金屬頂刊雙語導讀丨Acta Mater. Vol.213,1 Jul. 2021(上)
2021-08-08 來源:Goal Science
本期包含金屬材料領域論文11篇,涵蓋了馬氏體、不銹鋼、中熵合金等,國內科研單位包括北京計算科學研究中心、沈陽金屬所、北京航空航天大學、東北大學等(通訊作者單位)。
Vol. 213 目錄
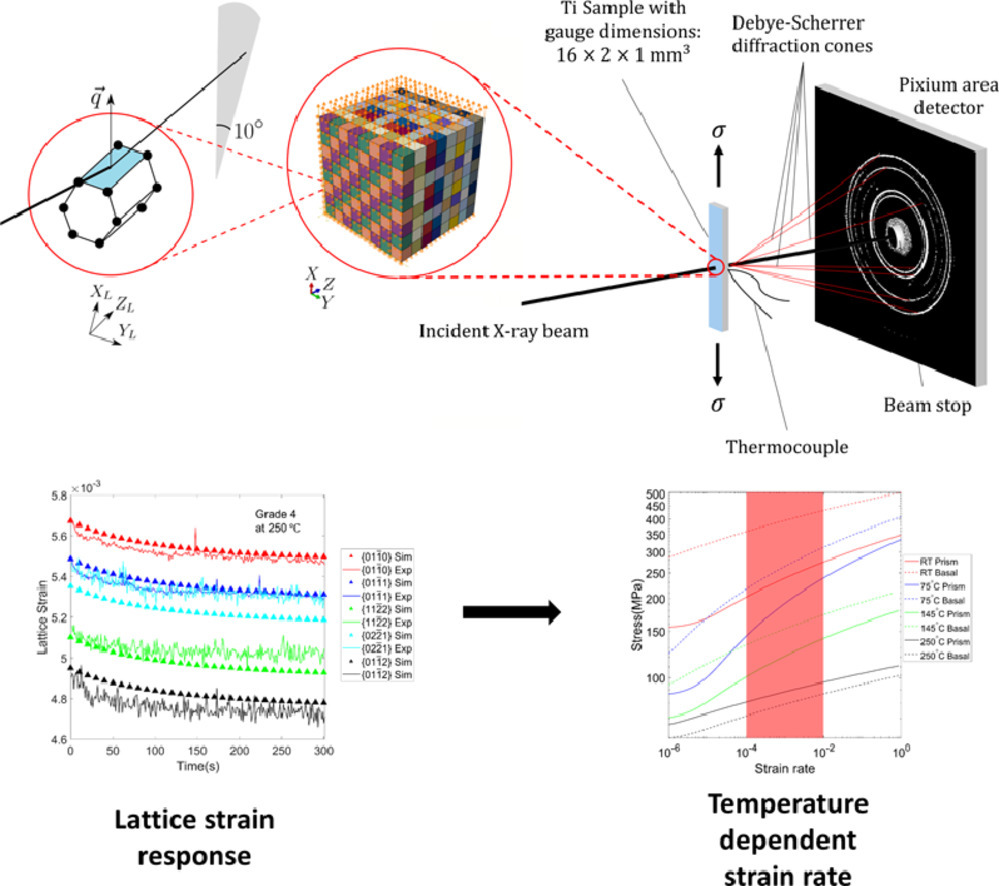
1. An in-situ synchrotron diffraction study of stress relaxation in titanium: Effect of temperature and oxygen on cold dwell fatigue
溫度和氧含量對鈦中應力松弛影響的原位同步衍射研究
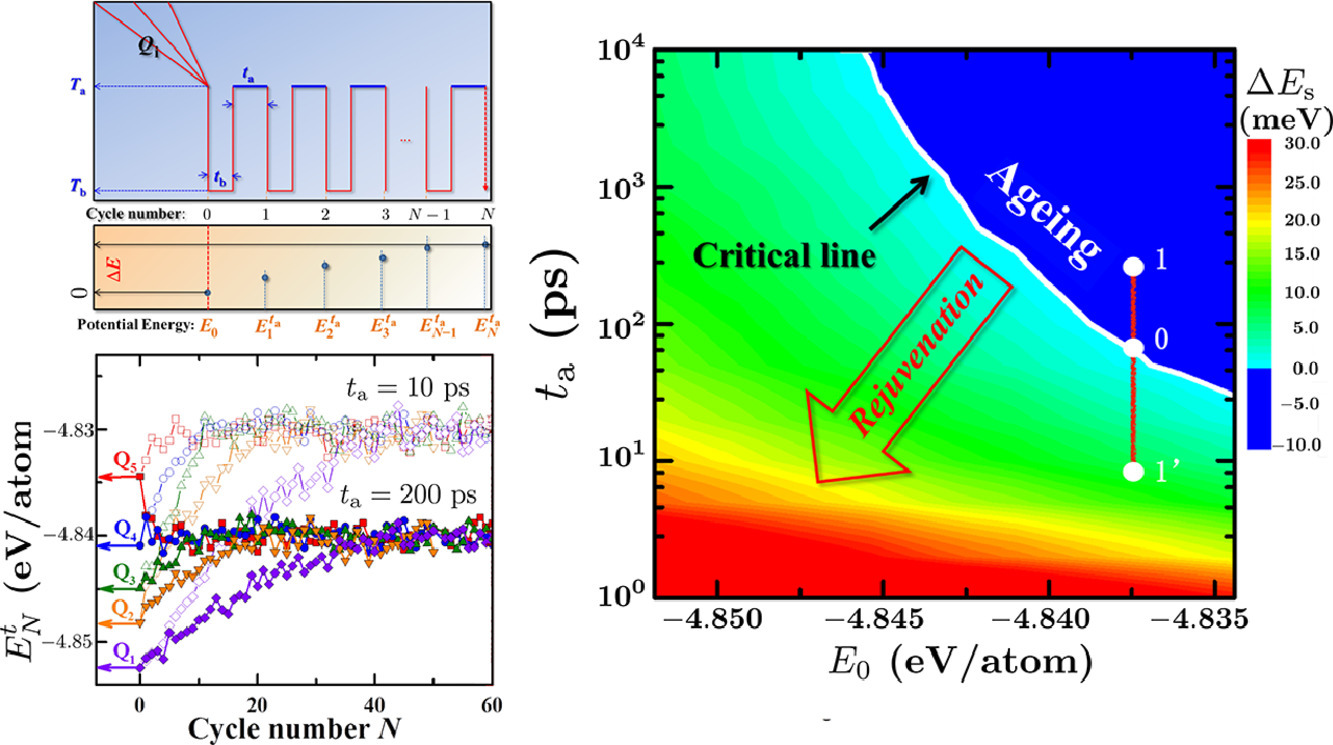
2. Atomistic modelling of thermal-cycling rejuvenation in metallic glasses
金屬玻璃熱循環恢復的原子尺度模型
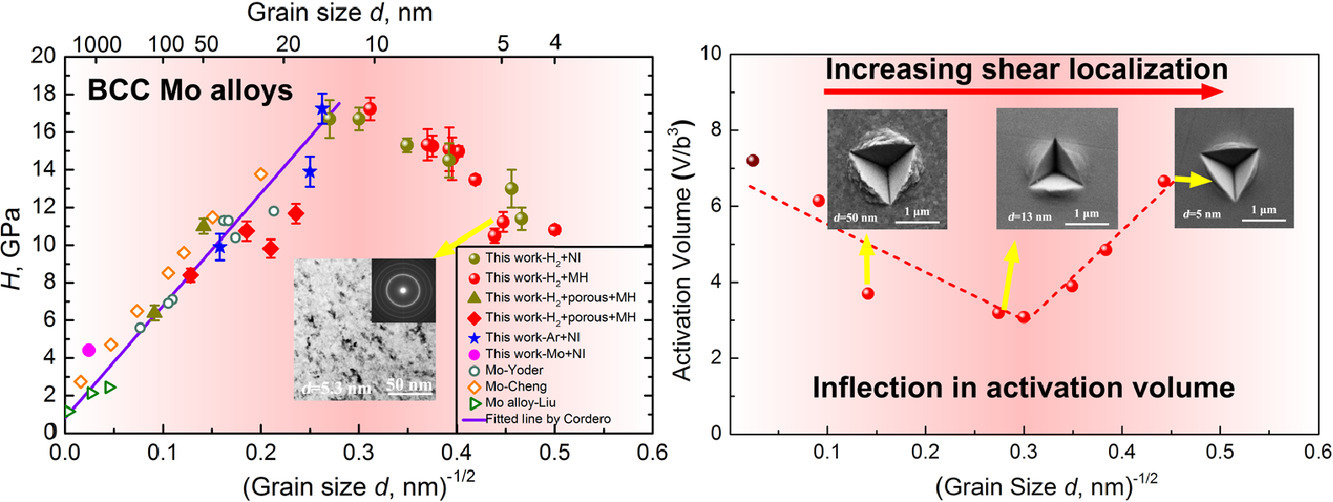
3. Breakdown of the Hall-Petch relationship in extremely fine nanograined body-centered cubic Mo alloys
納米晶體心立方Mo合金中Hall-Petch關系的失效原因
4. Coarsening of martensite with multiple generations of twins in laser additively manufactured Ti6Al4V
激光增材制造Ti6Al4V中的孿晶馬氏體粗化
5. Dislocation electron tomography: A technique to characterize the dislocation microstructure evolution in zirconium alloys under irradiation
輻照態鋯合金中位錯微觀結構演化的表征
6. Giant heterogeneous magnetostriction induced by charge accumulation-mediated nanoinclusion formation in dual-phase nanostructured systems
雙相納米結構體系中納米夾雜引起的顯著非均勻磁致伸縮效應
7. Influence of internal hydrogen content on the evolved microstructure beneath fatigue striations in 316L austenitic stainless steel
氫含量對316L奧氏體不銹鋼疲勞組織演化的影響
8. In situ studies of liquid-liquid phase separation, solidification sequence and dendrite growth kinetics in electrostatically levitated Ti–Y alloys
靜電懸浮Ti-Y合金中液相分離、凝固順序和枝晶生長的動力學原位研究
9. Interaction between nucleant particles and a solid-liquid interface in Al-4.5Cu alloy
Al-4.5Cu合金中形核粒子與固液界面的相互作用研究
10. Mechanical properties and deformation mechanisms of a Ni2Co1Fe1V0.5Mo0.2 medium-entropy alloy at elevated temperatures
Ni2Co1Fe1V0.5Mo0.2中熵合金的高溫力學性能及變形機制研究
11. Mesoscale hetero-deformation induced (HDI) stress in FeAl-based metallic-intermetallic laminate (MIL) composites
FeAl基金屬間化合物層狀復合材料的介觀尺度不均勻變形誘導應力研究
ACTA
Vol. 213,1 Jul. 2021, 116937
1. An in-situ synchrotron diffraction study of stress relaxation in titanium: Effect of temperature and oxygen on cold dwell fatigue
溫度和氧含量對鈦中應力松弛影響的原位同步衍射研究
Yi Xiong?, Phani S. Karamched, Chi-Toan Nguyen, David M. Collins, Nicolò Grilli, Christopher M. Magazzeni, Edmund Tarletond, Angus J. Wilkinson
Y. Xiong:yi.xiong@materials.ox.ac.uk
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116937
摘要
Ti合金在室溫循環加載過程中的應力殘余會導致疲勞壽命的急劇下降。為了更好地理解這一現象,需要對合金中主要滑移系隨時間的變化進行分析,尤其是闡明溫度和合金元素的影響。本研究中,我們在4個溫度條件下(室溫,75°C, 145°C和250°C),使用同步X射線衍射對兩種不同氧含量的商業純鈦樣品(1級和4級)在應力松弛過程塑性隨時間的變化進行了表征。我們通過測量晶格應變松弛響應,對晶體塑性有限元模型進行了修正,從而確定了主棱柱滑移和基底滑移系統中位錯運動的關鍵參數隨時間和氧含量的變化。研究表明,75℃時材料的劣化最為嚴重,由于棱柱和基底滑移系統活躍,導致松弛周期中宏觀塑性應變積累明顯。隨著溫度的升高,熱對位錯滑移的影響逐漸超過機械能。我們發現氧能夠改變滑移系統的臨界分切應力,且氧對棱柱滑移的強化作用大于基底滑移用。這種效應在高氧含量的商業純鈦中十分顯著。
ACTA
Vol. 213,1 Jul. 2021, 116952
2. Atomistic modelling of thermal-cycling rejuvenation in metallic glasses
金屬玻璃熱循環恢復的原子尺度模型
Baoshuang Shang, Weihua Wang, Alan Lindsay Greer, Pengfei Guan?
P. Guan:pguan@csrc.ac.cn(北京計算科學研究中心)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116952
摘要
金屬玻璃經室溫和低溫之間反復循環可導致材料在快速冷卻過程中形成高能態。這種現象是十分出人意料的,因為它是在很小的宏觀應變和遠低于熱激活結構變化溫度條件下發生的,這對于材料的塑性具有重要意義。我們通過分子動力學模擬,闡明了熱循環誘導弛豫和回復的機制。數十次的熱循環可以驅使原子發生局部重排,從而逐漸消除最初的玻璃結構。這一過程與每個熱循環加熱階段金屬玻璃固有的結構不均一性有關。雖然分子動力學模擬的時間較短,但模擬能夠很好地復現實驗觀測到的物理現象。以上研究對于通過熱循環調控金屬玻璃性能具有指導意義。
ACTA
Vol. 213,1 Jul. 2021, 116950
3. Breakdown of the Hall-Petch relationship in extremely fine nanograined body-centered cubic Mo alloys
納米晶體心立方Mo合金中Hall-Petch關系的失效原因
F.H. Duan, Y. Naunheim, C.A. Schuh?, Y. Li?
C.A. Schuh:schuh@mit.edu
Y. Li:liyi@imr.ac.cn (沈陽金屬研)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116950
摘要
人們對FCC金屬納米晶的力學性能和變形行為進行了大量研究,而對bcc金屬相關研究則卻較少。我們對晶粒尺寸120 ~ 4nm的BCC Mo(O)的硬度和變形行為進行了研究,其中既包括Hall-Petch公式適用的范圍,也包括不適用的范圍(11 ~ 4nm)。當材料晶粒尺寸為11nm時,材料的硬度最高,達17.3GPa。材料在晶粒尺寸極小時的失效可能與激活體積、應力集中等有關。而較大晶粒尺寸下的失效則與晶界剪切、晶間變形等有關。超細晶中引起應力集中的剪切帶尺寸遠大于晶粒尺寸的大剪切帶的形成有關。因此超細晶中的變形行為可能更加類似于玻璃的變形,這與材料中無序結構所占比例增加自洽。
ACTA
Vol. 213,1 Jul. 2021, 116954
4. Coarsening of martensite with multiple generations of twins in laser additively manufactured Ti6Al4V
激光增材制造Ti6Al4V中的孿晶馬氏體粗化
Mangesh V. Pantawane, Shashank Sharma, Abhishek Sharma, Sriswaroop Dasari, Srikumar Banerjee, Rajarshi Banerjee, Narendra B. Dahotre?
N.B. Dahotre:narendra.dahotre@unt.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116954
摘要
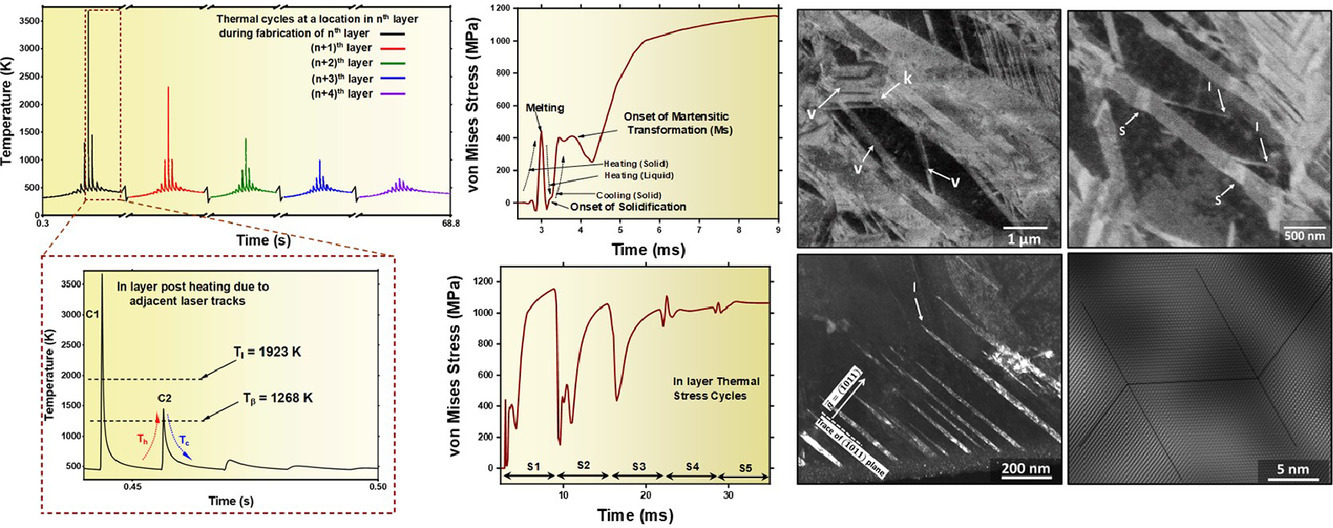
激光粉末熔煉過程中復雜的熱動力學條件大大提高了我們理解增材制造Ti6Al4V內部孿晶馬氏體結構演化的難度。我們通過基于有限元方法的熱、動力學模型,結合掃描電鏡和透射電鏡實驗,對此進行了研究。為了解增材制造過程中激光熱處理對馬氏體和孿晶形貌演化的影響,我們分別進行了單道次、雙道次、三道次激光和傳統鍛造態材料熱處理(1323K固溶后水淬至室溫)對比實驗。研究表明,與增材制造的Ti6Al4V相比,水淬Ti6Al4V樣品中的馬氏體板條更細。隨著激光道次增加,馬氏體板條逐漸粗化并發生變形。此外,在增材制造Ti6Al4V中還觀測到了孿晶的多次生成,而在固溶水淬的Ti6Al4V則很少發現。多代孿晶也是單一激光軌跡處理的變形Ti6Al4V的顯著特征。這些具有獨特形態和晶體學特征的馬氏體演化過程與模擬預測的激光粉末熔煉增材制造過程中的熱、動力學條件密切相關。
ACTA
Vol. 213,1 Jul. 2021, 116964
5. Dislocation electron tomography: A technique to characterize the dislocation microstructure evolution in zirconium alloys under irradiation
輻照態鋯合金中位錯微觀結構演化的表征
Alexandre Mussi?, Ahmed Addad, Fabien Onimus
A. Mussi:alexandre.mussi@univ-lille.fr
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116964
摘要
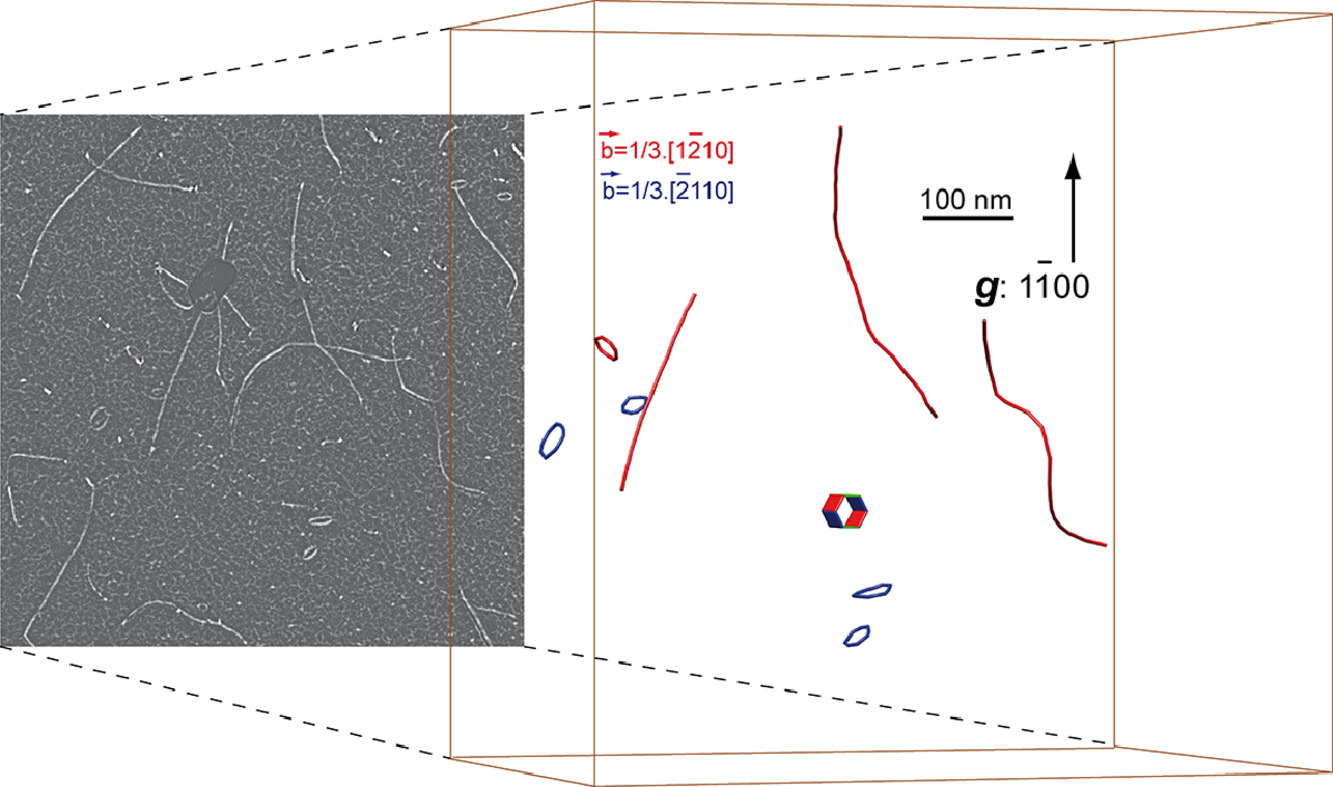
我們利用衍射-對比電子掃描技術對鋯合金輻照前后的位錯三維微觀結構進行了研究。輻照前,我們對材料在室溫下進行了拉伸。材料應變后出現大量具有<a>伯氏矢量的螺位錯。通過對含有非螺位錯段的慣析面進行分析,我們發現這類位錯主要在棱柱面內滑移,而較少在一階錐面內滑移。輻照后,我們在材料中觀測到了具有<a>伯氏矢量的位錯環。結果表明,位錯環的慣析面位于{10-10}面周圍,最多可向(0001)和{11-20}面傾斜20°。此外,我們證實了螺位錯在輻照下發生了攀移。攀移過程中位錯間發生相互作用。輻照下位錯攀移是鋯合金在機械載荷和輻照共同作用下在反應堆內變形的重要機制。該過程中位錯與位錯環間的相互作用對變形也有重要影響。
ACTA
Vol. 213,1 Jul. 2021, 116975
6. Giant heterogeneous magnetostriction induced by charge accumulation-mediated nanoinclusion formation in dual-phase nanostructured systems
雙相納米結構體系中納米夾雜引起的顯著非均勻磁致伸縮效應
Yijun Chen, Zhongheng Fu, Yuye Wu?, Yichen Xu, Yu Xiao, Jingmin Wang, Ruifeng Zhang, Chengbao Jiang?
Y. Wu:wuyuye@buaa.edu.cn(北京航空航天大學)
C. Jiang:jiangcb@buaa.edu.cn(北京航空航天大學)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116975
摘要
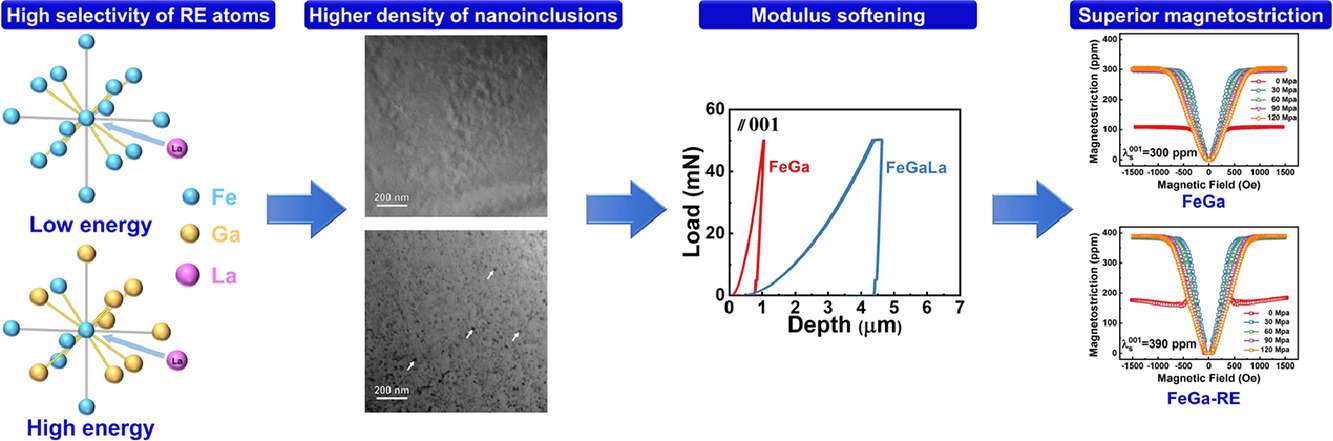
目前關于雙相納米結構超磁致伸縮效應的形成原因仍存在爭議。已有研究表明,形成四方納米夾雜會導致局部各向異性增大,從而增大磁致伸縮。納米夾雜對晶格彈性常數的影響是另一個關鍵因素,但相關研究尚不深入。我們基于稀土摻雜FeGa單晶中的理論計算和實驗結果提出了一種機制。由于稀土原子與Fe原子的鍵合作用強于Ga原子,因此摻雜有效增加了A2基體中納米夾雜的密度。結果表明,隨著納米夾雜物密度的增加,彈性常數c12相比c11顯著增加。由于磁致伸縮(λ001)與c11−c12存在直接關聯,因此磁致伸縮顯著增強。同時由于夾雜引起的晶格軟化,稀土摻雜后單晶樣品的磁致伸縮可達390ppm。以上研究揭示了稀土原子對FeGa單晶磁致伸縮的貢獻,為雙相磁致伸縮材料的設計提供了指導。
ACTA
Vol. 213,1 Jul. 2021, 116957
7. Influence of internal hydrogen content on the evolved microstructure beneath fatigue striations in 316L austenitic stainless steel
氫含量對316L奧氏體不銹鋼疲勞組織演化的影響
K.E. Nygren, A. Nagao, S. Wang, P. Sofronis, I.M. Robertson?
I.M. Robertson:irobertson@wisc.edu, ian.robertson@wisc.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116957
摘要
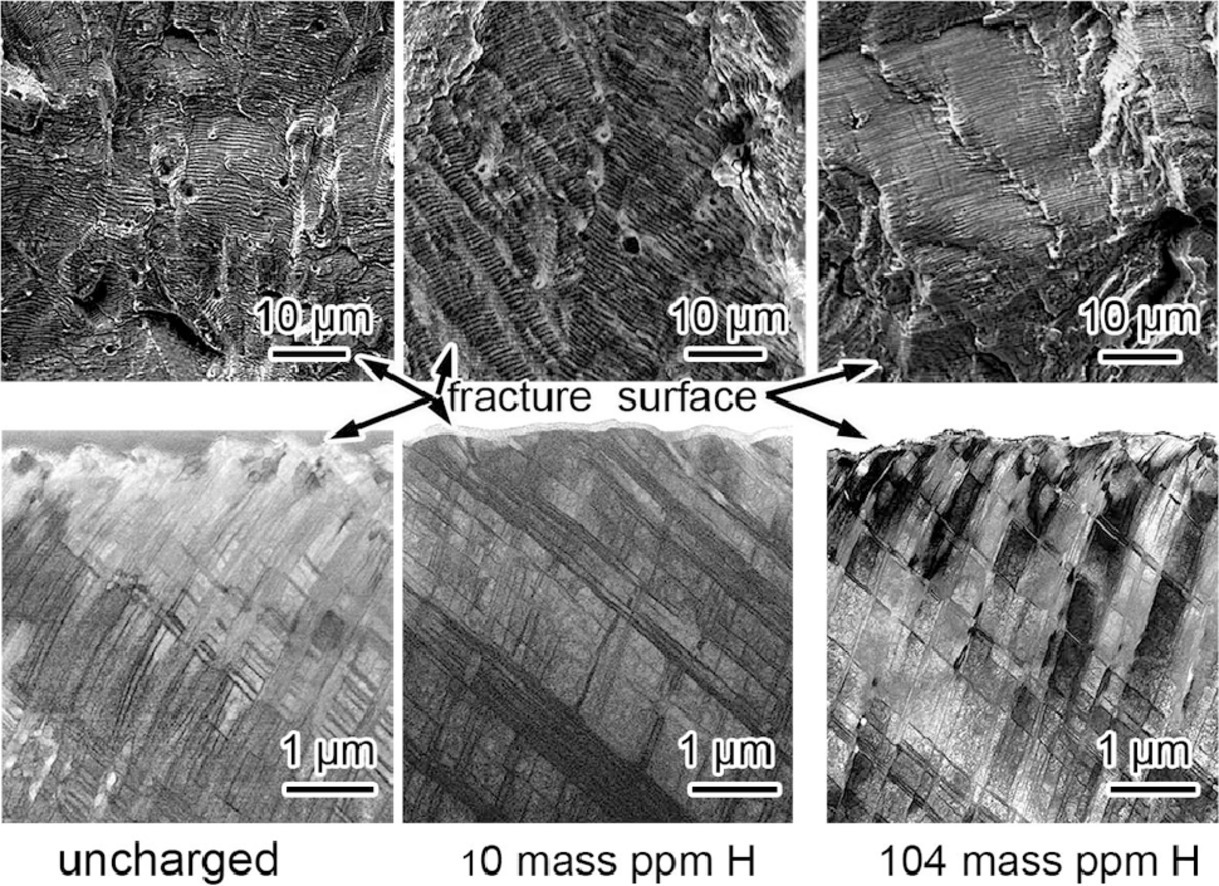
我們研究了SUS316L奧氏體不銹鋼中氫(最高達到104.2 mass ppm)對拉伸和疲勞性能的影響。研究表明,氫對拉伸性能的影響極小,但會降低材料的疲勞壽命,且這種影響不是單調變化的。疲勞斷口下的組織形貌在裂紋長度和氫含量等方面各有異同。氫的存在使得材料中形成了具有更厚胞壁的小位錯胞,并改變了變形孿晶的分布。隨著氫濃度的增加,疲勞響應非線性變化,這是由于材料在高濃度氫狀態下的宏觀性能發生了轉變。鑒于我們的研究重點是將氫引起的組織變化與材料力學性能的變化建立聯系,因此我們主要從氫對局部塑性的增強作用出發,對實驗結果進行了討論。
ACTA
Vol. 213,1 Jul. 2021, 116962
8. In situ studies of liquid-liquid phase separation, solidification sequence and dendrite growth kinetics in electrostatically levitated Ti–Y alloys
靜電懸浮Ti-Y合金中液相分離、凝固順序和枝晶生長的動力學原位研究
Dandan Zhao, Fan Yang Dirk Holland-Moritz, Matthias Kolbe, Thomas Buslaps, Jianrong Gao?
J. Gao:jgao@mail.neu.edu.cn(東北大學)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116962
摘要
我們采用了靜電懸浮方法對亞偏晶Ti75Y25、近偏晶Ti70Y30和過偏晶Ti60Y40熔體進行了過冷凝固。通過高能X射線衍射(HEXRD)和光學成像技術對過冷熔體中的液相分離、凝固順序和枝晶生長速度進行了原位研究。研究表明,三種Ti−Y成分的過冷熔體在凝固前分離成富Ti熔液和富Y熔液。熔液的凝固順序取決于富Y液體中HCP α-Y的形核和富Ti液中BCC β-Ti的形核。α-Y和β-Ti的枝晶生長速度只與時間有關,而不隨形核過冷度的增加而增加。這一獨特的長大動力學特征可能是由于生長的枝晶和熔液之間的動態相互作用導致的。掃描電鏡表征表明,相分離樣品凝固后形成核殼結構或島狀結構。對凝固過程中液相分離和液相-枝晶相互作用的深入研究能夠更好地幫助我們理解這一形貌產生的原因。
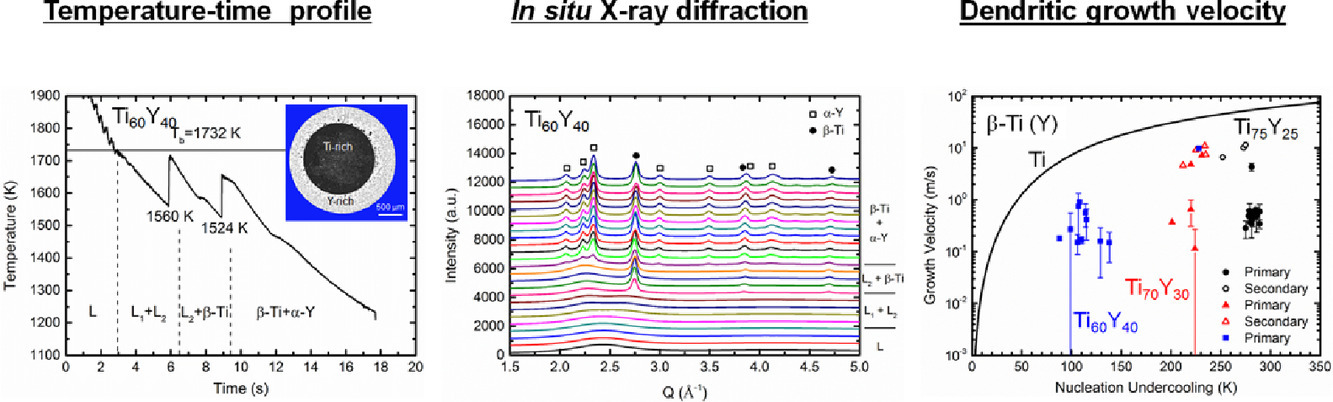
ACTA
Vol. 213,1 Jul. 2021, 116956
9. Interaction between nucleant particles and a solid-liquid interface in Al-4.5Cu alloy
Al-4.5Cu合金中形核粒子與固液界面的相互作用研究
Y. Liu, Q. Han?
Q. Han:hanq@purdue.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116956
摘要
我們通過添加鹵化物,在Al-4.5 wt % Cu合金中原位制備了Al3Ti和TiB2粒子。熔融鹵鹽能夠使氧化物溶解在熔融金屬中,從而確保新形成的Al3Ti和TiB2粒子與熔融金屬有密切的界面。在熔體中加入過量的鈦,可以保證顆粒與熔融合金之間的浸潤角較小,使得粒子顯著減小鋁合金的晶粒尺寸。當粒子被前進的固-液界面吞噬到固體中時,這種粒子/基體系統的總界面能減小,從而使得這一過程可以不斷發生。實驗結果表明,無論枝晶生長速度如何,這些粒子實際上總是被生長的枝晶推入枝晶間區域。在本研究的實驗條件下,基于界面能相互作用的粒子推動機制似乎不適用于這一體系。分析表明,這些粒子在固液界面緊密接觸,范德華力能夠發揮顯著作用之前,就不斷被長大的枝晶推動。糊狀區液體的收縮流動對粒子的運動起到重要作用。
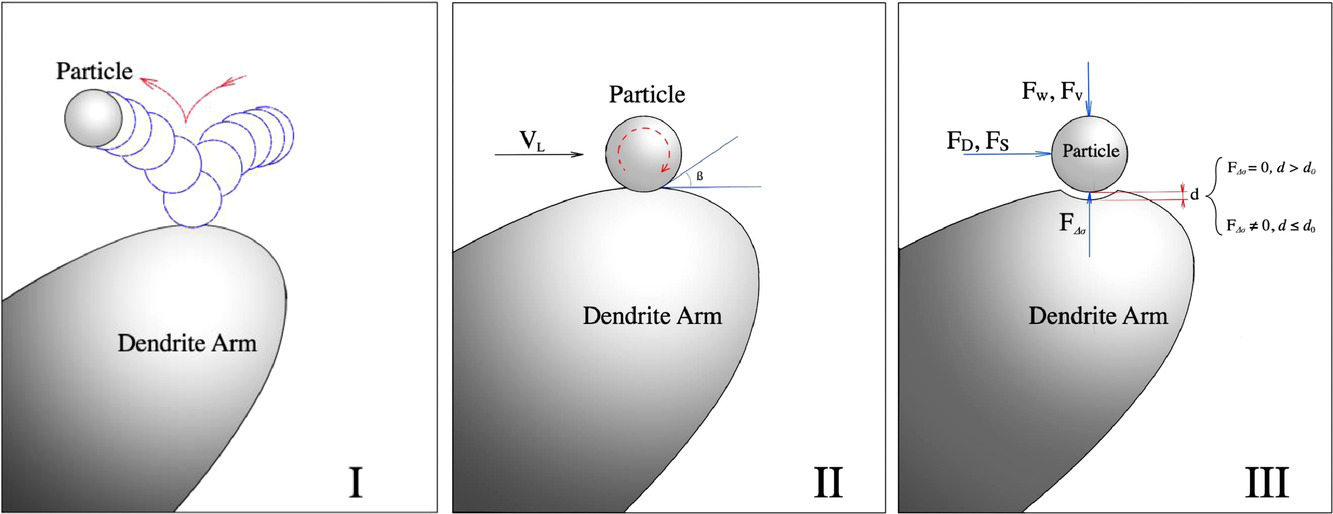
ACTA
Vol. 213,1 Jul. 2021, 116982
10. Mechanical properties and deformation mechanisms of a Ni2Co1Fe1V0.5Mo0.2 medium-entropy alloy at elevated temperatures
Ni2Co1Fe1V0.5Mo0.2中熵合金的高溫力學性能及變形機制研究
Wei Jiang, Shengyun Yuan, Yang Cao?, Yong Zhang?, Yonghao Zhao?
Y. Cao:y.cao@njust.edu.cn, cao_yang_leo@hotmail.com(南京理工大學)
Y. Zhang:yong@njust.edu.cn(南京理工大學)
Y. Zhao:yhzhao@njust.edu.cn(南京理工大學)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116982
摘要
我們鑄造了一種單相面心立方結構的Ni2Co1Fe1V0.5Mo0.2中熵合金(MEA)。這種鑄態中熵合金具有優異的加工硬化能力、屈服強度、抗拉強度和均勻延伸率。在25 ~ 800℃的拉伸變形過程中,中熵合金在彈塑性轉變后的應變硬化率呈上升趨勢。大量溶質原子和高密度位錯提供了充足的背應力強化,使得應變硬化率上升。研究表明,溫度對中熵合金力學性能的影響與位錯結構、位錯密度和動態應變時效密切相關。隨著變形溫度的升高,位錯密度發生波動,螺位錯比例不斷增加。溶質釘扎和位錯森林強化是引起400℃-700℃范圍內應變硬化率變化的原因。而在800℃時,隨著應變的增加,主要變形機制由位錯森林切割機制轉變為位錯交叉滑移,導致材料的應變硬化速率急劇上升。另一方面,動態應變時效造成塑性失穩,不利中熵合金的應變硬化。以上研究對中熵、高熵合金在高溫下的力學性能調控具有指導意義。
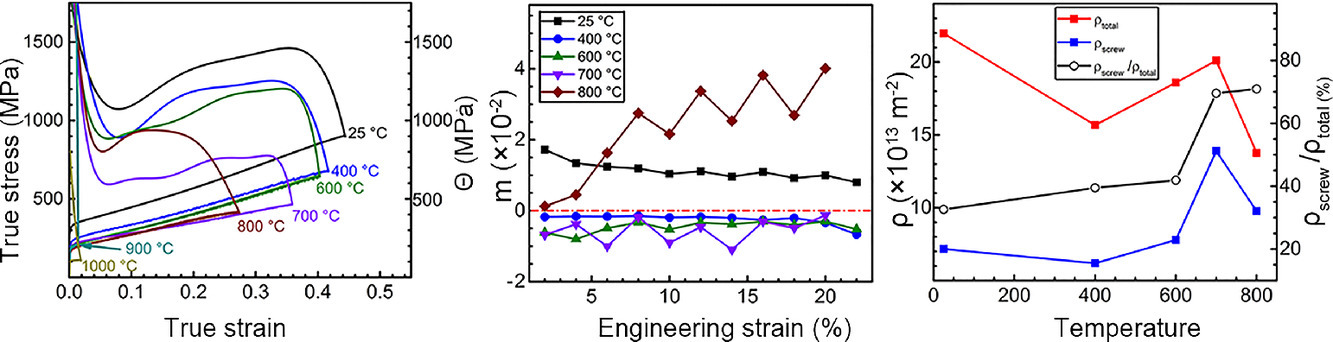
ACTA
Vol. 213,1 Jul. 2021, 116949
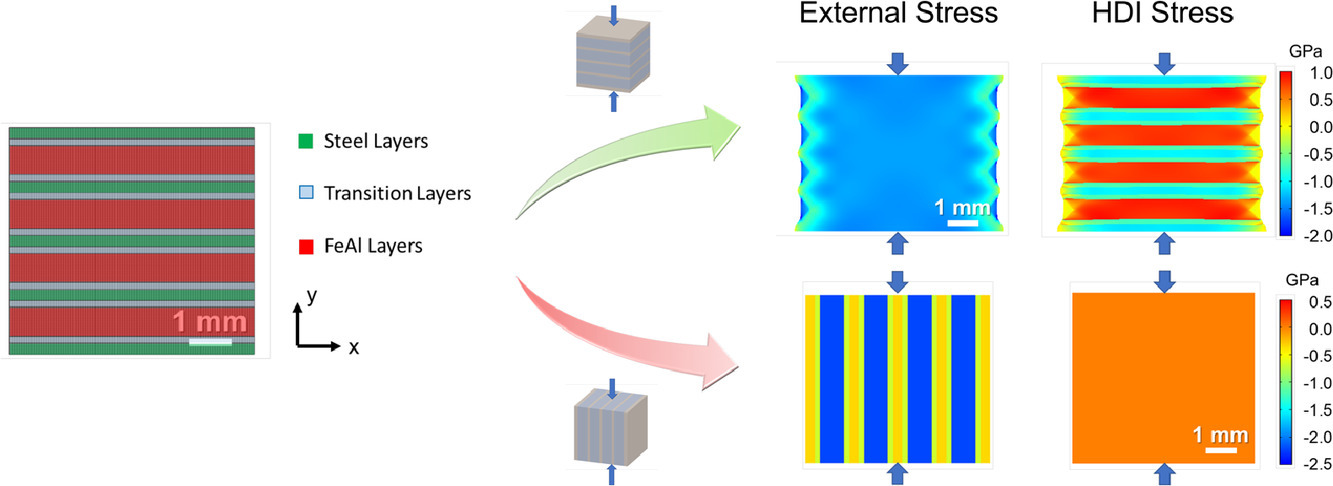
11. Mesoscale hetero-deformation induced (HDI) stress in FeAl-based metallic-intermetallic laminate (MIL) composites
FeAl基金屬間化合物層狀復合材料的介觀尺度不均勻變形誘導應力研究
Haoren Wang, Rui Kou, Haozhe Yi, Samuel Figueroa, Kenneth S. Vecchio?
K.S. Vecchio:kvecchio@ucsd.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116949
摘要
我們采用層箔法合成了單相FeAl層狀材料,并對FeAl基金屬間化合物層狀(MIL)復合材料的斷裂機理進行了研究。我們通過壓縮實驗研究了單相FeAl的力學性能和裂紋演化規律。顯微組織和成分表征表明,單相FeAl和FeAl基復合材料具有相似的層狀組織。當受壓方向垂直于疊層方向時,兩種材料均由于FeAl相沿加載方向開裂最終導致失效。MIL復合材料中的FeAl層由于介觀不均勻變形引起的應力(HDI)而受到拉伸作用,這加速了裂紋的形核和擴展,并導致材料發生破壞。430SS-FeAl和304SS-FeAl MIL復合材料具有相似的組織和成分,但強度差異很大,我們通過有限元模擬對此進行了解釋。當受壓方向平行于疊層方向時,介觀HDI效應可以忽略,幾何必要位錯的堆積可以提高復合材料的性能。我們通過四點彎試驗對FeAl基MIL復合材料的斷裂韌性進行了表征,結果表明,FeAl基MIL復合材料比單相FeAl具有更高的斷裂韌性。