金屬頂刊雙語導讀丨Scripta Mater. Vol.204, 1 Nov. 2021(上)
2021-08-08 來源:Goal Science
本期包含金屬材料領域論文9篇,涵蓋了高熵合金、高溫合金、形狀記憶合金等,國內科研單位包括吉林大學、西安交通大學、西北工業大學、北京科技大學等(通訊作者單位)。
Vol. 204 目錄
1. Enhanced ductility and strength of Mg-1Zn-1Sn-0.3Y-0.2Ca alloy achieved by novel micro-texture design
新型微織構設計提高Mg-1Zn-1Sn-0.3Y-0.2Ca合金的延展性和強度
2. A novel bulk eutectic high-entropy alloy with outstanding as-cast specific yield strengths at elevated temperatures
在高溫下具有出色的鑄態比屈服強度的新型塊狀共晶高熵合金
3. The environmental degradation behavior of FeNiMnCr high entropy alloy in high temperature hydrogenated water
FeNiMnCr高熵合金在高溫氫化水中的環境降解行為
4. Role of in-situ splat sintering on elastic and damping behavior of cold sprayed aluminum coatings
原位飛濺燒結對冷噴涂鋁涂層彈性和阻尼行為的影響
5. Hierarchical phase evolution in a lamellar Al0.7CoCrFeNi high entropy alloy involving competing metastable and stable phases
層狀Al0.7CoCrFeNi高熵合金中包含競爭亞穩相和穩定相的分層相演化
6. Unveiling the Re segregation at γ/γ′ interface in Ni-based superalloy
揭示Re在鎳基高溫合金γ/γ′界面的偏析
7. Anomalous stress-strain behavior of NiTi shape memory alloy close to the border of superelastic window
NiTi形狀記憶合金超彈窗邊界附近的異常應力應變行為
8. High-throughput approach for estimation of intrinsic barriers in FCC structures for alloy design
用于合金設計的FCC結構內勢壘估計的高通量方法
9. Achieving excellent superelasticity and extraordinary elastocaloric effect in a directionally solidified Co-V-Ga alloy
在定向凝固的Co-V-Ga合金中實現出色的超彈性和非凡的彈性熱效應
SCRIPTA
Vol. 204, 1 Nov. 2021, 114119
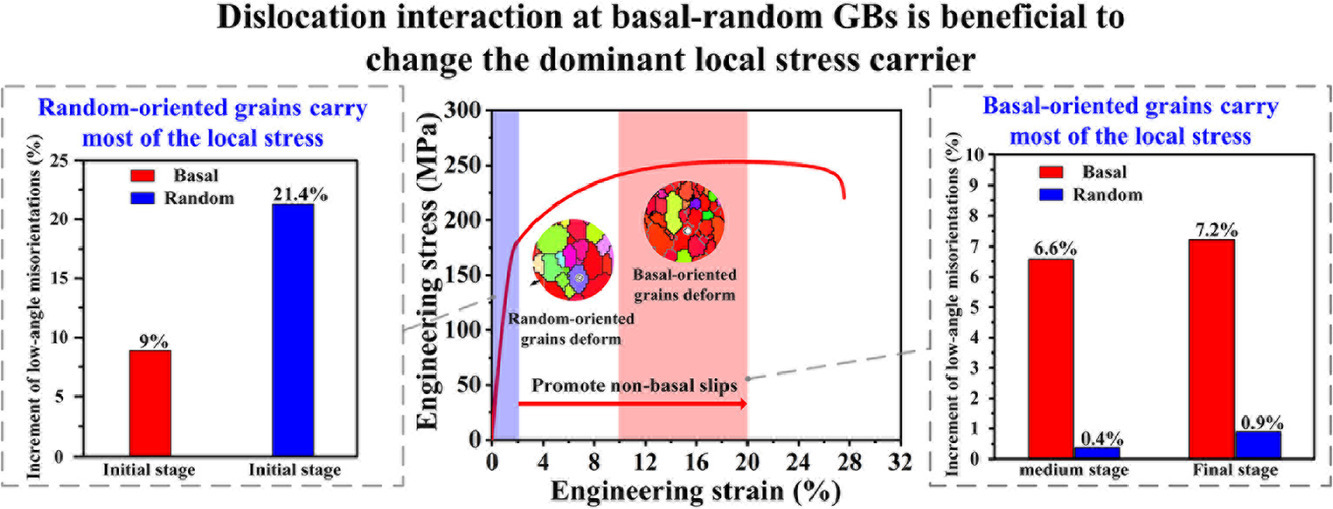
1. Enhanced ductility and strength of Mg-1Zn-1Sn-0.3Y-0.2Ca alloy achieved by novel micro-texture design
新型微織構設計提高Mg-1Zn-1Sn-0.3Y-0.2Ca合金的延展性和強度
Cheng Wang, Hong Ning, Shi Liu, Jiang You, Tong Wang, Hong-Jie Jia, Min Zha, Hui-Yuan
Wang?
Hui-Yuan Wang: wanghuiyuan@jlu.edu.cn 吉林大學
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114119
摘要
織構弱化是提高鎂合金延展性的主要方法之一。在這項工作中,我們通過精確控制的高壓下軋制,設計并制造了具有新型基底隨機異質(BRH)織構的Mg-1Zn-1Sn-0.3Y-0.2Ca (wt. % ZTWX1100)合金,該合金均勻分布著基底和隨機取向晶粒。與基底織構樣品相比,BRH織構同時提高了延展性和抗拉強度,這是由于基底取向晶粒內非基底滑移的作用以及基底隨機晶界貢獻的強加工硬化能力。此外,BRH織構中的基底-隨機晶界通過將局部應力的主要載體從原始隨機取向晶粒轉變為基底取向晶粒,有利于提高變形相容性。這項工作旨在為通過織構協調變形改善鎂合金的力學性能提供新的思路。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 204, 1 Nov. 2021, 114132
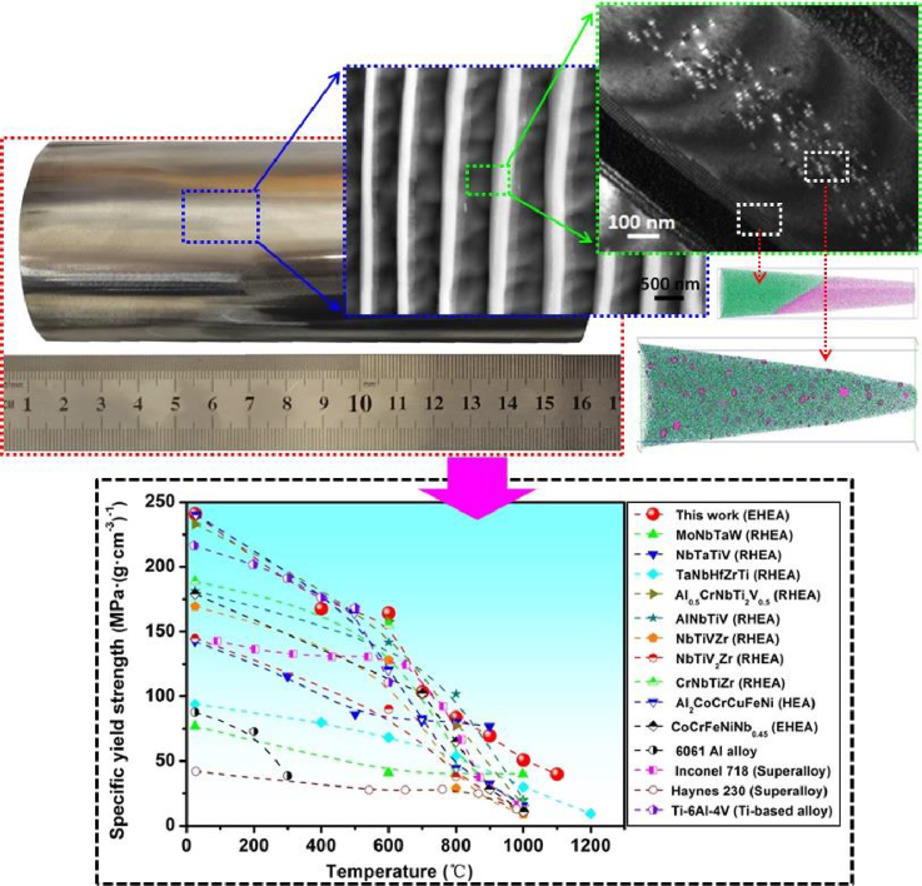
2. A novel bulk eutectic high-entropy alloy with outstanding as-cast specific yield strengths at elevated temperatures
在高溫下具有出色的鑄態比屈服強度的新型塊狀共晶高熵合金
Mingliang Wang, Yiping Lu?, Tongmin Wang, Chuan Zhang, Zhiqiang Cao, Tingju Li,
Peter K. Liaw
Yiping Lu: luyiping@dlut.edu.cn 大連理工大學
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114132
摘要
由于其優異的性能和巨大的工業應用潛力,共晶高熵合金(EHEAs)在過去幾年中一直是研究熱點。本研究報告了一種新型AlCr1.3TiNi2 EHEA,具有低的密度和優異的高溫機械性能。首先通過直接凝固法制備了具有均勻超細L21和BCC層狀結構(層間距~ 400 nm)的千克級EHEA錠。與大多數報道的難熔高熵合金(RHEA)、EHEA和傳統的鎳基和鈦基合金相比,鑄態AlCr1.3TiNi2 EHEA表現出更高的室溫和高溫硬度和比屈服強度值。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 204, 1 Nov. 2021, 114127
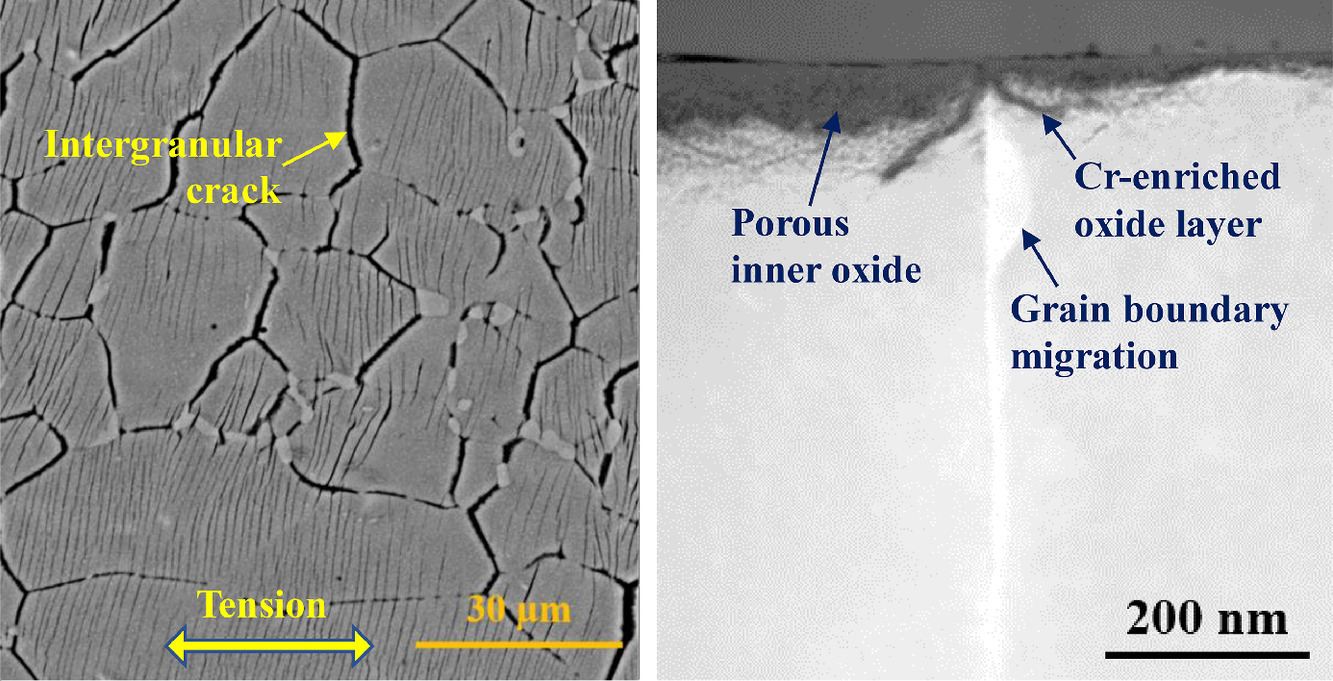
3. The environmental degradation behavior of FeNiMnCr high entropy alloy in high temperature hydrogenated water
FeNiMnCr高熵合金在高溫氫化水中的環境降解行為
Jiuyang Dong, Xingyu Feng, Xianchao Hao, Wenjun Kuang?
Wenjun Kuang: wjkuang66@gmail.com 西安交通大學
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114127
摘要
無鈷高熵合金(HEA)28%Fe-27%Ni-27%Mn-18%Cr具有良好的抗輻照性能,可作為核電工業潛在的候選材料。這項工作研究了該HEA在高溫氫化水中的環境降解行為。該HEA在恒定拉伸速率拉伸試驗后出現廣泛的晶間裂紋,表明它非常容易引發應力腐蝕開裂 (SCC)。微觀結構分析表明,Mn和Cr在氧化過程中沿晶界向外擴散,導致晶界遷移。Cr助熔劑促進在晶界上方形成富含Cr的氧化層,從而在樣品無應力時防止晶間氧化。然而,Mn在氧化物中不穩定并傾向于溶解到溶液中,使氧化物多孔。當受到壓力時,多孔氧化物很容易破裂,從而引發SCC。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 204, 1 Nov. 2021, 114125
4. Role of in-situ splat sintering on elastic and damping behavior of cold sprayed aluminum coatings
原位飛濺燒結對冷噴涂鋁涂層彈性和阻尼行為的影響
Tanaji Paul, Pranjal Nautiyal, Cheng Zhang, Benjamin Boesl, Arvind Agarwal?
Arvind Agarwal: agarwala@fiu.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114125
摘要
冷噴涂6061鋁涂層的動態彈性行為被研究,以了解從環境溫度到400°C的原位飛濺燒結對空氣和氦氣噴涂涂層的內在作用。噴涂狀態下,空氣噴涂涂層具有更高的表面能和更低的扁平率,使得濺射燒結過程中致密率達28%,而熱處理氦氣噴涂的致密率僅為15%。彈性模量和阻尼行為可以根據燒結和漸進式板間結構分為三個不同的溫度范圍。本工作建立了理論分析,表明歸一化彈性模量是板間孔隙度的指數函數。該研究確定了在高溫下,板間熱現象與涂層動態機械性能之間的相關性。
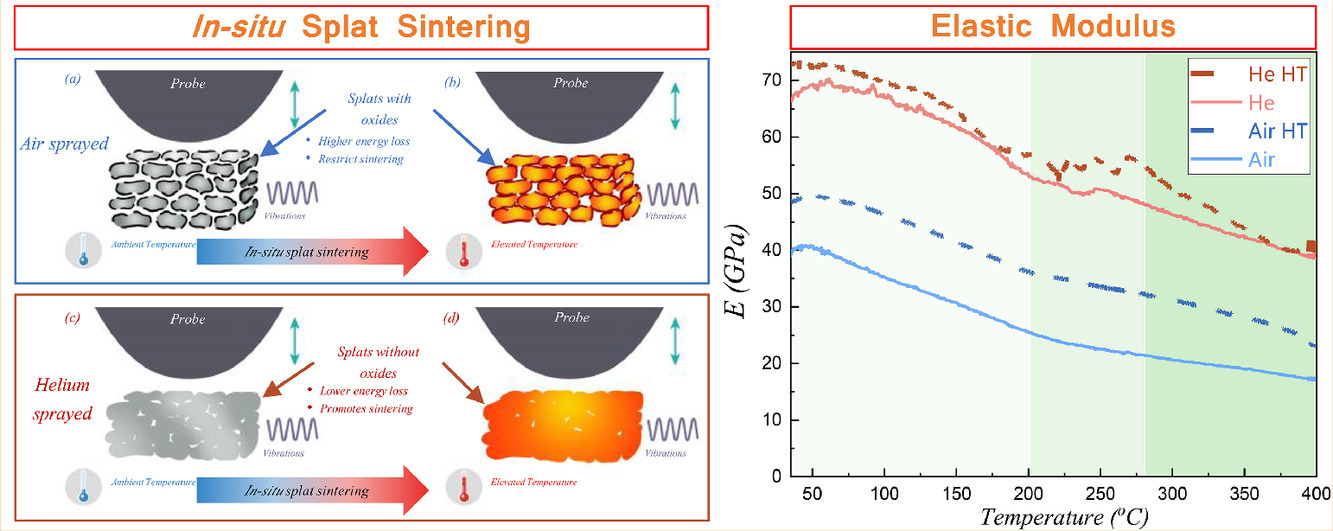
SCRIPTA
Vol. 204, 1 Nov. 2021, 114137
5. Hierarchical phase evolution in a lamellar Al0.7CoCrFeNi high entropy alloy involving competing metastable and stable phases
層狀Al0.7CoCrFeNi高熵合金中包含競爭亞穩相和穩定相的分層相演化
K. Srimark, S. Dasari, A. Sharma, P. Wangyao, B. Gwalani, T. Rojhirunsakool, S. Gorsse, R.
Banerjee?
R. Banerjee: raj.banerjee@unt.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114137
摘要
在溶液熱力學模型和詳細的實驗表征的指導下,本研究確定了Al0.7CoCrFeNi高熵合金中交替的FCC和BCC層狀微觀結構是,從液相到單B2相的非平衡無分配凝固并接著通過固態分解的結果。 Widmanstätten FCC片晶是由B2晶界處的同素異形FCC沉淀形成,最終導致了含兩個不同的子系統的層狀微觀結構。等溫退火通過使有序金屬間相沉淀,進一步推動了這些單獨的子系統達到平衡。FCC片晶的轉變開始于在較短的退火時間內形成的亞穩定L12沉淀物,最終被平衡的BCC和B2相取代,在長期退火時形成復合B2+BCC板條。這些結果進一步說明了,有趣的轉變途徑導致HEAs內的分層狀微觀結構,以及這些合金的加工條件通常遠離平衡。
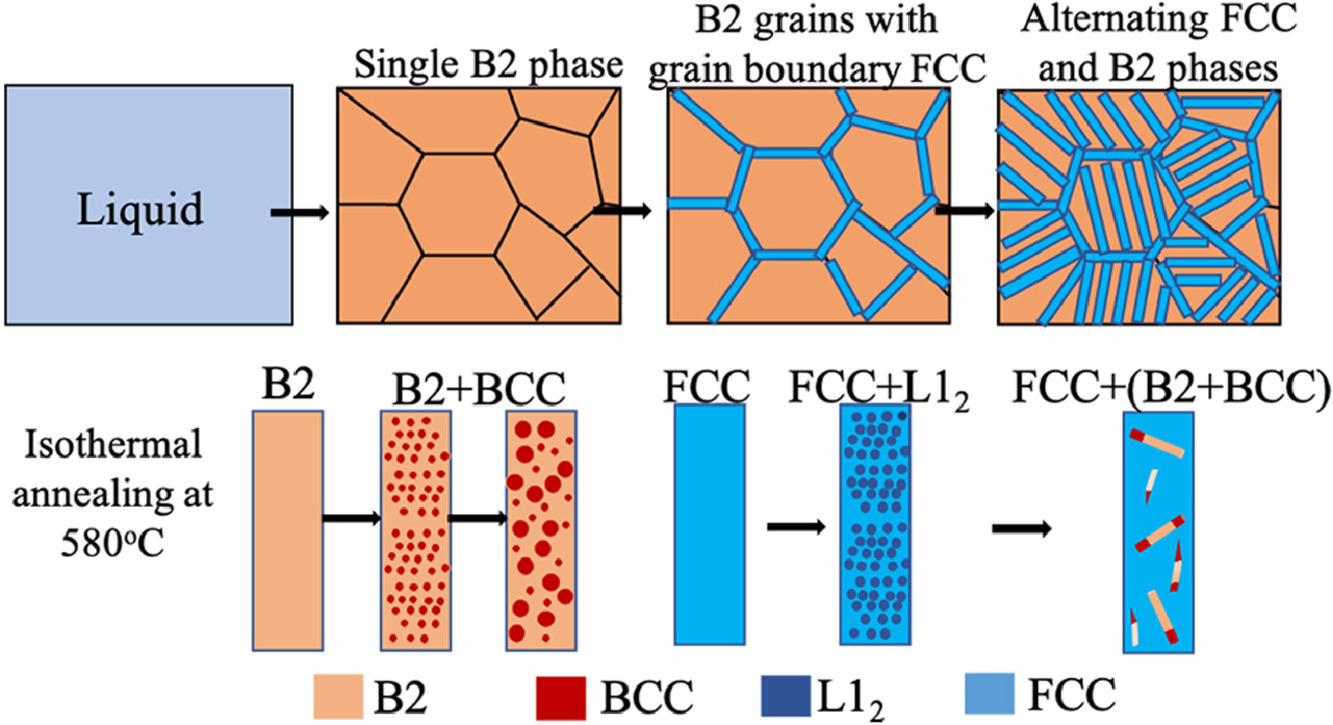
SCRIPTA
Vol. 204, 1 Nov. 2021, 114131
6. Unveiling the Re segregation at γ/γ′ interface in Ni-based superalloy
揭示Re在鎳基高溫合金γ/γ′界面的偏析
Jiachen Zhang, Taiwen Huang?, Fan Lu, Kaili Cao, Dong Wang, Jian Zhang, Jun Zhang,
Haijun Su, Lin Liu?
Taiwen Huang: taiwen_h@nwpu.edu.cn 西北工業大學
Lin Liu: linliu@nwpu.edu.cn 西北工業大學
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114131
摘要
通過原子探針斷層掃描不同熱處理后的鎳基單晶高溫合金確定Re的分布。在較高溫度(950-1100℃)下,γ基體中的Re擴散率小于為γ?生長的實際有效擴散率,這導致Re在隨后的冷卻和界面遷移過程中不夠擴散并保持積累,并在γ/γ?界面形成偏析。而在低溫(800-900℃)下,Re擴散能夠平衡γ?生長的有效擴散。通過對不同Re含量和不同時效溫度的合金進行研究,發現Re的偏析與Re含量無關,但高度依賴于溫度。這些結果為理解Re對Ni基高溫合金中γ?生長的影響提供了新的視角,對于提高γ/γ?共晶穩定性和設計高性能高溫合金具有重要價值。
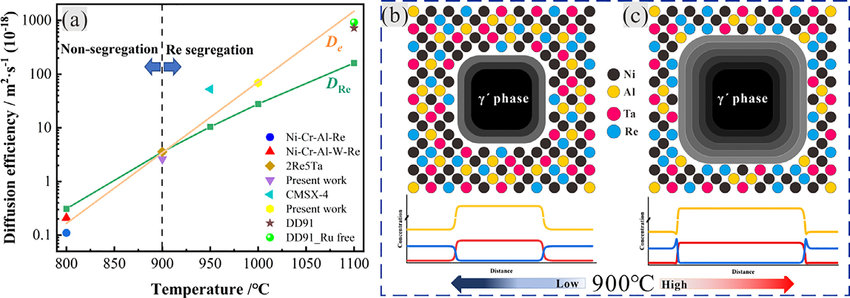
SCRIPTA
Vol. 204, 1 Nov. 2021, 114135
7. Anomalous stress-strain behavior of NiTi shape memory alloy close to the border of superelastic window
NiTi形狀記憶合金超彈窗邊界附近的異常應力應變行為
Xiebin Wang?, Xiayang Yao, Dominique Schryvers, Bert Verliden, Guilong Wang, Guoqun
Zhao, Jan Van Humbeeck, Sergey Kustov
Xiebin Wang: wangxiebin@sdu.edu.cn 山東大學
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114135
摘要
這項工作報告了NiTi形狀記憶合金在接近超彈性窗口邊界溫度下變形時的超彈性循環異常現象,發現了新的意想不到的效果——(i)在第二次加載循環期間誘導馬氏體轉變的臨界應力高于第一次循環;(ii)當應變超過第一個循環的極限時,第二個循環的平臺應力會下降到原來的水平;(iii)從第一個循環中良好的超彈性過渡到第二個循環中的完全不可逆應變。 我們提出在靠近超彈性窗口邊界的第一個超彈性循環期間產生的缺陷阻礙了應力誘導的馬氏體轉變,導致臨界應力增加并超過B2基體的屈服應力,從而導致NiTi合金的功能疲勞。
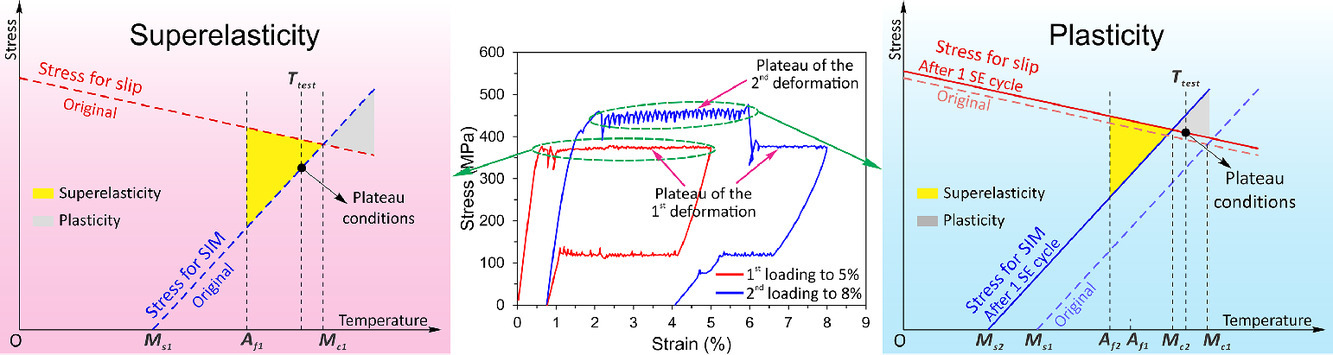
SCRIPTA
Vol. 204, 1 Nov. 2021, 114126
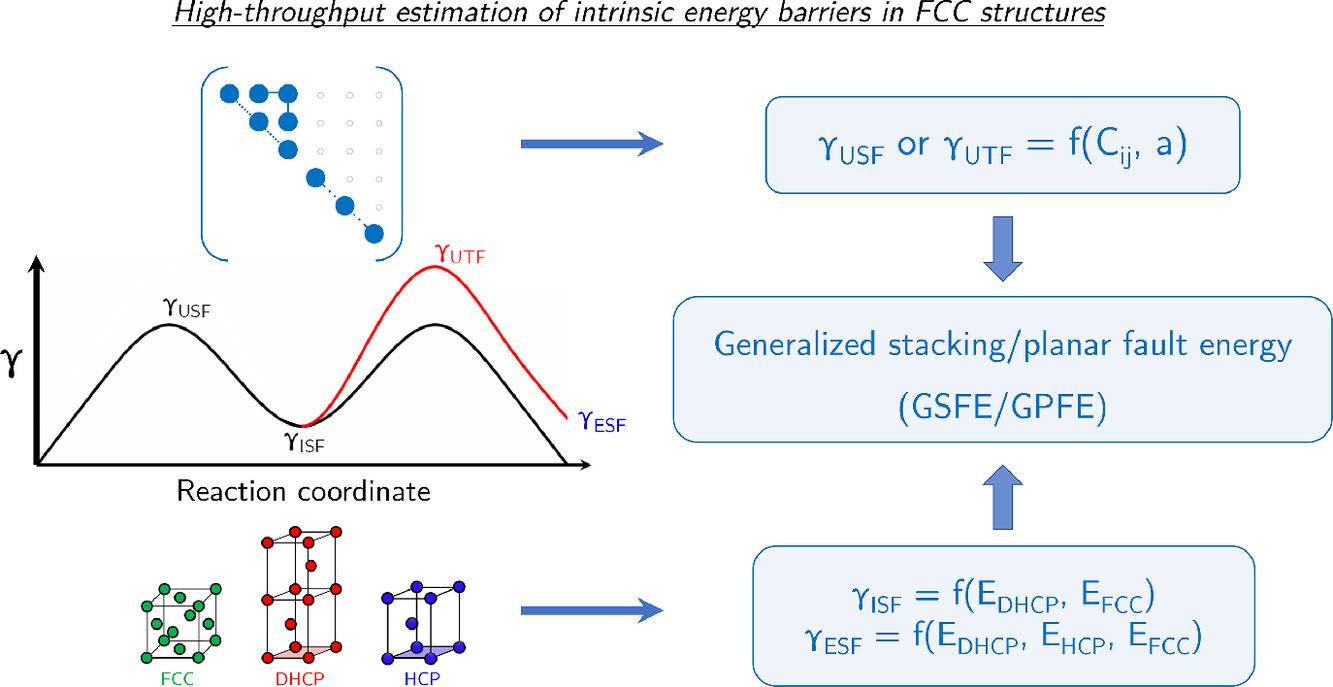
8. High-throughput approach for estimation of intrinsic barriers in FCC structures for alloy design
用于合金設計的FCC結構內勢壘估計的高通量方法
K.V. Vamsi?, M.A. Charpagne, T.M. Pollock
K.V. Vamsi: kvvamsi@ucsb.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114126
摘要
廣義堆積/平面斷層能(GSFE/GPFE)曲線為FCC結構中的塑性變形提供了內在能壘 (IEB)。 在這項研究中,我們提出了一種估計這些IEB的新方法。對于大量純FCC金屬,顯示出{111}平面上的不穩定斷層能和剪切模量之間的強相關性。有趣的是,文獻中的數據對于各種FCC固溶體也遵循這種相關性。對于純FCC金屬和FCC (Ni0.5Co0.5)1-xRux (x=0-0.5),展示了將這些相關性與穩定故障能量的多層擴散故障模型相結合的IEB的高通量估算。此外,還估算了合金設計的其他重要參數,包括滑移和孿晶的臨界應力。這種新方法為基于孿生和變形路徑傾向的多主元素合金(MPEA)的高通量設計開辟了道路。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 204, 1 Nov. 2021, 114123
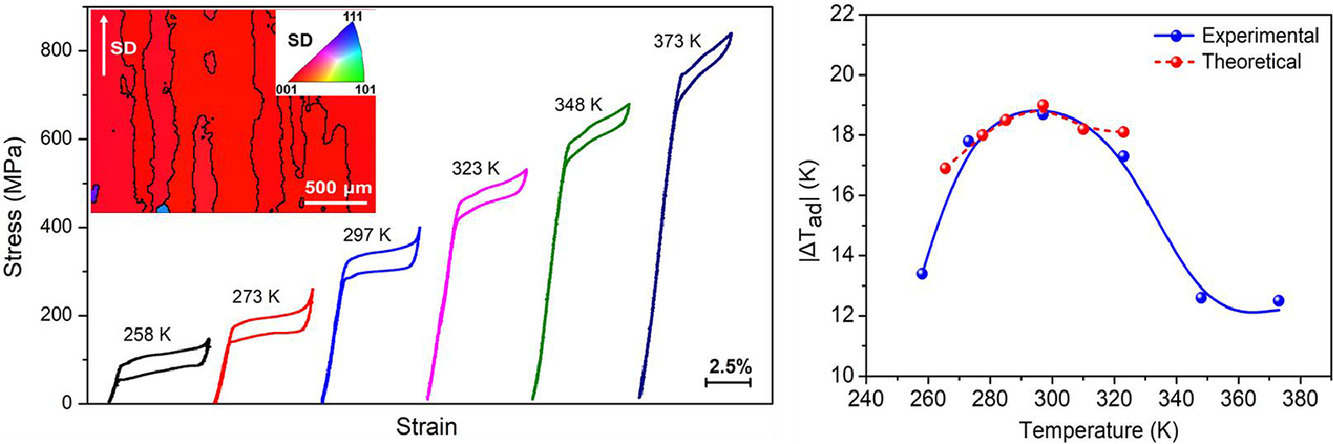
9. Achieving excellent superelasticity and extraordinary elastocaloric effect in a directionally solidified Co-V-Ga alloy
在定向凝固的Co-V-Ga合金中實現出色的超彈性和非凡的彈性熱效應
Yurong Niu, Haiyang Chen?, Xiangyu Zhang, Shengwei Li, Daoyong Cong, Tianyu Ma,
Shilei Li, Junping Lin, Yan-Dong Wang?
Haiyang Chen: haiyang_chen123@163.com 北京科技大學
Yan-Dong Wang: ydwang@ustb.edu.cn 北京科技大學
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114123
摘要
定向凝固的Co50.7V33.3Ga16合金中展示了出色的超彈性和巨大的彈性熱效應。由于形成了[001]A擇優取向的柱狀晶粒,凝固合金顯示出近乎完美的超彈性行為:完全可逆的壓縮應變高達5.4%,窄應力滯后約為40 MPa以及258-373 K的寬溫度范圍。同時,通過在室溫下去除400 MPa的單軸應力,獲得了-18.7 K的絕熱溫度變化(ΔTad),這與基于Maxwell關系式(-19.0 K)和量熱法的理論值非常吻合。在至少115 K的寬溫度范圍獲得了一個大于12.5 K的|ΔTad|。此外,超彈性和彈性熱效應均保持良好的功能穩定性,并在100次循環中沒有任何明顯的消退。