金屬頂刊雙語導(dǎo)讀丨Scripta Mater. Vol.203, 1 Oct. 2021(下)
2021-08-08 來源:Goal Science
本期包含金屬材料領(lǐng)域論文10篇,涵蓋了高熵合金、納米晶等,國內(nèi)科研單位包括西北工業(yè)大學(xué)、華南理工大學(xué)、蘭州理工大學(xué)、上海交通大學(xué)等(通訊作者單位)。
Vol. 203 目錄
1. Making selective-laser-melted high-strength Al–Mg–Sc–Zr alloy tough via ultrafine and heterogeneous microstructure
通過超細(xì)和異質(zhì)微觀結(jié)構(gòu)使選擇性激光熔化的高強(qiáng)度 Al-Mg-Sc-Zr合金變得堅(jiān)韌
2. Structure and hardness of in situ synthesized nano-oxide strengthened CoCrFeNi high entropy alloy thin films
原位合成納米氧化物強(qiáng)化CoCrFeNi高熵合金薄膜的結(jié)構(gòu)和硬度
3. Exploring the hydrogen absorption and strengthening behavior in nanocrystalline face-centered cubic high-entropy alloys
探索納米晶面心立方高熵合金的吸氫和強(qiáng)化行為
4. Insight into the preferential grain growth of intermetallics under electric current stressing – A phase field modeling
深入了解電流應(yīng)力下金屬間化合物的優(yōu)先晶粒生長——相場建模
5. Transformative high entropy alloy conquers the strength-ductility paradigm by massive interface strengthening
轉(zhuǎn)化型高熵合金通過大規(guī)模界面強(qiáng)化跨越了強(qiáng)度-延展性范式
6. Effect of N addition on nano-domain structure and mechanical properties of a meta-stable Ti-Zr based alloy
N添加對(duì)亞穩(wěn)態(tài)Ti-Zr基合金納米疇結(jié)構(gòu)和力學(xué)性能的影響
7. Precipitation-induced transition in the mechanical behavior of 3D printed Inconel 718 bcc lattices
3D打印Inconel 718 bcc晶格的沉淀誘導(dǎo)轉(zhuǎn)變的機(jī)械行為
8. Formation of stable equiaxial nanograined Al via combined plastic deformation
通過組合塑性變形形成穩(wěn)定的等軸納米晶鋁
9. An innovative way to fabricate γ-TiAl blades and their failure mechanisms under thermal shock
一種制造γ-TiAl葉片的新方法及其熱沖擊下的失效機(jī)制
10. Y-Hf co-doped Al1.1CoCr0.8FeNi high-entropy alloy with excellent oxidation resistance and nanostructure stability at 1200°C
Y-Hf共摻雜Al1.1CoCr0.8FeNi高熵合金在1200℃下具有優(yōu)異的抗氧化性和納米結(jié)構(gòu)穩(wěn)定性
SCRIPTA
Vol. 203, 1 Oct. 2021, 114052
1. Making selective-laser-melted high-strength Al–Mg–Sc–Zr alloy tough via ultrafine and heterogeneous microstructure
通過超細(xì)和異質(zhì)微觀結(jié)構(gòu)使選擇性激光熔化的高強(qiáng)度 Al-Mg-Sc-Zr合金變得堅(jiān)韌
Zihong Wang, Xin Lin?, Nan Kang?, Yanfang Wang, Xiaofang Wang, Xiaobin Yu, Hua Tan, Haiou Yang, Weidong Huang
Xin Lin: xlin@nwpu.edu.cn, 西北工業(yè)大學(xué)
Nan Kang: nan.kang@nwpu.edu.cn,西北工業(yè)大學(xué)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114052
摘要
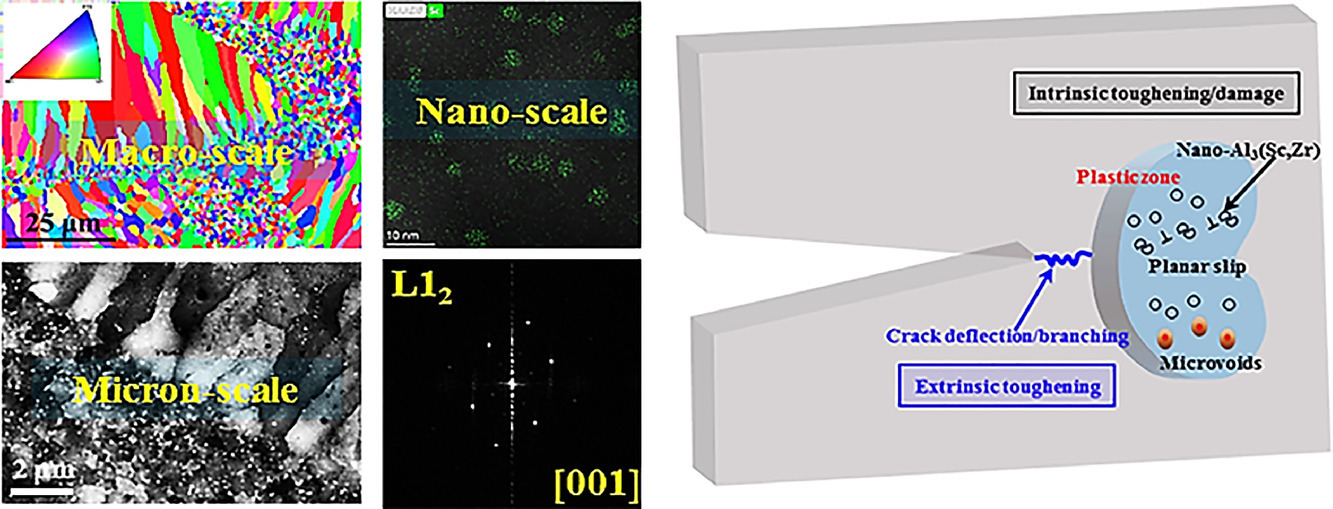
對(duì)于大多數(shù)對(duì)安全至關(guān)重要的應(yīng)用,實(shí)現(xiàn)高強(qiáng)度和高韌性是對(duì)結(jié)構(gòu)材料的關(guān)鍵要求之一。 然而,強(qiáng)度和韌性通常是相互排斥的。在這里,我們報(bào)告了一種選擇性激光熔化的Al-Mg-Sc-Zr 合金,它具有良好的強(qiáng)度和韌性組合,可與7075-T651高強(qiáng)度鍛造鋁合金相媲美。盡管由于二次Al3(Sc,Zr) 納米析出物引起的有序平面滑移會(huì)導(dǎo)致脆性裂紋,但通過與其超細(xì)和異質(zhì)微觀結(jié)構(gòu)相關(guān)的多種內(nèi)在/外在增韌機(jī)制,有效地提高了斷裂韌性。目前的工作為制造高強(qiáng)度和高韌性的鋁基合金提供了一種有效的策略。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 203, 1 Oct. 2021, 114044
2. Structure and hardness of in situ synthesized nano-oxide strengthened CoCrFeNi high entropy alloy thin films
原位合成納米氧化物強(qiáng)化CoCrFeNi高熵合金薄膜的結(jié)構(gòu)和硬度
Subin Lee?, Dominique Chatain, Christian H. Liebscher, Gerhard Dehm?
Subin Lee: s.lee@mpie.de
Gerhard Dehm: dehm@mpie.de
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114044
摘要
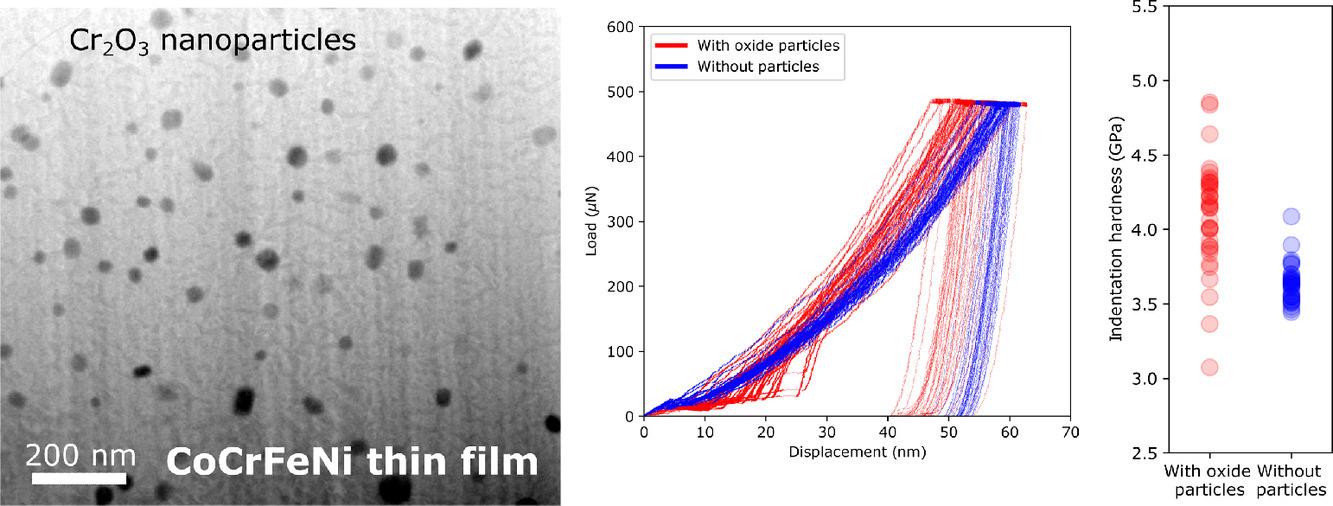
在這項(xiàng)研究中,我們報(bào)告了面心立方結(jié)構(gòu)的CoCrFeNi高熵合金薄膜,其具有通過內(nèi)氧化形成的分散的納米氧化物顆粒。分析型掃描透射電子顯微鏡成像發(fā)現(xiàn)這些顆粒是Cr2O3。與沒有析出物的薄膜相比,氧化物顆粒有助于薄膜的硬化,通過 Orowan型強(qiáng)化機(jī)制,其硬度提高了14%。我們的新方法為利用氧化物相設(shè)計(jì)具有高強(qiáng)度的中高熵合金鋪平了道路。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 203, 1 Oct. 2021, 114069
3. Exploring the hydrogen absorption and strengthening behavior in nanocrystalline face-centered cubic high-entropy alloys
探索納米晶面心立方高熵合金的吸氫和強(qiáng)化行為
Yakai Zhao?, Jeong-Min Park, Kotaro Murakami, Shin-ichi Komazaki, Megumi Kawasaki, Koichi Tsuchiya, Jin-Yoo Suh, Upadrasta Ramamurty, Jae-il Jang?
Yakai Zhao: yakai.zhao@ntu.edu.sg
Jae-il Jang: jijang@hanyang.ac.kr
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114069
摘要
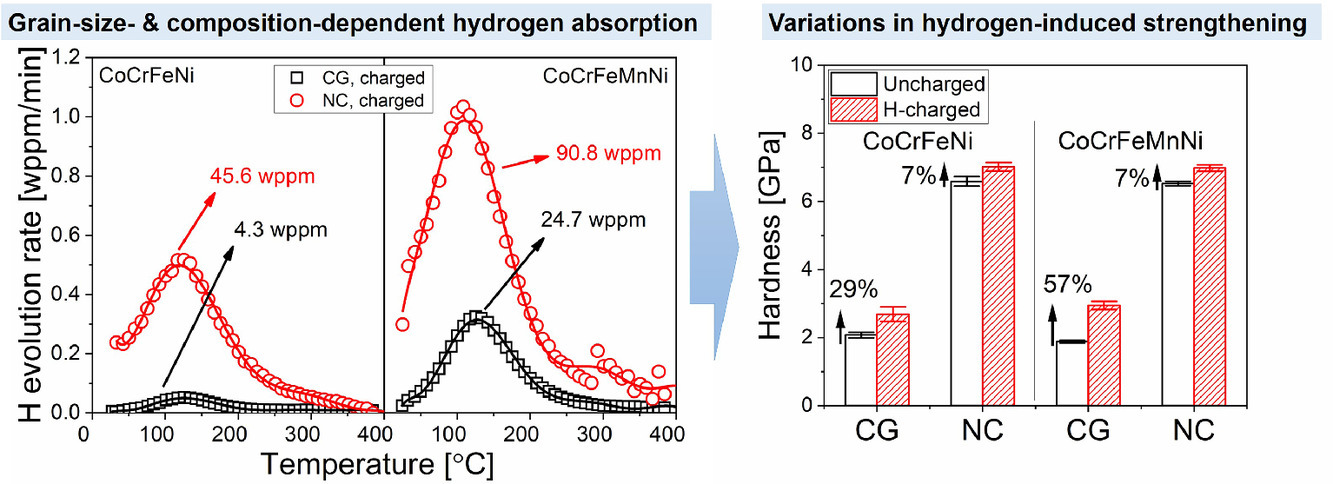
晶粒尺寸從粗晶到納米晶的顯著變化會(huì)影響兩種面心立方高熵合金(HEAs)的吸氫和塑性變形行為,即等原子數(shù)的CoCrFeNi和CoCrFeMnNi。充氫樣品的熱解吸分析證明,晶界充當(dāng)氫陷阱,因此大大增加了納米晶樣品中的氫含量。兩種HEA之間吸氫的直接比較證實(shí),化學(xué)成分和晶粒尺寸都是影響HEA氫溶解度的關(guān)鍵因素。來自納米壓痕率跳躍測試的熱激活變形參數(shù)表明氫增強(qiáng)了晶格摩擦,導(dǎo)致激活體積減少,從而改變了塑性變形過程。實(shí)驗(yàn)結(jié)果從兩個(gè)方面進(jìn)行討論,即晶粒尺寸和化學(xué)成分對(duì)氫影響塑性變形的影響。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 203, 1 Oct. 2021, 114071
4. Insight into the preferential grain growth of intermetallics under electric current stressing – A phase field modeling
深入了解電流應(yīng)力下金屬間化合物的優(yōu)先晶粒生長——相場建模
Shuibao Liang, Anil Kunwar, Cheng Wei, Changbo Ke?
Changbo Ke: mecbke@scut.edu.cn, 華南理工大學(xué)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114071
摘要
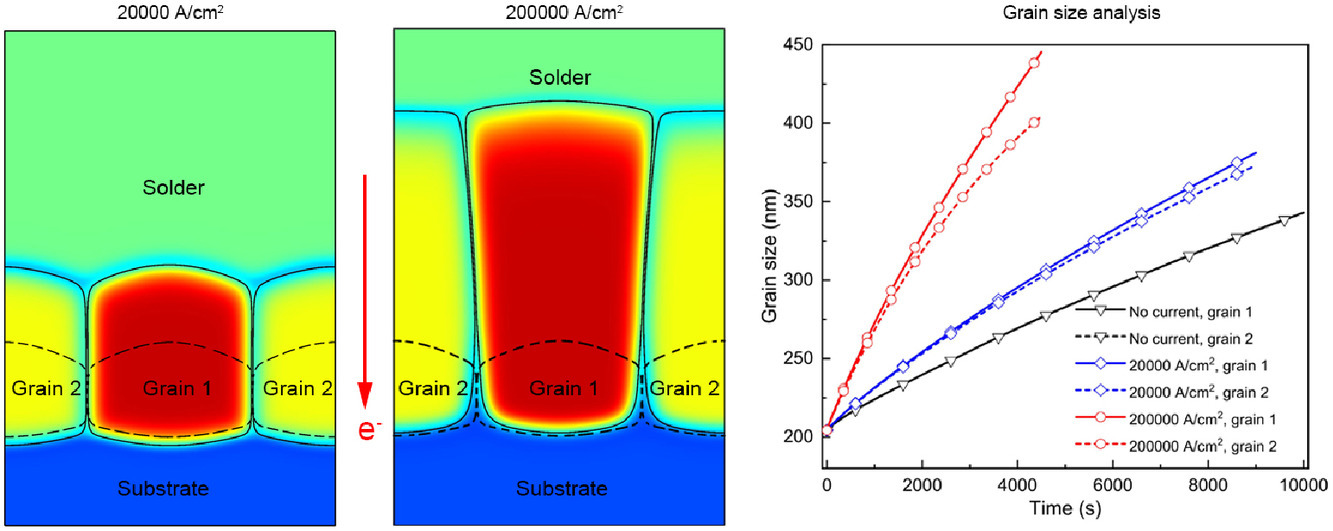
在電流應(yīng)力下金屬間化合物的優(yōu)先生長晶粒已經(jīng)在實(shí)驗(yàn)中觀察到并表征,但必須從機(jī)理上理解。這項(xiàng)工作采用結(jié)合靜電自由能和晶粒取向影響的相場模型來研究電流應(yīng)力下焊料/銅鍵合界面處金屬間化合物的生長行為。結(jié)果表明,由電遷移驅(qū)動(dòng)的晶界和相界的定向遷移誘導(dǎo)了具有更高電導(dǎo)率的金屬間化合物沿電子流的優(yōu)先生長行為。研究揭示了,具有較高電導(dǎo)率的金屬間化合物晶粒的更快相界遷移和生長是由穿過界面的較高擴(kuò)散通量引起的。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 203, 1 Oct. 2021, 114070
5. Transformative high entropy alloy conquers the strength-ductility paradigm by massive interface strengthening
轉(zhuǎn)化型高熵合金通過大規(guī)模界面強(qiáng)化跨越了強(qiáng)度-延展性范式
S.S. Nene, P. Agrawal, M. Frank, A. Watts, S. Shukla, C. Morphew, A. Chesetti, J.S. Park, R.S. Mishra?
R.S. Mishra: rajiv.mishra@unt.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114070
摘要
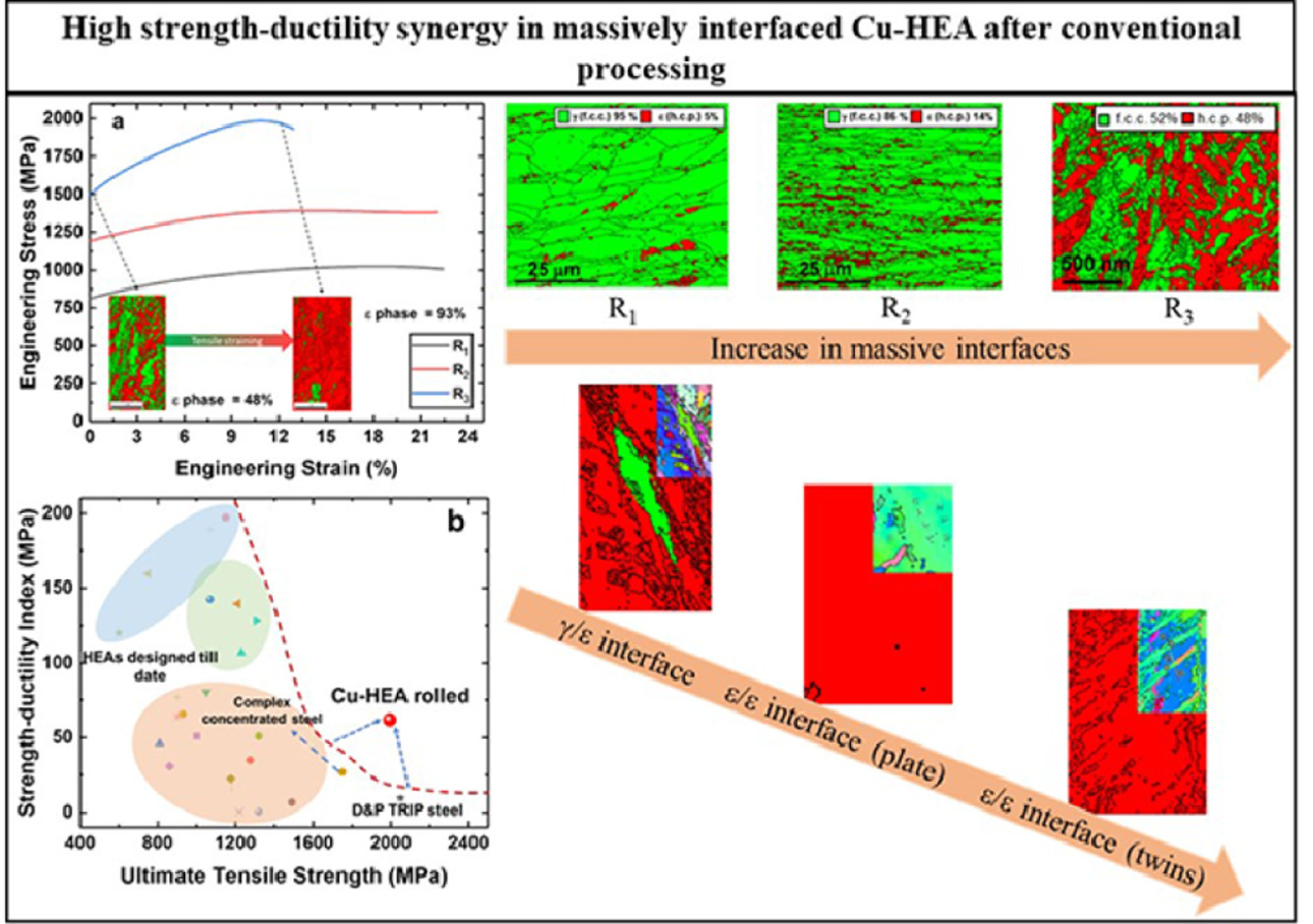
最近的亞穩(wěn)態(tài)合金設(shè)計(jì)已經(jīng)證明在高熵合金中同時(shí)獲得高極限拉伸強(qiáng)度 (UTS) 和延展性,但屈服強(qiáng)度低。在這里,我們提出了同時(shí)提高 Fe38.5Mn20Co20Cr15Si5Cu1.5高熵合金 (Cu-HEA) 的加工硬化性和屈服強(qiáng)度 (YS) 的新策略。YS(1.5 GPa)的急劇增加歸因于由于極端晶粒細(xì)化而在微觀結(jié)構(gòu)中形成γ/ε、ε/ε(孿晶型)和ε/ε(板型)界面,而高UTS-延展性協(xié)同作用(2.2 GPa, 15%) 是通過這些界面上的動(dòng)態(tài)霍爾-佩奇硬化(即大量界面強(qiáng)化)和γ相中的轉(zhuǎn)變誘導(dǎo)塑性獲得的。因此,這種在Cu-HEA中YS和UTS-延展性協(xié)同作用的組合優(yōu)于迄今為止的所有結(jié)構(gòu)材料。因此,變形誘導(dǎo)的大規(guī)模界面強(qiáng)化是一種新的但具有成本效益的途徑,可以通過常規(guī)加工路線在材料中協(xié)同使用先進(jìn)鋼和高熵合金的優(yōu)勢(shì)。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 203, 1 Oct. 2021, 114068
6. Effect of N addition on nano-domain structure and mechanical properties of a meta-stable Ti-Zr based alloy
N添加對(duì)亞穩(wěn)態(tài)Ti-Zr基合金納米疇結(jié)構(gòu)和力學(xué)性能的影響
Jie Fu, Hee Young Kim?, Shuichi Miyazaki
Hee Young Kim: heeykim@ims.tsukuba.ac.jp
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114068
摘要
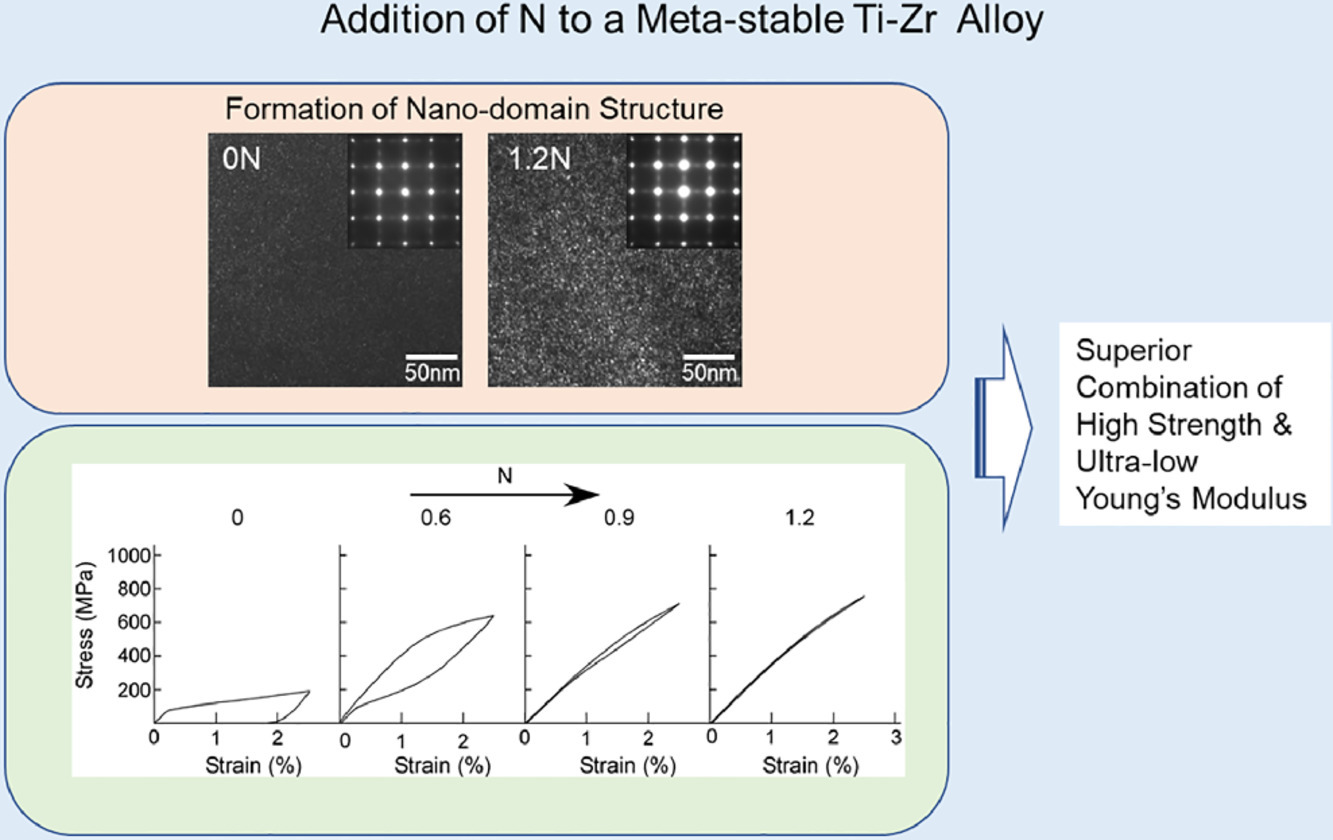
該研究表明,通過在應(yīng)力誘導(dǎo)馬氏體轉(zhuǎn)變的亞穩(wěn)態(tài)β型Ti-Zr基合金中添加N,可以實(shí)現(xiàn)高強(qiáng)度和超低模量的優(yōu)異組合。Ti-18Zr-3Nb-2Mo-3Sn合金表現(xiàn)出非常低的楊氏模量;然而,應(yīng)力誘導(dǎo)的馬氏體轉(zhuǎn)變發(fā)生在低應(yīng)力水平。N的加入促進(jìn)了納米晶格調(diào)制(納米域)結(jié)構(gòu)的形成,并阻礙了應(yīng)力誘導(dǎo)的馬氏體轉(zhuǎn)變,導(dǎo)致更高的表觀屈服應(yīng)力、更窄的應(yīng)力滯后和大的非線性彈性。Ti-18Zr-3Nb-2Mo-3Sn-1.2N合金表現(xiàn)出41 GPa的低楊氏模量和920 MP的高強(qiáng)度以及大的可恢復(fù)應(yīng)變的出色組合。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 203, 1 Oct. 2021, 114075
7. Precipitation-induced transition in the mechanical behavior of 3D printed Inconel 718 bcc lattices
3D打印Inconel 718 bcc晶格的沉淀誘導(dǎo)轉(zhuǎn)變的機(jī)械行為
S. Banait, X. Jin, M. Campos, M.T. Perez-Prado
X. Jin: xueze.jin@imdea.org
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114075
摘要
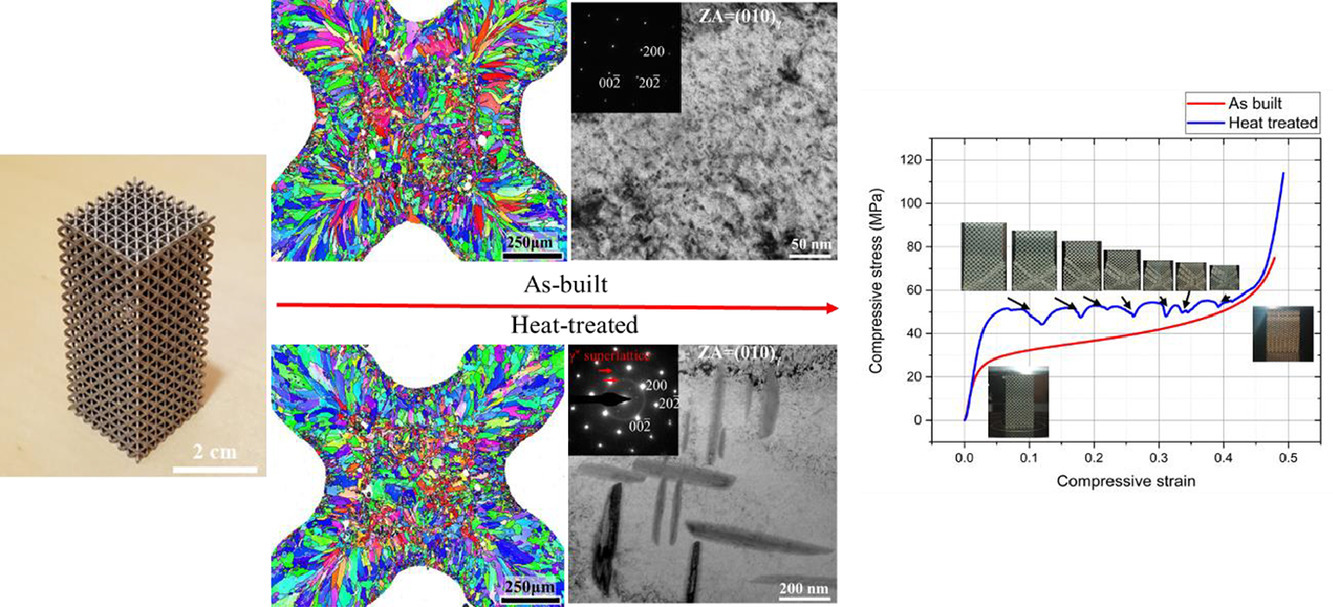
本工作旨在研究微觀結(jié)構(gòu)對(duì)金屬晶格結(jié)構(gòu)力學(xué)行為的影響。為此,通過選擇性激光熔化制造了Inconel 718 bcc晶格,比較了打印態(tài)和時(shí)效態(tài)的室溫壓縮行為。時(shí)效處理后發(fā)生了從彎曲主導(dǎo)向拉伸主導(dǎo)行為的明顯轉(zhuǎn)變,同時(shí)已生成的過飽和固溶體(含有少量納米顆粒)轉(zhuǎn)變成了具有較大比例的析出物的微觀結(jié)構(gòu),析出物的尺寸大約數(shù)百納米。析出物導(dǎo)致結(jié)構(gòu)更硬、更堅(jiān)固,具有更高的吸收能量的能力。將獲得的力學(xué)性能結(jié)果與麥克斯韋準(zhǔn)則的預(yù)測和體心立方晶格的Gibson-Ashby模型進(jìn)行比較。結(jié)果表明,微觀結(jié)構(gòu)變化至少部分解釋了文獻(xiàn)中 bcc實(shí)驗(yàn)數(shù)據(jù)與模型預(yù)測之間的低相關(guān)性。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 203, 1 Oct. 2021, 114054
8. Formation of stable equiaxial nanograined Al via combined plastic deformation
通過組合塑性變形形成穩(wěn)定的等軸納米晶鋁
B. Wang, W. Xu, X. Zhou, X.Y. Li, J.S. Qiao?
X.Y. Li: xyli@imr.ac.cn, 蘭州理工大學(xué),中國科學(xué)呀金屬研究所
J.S. Qiao: qjisen@163.com.cn,蘭州理工大學(xué)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114054
摘要
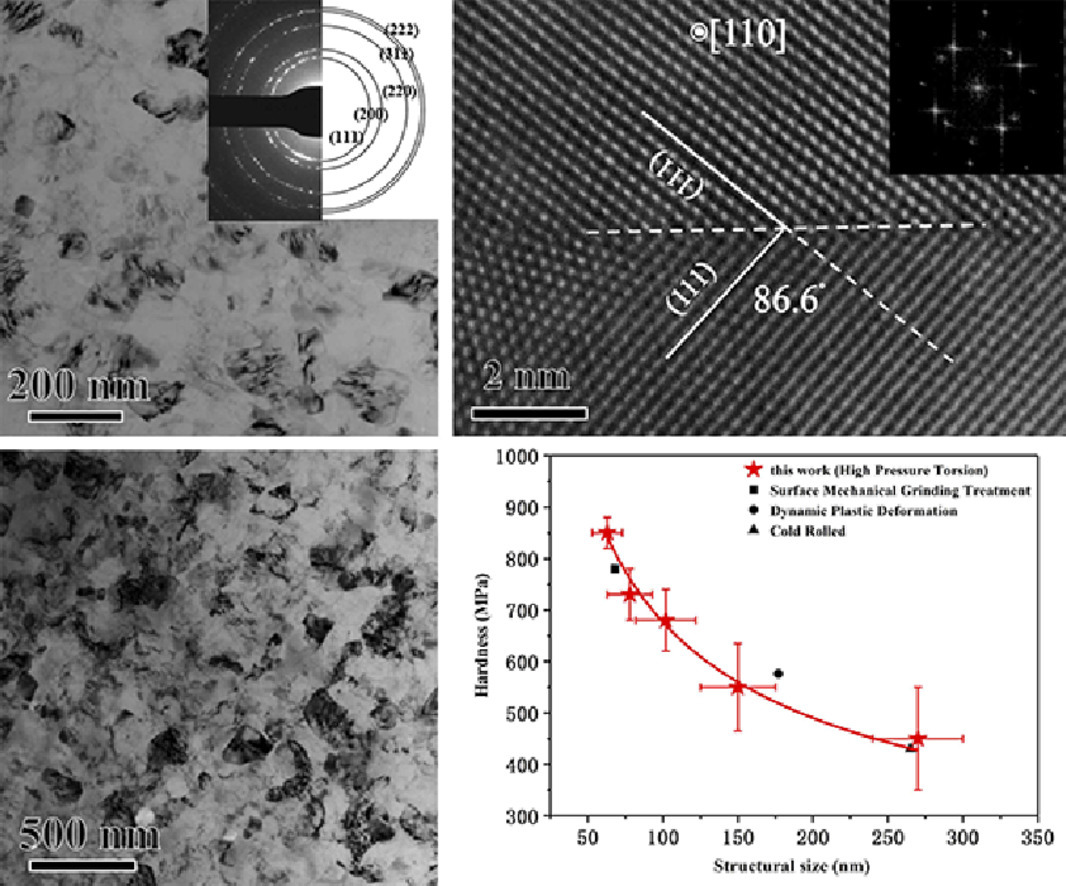
由于其低熔點(diǎn)和高堆垛層錯(cuò)能,將純鋁(Al)中的晶粒細(xì)化到納米級(jí)是困難的。在這里,通過冷軋和低溫高壓扭轉(zhuǎn)的組合塑性變形工藝,制造了平均晶粒尺寸為65 nm的等軸納米晶純鋁。晶粒取向統(tǒng)計(jì)和高分辨率透射電鏡觀察表明,大部分晶界為大角度晶界,其中存在大量低∑晶界,表明發(fā)生晶界弛豫。由于晶界松弛,等軸納米晶Al表現(xiàn)出高強(qiáng)度和優(yōu)異的熱穩(wěn)定性。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 203, 1 Oct. 2021, 114092
9. An innovative way to fabricate γ-TiAl blades and their failure mechanisms under thermal shock
一種制造γ-TiAl葉片的新方法及其熱沖擊下的失效機(jī)制
R. Gao, H. Peng, H. Guo. B. Chen?
B. Chen: bo.chen@leicester.ac.uk
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114092
摘要
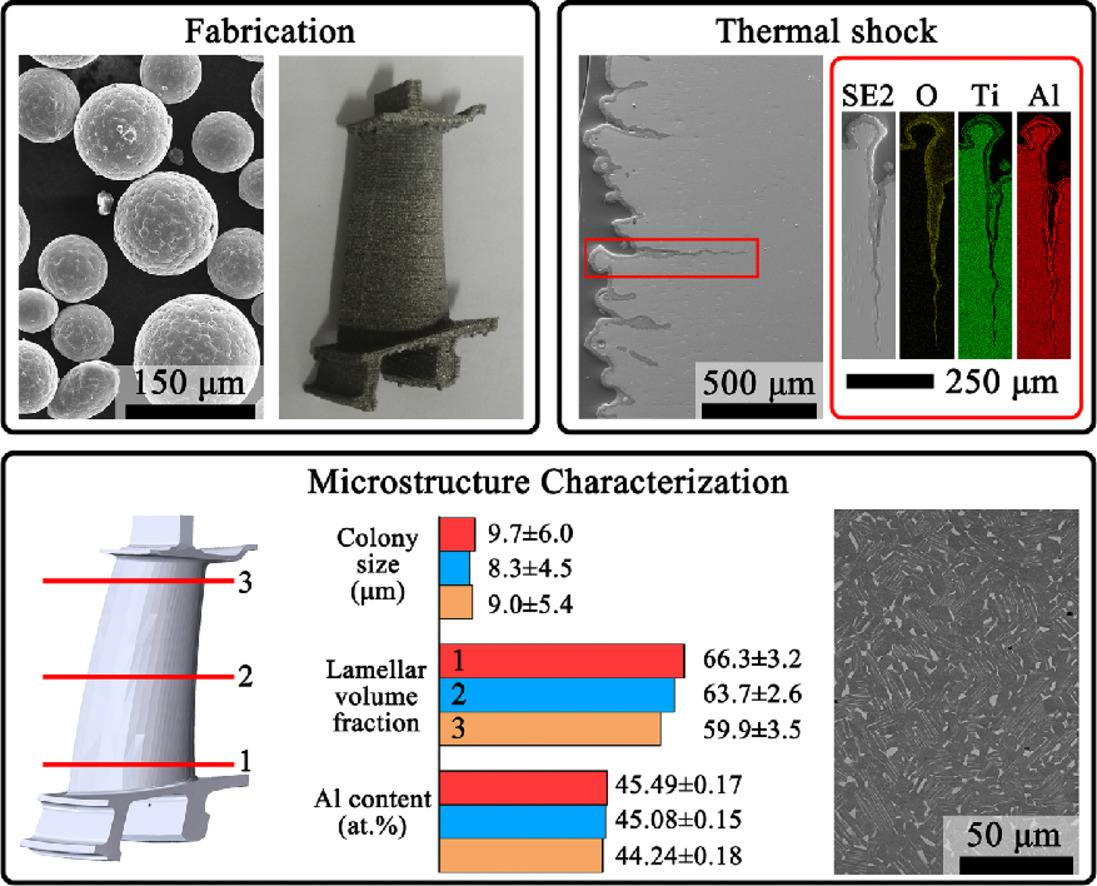
近網(wǎng)狀γ-TiAl葉片是通過選擇性電子束熔化制成的。由于優(yōu)化的工藝參數(shù),制造的材料在 700°C下表現(xiàn)出良好的微觀結(jié)構(gòu)均勻性、拉伸性能和抗熱震性。本文詳細(xì)闡述了實(shí)現(xiàn)這種成功制造的可靠方法。通過在900 °C的熱沖擊實(shí)驗(yàn),確定了一種新的開裂機(jī)制。通過事后檢驗(yàn),我們發(fā)現(xiàn)這種失效模式很可能與逐層策略有關(guān)。氧化結(jié)合表面拓?fù)浣Y(jié)構(gòu)是潛在的機(jī)制。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 203, 1 Oct. 2021, 114105
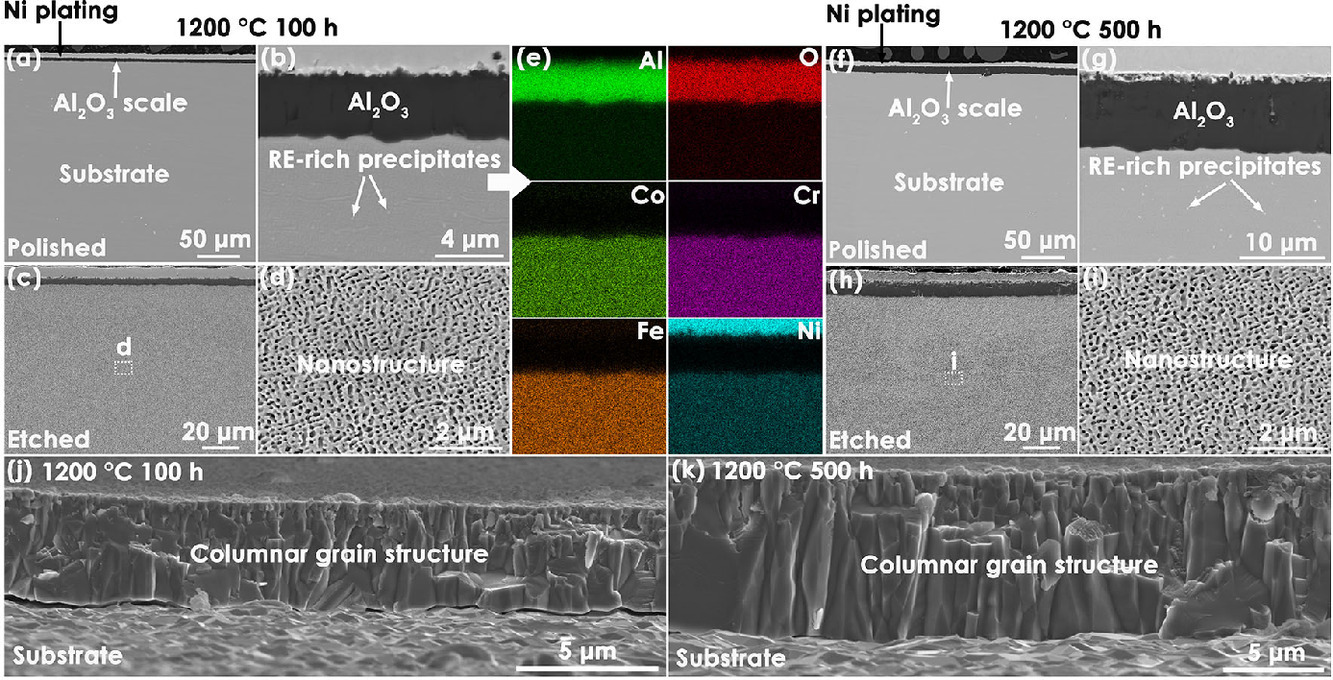
10. Y-Hf co-doped Al1.1CoCr0.8FeNi high-entropy alloy with excellent oxidation resistance and nanostructure stability at 1200°C
Y-Hf共摻雜Al1.1CoCr0.8FeNi高熵合金在1200℃下具有優(yōu)異的抗氧化性和納米結(jié)構(gòu)穩(wěn)定性
Jie Lu, Han Zhang, Ling Lin, Aihui Huang, Xuanzhen Liu, Ying Chen, Xiancheng Zhang, Fangwei Guo, Xiaofeng Zhao?
Xiaofeng Zhao: xiaofengzhao@sjtu.edu.cn, 上海交通大學(xué)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114105
摘要
本文報(bào)道了一種新型Y-Hf共摻雜Al1.1CoCr0.8FeNi高熵合金(HEA),其具有一致性納米結(jié)構(gòu)及其在1200°C下的氧化行為。納米結(jié)構(gòu)高度穩(wěn)定,在長時(shí)間氧化過程中幾乎沒有觀察到粗化現(xiàn)象。Y-Hf共摻雜Al1.1CoCr0.8FeNi HEA表現(xiàn)出非常低的氧化速率,甚至低于典型的 FeCrAlYHf 合金,而其抗氧化皮剝落性能明顯優(yōu)于典型的NiCoCrAlYHf合金。高度穩(wěn)定的納米結(jié)構(gòu)有利于增加Y和Hf分布的均勻性,從而加強(qiáng)反應(yīng)元素效應(yīng),從而降低氧化速率和Al2O3氧化皮的生長應(yīng)力。一般而言,Y-Hf共摻雜Al1.1CoCr0.8FeNi HEA在1200℃下具有優(yōu)異的結(jié)構(gòu)穩(wěn)定性、氧化皮生長速率低和氧化皮生長應(yīng)力低等優(yōu)點(diǎn)。