金屬頂刊雙語導讀丨Acta Mater. Vol.212,15 Jun. 2021(下)
2021-08-08 來源:Goal Science
本期包含金屬材料領域論文12篇,涵蓋了高溫合金、納米晶、高熵合金等,國內科研單位包括上海交通大學、北京科技大學等(通訊作者單位)。
Vol. 212 目錄
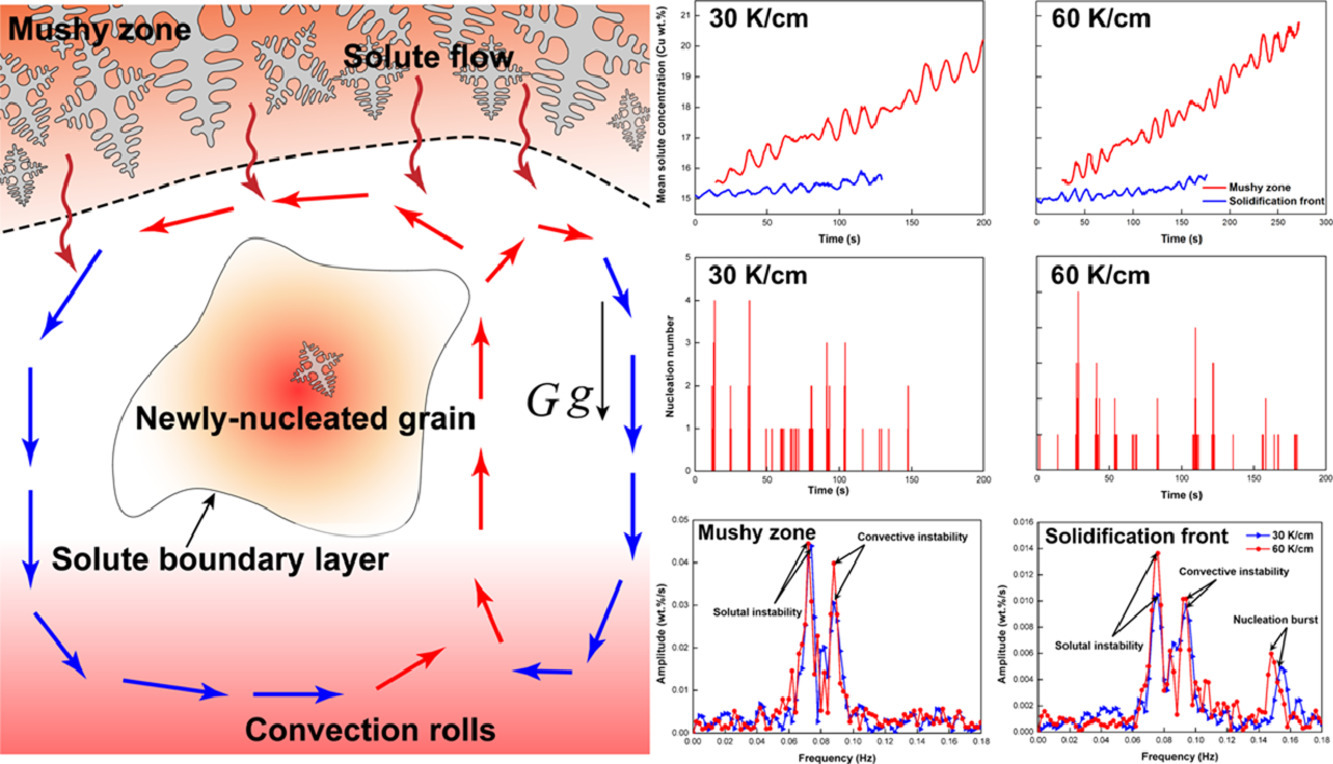
1. Intermittent nucleation and periodic growth of grains under thermo-solutal convection during directional solidification of Al-Cu alloy
Al-Cu合金定向凝固過程中對流條件下晶粒的間歇性形核和周期性長大
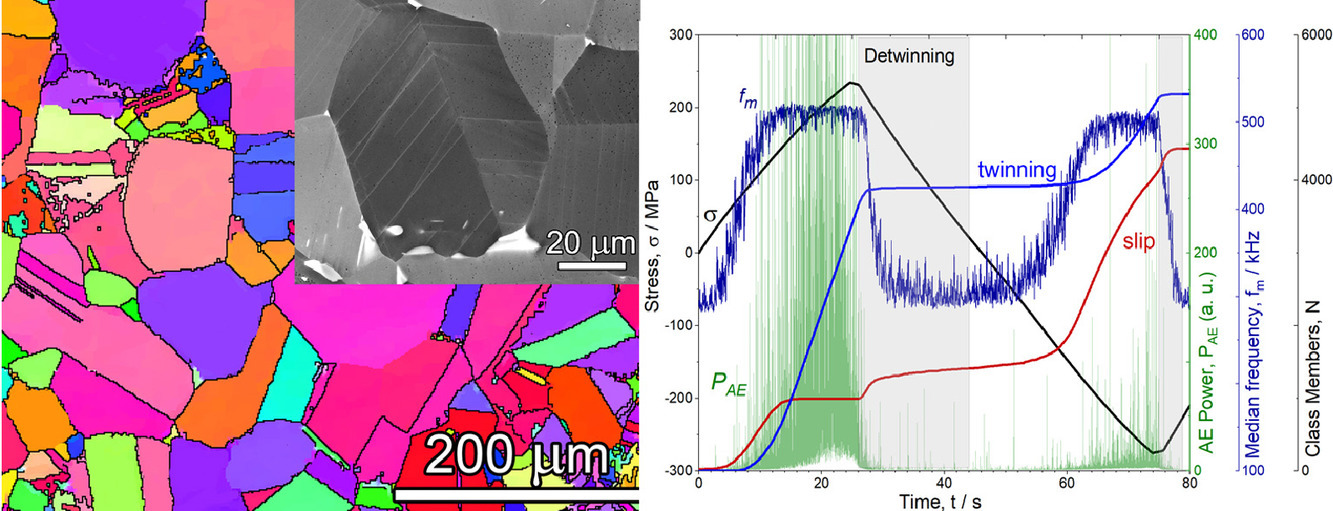
2. Kinetics of cyclically-induced mechanical twinning in γ-TiAl unveiled by a combination of acoustic emission, neutron diffraction and electron microscopy
γ-TiAl中循環應變誘導孿晶動力學的聲射、中子衍射和電子顯微研究
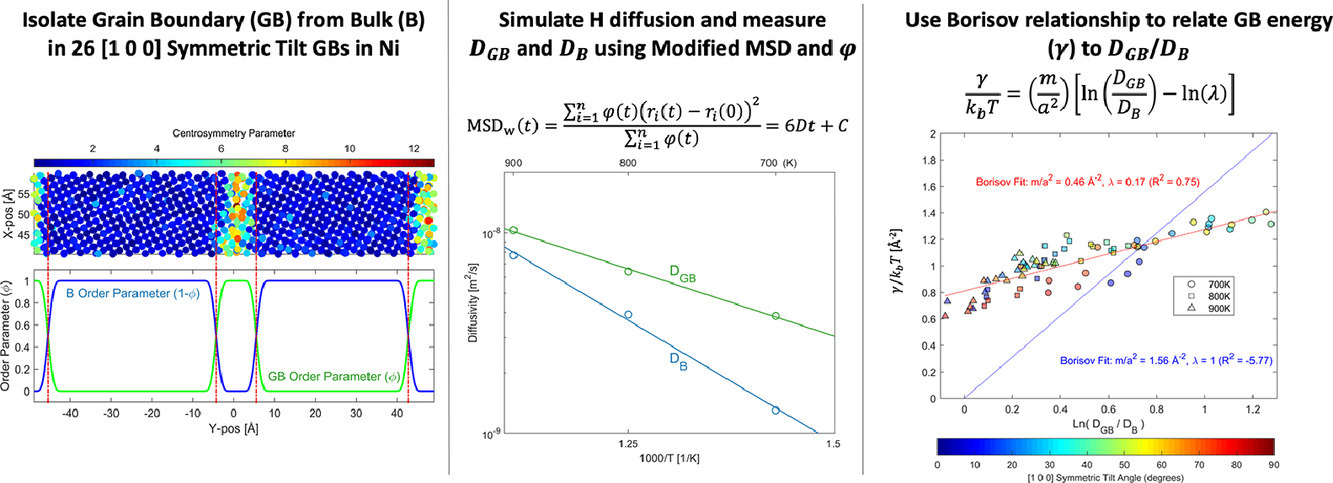
3. Measuring simulated hydrogen diffusion in symmetric tilt nickel grain boundaries and examining the relevance of the Borisov relationship for individual boundary diffusion
鎳對稱傾側晶界中的氫模擬擴散及其與Borisov模型的聯系
4. Mechanisms of Ti3Al precipitation in hcp α-Ti
密排六方α-Ti中的Ti3Al析出機理
5. Microstructure evolution under [110] creep in Ni-base superalloys
鎳基高溫合金[110]蠕變過程中的組織演變
6. Modeling solid solution strengthening in high entropy alloys using machine learning
高熵合金固溶強化的機器學習研究
7. Precipitation in reactor pressure vessel steels under ion and neutron irradiation: On the role of segregated network dislocations
離子和中子輻照條件下反應堆壓力容器鋼鐵材料中析出、偏聚和位錯網狀的演化及相互作用
8. Revealing Nanoscale deformation mechanisms caused by shear-based material removal on individual grains of a Ni-based superalloy
鎳基高溫合金單一晶粒在剪切加工中的納米尺度變形機制研究
9. Strength, plasticity, thermal stability and strain rate sensitivity of nanograined nickel with amorphous ceramic grain boundaries
非晶陶瓷晶界強化鎳納米晶材料的強度、塑性、熱穩定性和應變率敏感性研究
10. Tuning the degree of chemical ordering in the solid solution of a complex concentrated alloy and its impact on mechanical properties
多主元合金中的化學有序調控及其對力學性能的影響
11. Unique crystallographic texture formation in Inconel 718 by laser powder bed fusion and its effect on mechanical anisotropy
激光粉末熔煉Inconel 718中的獨特織構及其對機械性能各向異性的影響
12. Vapor phase dealloying kinetics of MnZn alloys
MnZn合金的氣相脫合金動力學
ACTA
Vol. 212,15 Jun. 2021, 116861
1. Intermittent nucleation and periodic growth of grains under thermo-solutal convection during directional solidification of Al-Cu alloy
Al-Cu合金定向凝固過程中對流條件下晶粒的間歇性形核和周期性長大
Yang Tang, Yue Wu, Ya Zhang, Yongbing Dai, Qing Dong, Yanfeng Han, Guoliang Zhu, Jiao Zhang?, Yanan Fu, Baode Sun?
J. Zhang:zj119@sjtu.edu.cn(上海交通大學)
B. Sun:bdsun@sjtu.edu.cn(上海交通大學)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116861
摘要
合金凝固過程的自然對流顯著影響液相中的傳熱傳質,從而影響晶粒的形核和長大。了解對流對鑄坯凝固過程的影響是控制鑄坯性能的關鍵。本研究中,我們采用同步輻射X射線技術對Al-15Cu(wt.%)在不同溫度梯度下的定向凝固過程進行了原位觀察。我們通過圖像處理技術可以得到了溶質在視場下的分布和固體的3D微觀結構,從而確定滲透率和瑞利數隨時間的變化。隨后,我們定量研究了溶體流動與組織間的相互作用。結果表明,溶質元素周期性地從熔融區排出,成分過冷的震蕩引起了晶粒的間歇性形核和周期性長大,進而引起了溶質滲透率和瑞利數的周期性振蕩。此外,在溶質流和對流作用的共同影響下,溶質濃度和形核數的振蕩幅度一般呈正弦變化。
ACTA
Vol. 212,15 Jun. 2021, 116921
2. Kinetics of cyclically-induced mechanical twinning in γ-TiAl unveiled by a combination of acoustic emission, neutron diffraction and electron microscopy
γ-TiAl中循環應變誘導孿晶動力學的聲射、中子衍射和電子顯微研究
A. Vinogradov?, M. Heczko, V. Mazánová, M. Linderov, T. Kruml
A. Vinogradov:alexei.vinogradov@ntnu.no
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116921
摘要
我們對主要為γ相的TiAl合金的循環響應和組織演變進行了實時研究。我們采用TEM和SEM - ECCI/EBSD對循環變形過程中位錯和機械孿晶的演化特征進行了定性描述。由于TEM只能提供局部和非原位信息,因此我們采用了原位中子衍射技術表征循環過程中的晶格應變分布。此外我們還測量了孿晶體積分數隨加載循環次數的變化規律。我們通過以下手段對每個變形循環中控制應變硬化的過程進行了分析:(i)磁滯回線形狀的統計分析, 從而表征與變形機制有關的應力分布,(ii) 原位聲學數據的統計分析,從而獲取變形機制的動力學信息。每種實驗方法在描述和解釋方面都自身的優點和局限性。多種手段的結合促進了對孿晶、位錯滑移等主要變形機制的全面了解。結果表明,在不同的加載周期內,這些機制間的相互作用可以全面地解釋TiAl合金的循環力學行為。這種相互作用決定了早期的疲勞損傷演化機制,并可能對室溫下γ -TiAl合金的整體疲勞響應有重要影響。
ACTA
Vol. 212,15 Jun. 2021, 116882
3. Measuring simulated hydrogen diffusion in symmetric tilt nickel grain boundaries and examining the relevance of the Borisov relationship for individual boundary diffusion
鎳對稱傾側晶界中的氫模擬擴散及其與Borisov模型的聯系
David E. Page, Kathryn F. Varela, Oliver K. Johnson, David T. Fullwood, Eric R. Homer?
E.R. Homer:eric.homer@byu.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116882
摘要
晶界是金屬中重要的擴散途徑。本文研究了氫在鎳中擴散時不同晶界類型的影響。我們模擬了26種[1 0 0]對稱傾斜晶界在幾種溫度下的變化,并提出了一種改進的均方位移法對晶界的擴散系數進行計算。我們分析了不同晶界的擴散率,晶界和體擴散速率隨溫度的變化有一交點。Borisov等人將晶界擴散速率與界面能進行了練習,我們對其模型進行了測試。盡管從未有研究采用Borisov關系研究溶質原子的間隙擴散,但當晶界擴散速率高于體擴散速率時,該關系式與模擬值吻合良好。由于晶界幾何形狀和激活狀態,Borisov關系中的一些參數難以測量而一直采用假設值。我們的模擬數據為這些參數提供了物理估計,結果表明其中的一些需要重新考慮。此外,這項工作還表明,雖然尚需進一步驗證,但Borisov關系可以合理地將氫的間隙擴散率與單個[1 0 0]對稱傾斜鎳晶界的界面能聯系起來。
ACTA
Vol. 212,15 Jun. 2021, 116811
4. Mechanisms of Ti3Al precipitation in hcp α-Ti
密排六方α-Ti中的Ti3Al析出機理
Felicity F. Dear, Paraskevas Kontis, Baptiste Gault, Jan Ilavsky, David Rugg, David Dye?
D. Dye:david.dye@imperial.ac.uk
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116811
摘要
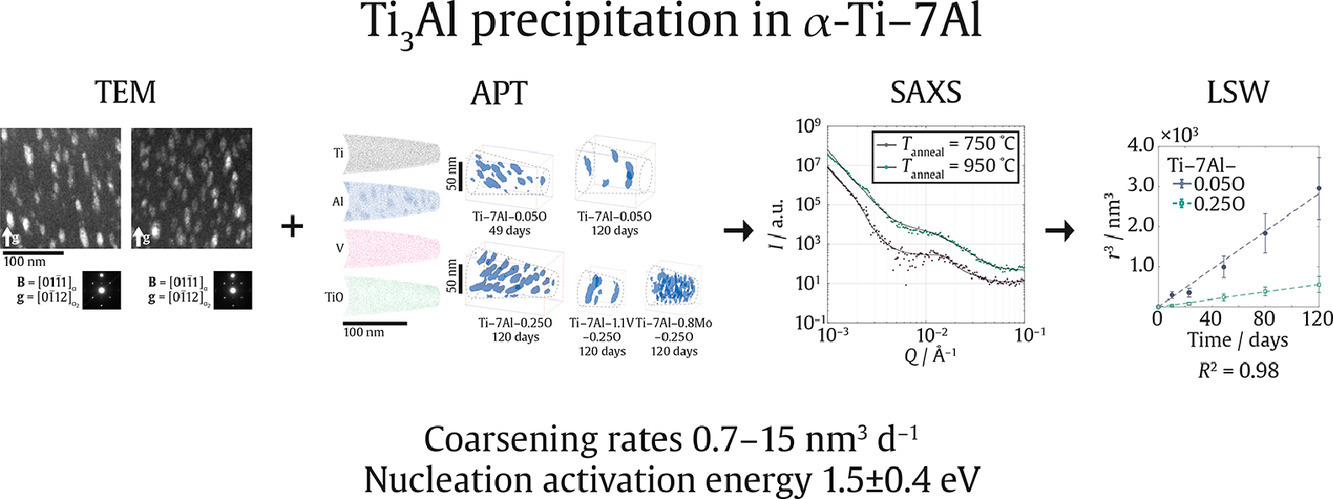
我們采用透射電鏡、原子探針和小角X射線散射相結合的方法對α-Ti-Al-X合金中Ti3Al α2有序疇的形核和長大進行了表征。我們將含有O、V或Mo的Ti-7Al (wt.%)模型合金在550℃時效最多120天,在中間時間點觀察析出相。結果表明,合金中的析出長大至約30nm,體積分數根據成分不同達到6-10%不等。間隙O原子增加了α2相的平衡體積分數,而V、Mo對α2平衡體積分數的影響較小。添加任何一種溶質元素都可以增加形核密度,減小析出相尺寸和粗化速率,但Mo的效果最顯著。粗化過程可以用LSW模型描述,這表明析出粗化主要由基體擴散控制,而非界面控制。固溶溫度對形核密度有影響,這一結果支持了空位濃度影響α2形核的假說。所有溶質均增加成核數密度,這也與空位控制形核機制相符。
ACTA
Vol. 212,15 Jun. 2021, 116851
5. Microstructure evolution under [110] creep in Ni-base superalloys
鎳基高溫合金[110]蠕變過程中的組織演變
M. Cottura?, B. Appolaire, A. Finel, Y. Le Bouar
M. Cottura:maeva.cottura@univ-lorraine.fr
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116851
摘要
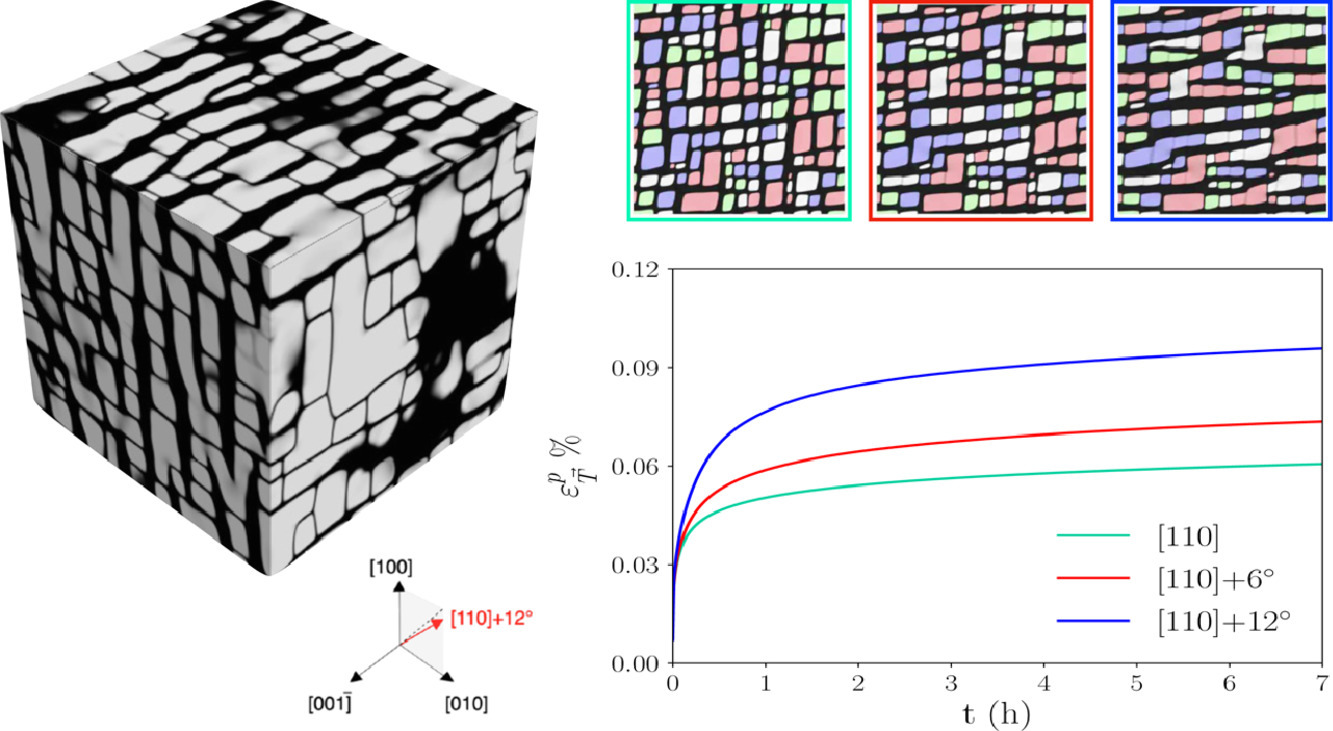
我們采用二維和三維相場模擬研究了[110]方向蠕變加載過程中Ni基高溫合金的微觀組織演變。我們將相場模型和基于位錯密度的晶體塑性模型進行了耦合。該模型中,每個滑移系統的位錯密度遵循存儲-恢復定律,并采用硬化矩陣來考慮位錯之間的短程相互作用。研究表明,拉伸軸的微小取向差對組織演化有顯著影響。完美對齊加載方向時,組織中形成棒狀析出,而有微小偏差時,則形成筏狀析出。機械載荷的精確方向不同,宏觀蠕變行為也不同,這解釋了實驗結果的偏差。我們研究了非均勻和各向異性的彈塑和塑性驅動力的相對作用,發現塑性是筏狀析出形成的主要驅動力。此外,我們的計算還表明,初始位錯密度對析出形貌影響較小,但對蠕變曲線影響顯著。
ACTA
Vol. 212,15 Jun. 2021, 116917
6. Modeling solid solution strengthening in high entropy alloys using machine learning
高熵合金固溶強化的機器學習研究
Cheng Wen, Changxin Wang, Yan Zhang, Stoichko Antonov, Dezhen Xue, Turab Lookman, Yanjing Su?
Y. Su:yjsu@ustb.edu.cn(北京科技大學)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116917
摘要
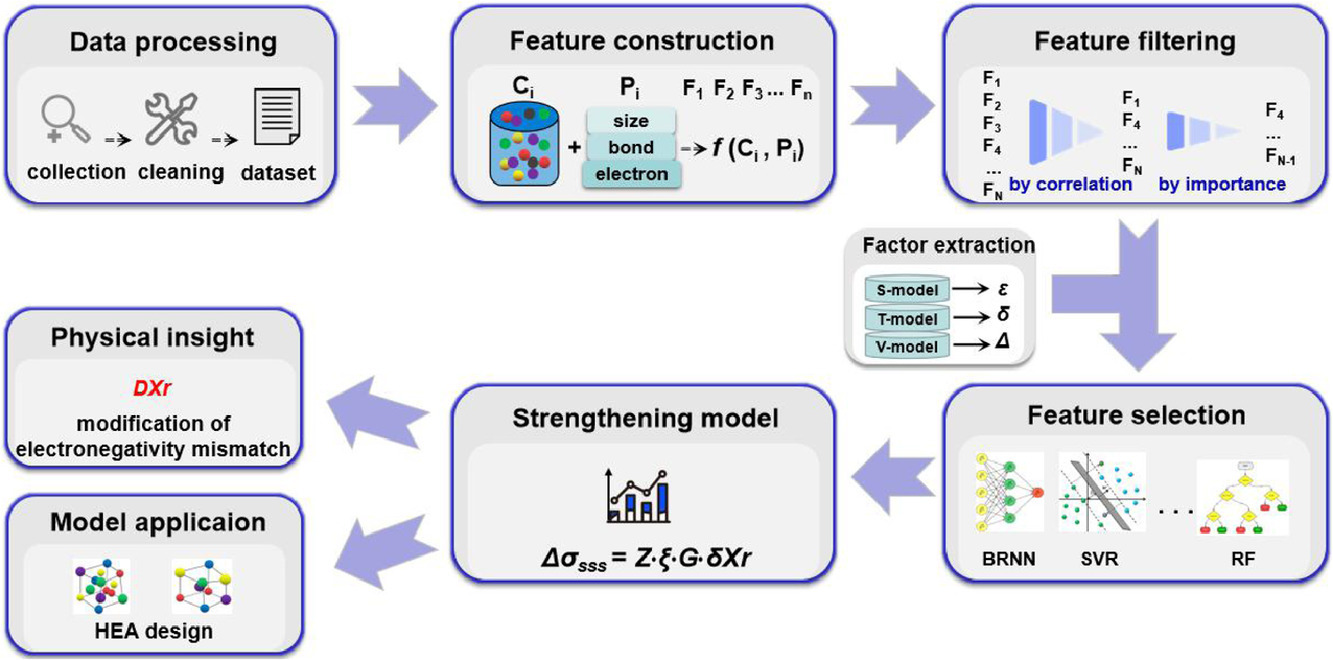
固溶強化對單相高熵合金(HEAs)的力學性能至關重要。而由于高熵合金的成分范圍極廣,因此通過識別控制固溶強化的潛在因素來加速高熵合金的設計是一項具有重大意義的工作。本研究中,我們通過機器學習方法,包括特征構建和特征選擇,證明了可以通過元素的電負性差導來表征高熵合金的固溶強化作用。與現有的物理模型相比,我們的模型在預測高熵合金的強度/硬度上表現出更加優越的性能。我們對模型在AlCoCrFeNi, CoCrFeNiMn, HfNbTaTiZr和MoNbTaWV這四種合金體系中的應用和預測進行了討論。
ACTA
Vol. 212,15 Jun. 2021, 116922
7. Precipitation in reactor pressure vessel steels under ion and neutron irradiation: On the role of segregated network dislocations
離子和中子輻照條件下反應堆壓力容器鋼鐵材料中析出、偏聚和位錯網狀的演化及相互作用
G.R. Odette?, N. Almirall, P.B. Wells, T. Yamamoto
G.R. Odette:odette@engineering.ucsb.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116922
摘要
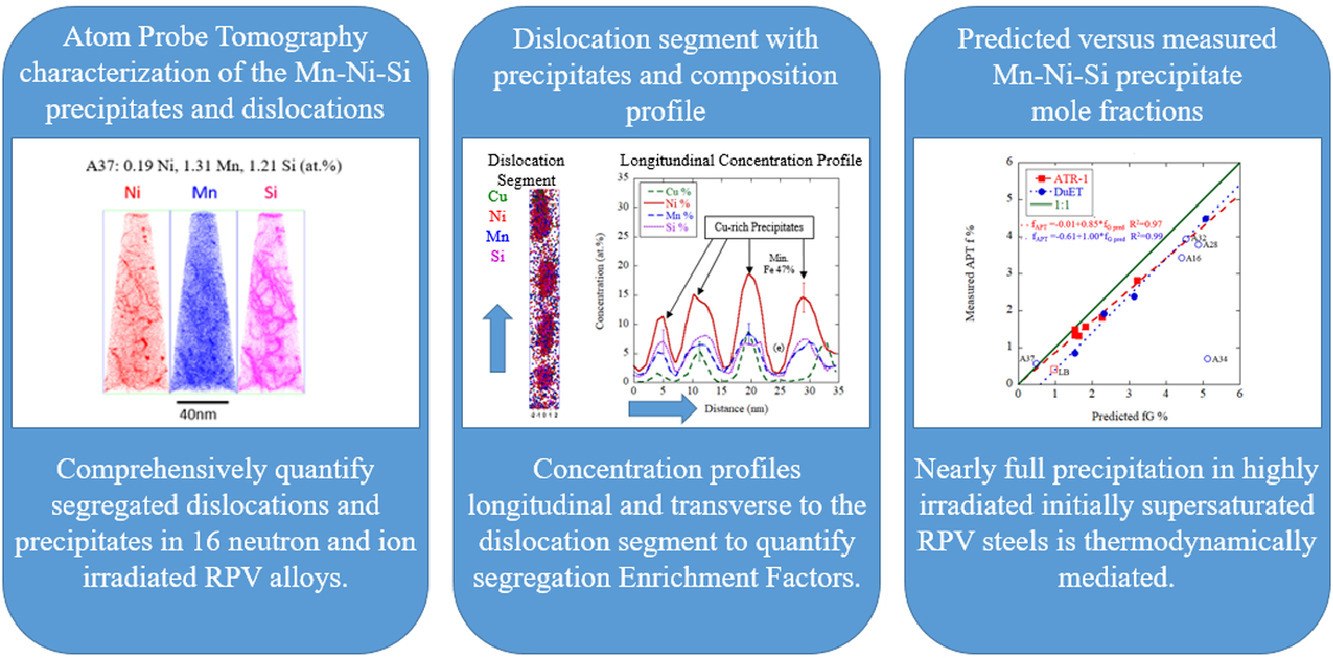
輻照后反應堆壓力容器(RPV)中的高密度Mn-Ni-Si-Cu析出會引起硬化和脆化,從而限制反應堆使用壽命。本研究中,我們對輻照后低合金RPV鋼中位錯網狀處的元素偏聚和析出進行了定量分析。分析主要基于熱力學框架,該框架能夠較好地描述輻照引起的非平衡擾動效應,如輻射誘導偏聚(RIS)。我們首次將Cu、Mn、Ni、Si的偏聚量化為了5 - 10nm的網狀位錯段,這些位錯段通常被MnNiSi析出相(MNSPs)隔開;在含銅鋼中,MNSPs常常附著形成富銅共析出(CRPs)。我們報道了16種RPV鋼的原子探針(APT)數據,這些鋼具有較寬的成分范圍,分別在320℃和290℃受到中子和6.4 MeV Fe3+輻照。這項研究的關鍵在于,非極高的損傷劑量和輻照導致的擴散增強,有助于區分熱力學平衡態和非平衡態效應導致。我們用一套完整的描述符來描述離子和中子輻照下的偏聚和析出,包括:a)位錯處的溶質富集因子(EFs)及其隨成分的變化; b)基體與位錯析出相的各自特征。這些位錯特征的形成可能是由于輻射誘導偏析,或熱力學因素,或兩者兼有。結合簡單的模型,我們發現低銅鋼中,偏聚促進了MNSP的形核。而在典型過飽和RPV鋼中,析出相的快速生長由熱力學驅動,直至達到可預測的平衡摩爾分數。
ACTA
Vol. 212,15 Jun. 2021, 116929
8. Revealing Nanoscale deformation mechanisms caused by shear-based material removal on individual grains of a Ni-based superalloy
鎳基高溫合金單一晶粒在剪切加工中的納米尺度變形機制研究
Dongdong Xu, Thomas E.J. Edwards, Zhirong Liao, Xavier Maeder, Rajaprakash Ramachandramoorthy, Manish Jain, Johann Michler, Dragos Axinte?
D. Axinte:Dragos.axinte@nottingham.ac.uk
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116929
摘要
剪切去除工藝對工件表面質量和工件性能有重要影響。我們通過原位掃描電子顯微鏡(SEM)對多晶鎳基高溫合金在切削過程中的晶體流變和晶格旋轉進行了研究。對單晶進行納米切削時,會出現一個變形納米層,它由只在切削平面內旋轉的晶格組成的;隨著晶粒剪切引起的納米切屑增加,變形納米層的深度增加。當切削多個晶粒時,大角度晶界處發生納米再結晶,并伴隨著沿切削方向的晶界(GB)彎曲,這一現象也顯著影響了晶粒的變形行為。在納米尺度闡明以上問題對于理解切削后工件表面的損傷形成至關重要。
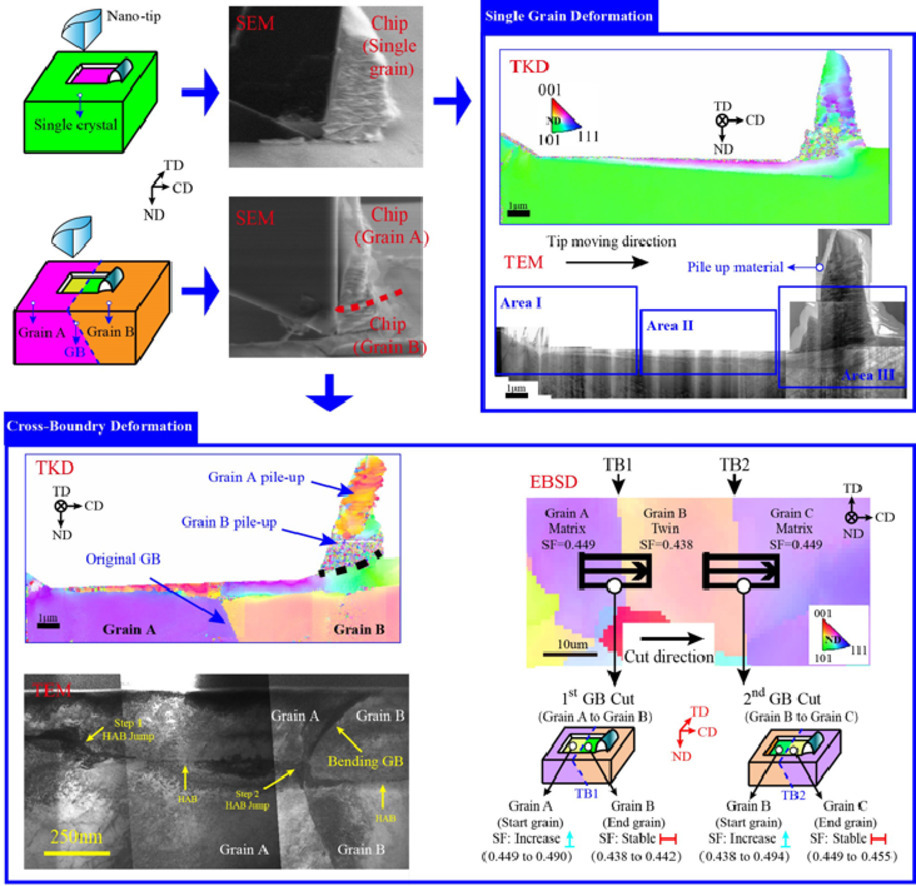
ACTA
Vol. 212,15 Jun. 2021, 116918
9. Strength, plasticity, thermal stability and strain rate sensitivity of nanograined nickel with amorphous ceramic grain boundaries
非晶陶瓷晶界強化鎳納米晶材料的強度、塑性、熱穩定性和應變率敏感性研究
Bingqiang Wei, Wenqian Wu, Dongyue Xie, Michael Nastasi, Jian Wang?
J. Wang:jianwang@unl.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116918
摘要
納米晶(NC)金屬材料中的大量晶界使得材料具有極高的強度。但納米晶高溫下的組織熱穩定性較低,導致強度顯著降低。因此,需要保持組織在高溫下的穩定。本研究中,我們通過75 at.%Ni和25 at.% SiOC共濺射,在晶粒尺寸13 nm的納米晶Ni中形成了1 ~ 2nm厚的非晶SiOC晶界,即制備得到了具有核殼結構的非晶陶瓷增強金屬(NiSiOC ACRMs)。我們對材料的原始態、400℃退火態和壓縮變形后的顯微組織進行了表征,證實核殼結構的熱穩定性。我們采用SEM下的原位微柱壓縮實驗測量了材料在室溫至400℃范圍內的機械性能,應力-應變響應和應變率敏感性。這一非晶陶瓷晶界增強材料具有極高的強度(室溫~2.5 GPa,400℃~1.6 GPa)、優異的塑性(均勻壓縮應變大于35%,無剪切失穩)和良好的熱穩定性。材料的應變速率敏感性高(室溫~0.015, 400℃~0.042),激活體積小(約13b3),且無明顯的應變硬化/軟化行為,這表明晶粒中存在位錯滑移。非晶陶瓷晶界能夠有效阻礙和捕獲位錯,強化材料,并促進Ni納米晶與非晶陶瓷晶界的塑性協同變形; 位錯沿非晶界面堆積,有效抑制了納米晶間局部剪切帶的形成。
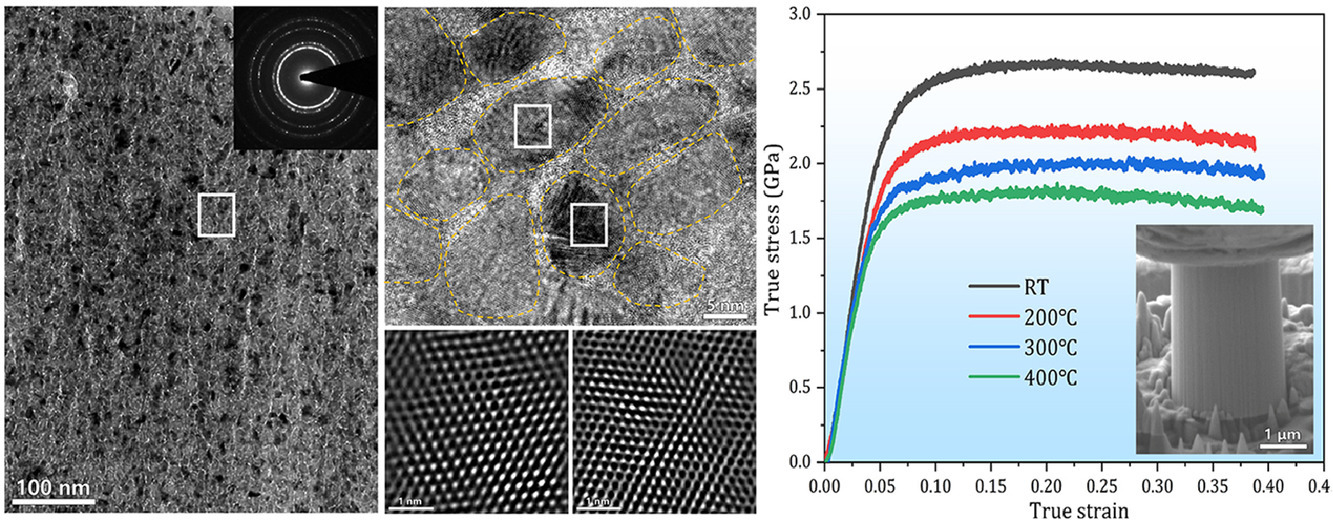
ACTA
Vol. 212,15 Jun. 2021, 116938
10. Tuning the degree of chemical ordering in the solid solution of a complex concentrated alloy and its impact on mechanical properties
多主元合金中的化學有序調控及其對力學性能的影響
S. Dasari, A. Jagetia, A. Sharma, M.S.K.K.Y. Nartu, V. Soni, B. Gwalani, S. Gorsse, R. Banerjee?
R. Banerjee:raj.banerjee@unt.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116938
摘要
我們基于二元混合焓,在Co-Cr-Fe-Ni體系中成功發現了一種高熵合金,即等原子比CoFeNi合金。隨后的實驗證實,該合金確實是一種接近理想狀態的面心立方(FCC)隨機固溶體。我們基于相同的熱力學分析,通過添加適量的Al和Ti,對隨機CoFeNi合金的化學有序狀態,包括短程有序和長程有序進行了設計,因為這些元素與Co、Fe、Ni有很強的有序傾向(負混合焓)。基于3d過渡族金屬之間的混合焓,我們設計了7種合金。研究表明,化學有序狀態對合金屈服強度有顯著影響,在相同的晶粒尺寸下,CoFeNi合金的屈服強度為~181 MPa, 而Al0.3Ti0.2Co0.7FeNi1.7合金的屈服強度為~793 MPa。實驗測得的候選高熵合金屈服強度與簡單強化模型的預測值基本一致。
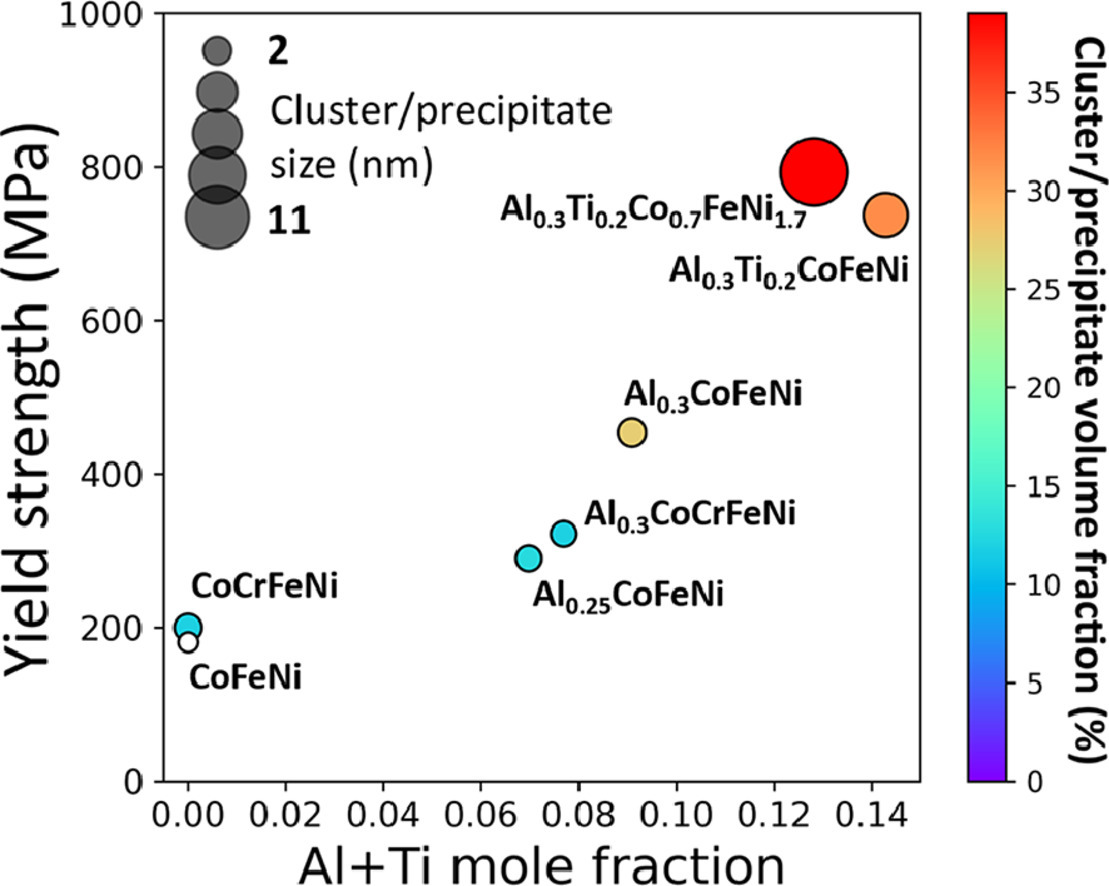
ACTA
Vol. 212,15 Jun. 2021, 116876
11. Unique crystallographic texture formation in Inconel 718 by laser powder bed fusion and its effect on mechanical anisotropy
激光粉末熔煉Inconel 718中的獨特織構及其對機械性能各向異性的影響
Ozkan Gokcekaya, Takuya Ishimoto, Shinya Hibino, Jumpei Yasutomi, Takayuki Narushima, Takayoshi Nakano?
T. Nakano:nakano@mat.eng.osaka-u.ac.jp
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116876
摘要
增材制造的工藝參數有很高的自由度,因此很夠很好地對各向異性組織進行調控。本研究中,我們用雙向激光掃描,制備了一種具有特殊織構的IN718合金,從而調控其力學性能。我們在IN718中實現了3中不同的織構:< 110 >方向平行于制備方向的類單晶組織SCM,具有特定取向的層狀組織CLM和弱織構的多晶組織。組織表征和有限元模擬表明,SCM和CLM的織構演變主要受熔池形狀和相應的熱流方向控制。與鑄態IN718相比,由于層間界面的作用,CLM試樣具有更好的力學性能。通過改變加載方向來調整應力傳遞系數和施密特系數,可以對CLM構件的強度-延性平衡進行調控。綜上所述,我們為提高結構材料的力學性能提出了一種有前景的新方法。
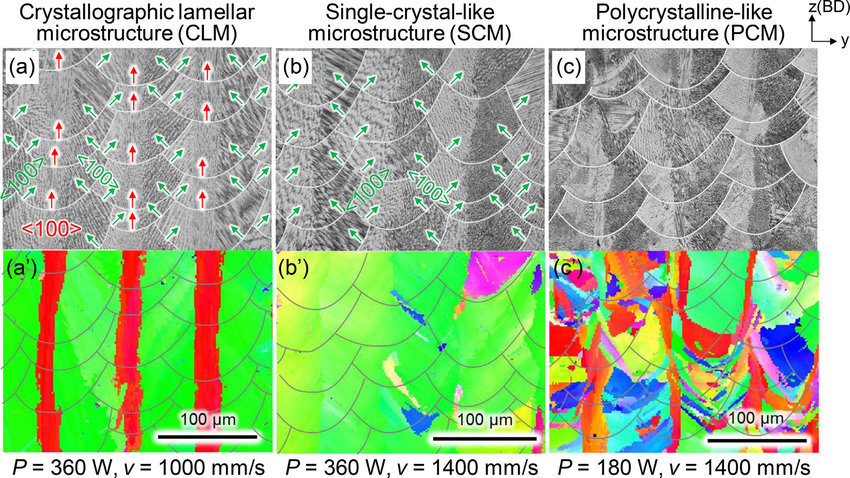
ACTA
Vol. 212,15 Jun. 2021, 116916
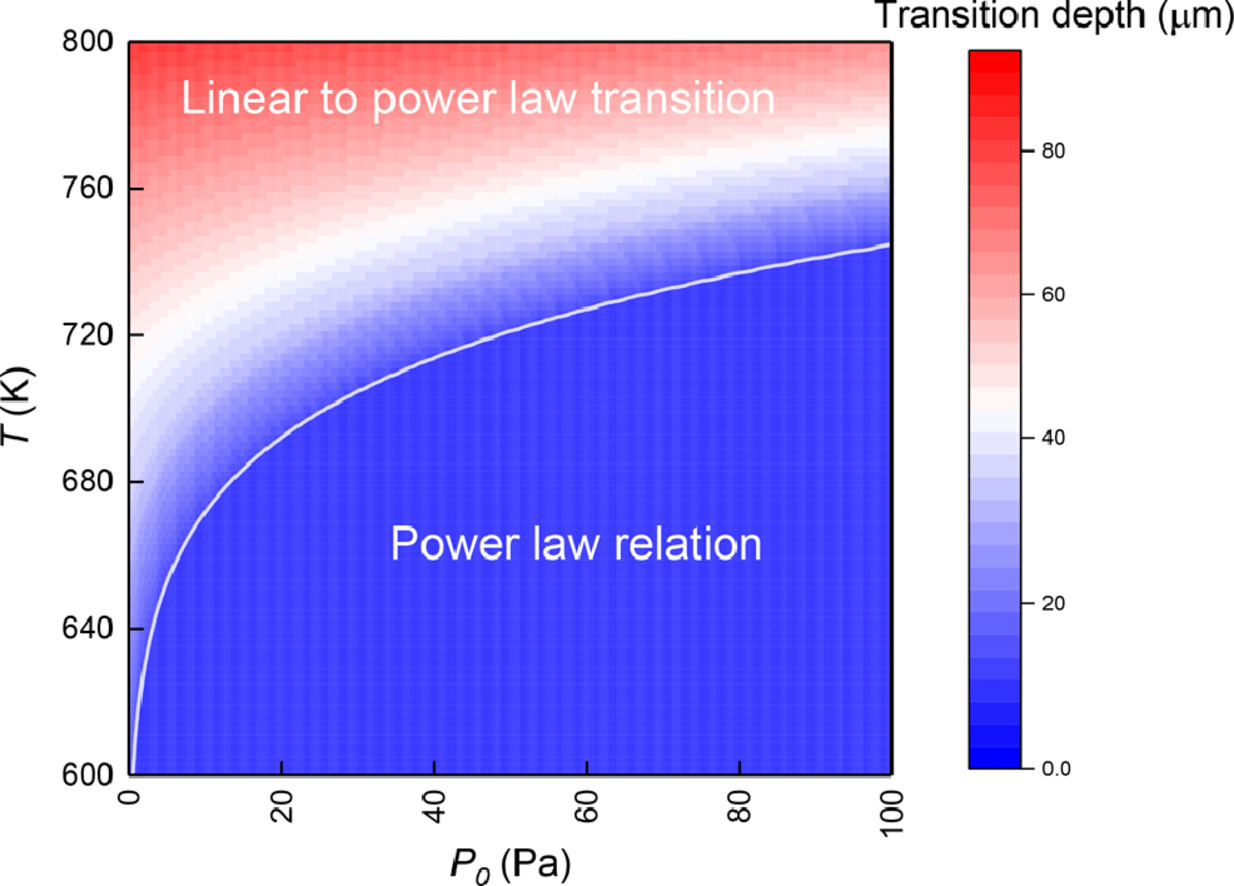
12. Vapor phase dealloying kinetics of MnZn alloys
MnZn合金的氣相脫合金動力學
Zhen Lu, Fan Zhang, Daixiu Wei, Jiuhui Han, Yanjie Xia, Jing Jiang, Mingwang Zhong, Akihiko Hirata, Kentaro Watanabe, Alain Karma?, Jonah Erlebacher?, Mingwei Chen?
A. Karma:alainkarma@gmail.com
J. Erlebacher:jonah.erlebacher@jhu.edu
M. Chen:mwchen@jhu.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116916
摘要
氣相脫合金化(VPD)是一種環保的納米多孔材料制備方法,它利用元素飽和蒸氣壓不同的特點選擇性對合金中一種或多種組分進行升華。目前關于復雜結構中固-氣相變速率控制因素和VPD動力學的研究較少。我們以Mn-Zn合金為例,系統研究了脫合金速度隨溫度和壓力的變化關系,并建立了定量的動力學模型。研究發現,由于動力學與微觀組織的相互作用,脫合金速度的變化規律在某一臨界深度將發生線性到冪律的轉變。這種轉變將早期蒸發過程和孔道中的Zn蒸氣擴散聯系了起來,而孔道中前沿的Zn分壓處于固氣平衡狀態。我們通過比較VPD和Zn升華的活化能,測定了整個VPD過程的能量分布。以上VPD動力學研究對VPD材料的設計和組織優化提供了有效指導。