金屬頂刊雙語導讀丨Scripta Mater. Vol.204, 1 Nov. 2021(下)
2021-08-29 來源:Goal Science
本期包含金屬材料領域論文11篇,涵蓋了高熵合金、馬氏體等,國內科研單位包括中南大學、合肥固體物理研究所、南京理工大學等(通訊作者單位)。
Vol. 204 目錄
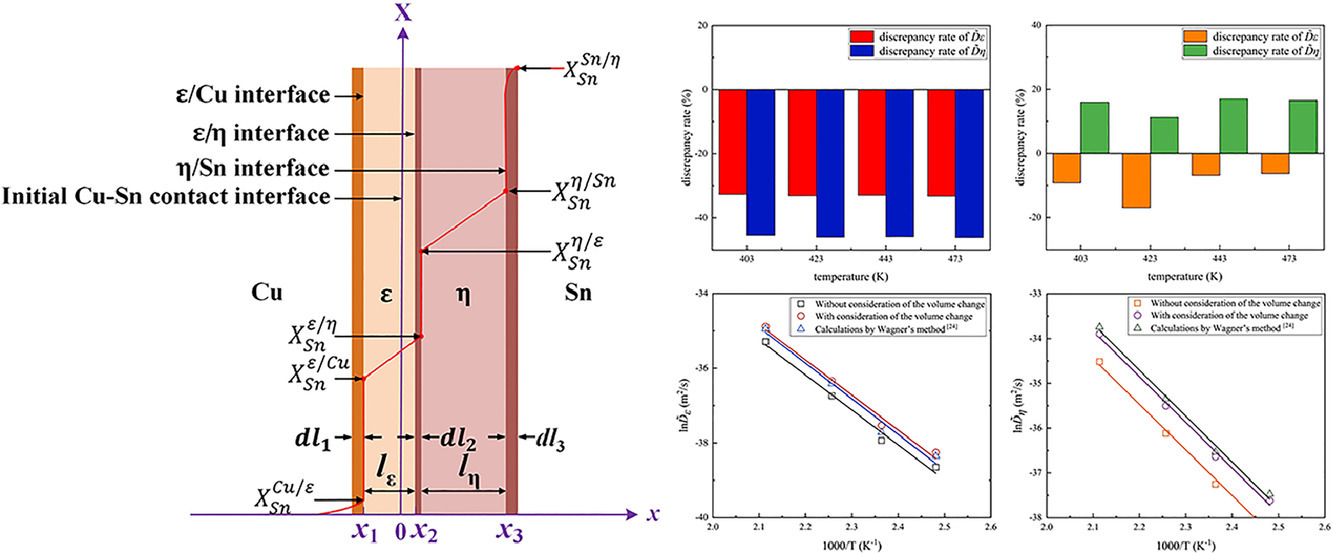
1. Studies of Cu-Sn interdiffusion coefficients in Cu3Sn and Cu6Sn5 based on the growth kinetics
基于生長動力學的Cu3Sn和Cu6Sn5中Cu-Sn相互擴散系數的研究
2. Hydrogen-induced transgranular to intergranular fracture transition in bi-crystalline nickel
雙晶鎳中氫致穿晶向晶間斷裂轉變
3. Short-range ordering governs brittleness and ductility in W-Ta solid solution: Insights from Pugh's shear-to-bulk modulus ratio
W-Ta固溶體中的短程有序控制脆性和延展性:來自Pugh的剪切體積模量比的見解
4. Multicomponent Ni-rich high-entropy alloy toughened with irregular-shaped precipitates and serrated grain boundaries
具有不規則形狀析出物和鋸齒狀晶界的多組元富鎳高熵合金
5. Role of thermo-mechanical gyrations on the α/β interface stability in a Ti6Al4V AM alloy
熱機械旋轉對Ti6Al4V AM合金中α/β界面穩定性的影響
6. Grain boundary relaxation behavior and phase stability of AlCrTiVx (x = 0, 0.5 and 1) high-entropy alloys
AlCrTiVx (x = 0, 0.5 and 1)高熵合金的晶界弛豫行為和相穩定性
7. New mechanism and criterion for forming multi-component solid-solution alloys
形成多組元固溶體合金的新機制和判據
8. 5M and 7M martensitic stability and associated physical properties in Ni50Mn35In15 alloy: first-principles calculations and experimental verification
Ni50Mn35In15合金的5M和7M馬氏體穩定性及相關物理性能:第一性原理計算和實驗驗證
9. Revealing tribo–oxidation mechanisms of the copper–WC system under high tribological loading
揭示高摩擦載荷下Cu-WC系統的摩擦氧化機制
10. Machine learning to predict aluminum segregation to magnesium grain boundaries
機器學習預測鋁在鎂晶界的偏析
11. In-situ TEM observation and MD simulation of the reaction and transformation of <100> loops in tungsten during H2+ & He+ dual-beam irradiation
H2+和He+雙光束輻照過程中鎢<100>環反應和轉變的原位TEM觀察和MD模擬
SCRIPTA
Vol. 204, 1 Nov. 2021, 114138
1. Studies of Cu-Sn interdiffusion coefficients in Cu3Sn and Cu6Sn5 based on the growth kinetics
基于生長動力學的Cu3Sn和Cu6Sn5中Cu-Sn相互擴散系數的研究
Yue Wang, Xianwen Peng, Jihua Huang?, Zheng Ye, Jian Yang, Shuhai Chen
Jihua Huang: jhhuang62@sina.com 北京科技大學
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114138
摘要
在這項工作中,我們基于反應/擴散理論建立了Cu3Sn(ε)和Cu6Sn5(η)生長的動力學模型。基于Cu和Sn原子的相互擴散控制生長的理論,建立了ε和η層生長的動力學方程。 在考慮和不考慮相變引起的體積變化的兩種情況下推導了動力學方程,其中Cu-Sn相互擴散系數(,
)都被列為主要因素。在此基礎上,測定了兩種條件下在130~200℃范圍內的互擴散系數,結果表明在某種程度上體積變化影響了
和
的計算精度。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 204, 1 Nov. 2021, 114122
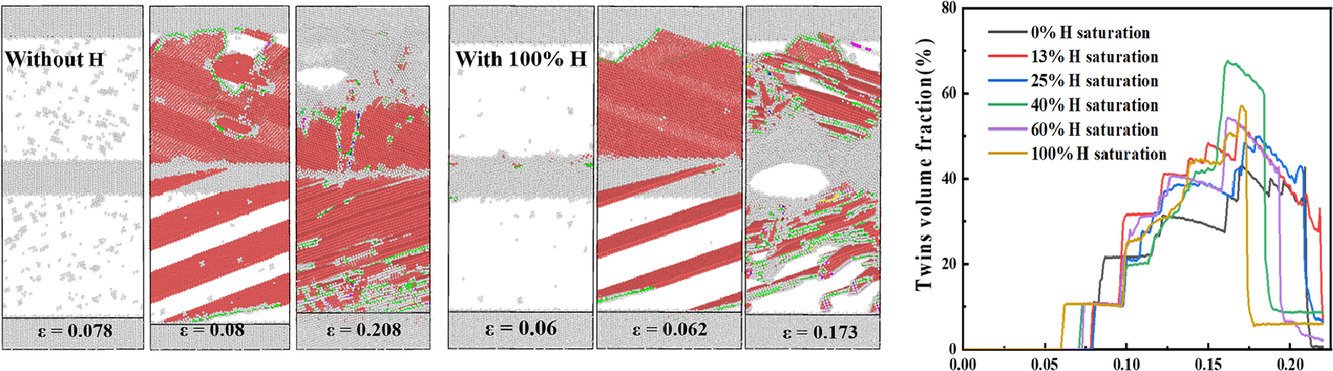
2. Hydrogen-induced transgranular to intergranular fracture transition in bi-crystalline nickel
雙晶鎳中氫致穿晶向晶間斷裂轉變
Yu Ding, Haiyang Yu, Kai Zhao, Meichao Lin, Senbo Xiao, Michael Ortiz, Jianying He,
Zhiliang Zhang?
Zhiliang Zhang: zhiliang.zhang@ntnu.no
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114122
摘要
眾所周知,氫會影響金屬材料的位錯塑性和斷裂模式。然而,氫與晶界之間的納米級相互作用機制在很大程度上仍然不清晰。通過對具有Σ5(210)[001]晶界的雙晶Ni進行單軸應變,原子模型闡明了由氫促進的穿晶到晶間斷裂轉變,并揭示了特定的氫控制塑性機制。研究發現氫在晶界附近形成局部氣氛,這會引起局部應力集中并抑制隨后在變形過程中晶界處的應力松弛。正是這種局部應力集中促進了位錯更早的發展、孿晶演化和更多空位的產生,從而促進了納米空隙。與無氫樣品的穿晶斷裂相反,納米空隙的成核和生長最終導致晶界處的晶間斷裂。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 204, 1 Nov. 2021, 114136
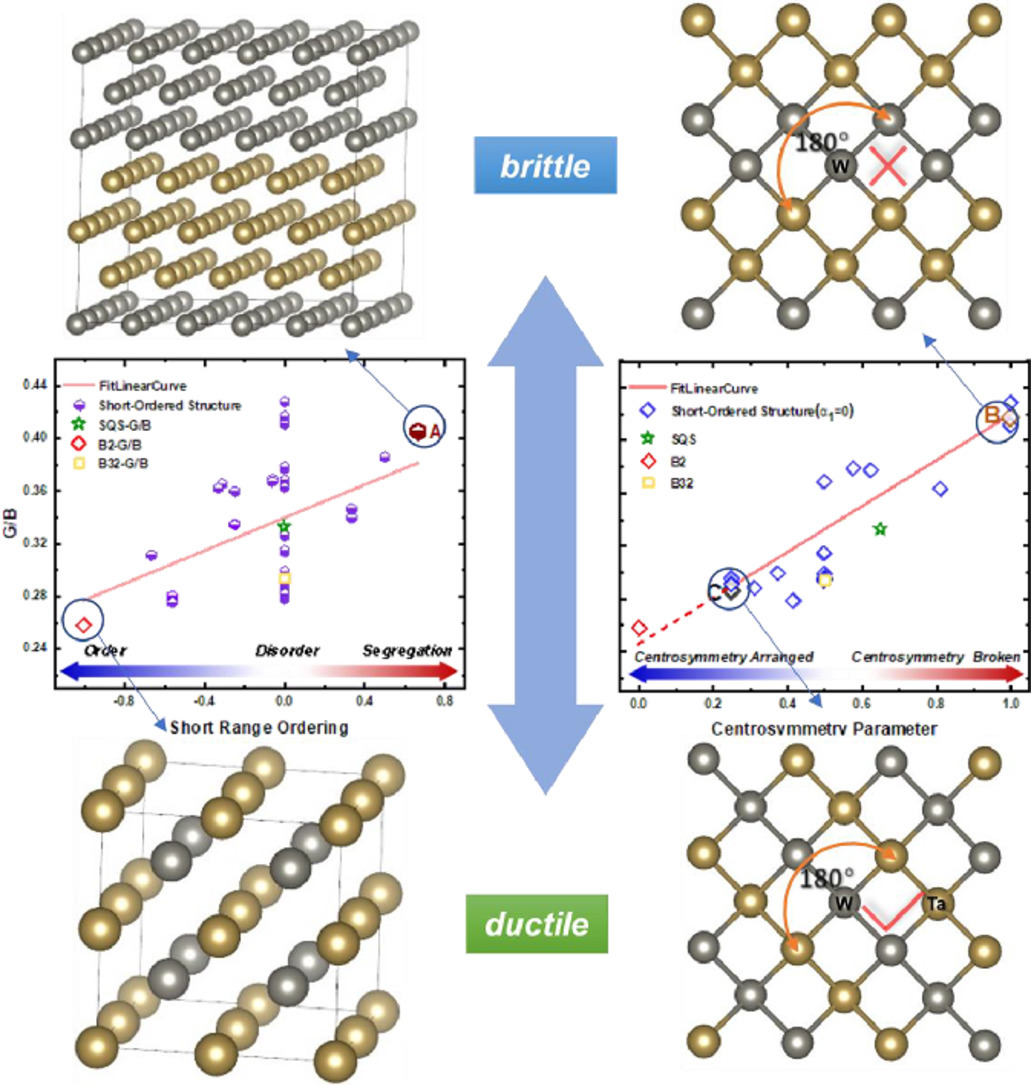
3. Short-range ordering governs brittleness and ductility in W-Ta solid solution: Insights from Pugh's shear-to-bulk modulus ratio
W-Ta固溶體中的短程有序控制脆性和延展性:來自Pugh的剪切體積模量比的見解
Honggang Liu, Sai Tang, YunZhu Ma, Wensheng Liu, Chaoping Liang?
Chaoping Liang: cpliang@csu.edu.cn 中南大學
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114136
摘要
在這項工作中,通過第一性原理計算研究了W-Ta固溶體中,從Pugh的剪切體積模量(G/B)比推導出的短程有序對固有脆性和延展性的影響。結果表明,作為脆性指標的G/B值隨W-Ta固溶體中Ta濃度的降低而降低。依據G/B值,與理想固溶體和原子偏析結構相比,短程有序結構表現出延展性。這種短程有序結構的延展性源于部分共價W-W鍵數量的減少和W-Ta固溶體中W-W相互作用的中心對稱屏蔽。研究結果表明,短程有序化應該在W固溶體中的固溶軟化和輻照硬化現象中起一定作用,這可以用于未來的W合金設計。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 204, 1 Nov. 2021, 114066
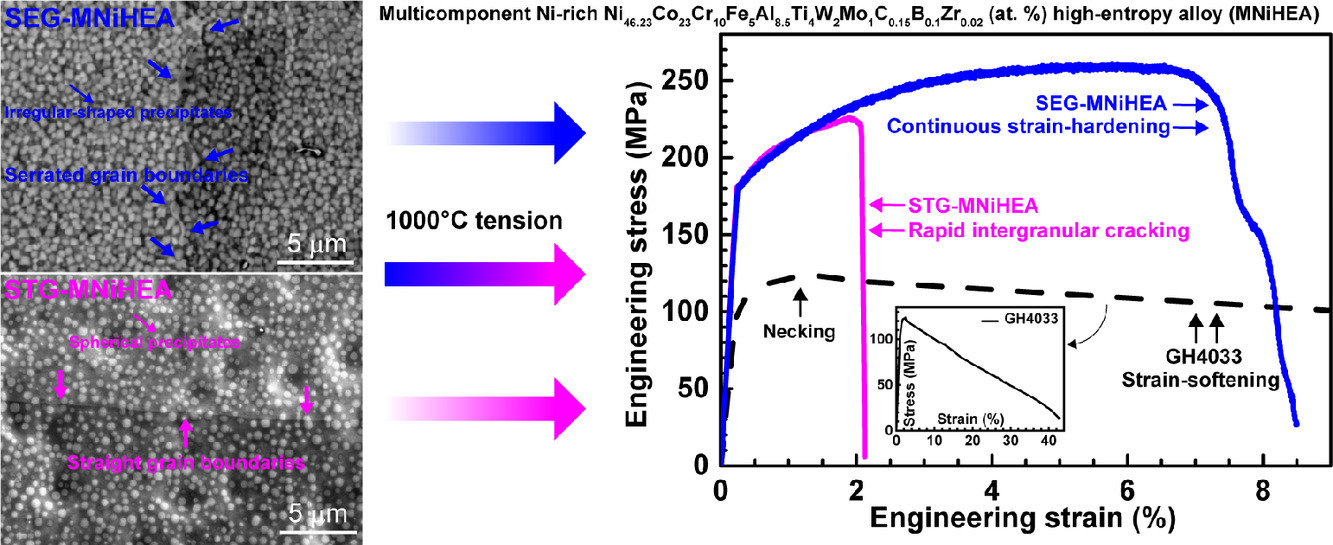
4. Multicomponent Ni-rich high-entropy alloy toughened with irregular-shaped precipitates and serrated grain boundaries
具有不規則形狀析出物和鋸齒狀晶界的多組元富鎳高熵合金
S.W. Wu, T. Yang, B.X. Cao, J.H. Luan, Y.F. Jia, L. Xu, Y.K. Mu, T.L. Zhang, H.J. Kong,
X. Tong, J.C. Peng, G. Wang, Q.J. Zhai, J. Lu, C.T. Liu?
C.T. Liu: chainliu@cityu.edu.hk 深圳福田研究所
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114066
摘要
一種新型的沉淀強化多元富鎳Ni46.23Co23Cr10Fe5Al8.5Ti4W2Mo1C0.15B0.1Zr0.02 (at.%) 高熵合金(HEA),設計其在1000°C屈服后發生應變硬化而不是應變軟化。由于晶間開裂的快速發生,具有球形析出物和垂直晶界的HEA很脆,抗拉強度約220 MPa,均勻伸長率僅為約1.9%。鋸齒狀晶界結構有效地克服了這種晶間開裂問題。該HEA具有不規則形狀的沉淀物和鋸齒狀的晶界,使其顯示出脆性到韌性的轉變,具有高達~260 MPa的優異強度和~6.5% 的均勻延伸率。強度和延展性的提高歸因于鋸齒狀晶界對晶間裂紋形核和擴展的抵抗力增強。該研究結果為具有優異機械性能的高溫結構材料的創新設計提供了一種新方法。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 204, 1 Nov. 2021, 114134
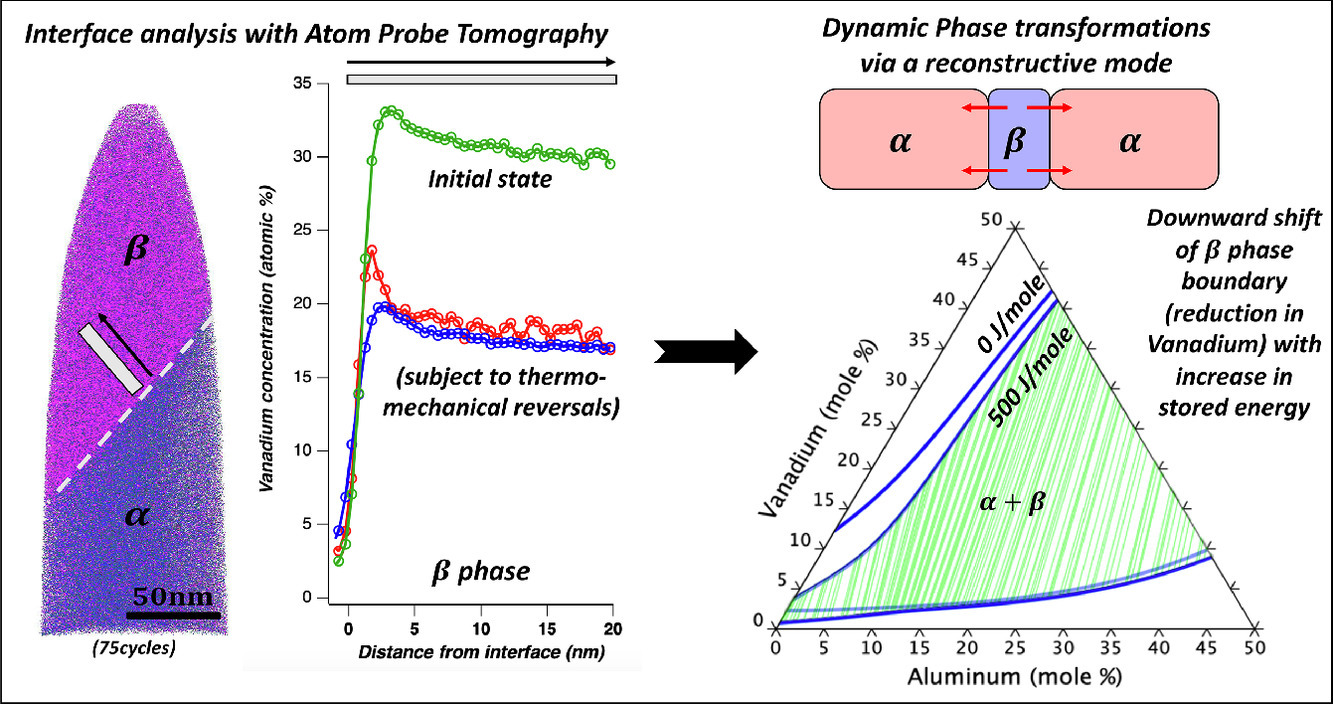
5. Role of thermo-mechanical gyrations on the α/β interface stability in a Ti6Al4V AM alloy
熱機械旋轉對Ti6Al4V AM合金中α/β界面穩定性的影響
Sabina Kumar?, Sri Ram Vijayan, Peeyush Nandwana, Jonathan D. Poplawsky, Chen Yan,
Sudaranam Suresh Babu
Sabina Kumar: skumar17@vols.utk.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114134
摘要
增材制造過程中經歷的能量波動會導致零件內空間和時間瞬變的演變。一般來說,在制造過程中對這些瞬變的原位監測幾乎是不可能的。為了深入了解這些局部熱機械瞬變對界面穩定性的影響,在AM Ti6Al4V合金上施加具有已知邊界條件的快速熱機械反轉,這會導致相變從而增加β相穩定性。這項研究的目標是,通過由于塑性應變積累和擴散動力學而產生的儲存能量的概念來理解這種相變的動力學。原子探針斷層掃描用于研究跨界面的溶質元素的分配。正如預期的那樣,經歷熱機械循環的樣品的整個β相中顯示出較低的釩濃度。整個界面的濃度分布以及全寬半分析提供了對受熱機械旋轉影響的α → β轉變所涉及的潛在相變動力學的深入了解。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 204, 1 Nov. 2021, 114144
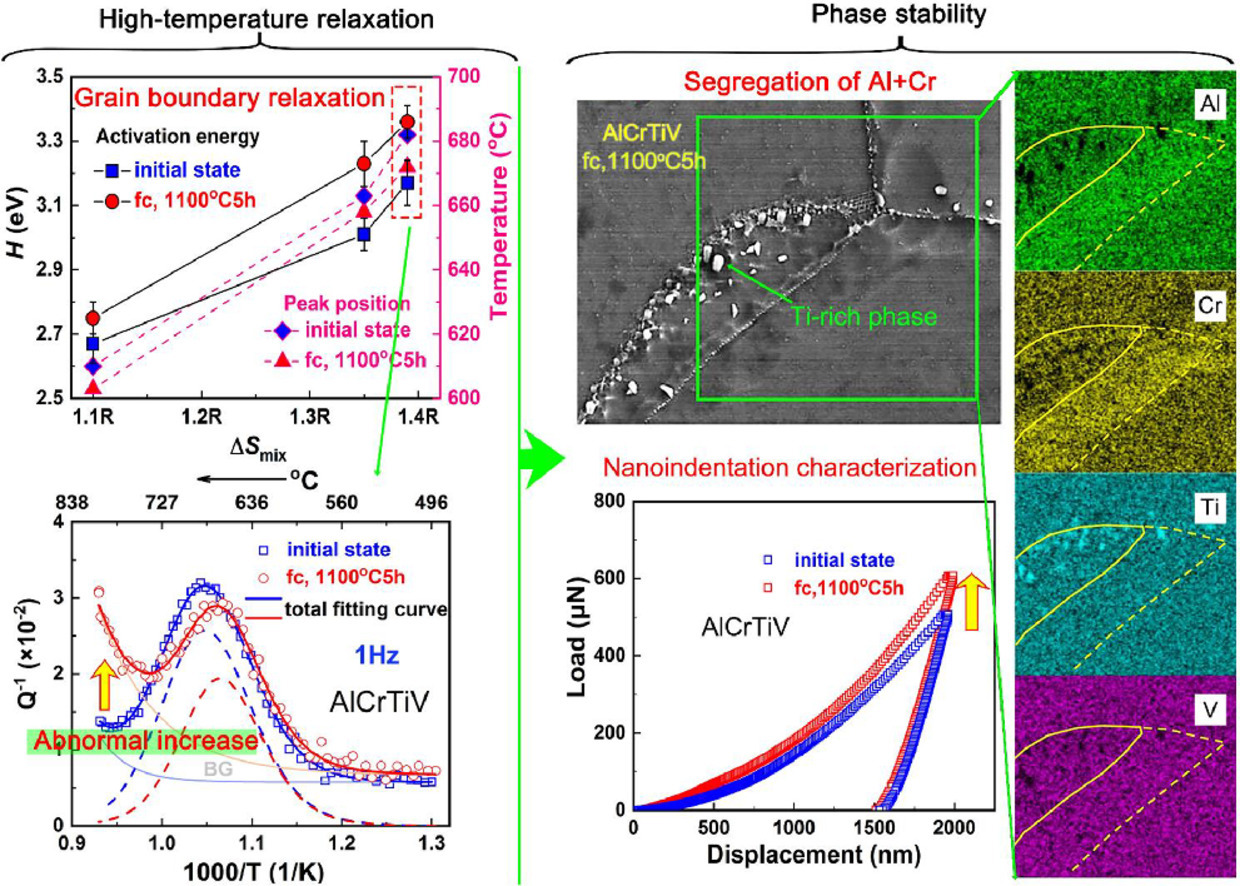
6. Grain boundary relaxation behavior and phase stability of AlCrTiVx (x = 0, 0.5 and 1) high-entropy alloys
AlCrTiVx (x = 0, 0.5 and 1)高熵合金的晶界弛豫行為和相穩定性
Meng Sun?, Xueqing Liu, Weibin Jiang, Yawei Lei, Jianggang Ke, Rui Liu, Xianping
Wang?, Xuebang Wu, Qianfeng Fang?, Changsong Liu
Meng Sun: mengsun@issp.ac.cn 合肥固體物理研究所
Xianping Wang: xpwang@issp.ac.cn 合肥固體物理研究所
Qianfeng Fang: qffang@issp.ac.cn 合肥固體物理研究所
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114144
摘要
本文報道了AlCrTiVx(x = 0、0.5 和 1)高熵合金的缺陷弛豫行為。在所有樣品中都觀察到明顯的內摩擦(IF)峰疊加在單調增加的高溫背景(HTBG)上,這歸因于晶界峰。晶界弛豫的活化能隨著V含量的增加而增加,這意味著隨著混合熵的增加,原子擴散的復雜性和難度增加。在1100 °C退火5 h后,AlCrTiV合金的HTBG異常增加。微觀結構分析證實,這是由于納米富鈦相的析出引起的錯配位錯的出現。這些發現可能為評估和設計具有高熱穩定性的高熵合金提供新的自由度。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 204, 1 Nov. 2021, 114128
7. New mechanism and criterion for forming multi-component solid-solution alloys
形成多組元固溶體合金的新機制和判據
Tsang-Tse Fang?
Tsang-Tse Fang: ttfang@mail.ncku.edu.tw
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114128
摘要
評估了形成單相多組元固溶體合金(MCSSAs)的一些現有標準,并提出了基于原子堆積拓撲的新標準。提出了一種關于MCSSAs發展的新機制,其中,表面層的多組分效應降低納米晶核的表面自由能,起著重要的作用。對不同溫度退火的CoCrFeMnNi合金的相穩定性提供了更合理的解釋。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 204, 1 Nov. 2021, 114140
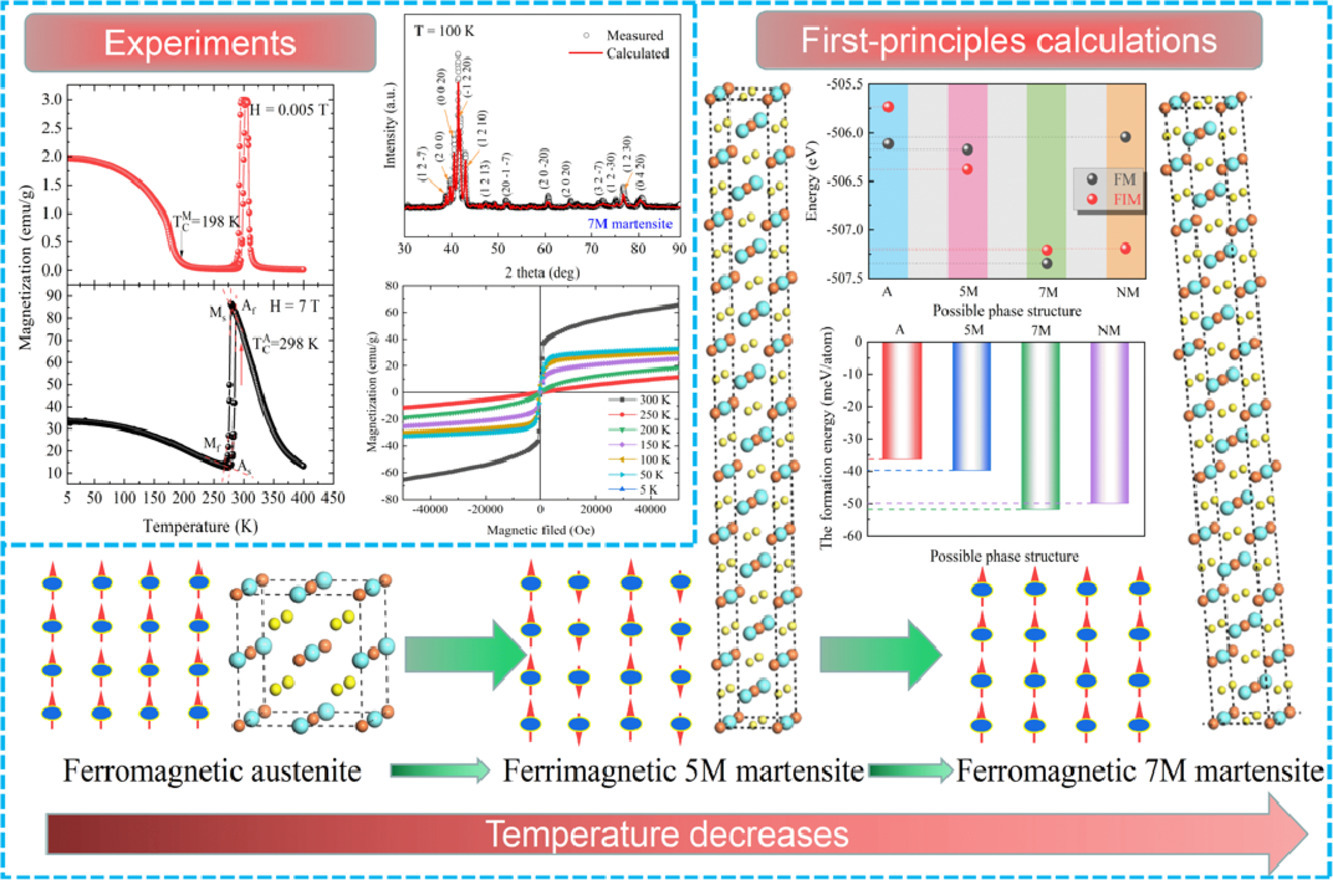
8. 5M and 7M martensitic stability and associated physical properties in Ni50Mn35In15 alloy: first-principles calculations and experimental verification
Ni50Mn35In15合金的5M和7M馬氏體穩定性及相關物理性能:第一性原理計算和實驗驗證
Xinzeng Liang, Xinjun Jiang, Jianglong Gu, Jing Bai?, Ziqi Guan, Zhenzhuang Li, Haile
Yan, Yudong Zhang, Claude Esling, Xiang Zhao?, Liang Zuo
Jing Bai: baijing@neuq.edu.cn 東北大學,東北大學秦皇島分校
Xiang Zhao: zhaox@mail.neu.edu.cn 東北大學
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114140
摘要
Ni-Mn基鐵磁形狀記憶合金優異的磁驅動性能本質上與調制馬氏體的存在有關。 然而,調制馬氏體的亞穩定性阻礙了這些特性的可用性。在此,通過第一性原理計算和實驗研究了 Ni50Mn35In15合金中5M和7M調制馬氏體的相穩定性和相關物理性能。結果表明,該合金經歷了磁結構耦合轉變(即鐵磁奧氏體→亞鐵磁5M馬氏體→鐵磁7M馬氏體)。基于狀態密度和微分電荷密度分析,可理解可能相的穩定性。7M馬氏體中Ni和Mn原子之間的強鍵合能力使其成為最穩定的相。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 204, 1 Nov. 2021, 114142
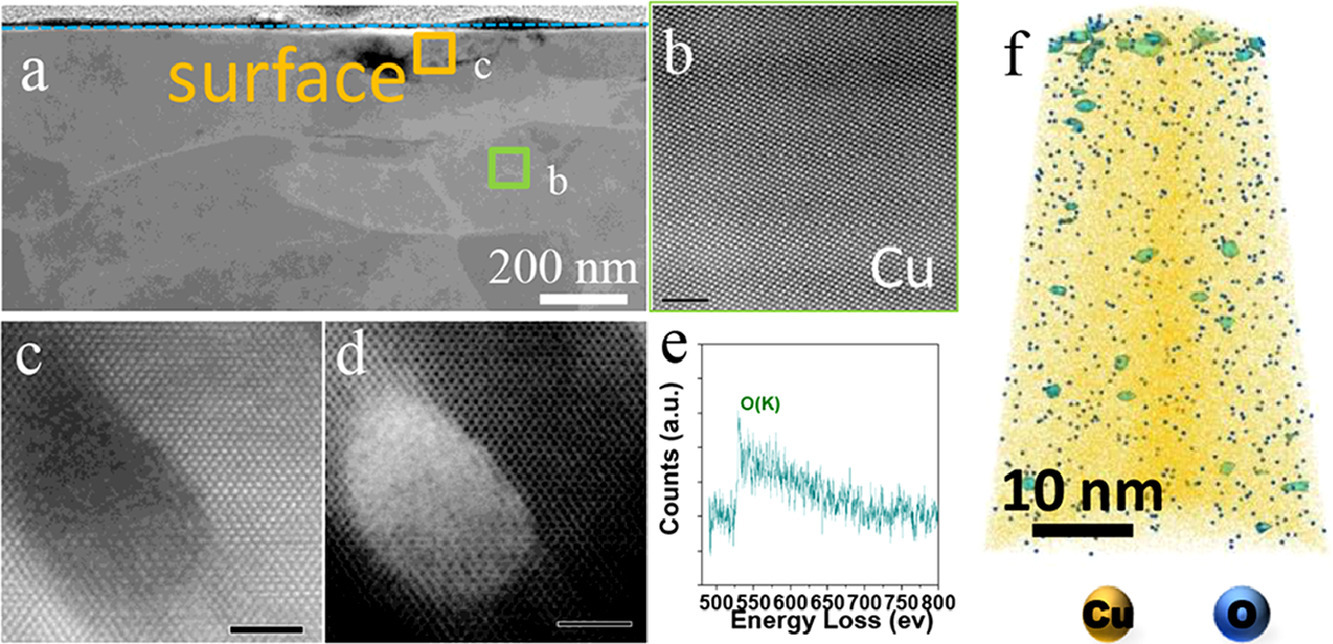
9. Revealing tribo–oxidation mechanisms of the copper–WC system under high tribological loading
揭示高摩擦載荷下Cu-WC系統的摩擦氧化機制
X. Chen?, Y. Ma?, Y. Yang, A. Meng, Z.X. Han, Z. Han, Y.H. Zhao?
X. Chen: xiang.chen@njust.edu.cn 南京理工大學
Y. Ma: y.ma@mpie.de
Y.H. Zhao: yhzhao@njust.edu.cn 南京理工大學
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114142
摘要
在高摩擦載荷期間,研究了純銅相對于碳化鎢(WC)球體的近表面結構和化學變化。 在Cu-WC摩擦系統中確定了基本階段:(i)在最初階段,高摩擦應力促進了晶粒細化到超細晶粒狀態;(ii)極細(~3 nm)富氧銅納米顆粒在近表層中的成核和氧化銅隨后的生長;(iii)具有異質Cu和O分布的連續納米結構混合層在后期的形成。近表面機械混合可能是高摩擦載荷下化學改性的主要原因。該發現為復雜的摩擦化學修飾提供了原子解釋,這是面向材料的摩擦學中最有趣的現象之一。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 204, 1 Nov. 2021, 114150
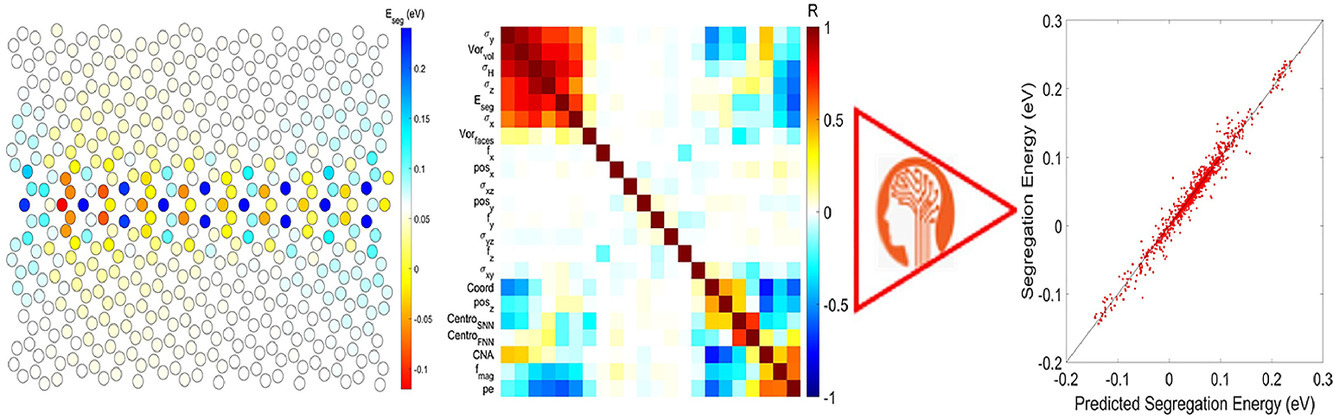
10. Machine learning to predict aluminum segregation to magnesium grain boundaries
機器學習預測鋁在鎂晶界的偏析
Joseph Messina, Renjie Luo, Ke Xu, Guanghong Lu, Huiqiu Deng, Mark A Tschopp, Fei
Gao?
Fei Gao: eigaoum@umich.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114150
摘要
鎂合金由于其高的強度重量比而成為許多應用的優質候選材料,但其他性能如耐腐蝕性、可成形性和蠕變仍是問題。在鎂鋁合金中,Mg17Al12相在晶界(GBs)析出會對機械性能和腐蝕行為產生重要影響。為了更好地理解這些影響,必須首先評估鋁對GB的原子偏析的作用。本研究使用原子模擬來量化鋁偏析能,以訓練機器學習模型。鋁原子被反復放置在近30個不同的鎂對稱傾斜晶界(STGB)的原子位置。結果顯示了鋁偏析如何受GB結構和局部原子環境的影響。使用機器學習技術計算感興趣的晶界物理特性可以對晶界科學和工程領域產生廣泛的影響。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 204, 1 Nov. 2021, 114154
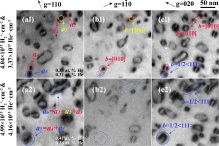
11. In-situ TEM observation and MD simulation of the reaction and transformation of <100> loops in tungsten during H2+ & He+ dual-beam irradiation
H2+和He+雙光束輻照過程中鎢<100>環反應和轉變的原位TEM觀察和MD模擬
Yifan Ding, Long Guo, Yipeng Li, Xinyi Liu, Guang Ran?, Lu Wu, Xi Qiu, Huiqiu Deng,
Xiaoyong Wu, Yuanming Li, Xiuyin Huang
Guang Ran: gran@xmu.edu.cn 廈門大學,福建核工程研究中心
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114154
摘要
低遷移率<100>環顯著影響體心立方材料的力學性能,其產生和演化是近年來的研究熱點。然而,對于后續輻照過程中形成的<100>環的反應仍然缺乏直接觀察,這阻礙了更好地理解輻照引起的機械性能退化。在這里,我們首次報道了鎢30 keV H2+和He+雙光束照射期間,通過原位TEM觀察到了<100>環之間的反應產生了1/2<111>環。分子動力學模擬表明,該反應需要初始<100>環的合適位置和高溫,以誘導<100>環分裂成1/2<111>段,然后轉化為1/2<111>環。同時,原位觀察到<100>環的演變,<100>環的平均尺寸和面數密度被量化為輻射通量的函數。