金屬頂刊雙語導(dǎo)讀丨Acta Mater. Vol.211,1 Jun. 2021(下)
2021-08-08 來源:Goal Science
本期包含金屬材料領(lǐng)域論文9篇,涵蓋了馬氏體、高熵合金、高溫合金等,國內(nèi)科研單位包括上海交通大學(xué)等(通訊作者單位)。
Vol. 211 目錄
1. Unveiling the mechanism of yttrium-related microstructure inhibiting or promoting high-temperature oxidation based on Ni-Al-Y alloys
Y對Ni-Al-Y合金微觀組織和高溫氧化性能的影響
2. Atomic scale modeling of the coherent strain field surrounding Ni4Ti3 precipitate and its effects on thermally-induced martensitic transformation in a NiTi alloy
Ni4Ti3析出相共格應(yīng)變場及其對NiTi合金熱誘導(dǎo)馬氏體相變影響的原子尺度模擬研究
3. In-situ synchrotron X-ray tomography investigation of damage mechanism of an extruded magnesium alloy in uniaxial low-cycle fatigue with ratchetting
受壓鎂合金棘輪單軸低周疲勞損傷機理的原位同步X射線斷層掃描研究
4. Nitrogen-induced hardening of refractory high entropy alloys containing laminar ordered phases
通過N摻雜形成層片狀有序相實現(xiàn)高熔點高熵合金的顯著硬化
5. Cross-kinks control screw dislocation strength in equiatomic bcc refractory alloys
等原子比BCC高熔點合金中交叉扭結(jié)對螺位錯強化作用的影響
6. Temperature-dependent mechanisms of dislocation–twin boundary interactions in Ni-based equiatomic alloys
等原子比Ni基體合金中位錯-孿晶界相互作用機制隨溫度的變化
7. Designing L21-strengthened Al-Cr-Fe-Ni-Ti complex concentrated alloys for high temperature applications
L21相強化的Al-Cr-Fe-Ni-Ti多主元高溫合金設(shè)計
8. Quantitative prediction of rapid solidification by integrated atomistic and phase-field modeling
通過耦合原子尺度模擬和相場模型實現(xiàn)快速凝過程的定量預(yù)測
9. A tale of two phase diagrams: Interplay of ordering and hydrogen uptake in Pd–Au–H
Pd-Au-H體系中有序態(tài)和氫相互作用的相圖研究
ACTA
Vol. 211,1 Jun. 2021, 116879
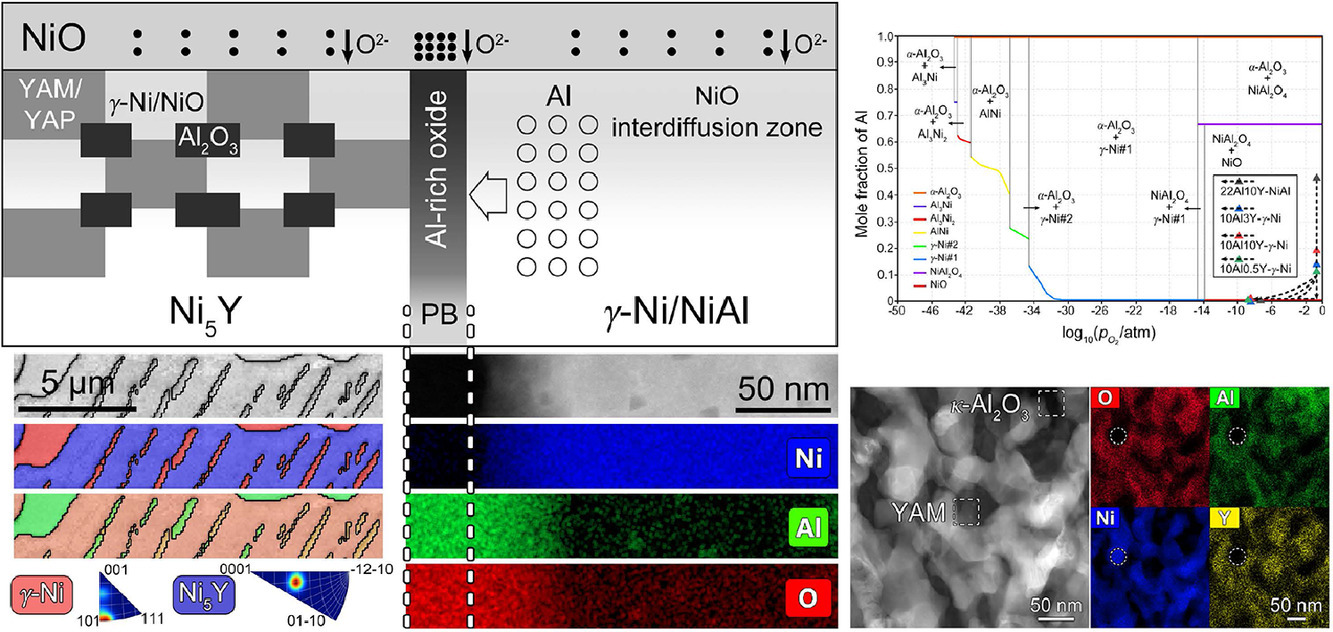
1. Unveiling the mechanism of yttrium-related microstructure inhibiting or promoting high-temperature oxidation based on Ni-Al-Y alloys
Y對Ni-Al-Y合金微觀組織和高溫氧化性能的影響
Yun Wu, Yunting Li, Yuantao Xu, Maodong Kang?, Jun Wang?, Baode Sun
M. Kang:kangmd518@sjtu.edu.cn(上海交通大學(xué))
J. Wang:junwang@sjtu.edu.cn(上海交通大學(xué))
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116879
摘要
釔的添加能夠提高鎳基合金的高溫氧化性能。然而,我們目前對于Y氧化行為的理解尚不深入,特別是與其他關(guān)鍵成分(如Al)的相互作用。我們對四種簡單Ni-Al-Y 合金在800°/1000°℃空氣中的氧化行為進行了研究。通過多尺度表征和熱力學(xué)計算,我們發(fā)現(xiàn)四種合金的氧化層厚度隨Y和Al濃度的變化而變化。在三種高Y含量的合金中,Y相關(guān)的微觀組織對氧化過程具有強烈的驅(qū)動作用。初始組織中的Ni5Y化合物具有強烈的二次γ-Ni條帶析出傾向,因此有利于形成含有混合氧化物顆粒的內(nèi)氧化層,而初始組織中的γ-Ni則驅(qū)動外層NiO的形成。于粗化的不規(guī)則相界相比,密集的層狀相界更有利于抑制內(nèi)層的長大。在1000°C下,得益于晶界(GBs)和內(nèi)氧化層前端混合氧化物的形成,少量添加Y的鎳基合金抗內(nèi)氧化性能顯著提高。我們基于三元相圖等溫截面,進行了一些熱力學(xué)計算,用于闡明氧化物的演化過程。通過對比復(fù)雜產(chǎn)物的形成情況可知,計算結(jié)果與實驗結(jié)果基本吻合。
ACTA
Vol. 211,1 Jun. 2021, 116883
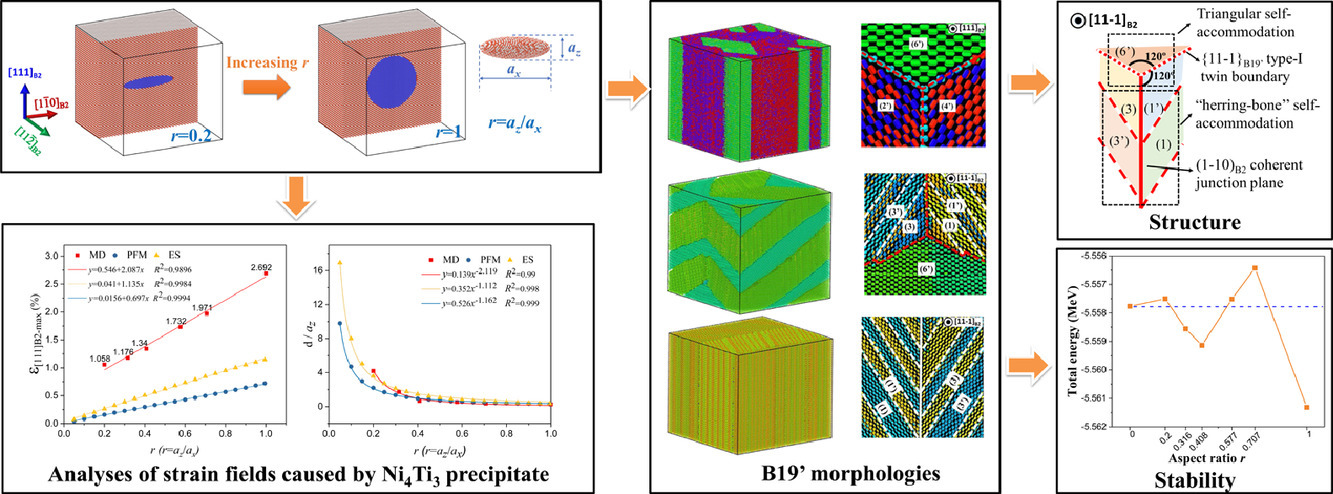
2. Atomic scale modeling of the coherent strain field surrounding Ni4Ti3 precipitate and its effects on thermally-induced martensitic transformation in a NiTi alloy
Ni4Ti3析出相共格應(yīng)變場及其對NiTi合金熱誘導(dǎo)馬氏體相變影響的原子尺度模擬研究
Zhu Li, Fei Xiao?, Hong Chen, Ruihang Hou, Xiaorong Cai, Xuejun Jin?
F. Xiao:xfei@sjtu.du.cn
X. Jin:jin@sjtu.edu.cn(上海交通大學(xué))
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116883
摘要
NiTi合金中的Ni4Ti3析出對于材料性能有重要影響,但析出的共格應(yīng)變場及其對馬氏體相變的影響,特別是對B19’變體和形貌的影響,目前尚不清楚。本研究中,我們通過分子動力學(xué)模擬,結(jié)合Eshelby方法和微彈性相場理論理論,對具有不同長寬比的Ni4Ti3析出所引起的應(yīng)變場進行了研究。通過方程描述了基體中的最大應(yīng)變(沿析出的中軸)及其相對位置。并對材料的馬氏體形變起始溫度Ms和奧氏體相變終止溫度Af進行了分析預(yù)測。此外,我們還詳細(xì)地對之前已發(fā)表過的三角形和人字形兩種B19’自適應(yīng)結(jié)構(gòu)進行了詳細(xì)研究。我們首次觀察到了三角形和人字形的中間狀態(tài),我們把它稱為混合自適應(yīng)態(tài)。這種結(jié)構(gòu)十分不穩(wěn)定,我們對其形成過程進行了分析討論。綜上所述,本研究首次解釋了析出相對于不同孿晶B19’形貌的選擇作用及其對熱誘導(dǎo)馬氏體相變的原子尺度影響。
ACTA
Vol. 211,1 Jun. 2021, 116881
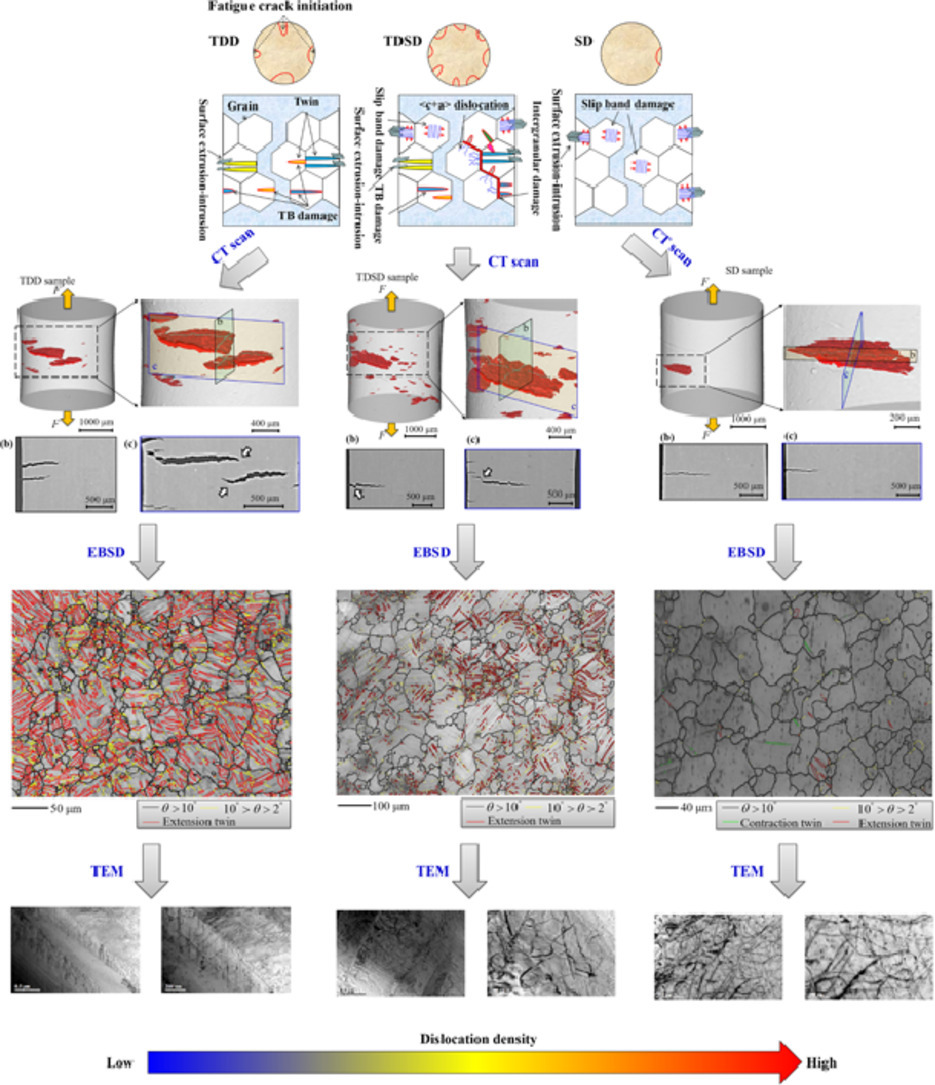
3. In-situ synchrotron X-ray tomography investigation of damage mechanism of an extruded magnesium alloy in uniaxial low-cycle fatigue with ratchetting
受壓鎂合金棘輪單軸低周疲勞損傷機理的原位同步X射線斷層掃描研究
Ziyi Wang, Shengchuan Wu, Guozheng Kang?, Hang Li, Zhengkai Wu, Yanan Fu, Philip J. Withers
G. Kang:guozhengkang@swjtu.edu.cn, guozhengkang@126.com(西南交通大學(xué))
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116881
摘要
我們研究了受壓AZ31Mg合金在單軸低周棘輪疲勞下的變形過程與損傷機制。我們采用不同的平均應(yīng)力和應(yīng)力振幅分別研究了由孿晶控制 (TDD)、滑移控制(SD)和孿晶、滑移混合控制(TDSD)下的循環(huán)變形。通過同步輻射斷層掃描和掃描電子顯微鏡對材料中的損傷進行觀測;通過電子背散射衍射和透射電子顯微鏡對不同載荷條件下的塑性變形機制進行表征。我們在TDD和TDSD樣品中觀測到大量孿晶,而在TDSD和SD樣品中觀測到了高密度位錯和其他復(fù)雜結(jié)構(gòu)。三種樣品按照損傷起始位點數(shù)量由多到少排列依次為TDSD樣品、TDD樣品和SD樣品。因為TDSD樣品中存在大量孿晶引起的穿晶損傷以及<c+a>位錯和孿晶共同引起的晶間損傷使;TDD樣品中位錯密度較低;SD樣品不含孿晶。我們僅在TDSD樣品中觀察到了獨立裂紋之間的連接。以上研究為受壓鎂合金的損傷演化模型提供了豐富的實驗證據(jù)。
ACTA
Vol. 211,1 Jun. 2021, 116884
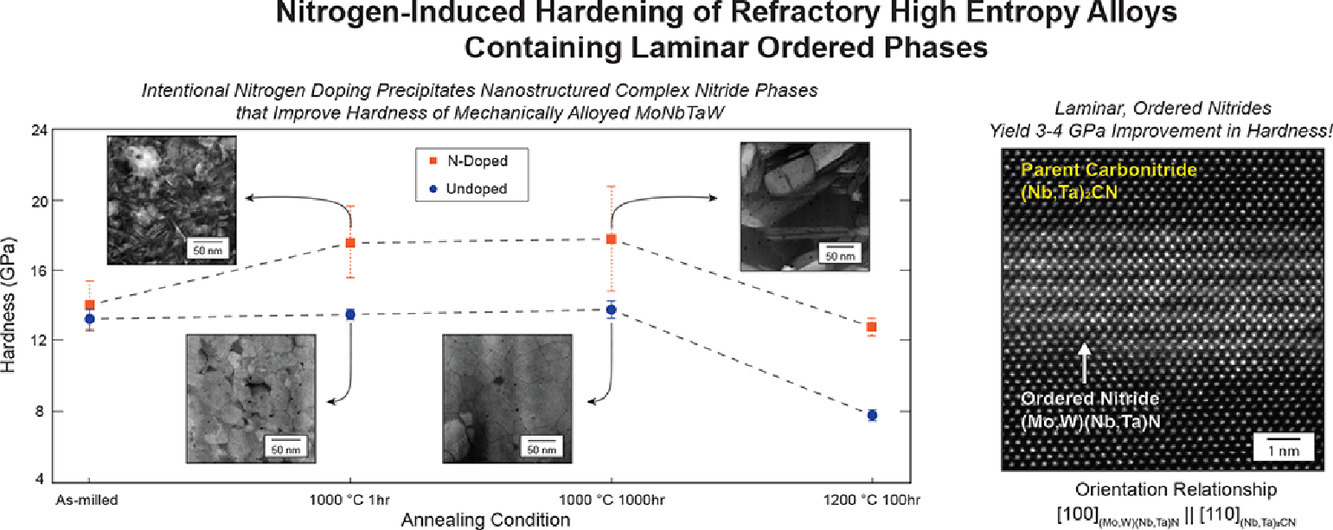
4. Nitrogen-induced hardening of refractory high entropy alloys containing laminar ordered phases
通過N摻雜形成層片狀有序相實現(xiàn)高熔點高熵合金的顯著硬化
Joshua A. Smeltzer, B. Chad Hornbuckle, Anit K. Giri, Kristopher A. Darling, Martin P. Harmer, Helen M. Chan, Christopher J. Marvel?
C.J. Marvel:cjm312@lehigh.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116884
摘要
調(diào)控成分和組織是提高高熵合金(HEAs)性能的主要方法。本研究中,我們發(fā)現(xiàn)可以通過非金屬元素?fù)诫s形成共格有序析出,大幅提高高熵合金的硬度。我們以液氮為制冷劑,通過低溫機械合金化成功制備了N摻雜的MoNbTaW高熵合金。我們在材料中觀測到了富N的二次相,因此摻雜是成功的。特別地,我們通過像差校正掃描透射電鏡(STEM)發(fā)現(xiàn)了一種獨特的有序?qū)悠啵?jīng)鑒定,為四方(Mo、W)(Nb、Ta)N氮化物。此外,我們還發(fā)現(xiàn)了另一種復(fù)雜的碳氮化物(Nb,Ta)2CN。我們將材料在1200°C下進行了100小時的時效處理以研究陶瓷相的長大。我們利用液Ar作為冷卻劑,通過高能球磨方法制備了第二種MoNbTaW合金。對這兩種合金組織和性能的比較表明,復(fù)雜氮化物的形成使得MoNbTaW的硬度大幅提高,可至3-4GPa。
ACTA
Vol. 211,1 Jun. 2021, 116875
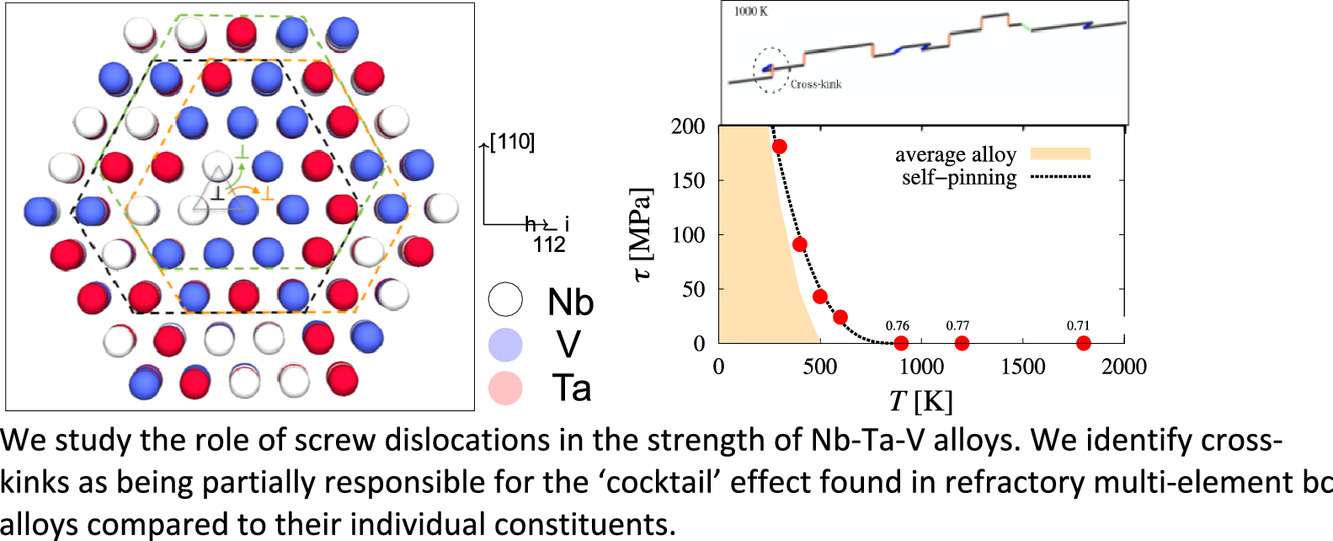
5. Cross-kinks control screw dislocation strength in equiatomic bcc refractory alloys
等原子比BCC高熔點合金中交叉扭結(jié)對螺位錯強化作用的影響
Xinran Zhou?, Sicong He, Jaime Marian?
X. Zhou:Xinranz1216104@g.ucla.edu
J. Marianjmarian@ucla.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116875
摘要
具有BCC結(jié)構(gòu)的高熔點多主元合金(RMEA)由于具有優(yōu)異的高溫應(yīng)用前景,而在過去十年中受到廣泛研究。這些合金大都在高溫下表現(xiàn)出極高的強度,無法用基于熱激活螺位錯運動的BCC塑性標(biāo)準(zhǔn)模型解釋。有研究指出,化學(xué)能量起伏是影響RMEA強度重要因素,而沒有在標(biāo)準(zhǔn)模型中被考慮。本研究中,我們使用蒙特卡洛動力學(xué)模型量化了螺位錯對等原子比Nb-Ta-V合金強度的貢獻(xiàn)。我們發(fā)現(xiàn)沿位錯線的化學(xué)能量波動會在較寬的溫度范圍內(nèi)導(dǎo)致較高的平衡扭結(jié)含量,這與分子動力學(xué)模擬結(jié)果一致。其中的部分形成了交叉扭結(jié)結(jié)構(gòu),它們對螺位錯運動和材料強度有重要影響。我們的模擬證實了(i)交叉扭結(jié)和自釘扎是低溫下形成所謂“雞尾酒”效應(yīng)的主要原因;(ii)僅螺位錯塑性不能有效解釋BCC RMEA的高溫強度。
ACTA
Vol. 211,1 Jun. 2021, 116886
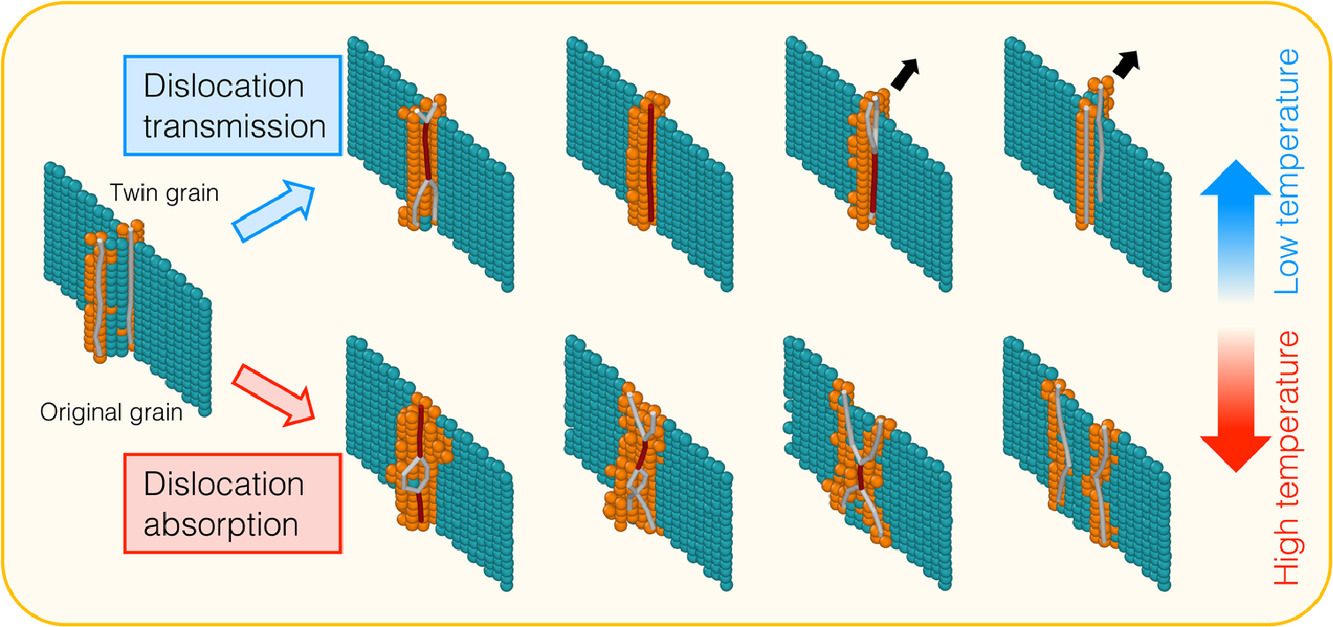
6. Temperature-dependent mechanisms of dislocation–twin boundary interactions in Ni-based equiatomic alloys
等原子比Ni基體合金中位錯-孿晶界相互作用機制隨溫度的變化
Sho Hayakawa, Haixuan Xu?
H. Xu:xhx@utk.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116886
摘要
FeNiCoCrMn高熵合金具有優(yōu)異的強韌性組合,且隨溫度降低,材料延展性顯著增加。這一現(xiàn)象的潛在機制對于理解材料機械性能至關(guān)重要。我們通過原子尺度模擬研究了等原子比鎳基合金中螺位錯與共格孿晶界之間的相互作用。我們發(fā)現(xiàn),這種相互作用的主要機制會隨溫度而變化,這可能是合金在低溫下延展性增強的原因之一。進一步研究表明,與層錯能和Shockley分位錯間離有關(guān)的一個臨界參數(shù)對這種相互作用隨溫度的變化有重要影響。以上研究有助于我們深入理解等原子比鎳基合金的塑性變形機理,對高強塑性材料設(shè)計具有重要意義。
ACTA
Vol. 211,1 Jun. 2021, 116890
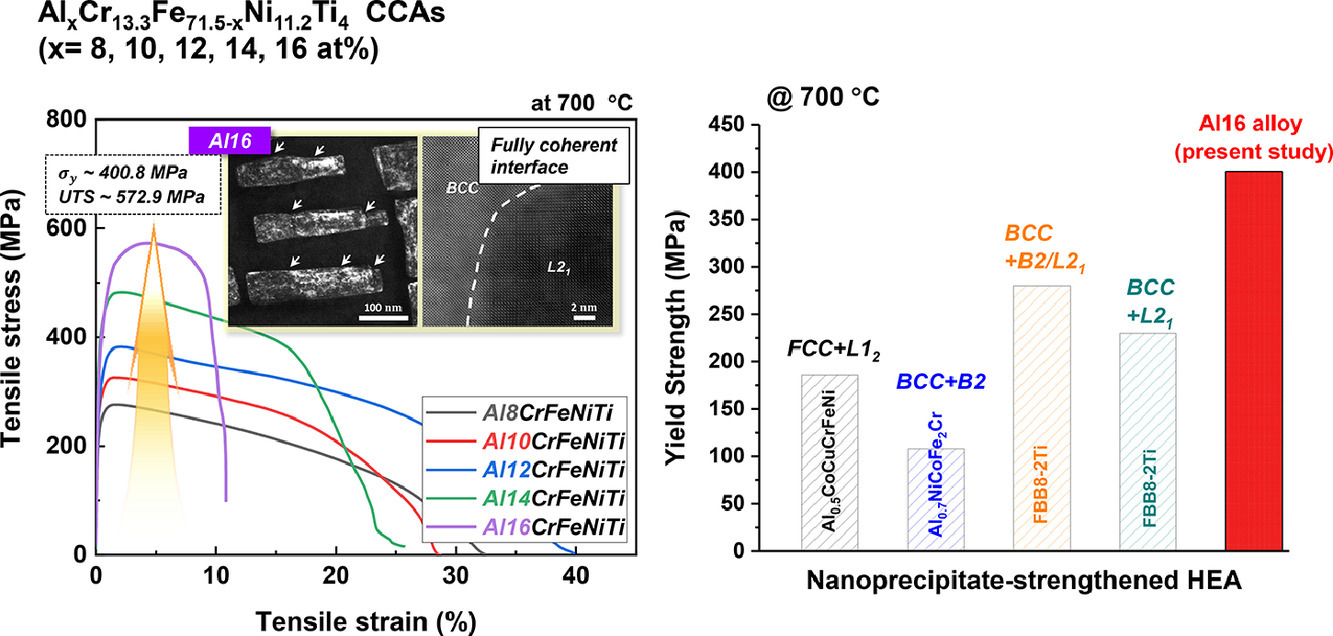
7. Designing L21-strengthened Al-Cr-Fe-Ni-Ti complex concentrated alloys for high temperature applications
L21相強化的Al-Cr-Fe-Ni-Ti多主元高溫合金設(shè)計
Woo Chul Kim, Min Young Na, Heoun Jun Kwon, Young Sang Na, Jong Woo Won, Hye Jung Chang?, Ka Ram Lim?
H.J. Chang:almacore@kist.re.kr
K.R. Lim:krlim@kims.re.kr
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116890
摘要
對于具有納米析出的合金而言,析出與基體之間的共格性對材料的高溫機械性能至關(guān)重要。在這項工作中,我們對AlxCr13.3Fe71.5-xNi11.2Ti4 (x=8, 10, 12, 14, 16 at%) 多主元合金中BCC基體與L21析出的共格性進行了系統(tǒng)研究,包括析出的結(jié)構(gòu)、晶格錯配和由此產(chǎn)生的共格應(yīng)變演化。當(dāng)Al含量從8 at%增加到16 at%時,析出的尺寸和晶格錯配減小,界面從半共格逐漸變?yōu)橥耆哺瘢瑥亩沟没w與析出之間的彈性相互作用增加。同時析出的晶體結(jié)構(gòu)從立方變?yōu)樗姆健kS著Al含量的增加,由于固溶強化和析出強化的作用,材料室溫強度連續(xù)增加。析出的強化機制也由Orowan強化變?yōu)楣哺駨娀S腥さ氖牵煸囼灡砻?/span>700°C下鋁增加引起的強化效應(yīng)進一步增強。更高程度的共格和結(jié)構(gòu)畸變引起了更顯著的有效應(yīng)變轉(zhuǎn)移和析出強化。因此,Al16Cr13.3Fe55.5Ni11.2Ti4具有更加優(yōu)異的屈服強度(400.8MPa)和抗拉強度(572.9MPa)。這一強度遠(yuǎn)高于此前報導(dǎo)的納米析出強化合金,表明這種合金具有優(yōu)異的高溫應(yīng)用前景。
ACTA
Vol. 211,1 Jun. 2021, 116885
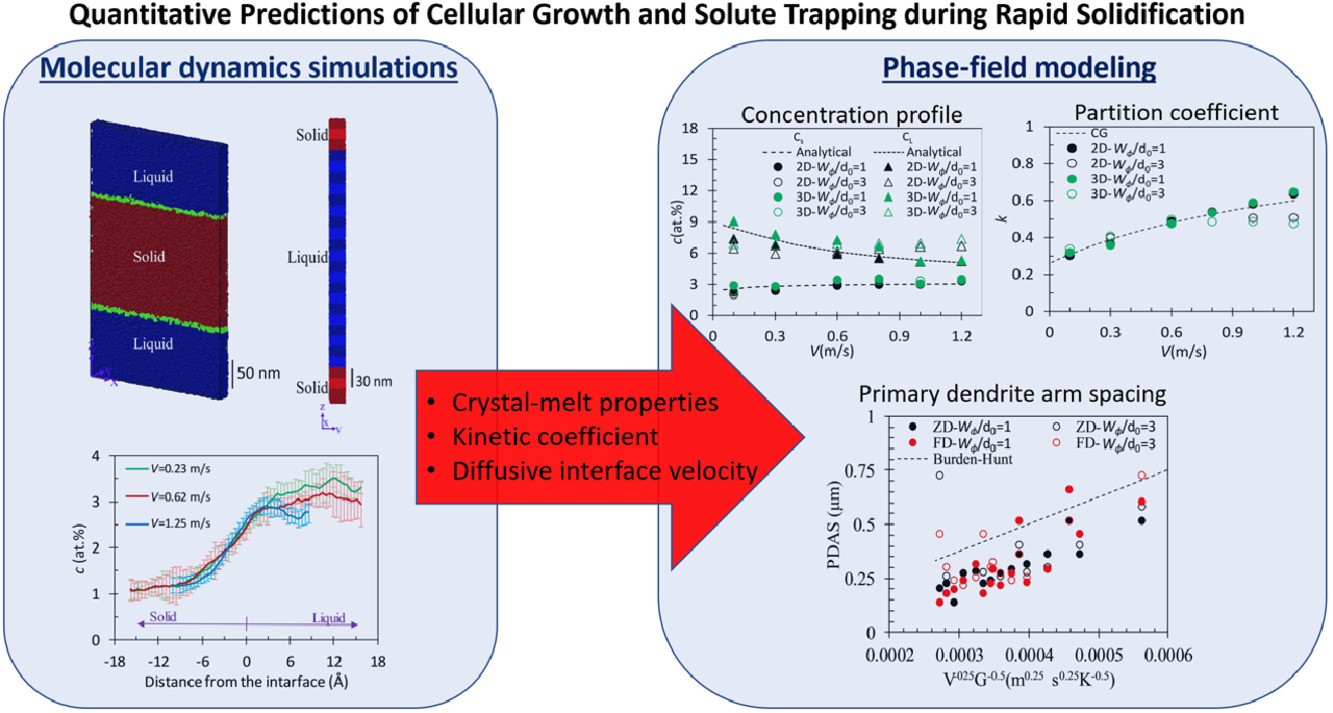
8. Quantitative prediction of rapid solidification by integrated atomistic and phase-field modeling
通過耦合原子尺度模擬和相場模型實現(xiàn)快速凝過程的定量預(yù)測
Sepideh Kavousi, Brian R. Novak, Dorel Moldovan, Mohsen Asle Zaeem
M. Asle Zaeem:zaeem@mines.edu?
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116885
摘要
我們通過耦合原子尺度模擬和相場建模,對增材制造合金凝固過程中的胞結(jié)構(gòu)生長和溶質(zhì)元素捕獲進行了定量預(yù)測。我們通過分子動力學(xué)模擬代替復(fù)雜實驗,得到了各向異性晶體-熔體界面的自由能、動力學(xué)參數(shù)和擴散界面速度,并將其作為相場中的參數(shù)。我們在Ti-3.4at.%Ni合金中測試了耦合模型模擬快速凝固的準(zhǔn)確性。結(jié)果表明,相場模型預(yù)測的溶質(zhì)捕獲與凝固界面的連續(xù)生長模型結(jié)果大體相當(dāng)。預(yù)測得到的一次枝晶臂間距對擴散界面寬度不敏感,因此模型可以使用于更大尺度的體系。二維和三維相場模型模擬得到的濃度分布與配分系數(shù)分別與可與Kurz-Fisher模型和連續(xù)生長模型結(jié)果相當(dāng)。與其他快速凝固計算模型相比,本模型的優(yōu)勢在于可以完全基于計算進行預(yù)測,而不需要進行任何實驗擬合。
ACTA
Vol. 211,1 Jun. 2021, 116893
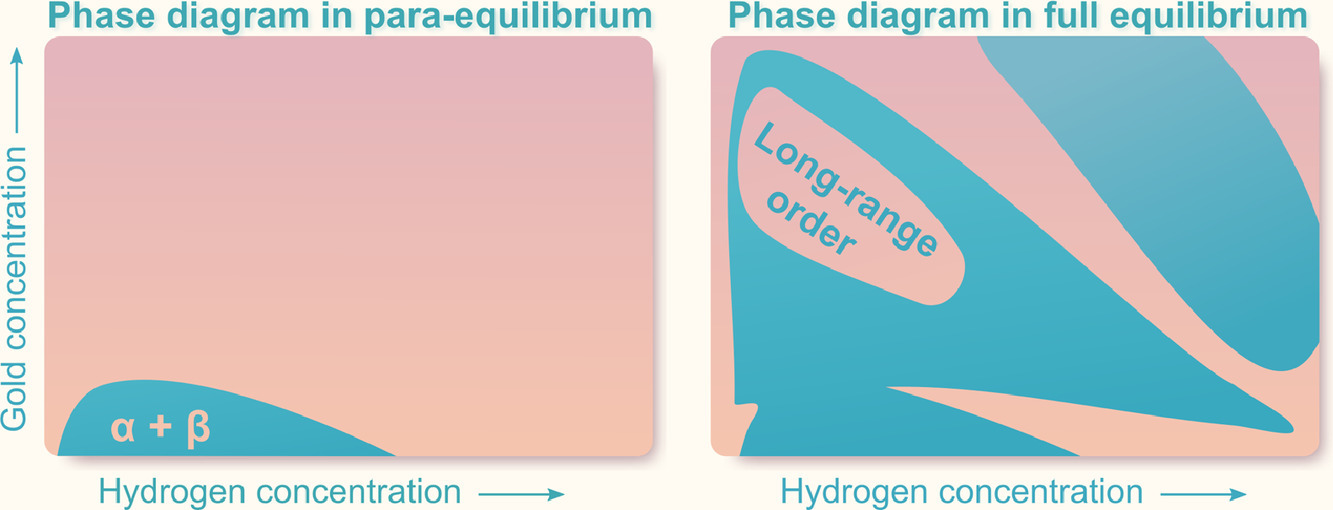
9. A tale of two phase diagrams: Interplay of ordering and hydrogen uptake in Pd–Au–H
Pd-Au-H體系中有序態(tài)和氫相互作用的相圖研究
J. Magnus Rahm, Joakim Löfgren, Erik Fransson, Paul Erhart?
P. Erhart:erhart@chalmers.se
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116893
摘要
Pd-Au納米合金能夠無延遲地可逆吸收/釋放氫,因此是一種優(yōu)秀的氫傳感材料。對于傳感材料而言,吸放氫等溫線的可重復(fù)性和穩(wěn)定性十分重要。研究表明,短程和長程化學(xué)有序?qū)Φ葴鼐€有一定影響,但相關(guān)研究并不深入。本研究中,我們使用合金團簇的膨脹來描述在較寬濃度范圍內(nèi)Pd-Au合金的吸放氫熱力學(xué)。我們通過調(diào)控退火溫度和氫分壓得到了樣品的不同有序狀態(tài),并研究了這些不同化學(xué)有序態(tài)是如何影響合金的吸放氫等溫線,進而影響材料性能的。研究表明,當(dāng)H2分壓足夠高時,材料中將形成長程有序的L12相。我們繪制了250K到500K的相圖,當(dāng)體系中存在氫氣時,體系在完全平衡態(tài)下將發(fā)生相分離,這與準(zhǔn)平衡條件下截然不同。我們研究成功解釋了Pd-Au合金吸放氫等溫線隨時間推移保持穩(wěn)定的實驗現(xiàn)象,并揭示了這一特性失效的可能情況。