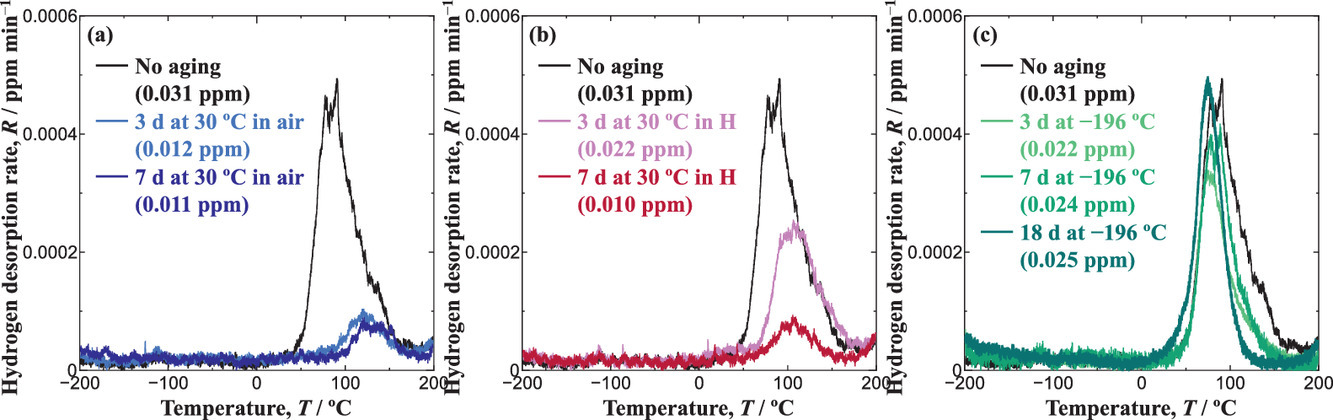
8. The effects of interstitial hydrogen and carbon atoms and aging temperature on annihilation behavior of hydrogen-enhanced strain-induced vacancies in iron
間隙氫和碳原子以及時效溫度對鐵中氫增強應變誘導空位的湮沒行為的影響
Yuri Sugiyama, Nami Kurihara, Yuya Matsumoto, Kenichi Takai?
Kenichi Takai: takai-k@sophia.ac.jp
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114031
摘要
利用低溫熱脫附光譜(L-TDS)研究了間隙氫、碳原子和時效溫度對鐵中氫增強應變誘導空位(HESIVs)湮沒行為的影響,其中L-TDS可以從-200°C開始升溫。含HESIVs的樣品在不同條件下進行時效,并充以示蹤氫以檢測晶格缺陷。隨著時效時間的延長,在30°C的自然時效減少了熱力學上不穩定的單個空位和雙空位等小空位,但7天后仍存在聚集的空位。相比之下,在-196℃時效幾乎不會引起任何空位擴散、聚集或湮滅。在30°C有氫和碳的條件下時效,降低了空位湮沒率,并留下更多的空位。這些結果表明,鐵中間隙碳和氫原子抑制了空位的擴散和湮滅,從而實現了空位的穩定。