金屬頂刊雙語導讀丨Acta Mater. Vol.213,1 Jul. 2021(下)
2021-08-29 來源:Goal Science
本期包含金屬材料領域論文11篇,涵蓋了金屬玻璃、增材制造、高熵合金等,國內科研單位包括北京科技大學等(通訊作者單位)。
Vol. 213 目錄
1. Microstructural and compositional design principles for Mo-V-Nb-Ti-Zr multi-principal element alloys: a high-throughput first-principles study
Mo-V-Nb-Ti-Zr多主元合金組織和成分設計的高通量第一性原理研究
2. Microstructure and properties of NbVZr refractory complex concentrated alloys
NbVZr合金的組織與性能研究
3. Nanoporosity evolution during dealloying: Interplay between chemical dissolution, material defects, coarsening and local structural rearrangements over long timescales
脫合金化過程中化學溶解、材料缺陷、粗化和局部結構重排在長時間尺度上的相互作用研究
4. Noble gas bubbles in bcc metals: Ab initio-based theory and kinetic Monte Carlo modeling
BCC金屬中惰性氣泡的第一性原理計算和動力學蒙特卡羅模擬
5. Novel class of nanostructured metallic glass films with superior and tunable mechanical properties
具有優越和可調力學性能的新型納米結構金屬玻璃薄膜
6. Optimizing the cellular automata finite element model for additive manufacturing to simulate large microstructures
增材制造大面積組織的元胞自動機有限元模型優化
7. Shear fracture in bulk metallic glass composites
塊體金屬玻璃復合材料的剪切斷裂機理研究
8. Simulations of primary damage in a High Entropy Alloy: Probing enhanced radiation resistance
基于對初級損傷的模擬探究高熵合金的抗輻照機理
9. Strain hardening mediated by coherent nanoprecipitates in ultrahigh-strength steels
共格納米析出對超高強度鋼應變硬化的影響
10. Tool-workpiece stick-slip conditions and their effects on torque and heat generation rate in the friction stir welding
攪拌摩擦焊接過程中的工具-工件粘滑狀態及其對扭矩和產熱率的影響
11. Twin-boundary assisted crack tip plasticity and toughening in lamellar γ-TiAl
孿晶界對層狀γ-TiAl裂紋尖端塑性的影響及其增韌作用研究
ACTA
Vol. 213,1 Jul. 2021, 116958
1. Microstructural and compositional design principles for Mo-V-Nb-Ti-Zr multi-principal element alloys: a high-throughput first-principles study
Mo-V-Nb-Ti-Zr多主元合金組織和成分設計的高通量第一性原理研究
Zhidong Leong?, Upadrasta Ramamurty?, Teck Leong Tan?
Z. Leong:leong_zhidong@ihpc.a-star.edu.sg
U. Ramamurty:uram@ntu.edu.sg
T.L. Tan:tantl@ihpc.a-star.edu.sg
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116958
摘要
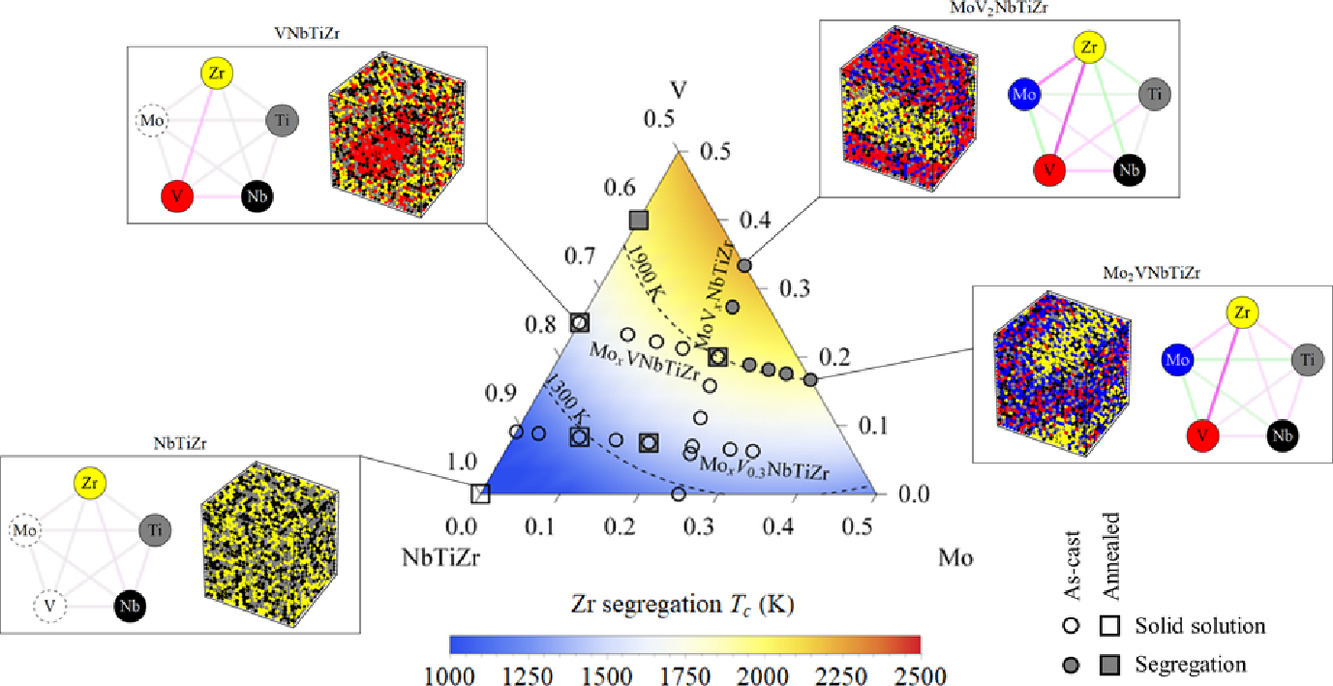
由于多主元合金具有廣闊的成分空間,因此對其進行組織設計和優化十分困難。我們對Mo-V-Nb-Ti-Zr多主元合金進行了高通量第一性原理研究,以深入了解這一體系原子尺度的微觀結構。借助蒙特卡羅模擬,我們揭示了多主元合金在廣闊組成空間中微觀結構的控制原理,包括非等原子比的二元、三元和四元合金。基于完全固溶體的Hume-Rothery規則,我們提出了一個定量表達式來從組成預測固溶的形成。我們的模型結果與大量實驗觀測一致,并對成分空間中未探索的區域提供了預測。該工作從元素的偏聚和團簇傾向的角度闡明了多主元合金的微觀結構,為具有優異性能多主元合金的設計提供了指導。
ACTA
Vol. 213,1 Jul. 2021, 116919
2. Microstructure and properties of NbVZr refractory complex concentrated alloys
NbVZr合金的組織與性能研究
Mu Li, Zhaohan Zhang, Arashdeep S. Thind, Guodong Ren, Rohan Mishra, Katharine M Flores
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116919
摘要
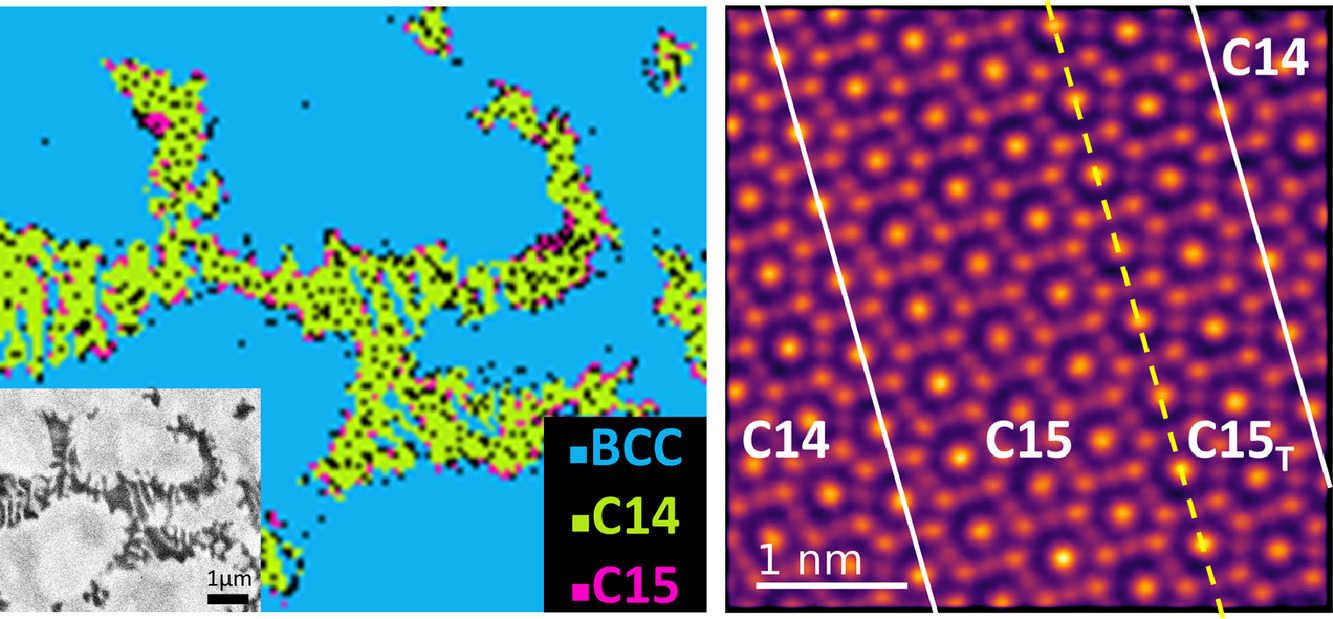
我們對等原子比NbVZr合金的組織和力學性能進行了研究。鑄態和激光處理樣品均表現為BCC枝晶固溶體,枝晶間存在六方C14和立方C15 Laves相。我們基于第一性原理計算,對Laves相的穩定性進行了討論,發現Nb能夠提高C14和C15相的穩定性。通過納米壓痕和對變形樣品的TEM表征,我們發現Laves相能夠阻礙位錯運動,提高材料強度。我們在Laves相區域發現了大量的層錯,這與第一性原理預測的低層錯能吻合,并能夠提高材料塑性。本研究為基于高通量方法系統研究難熔復雜合金中金屬間化合物的穩定性提供了范例。這些金屬間化合物對合金的綜合力學性能具有重要作用。
ACTA
Vol. 213,1 Jul. 2021, 116974
3. Nanoporosity evolution during dealloying: Interplay between chemical dissolution, material defects, coarsening and local structural rearrangements over long timescales
脫合金化過程中化學溶解、材料缺陷、粗化和局部結構重排在長時間尺度上的相互作用研究
Aditya Shankar Sandupatla, Abhijit Chatterjee
A. Chatterjee:abhijit@che.iitb.ac.in
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116974
摘要
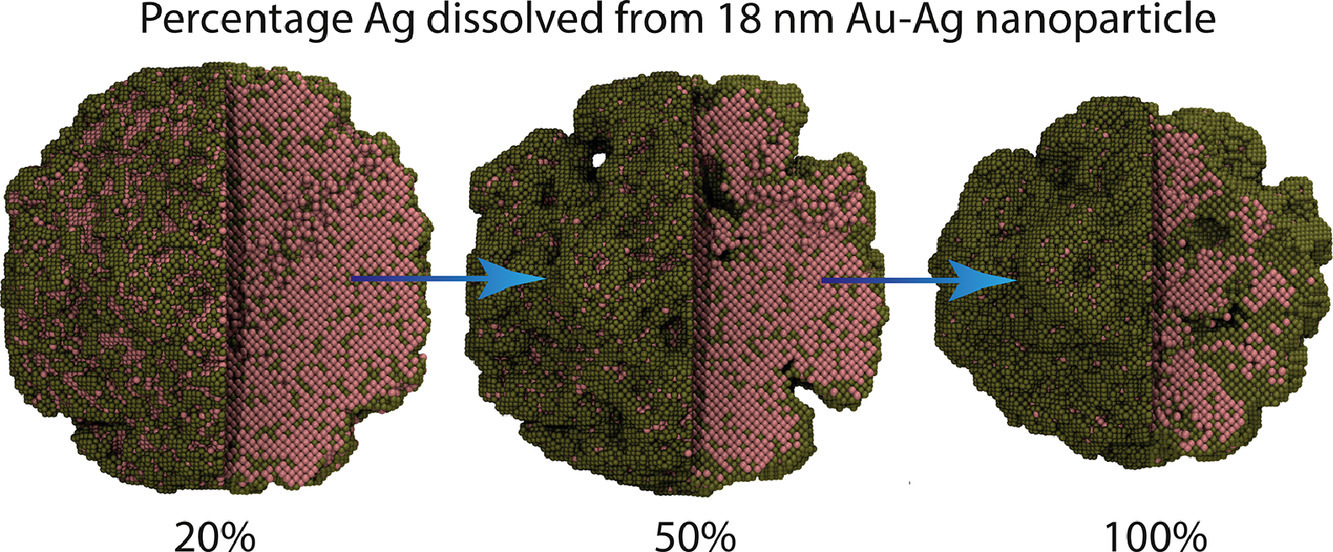
合金的選擇性溶解/脫合金化是合成納米多孔結構的常用方法。在幾分鐘的脫合金化過程中,材料的組織結構演化涉及化學溶解、紐帶形成、紐帶粗化、局部塌陷和缺陷形成的復雜相互作用。紐帶松弛的時間尺度在皮秒-納秒量級,而溶解的時間尺度在秒量級。本研究中,我們建立了一種新的多尺度框架,將晶格動力學蒙特卡羅方法(KMC)和分子動力學(MD)進行了結合。我們的算法對時間尺度進行了分割,發現了以下關鍵特征:(1)在溶解過程中不發生紐帶斷裂 (2) 模型可以獲得比KMC模型直徑粗10倍的紐帶 (3) 溶解50-60%時表面積最大 (4) 紐帶斷裂導致了粒子收縮 (5) 溶解50%以上,孔隙率基本保持恒定 (6)位錯密度隨著電活性原子溶解的增多而增加。此外,我們也研究了粒子尺寸、溫度、合金成分和電位的影響。以上研究表明,在模擬合金選擇性溶解過程時,考慮紐帶的持續松弛是十分必要的。
ACTA
Vol. 213,1 Jul. 2021, 116961
4. Noble gas bubbles in bcc metals: Ab initio-based theory and kinetic Monte Carlo modeling
BCC金屬中惰性氣泡的第一性原理計算和動力學蒙特卡羅模擬
Chao Jiang?, Yongfeng Zhang, Larry K. Aagesen, Andrea M. Jokisaari, Cheng Sun, Jian Gan
C. Jiang:chao.jiang@inl.gov
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116961
摘要
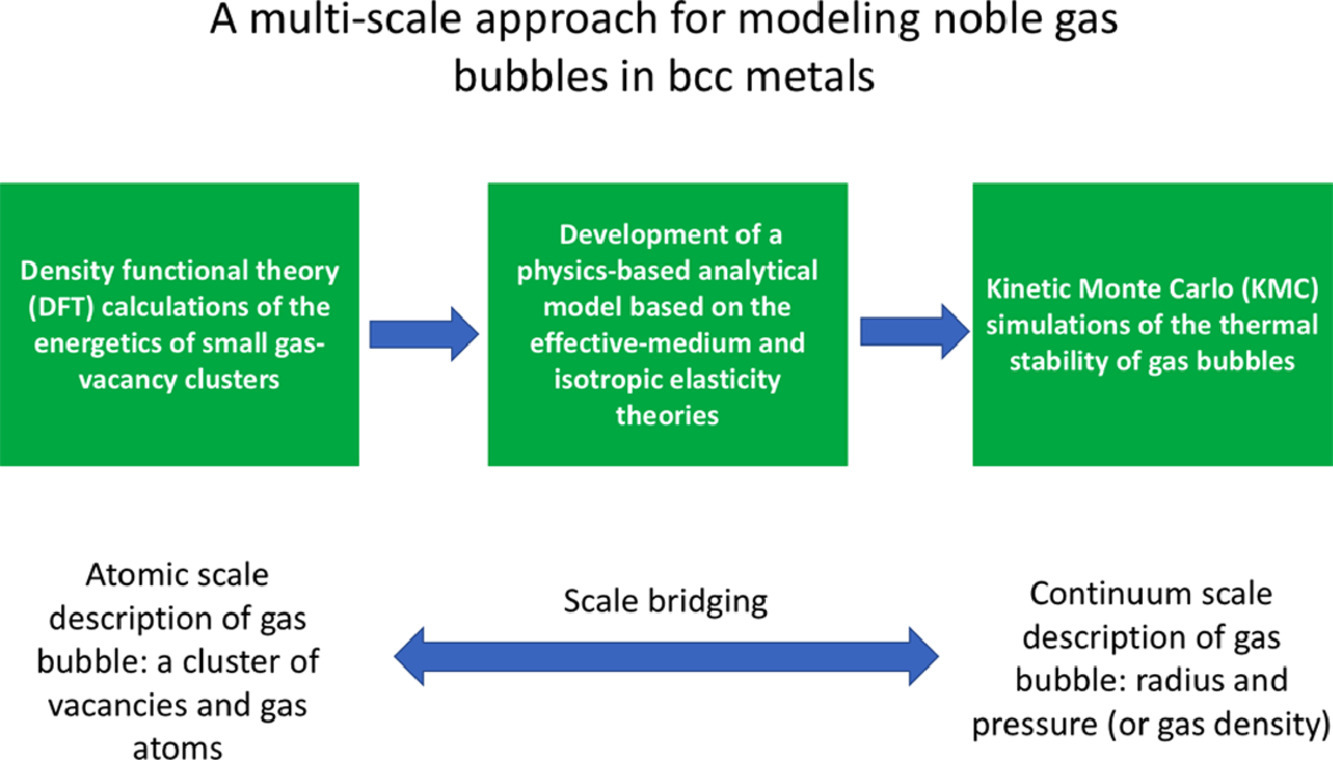
了解稀有氣體與金屬的相互作用對核反應堆的抗輻照結構材料設計具有重要意義。我們提出了一個普適的理論,用于描述He、Ne、Ar、Kr等惰性氣泡在5B (V, Nb, Ta), 6B (Cr, Mo, W)和8B (Fe)族bcc金屬中的能量狀態。模型基于有效介質和各向同性彈性理論,并通過密度泛函理論(DFT)對氣體-空位團簇的計算對模型參數進行了量化。通過將我們的模型與蒙特卡羅模擬結合,我們預測了惰性氣泡的壽命和Ostwald熟化。研究發現,bcc金屬中的Ne、Ar、Kr泡的熱穩定性比He泡高得多,能夠較好地抑制Ostwald熟化。我們進一步闡明了大原子序數惰性氣泡穩定的原因。我們的理論發現與退火條件下He泡超晶格(GBS)粗化的實驗觀察一致,并為bcc U-Mo合金中裂變GBS在高溫下的異常穩定提供了新的見解。研究的計算結果與文獻中已有的熱氦脫附光譜實驗結果比較吻合。
ACTA
Vol. 213,1 Jul. 2021, 116955
5. Novel class of nanostructured metallic glass films with superior and tunable mechanical properties
具有優越和可調力學性能的新型納米結構金屬玻璃薄膜
M. Ghidelli?, A. Orekhov, A. Li Bassi, G. Terraneo, P. Djemia, G. Abadias, M. Nordd, A. Béché, N. Gauquelin, J. Verbeeck, J.-P. Raskin, D. Schryvers, T. Pardoen, H. Idrissi?
M. Ghidelli:matteo.ghidelli@lspm.cnrs.fr
H. Idrissi:hosni.idrissi@uclouvain.be
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116955
摘要
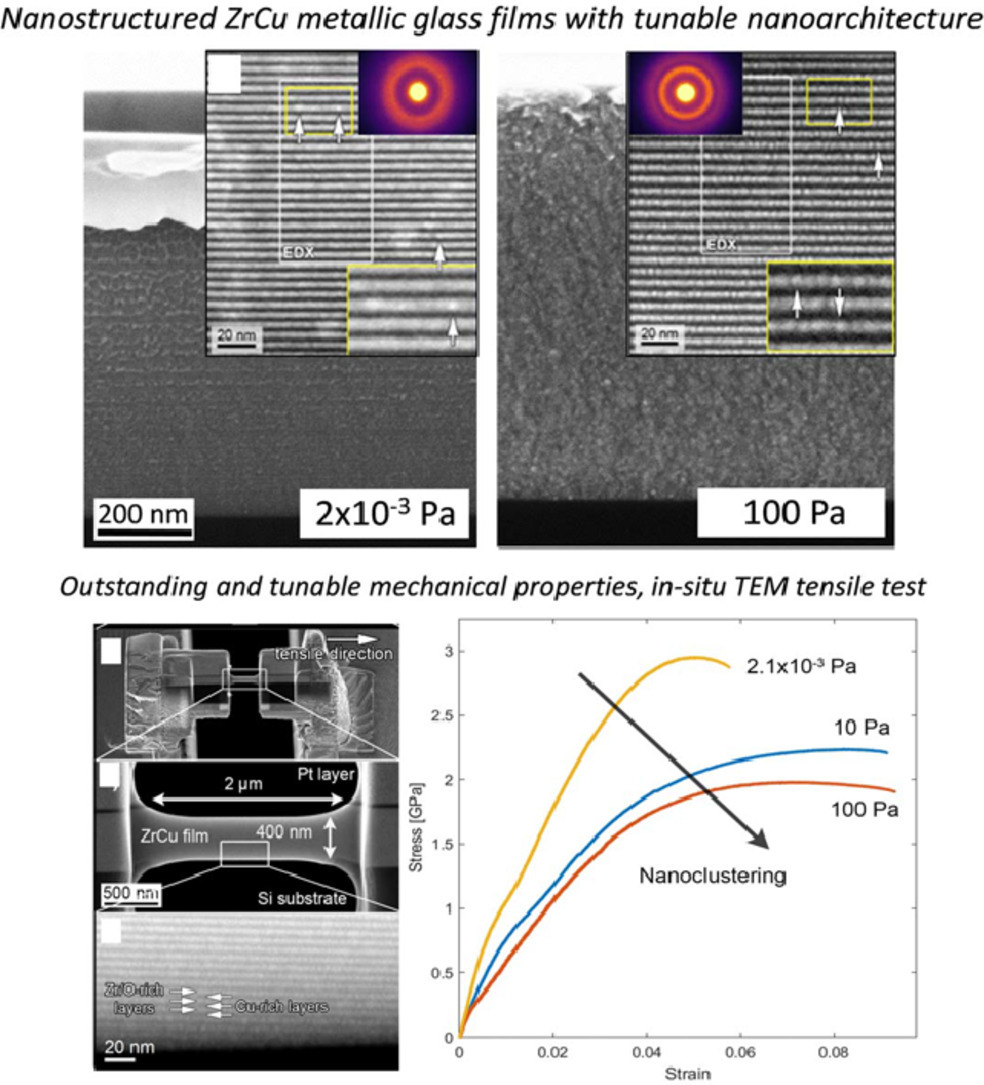
我們利用脈沖激光沉積方法制備得到了一種新型的具有優良力學性能的納米結構Zr50Cu50 (at.%)金屬玻璃薄膜。通過對工藝進行調控,可以合成多種薄膜結構,包括致密非晶、嵌有納米晶的非晶和非晶納米顆粒等。我們發現了一種獨特的致密自組裝納米層狀原子排列結構,即交替的富Cu和富Zn/O納米層組成的非晶態或晶態-非晶態復合結構。這種納米結構具有優越的力學性能,硬度達10GPa,彈性模量達140 GPa,總斷裂伸長率>9%。并且這種優異的強度/延性平衡還可以通過薄膜結構實現進一步調控。以上結果對高性能納米金屬玻璃薄膜合成具有重要意義,這一材料在微電子和涂裝領域可能具有良好的應用潛力。
ACTA
Vol. 213,1 Jul. 2021, 116930
6. Optimizing the cellular automata finite element model for additive manufacturing to simulate large microstructures
增材制造大面積組織的元胞自動機有限元模型優化
Kirubel Teferr?, David J. Rowenhorst
K. Teferra:kirubel.teferra@nrl.navy.mil
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116930
摘要
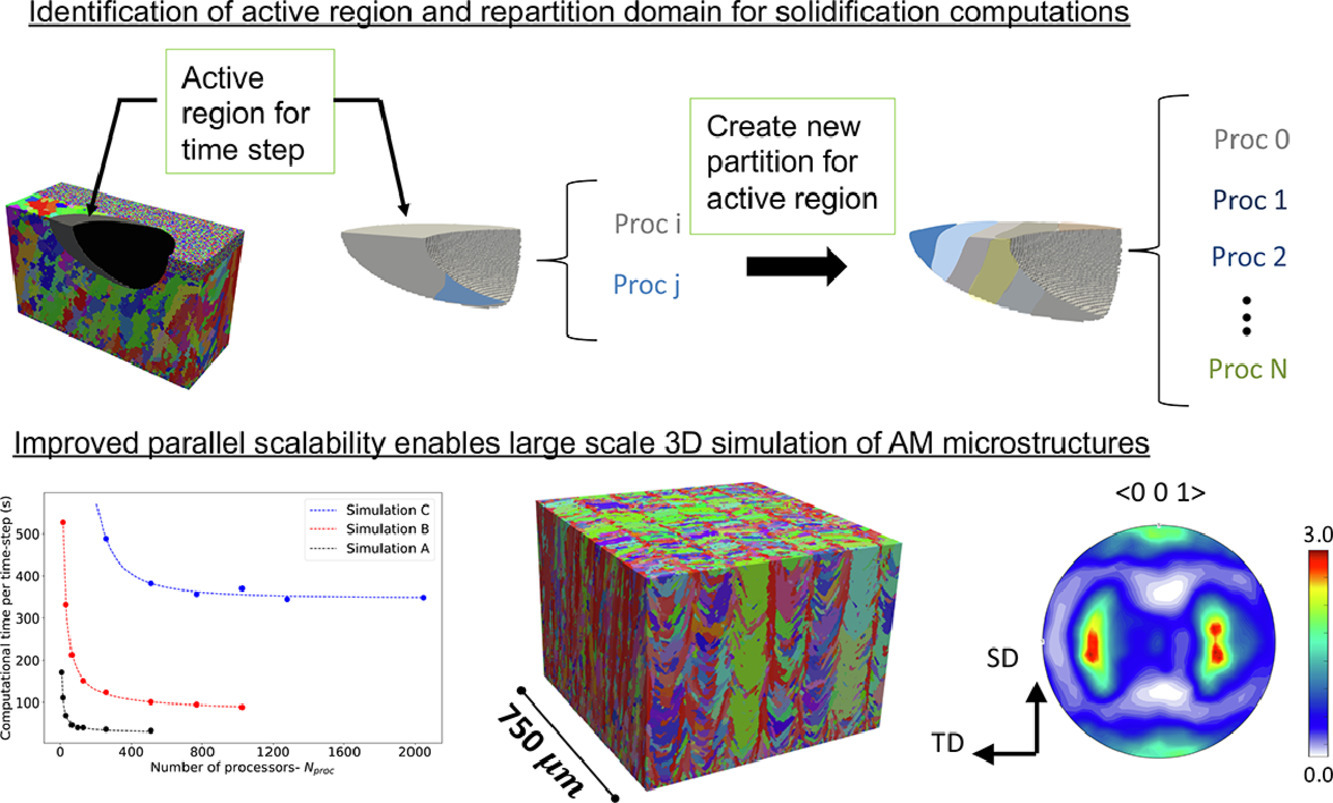
我們提出了一種元胞自動機有限元(CAFE)模型,用于模擬增材制造中的材料凝固過程。在任何時間,熔池都是一個高度局域的高能區域。溫度場隨時間演化的尺度遠大于晶粒凝固的時間尺度。我們提出了一種將時間尺度離散化的方法,從而在激光掃描的每個時間步長獨立對凝固進行分析。在每個時間步長中,材料只有一小部分過冷但尚未凝固的區域。我們找到這一區域,并建立分區,使得凝固計算的算力分配達到平衡。研究表明,這一方法通過并行運算極大地提高了計算效率。這種改進對三維多晶組織的形貌和織構模擬具有重要意義。我們用模型對316L不銹鋼的激光粉末熔煉過程進行了驗證,模擬得到的多晶組織形貌和織構與實驗數據吻合較好。我們對不同的激光掃描模式進行了模擬,以闡明其對材料組織特征的影響。
ACTA
Vol. 213,1 Jul. 2021, 116963
7. Shear fracture in bulk metallic glass composites
塊體金屬玻璃復合材料的剪切斷裂機理研究
Devashish Rajpoot, R. Lakshmi Narayan?, Long Zhang?, Punit Kumar, Haifeng Zhang, Parag Tandaiya?, Upadrasta Ramamurty
R.L. Narayan:rlnarayan@mse.iitd.ac.in
L. Zhang:zhanglong@imr.ac.cn(沈陽金屬所)
P. Tandaiya:parag.ut@iitb.ac.in
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116963
摘要
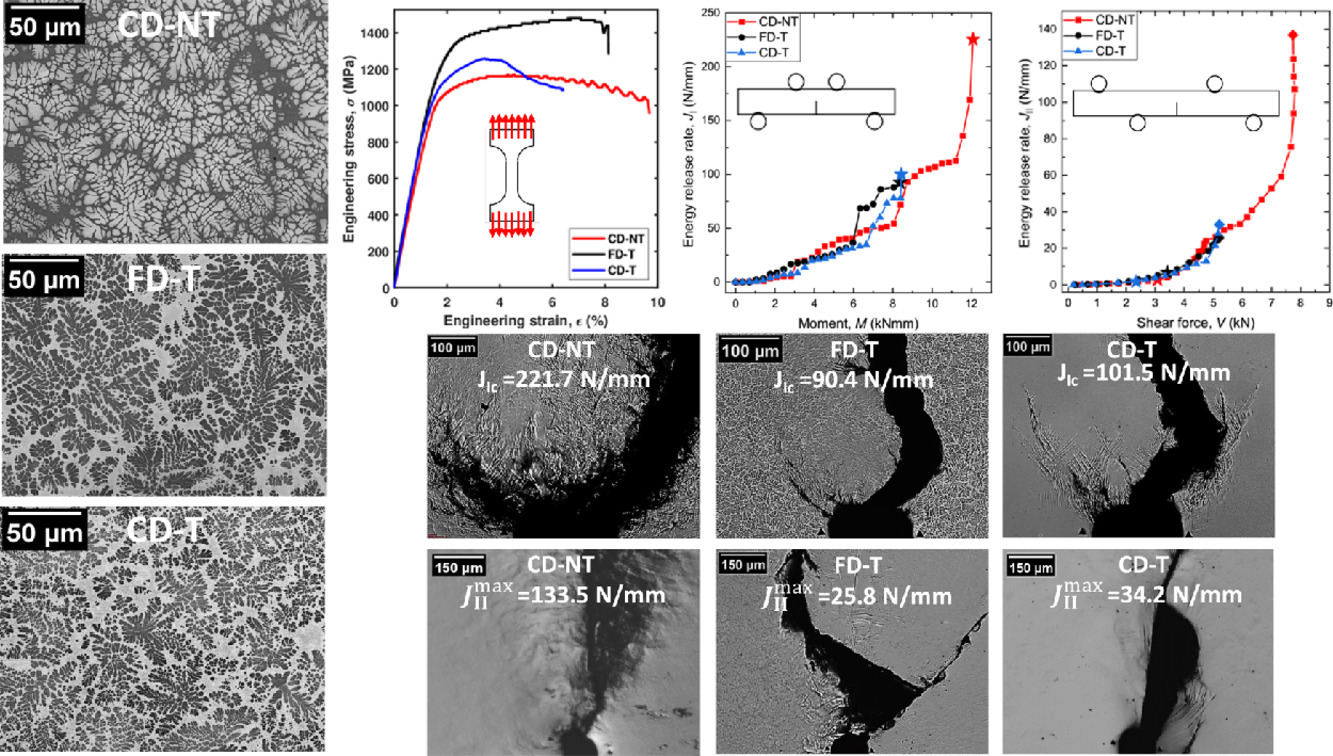
我們對含有相變或非相變β-Ti枝晶的塊體金屬玻璃基復合材料(BMGCs) 在剪切和張開模式下的斷裂行為進行了研究。實驗結果表明,材料在II型斷裂模式下的韌性顯著低于I型斷裂模式,這主要是由于前者處于剪切應力狀態下,容易產生剪切帶。I型模式下的裂紋擴展不明顯,而II型模式下裂紋發生了一定擴展。盡管相變β-Ti具有較強的應變硬化能力,能夠提高材料延性,但在兩種斷裂模式下,含有非相變粗枝晶的BMGCs均表現出了更高的韌性。I型和II型試樣的斷口表面特征和尖端剪切帶形貌表明,盡管枝晶和剪切帶間存在相互作用,但金屬玻璃基復合材料的斷裂準則和斷裂機制與金屬玻璃相同。我們基于非晶基體的弛豫焓、枝晶尺寸和枝晶的相變趨勢對剪切帶向裂紋轉變的影響,對BMGCs的斷裂行為進行了解釋。以上研究對提高含相變枝晶BMGCs的斷裂韌性具有指導作用。
ACTA
Vol. 213,1 Jul. 2021, 116951
8. Simulations of primary damage in a High Entropy Alloy: Probing enhanced radiation resistance
基于對初級損傷的模擬探究高熵合金的抗輻照機理
O.R. Deluigi, R.C. Pasianot, F.J. Valencia, A. Caro, D. Farkas, E.M. Bringa?
E.M. Bringa:ebringa@yahoo.com
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116951
摘要
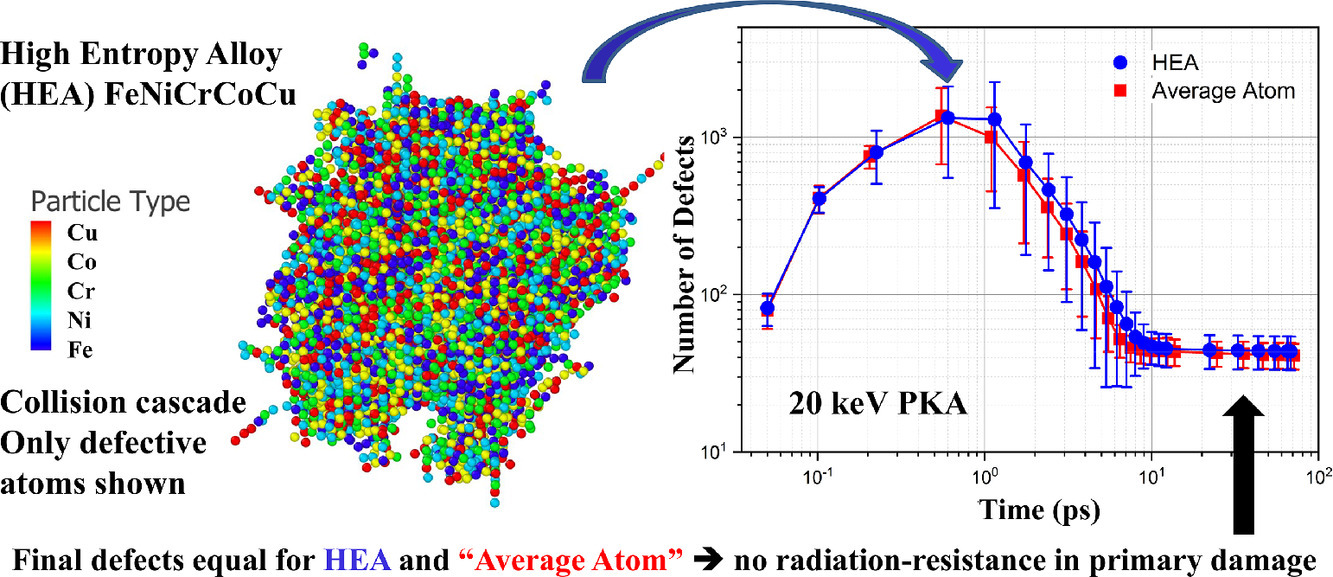
高熵合金(High Entropy Alloys, HEA)作為一種可能的抗輻照材料而受到廣發關注。高熵合金具有一些獨特的特征,比如由于原子無序排列導致熱導率低,以及化學成分復雜引起某些特殊缺陷等。本研究中,我們采用分子動力學模擬了FCC 等原子比FeNiCrCoCu高熵合金和純鎳中的級聯損傷,以研究材料在輻照早期(0.1ns)的損傷行為。模擬條件為室溫,撞擊粒子能量為10、20、40eV。我們通過修正精確描述了級聯過程中原子的短程相互作用。結果表明,在所有模擬條件下,高熵合金中的平均缺陷數都少于純Ni。然而,兩種材料中的Frenkel對、缺陷團簇尺寸分布等均可在誤差范圍內認為基本沒有差別。純Ni材料中的缺陷產生模型可以較好地預測合金中的剩余Frenkel對數量。這表明,實驗中觀察到的高熵合金的抗輻照能力可能并非是由于化學成分復雜導致初級損傷減少,而是由長時間缺陷演化引起。
ACTA
Vol. 213,1 Jul. 2021, 116984
9. Strain hardening mediated by coherent nanoprecipitates in ultrahigh-strength steels
共格納米析出對超高強度鋼應變硬化的影響
S. H. Jiang, X.Q. Xu, W. Li, B. Peng, Y. Wu, X.J. Liu, H. Wang?, X.Z. Wang, Z.P. Lu?
H. Wang:wanghui@ustb.edu.cn(北京科技大學)
Z.P. Lu:luzp@ustb.edu.cn, luzhaoping@163.com(北京科技大學)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116984
摘要
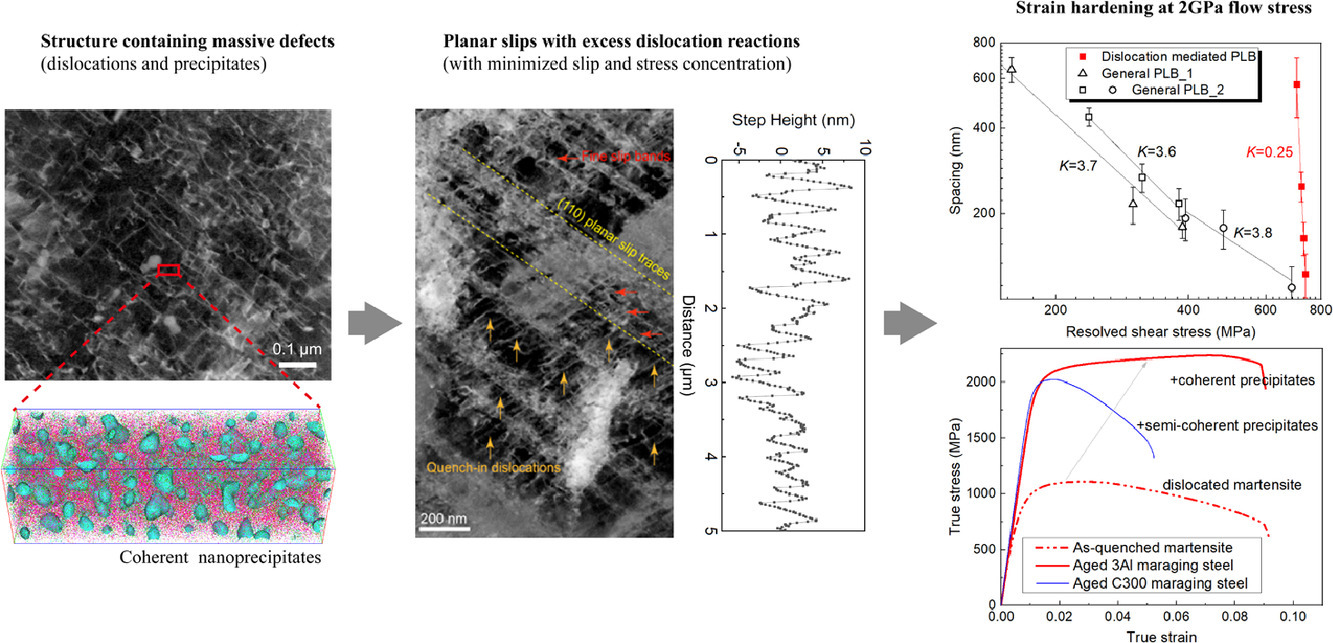
通過位錯或納米析出達成材料強化往往會受到強塑性平衡的限制,這在強度超過2GPa的材料中尤為明顯。本研究中,我們報道了一種通過調控不同晶格缺陷間的相互作用實現超高強度馬氏體鋼中持續應變硬化的機制。我們發現,快速析出的低錯配的B2 Ni(Al, Fe)有序相可以有效地抑制淬火位錯的回復。在塑性變形過程中,有序納米相引起的高切削應力不僅可以使得大量位錯在平面中移動,而且大幅增加了馬氏體中位錯的平均自由程。同時,位錯的平面滑移使得這些位錯與之前已經存在的位錯之間產生大量位錯反應,從而及時恢復因切割析出而減弱的局部切削應力。這種機制不僅減小了滑移集中和滑移帶內的共面位錯密度,而且促進了滑移帶細化,使得材料能夠實現2GPa的屈服強度和9%的斷裂延伸率。這一研究表明,通過調控材料中不同類型晶格缺陷間的相互作用,可以同時提高材料的強度和延性。
ACTA
Vol. 213,1 Jul. 2021, 116969
10. Tool-workpiece stick-slip conditions and their effects on torque and heat generation rate in the friction stir welding
攪拌摩擦焊接過程中的工具-工件粘滑狀態及其對扭矩和產熱率的影響
Xue Wang, Yanfei Gao?, Xun Liu, Martin McDonnell, Zhili Feng?
Y. Gao:ygao7@utk.edu
Z. Feng:fengz@ornl.gov
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116969
摘要
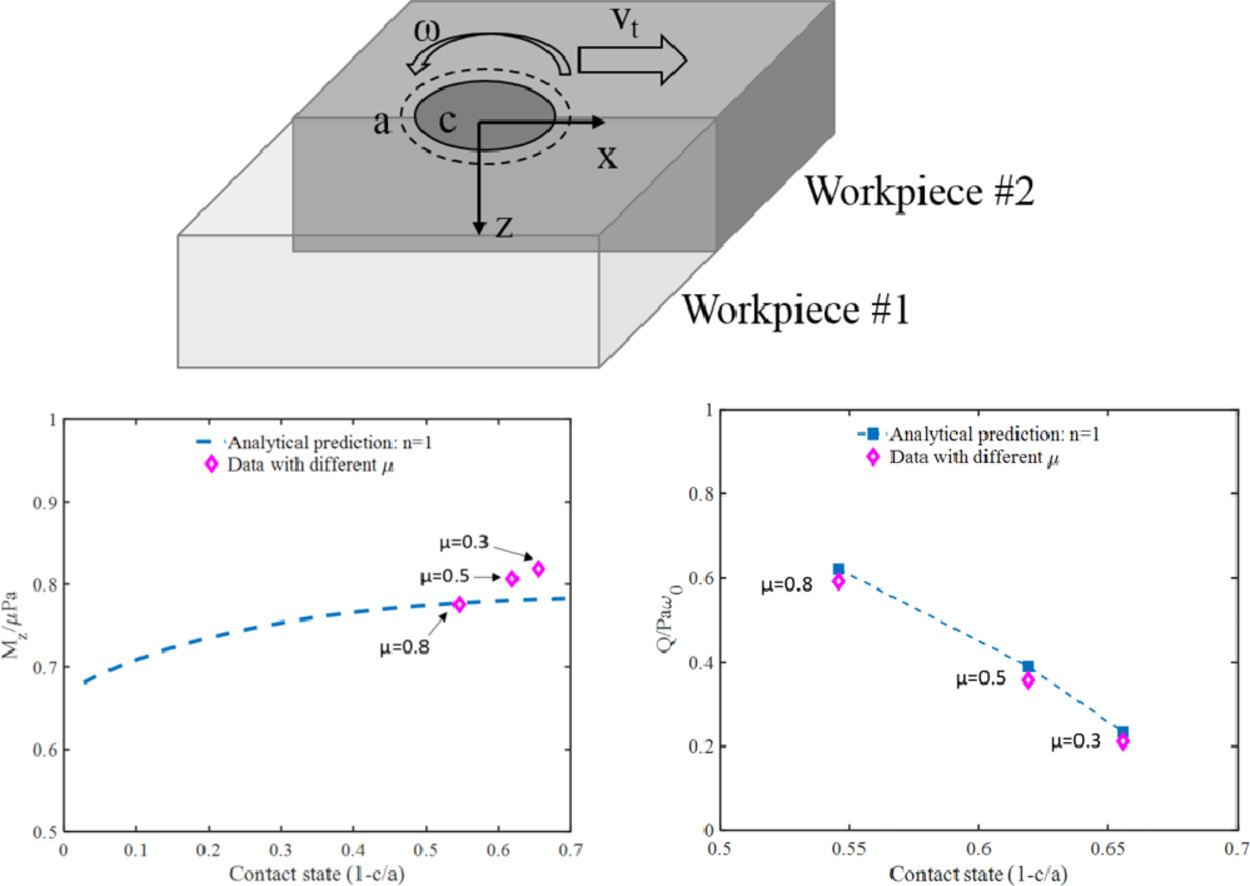
攪拌摩擦焊接(FSW)在固態連接過程中不需要熔化,可在各種工況和材料中應用,在汽車和航空航天工業中應用尤其廣泛。然而由于我們缺乏對工具-工件摩擦過程中材料組織演變和界面結合的深入理解,因此目前加工參數、材料性能、結合程度等之間的關系仍是經驗性的。雖然一般認為,工具-工件間的粘著和滑動是影響扭矩和產熱的主要因素,但界面場的定量測量卻十分困難。另一方面,基于計算流體力學(CFD)的數值模擬強烈依賴于界面壓力和剪切應力條件,只能通過中遠距離的溫度場來驗證模擬預測,但溫度場對界面摩擦行為不敏感。本文首先對兩種基于CFD的模擬方法和基于有限元的歐拉拉格朗日耦合(CEL)模型,進行了比較,其中CEL模型采用庫侖摩擦實現了粘著滑動的自發演化。之后,我們基于Hill-Bower相似關系建立了一個解析模型,模型解釋了為何在穩態條件下粘著-滑動分數會保持不變,并將粘著-滑動分數與工藝參數建立了聯系。我們進一步推導了轉矩和產熱率的無量綱函數,討論了各種數值方法的優缺點。研究表明,我們的解析模型與數值模擬和文獻實驗結果吻合良好。以上結果對焊接過程中的臨界應變速率和溫度場分析具有重要意義。
ACTA
Vol. 213,1 Jul. 2021, 116924
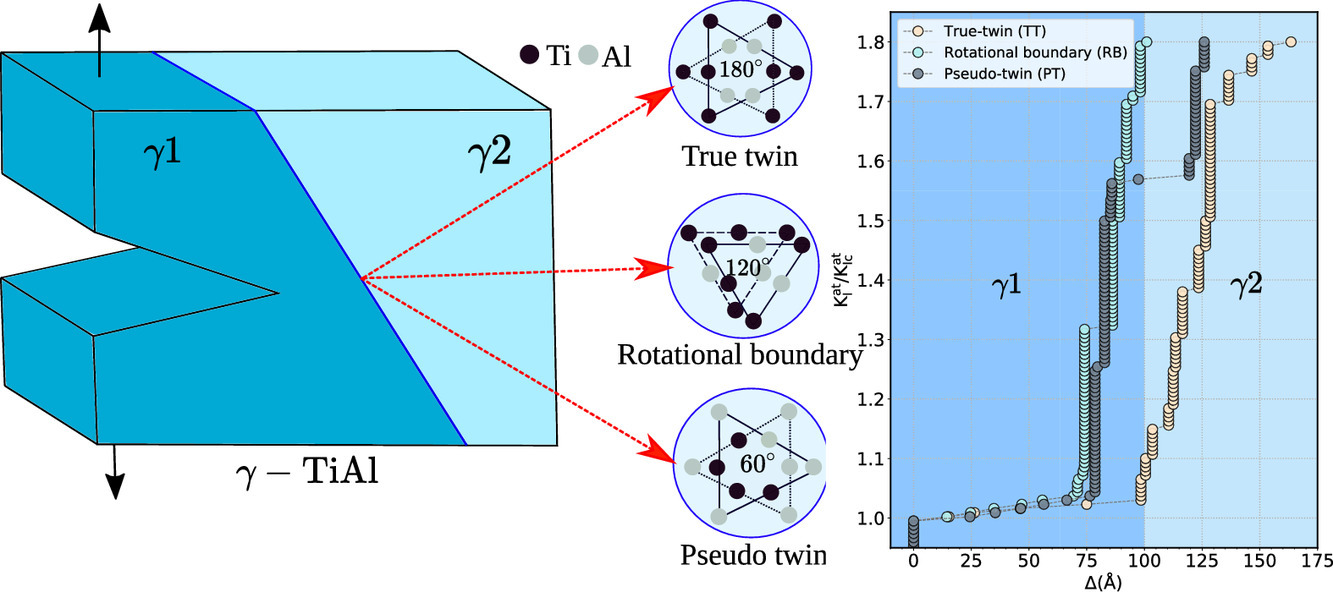
11. Twin-boundary assisted crack tip plasticity and toughening in lamellar γ-TiAl
孿晶界對層狀γ-TiAl裂紋尖端塑性的影響及其增韌作用研究
Anupam Neogi?, Rebecca Janisch?
A. Neogi:anupam.neogi@rub.de
R. Janisch:rebecca.janisch@rub.de, rebecca.janisch@icams.ruhr-uni-bochum.de
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116924
摘要
層狀γ -TiAl合金內部的孿晶界,包括真孿晶界(TT)、轉動孿晶界(RB)和偽孿晶界(PT)都能夠有效地強化組織。為設計具有優異力學性能的微觀組織,我們需要深入理解界面對斷裂行為的影響。為此,我們采用分子靜力學模擬結合線彈性斷裂力學分析,研究了不同孿晶界的局部晶格取向和原子結構對裂紋擴展的影響。研究表明,裂紋擴展方向對斷裂韌性和層間裂紋的擴展機制有重要影響。例如,TT、RB和PT面的<11-2]方向裂紋尖端能夠發射出大量位錯,而沿相反方向的裂紋則是脆性的。而對于穿層裂紋,其尖端則表現出明顯的韌性。在TT處,高應力條件寫,脆性裂紋能夠穿過界面傳播至近鄰的γ’ 相,而在RB和PT處,裂紋尖端發生鈍化,引起位錯發射和增韌。以上研究表明,改變界面的方向是調控層狀TiAl塑性和韌性的有效手段。