金屬頂刊雙語導(dǎo)讀丨Acta Mater. Vol.214,1 Aug. 2021(下)
2021-10-07 來源:GS_Metals

本期包含金屬材料領(lǐng)域論文10篇,涵蓋了馬氏體、奧氏體、高溫合金等,國內(nèi)科研單位包括燕山大學(xué)、重慶大學(xué)、上海交通大學(xué)等(通訊作者單位)。
Vol. 214 目錄
1. High pressure effect on the substructure and hardness of IF steel during martensitic transformation
高壓對IF鋼馬氏體相變組織和硬度的影響
2. Interaction between hydrogen and solute atoms in {10-12} twin boundary and its impact on boundary cohesion in magnesium
鎂{10-12}孿晶界處氫與溶質(zhì)原子的相互作用及其對晶界結(jié)合力的影響
3. Multiphase and multiphysics modeling of dendrite growth and gas porosity evolution during solidification
凝固過程中枝晶生長和氣孔演化的多相物理模型
4. Origins of size effects in initially dislocation-free single-crystal silver micro- and nanocubes
無位錯單晶銀微納米立方體中尺寸效應(yīng)的原因
5. Representative volume elements for plasticity and creep measured from high-resolution microscale strain fields
基于微觀應(yīng)變場的高分辨表征測量材料塑性和蠕變的代表體積元
6. Role of the local stress systems on microstructural inhomogeneity during semisolid injection
鑄造過程中局部應(yīng)力對微觀組織不均勻性的影響研究
7. Segmentation of experimental datasets via convolutional neural networks trained on phase field simulations
利用相場模擬訓(xùn)練的卷積神經(jīng)網(wǎng)絡(luò)實(shí)現(xiàn)對實(shí)驗(yàn)數(shù)據(jù)集的圖像分割
8. Studying the micromechanical behaviors of a polycrystalline metal by artificial neural networks
多晶金屬微觀力學(xué)行為的人工神經(jīng)網(wǎng)絡(luò)研究
9. Tailoring the metastable reversed austenite from metastable Mn-rich carbides
通過富錳碳化物調(diào)控亞穩(wěn)逆相變奧氏體
10. Understanding creep of a single-crystalline Co-Al-W-Ta superalloy by studying the deformation mechanism, segregation tendency and stacking fault energy
基于變形機(jī)制、合金元素偏聚和層錯能研究單晶Co-Al-W-Ta高溫合金的蠕變性能
ACTA
Vol. 214,1 Aug. 2021, 116978
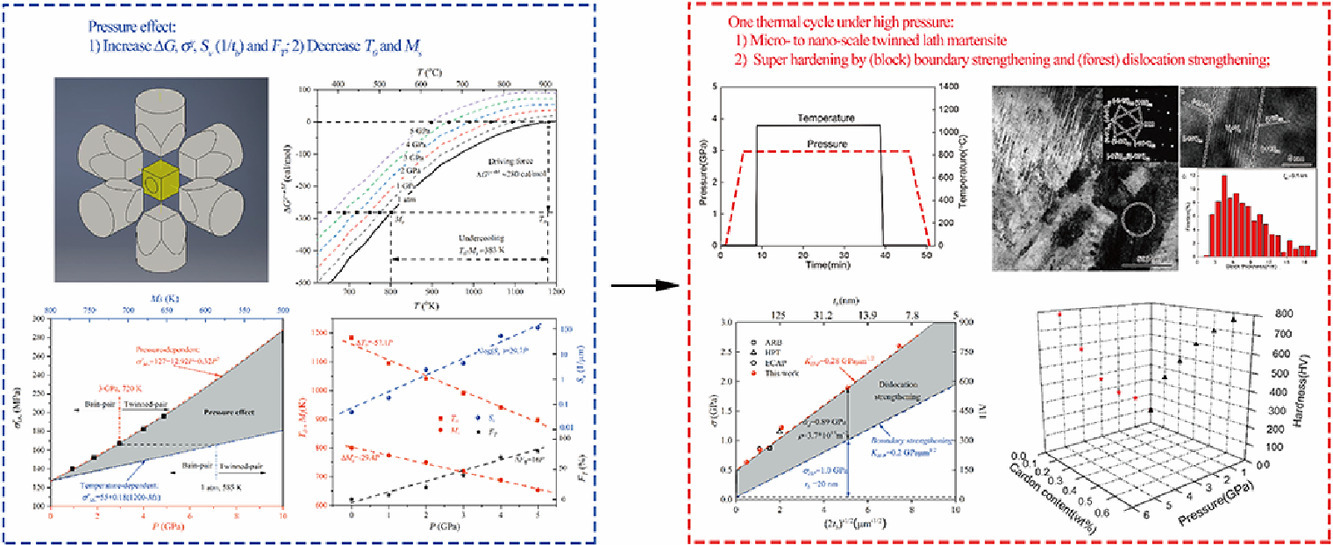
1. High pressure effect on the substructure and hardness of IF steel during martensitic transformation
高壓對IF鋼馬氏體相變組織和硬度的影響
Zuohua Wang, Haidong Sun, Changji Li, Ning Liu, Shuai Zhang, Pinwen Zhu, Dongli Yue, Hongwang Zhang?
H. Zhang:hwzhang@ysu.edu.cn(燕山大學(xué))
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116978
摘要
我們對1050°C保溫30 min,隨后10°C/s冷卻至室溫的IF鋼進(jìn)行了1- 5GPa等靜壓處理,并研究了這一過程中的組織演化和硬化。實(shí)驗(yàn)結(jié)果表明,材料中形成了典型的板條馬氏體,硬度從80HV大幅提高至780HV。馬氏體表現(xiàn)出板條束-板條塊-板條的層級結(jié)構(gòu),與奧氏體之間遵循經(jīng)典K-S取向關(guān)系。壓力對馬氏體變體的傾向和尺寸有調(diào)控作用。當(dāng)壓力從1 GPa增加到5 GPa時:(1)單變體馬氏體半條塊逐漸被同一Bain組的雙變體馬氏體半條塊取代 (2)與孿晶有關(guān)的變體逐漸增加(3)異體厚度從微米級減小到納米級。我們假設(shè)界面強(qiáng)化和位錯強(qiáng)化的貢獻(xiàn)可進(jìn)行線性疊加,對硬化機(jī)制進(jìn)行了分析。以上研究表明,高壓作為一種不依賴合金元素的馬氏體相變調(diào)控方法,具有巨大的開發(fā)潛力。
ACTA
Vol. 214,1 Aug. 2021, 117009
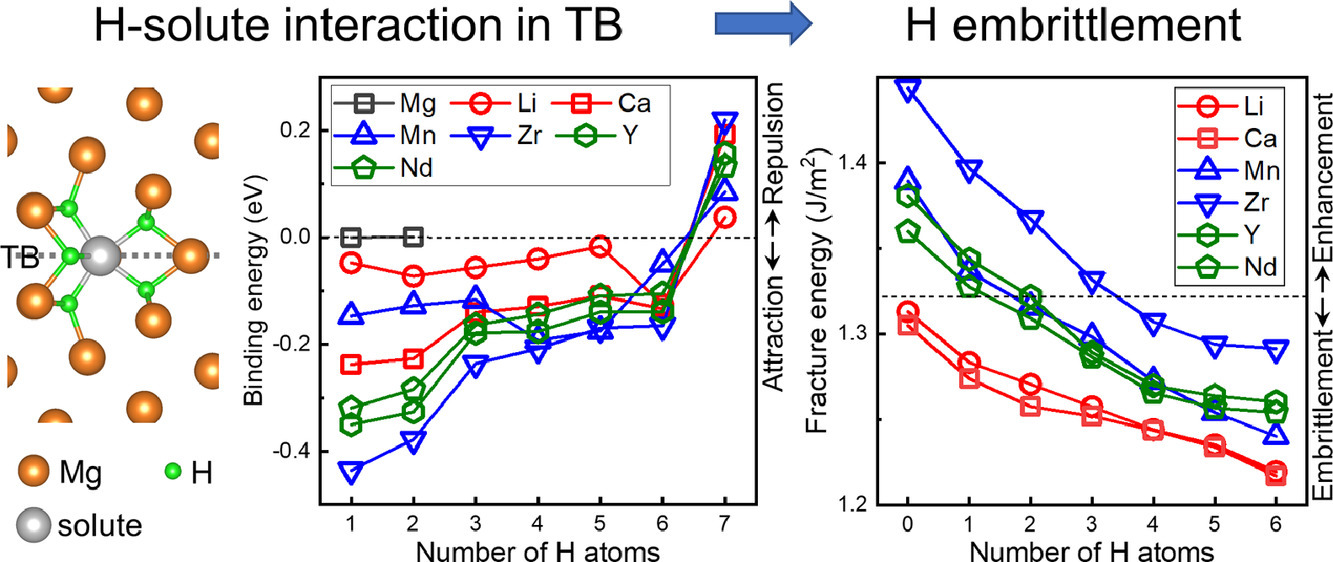
2. Interaction between hydrogen and solute atoms in {10-12} twin boundary and its impact on boundary cohesion in magnesium
鎂{10-12}孿晶界處氫與溶質(zhì)原子的相互作用及其對晶界結(jié)合力的影響
Zhifeng Huang, Jian-Feng Nie?
J.-F. Nie:jianfeng.nie@monash.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117009
摘要
氫是鎂合金中常見的雜質(zhì)或添加元素,對于沿晶界的裂紋擴(kuò)展有重要影響。關(guān)于氫原子與晶界偏聚的其他合金元素間的相互作用及其對鎂合金界面結(jié)合力的影響目前尚不清楚。我們通過第一性原理計(jì)算,對氫與Mg合金中常見的18種合金元素在{10-12}孿晶界的相互作用,及其對{10-12}孿晶界結(jié)合力的影響進(jìn)行了研究。結(jié)果表明,氫傾向于與Mg晶格和孿晶界中的Li、Ca、Mn、Zr、Y、La、Pr、Nd、Sm、Gd、Tb、Dy、Ho等溶質(zhì)原子結(jié)合,而不易與Al、Sn、Bi、Zn、Ag結(jié)合。因此,當(dāng){10-12}孿晶界處存在Al、Bi、Zn、Ag等元素時,氫不易向?qū)\晶界處偏聚;而當(dāng)孿晶界處已有 Li、Ca、Mn、Zr、Y、Nd等元素的偏聚時,氫很容易與他們形成氫-溶質(zhì)原子對。偏聚溶質(zhì)原子及其與氫原子的相互作用對孿晶界結(jié)合力的增強(qiáng)或減弱與Mg原子和偏聚溶質(zhì)原子間的電子相互作用密切相關(guān)。Mn、Zr、Y、Nd等原子在沒有氫偏聚的條件下,由于溶質(zhì)原子d電子與Mg原子p電子間的強(qiáng)烈相互作用,可以顯著增強(qiáng)孿晶界的結(jié)合力。然而,與氫原子形成原子對后,發(fā)生的電子轉(zhuǎn)移會減弱這種強(qiáng)化效果,從而使界面的抗斷裂能力發(fā)生劣化。本研究從氫與合金元素相互作用的角度揭示了氫致界面斷裂,這對于深入理解鎂合金中的氫脆具有重要意義。
ACTA
Vol. 214,1 Aug. 2021, 117005
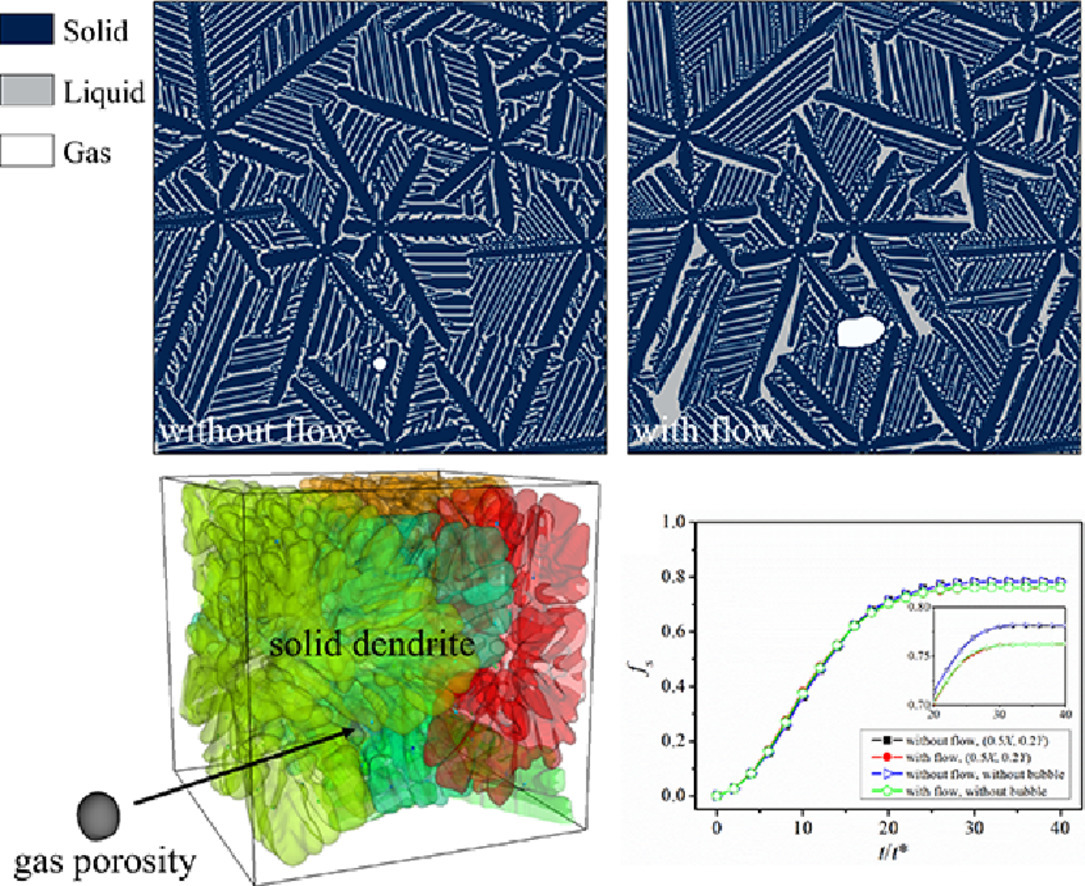
3. Multiphase and multiphysics modeling of dendrite growth and gas porosity evolution during solidification
凝固過程中枝晶生長和氣孔演化的多相物理模型
Ang Zhang?, Zhipeng Guo, Bin Jiang?, Jinglian Du, Cuihong Wang, Guangsheng Huang, Dingfei Zhang, Feng Liu, Shoumei Xiong, Fusheng Pan
A. Zhang:angzhang@cqu.edu.cn(重慶大學(xué)/清華大學(xué))
B. Jiang: jiangbinrong@cqu.edu.cn(重慶大學(xué))
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117005
摘要
氣孔缺陷會極大地劣化鑄件的力學(xué)性能。本研究中,我們建立了固-液-氣多相場晶格-玻爾茲曼模型來描述凝固過程中復(fù)雜的多相相互作用。模型放寬了純金屬體系假設(shè),簡化了氣泡形狀和純擴(kuò)散條件,可以考慮固相生長、氣泡運(yùn)動、界面變形、成分輸運(yùn)、熔體流動以及合金溶質(zhì)和溶解氣體的配分。我們從質(zhì)量守恒、雙相模型映射、氣泡動力學(xué)等方面對模型進(jìn)行了驗(yàn)證。通過將其與其他四種模型以及實(shí)驗(yàn)進(jìn)行比較,進(jìn)一步評價了模型的有效性。模型成功地描述了鎂合金中氣孔與枝晶間的相互作用。我們通過定量分析熔體過冷度、界面流動性、氣泡壓力等特征參數(shù)對相分?jǐn)?shù)的影響,深入討論了多相平衡問題。該模型是對現(xiàn)有模型的補(bǔ)充,特別適合用于涉及固-液-氣多相的復(fù)雜問題。
ACTA
Vol. 214,1 Aug. 2021, 117020
4. Origins of size effects in initially dislocation-free single-crystal silver micro- and nanocubes
無位錯單晶銀微納米立方體中尺寸效應(yīng)的原因
Claire Griesbach, Seog-Jin Jeon, David Funes Rojas, Mauricio Ponga, Sadegh Yazdi, Siddhartha Pathak, Nathan Mara, Edwin L. Thomas, Ramathasan Thevamaran?
R. Thevamaran:thevamaran@wisc.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117020
摘要
我們通過多步形核-長大工藝制備得到了無位錯的銀納米立方,該材料在隨后的微柱壓縮試驗(yàn)中表現(xiàn)出了驚人的屈服強(qiáng)度——高達(dá)銀理論強(qiáng)度的四分之一。材料極高的強(qiáng)度和屈服瞬間應(yīng)變是單晶樣品位錯自發(fā)形核的結(jié)果。若樣品微柱是通過聚焦離子束制備的,則壓縮時不會發(fā)生劇烈的應(yīng)變爆發(fā),其屈服強(qiáng)度只有對比組樣品的四分之一。無論測試前樣品的缺陷狀態(tài)如何,尺寸效應(yīng)都很明顯——屈服強(qiáng)度隨著樣品尺寸的減小而增加。由于位錯貧乏和單源機(jī)制都不能解釋尺寸效應(yīng)對無位錯樣品屈服強(qiáng)度的影響,因此我們通過實(shí)驗(yàn)觀測和分子靜力學(xué)模擬從位錯形核機(jī)制的角度進(jìn)行了研究。研究表明,破壞材料對稱性的因素,如表面缺陷、邊緣圓度、樣品形狀或高空位濃度,都會影響位錯形核,從而導(dǎo)致尺寸對無位錯樣品的屈服強(qiáng)度產(chǎn)生影響。
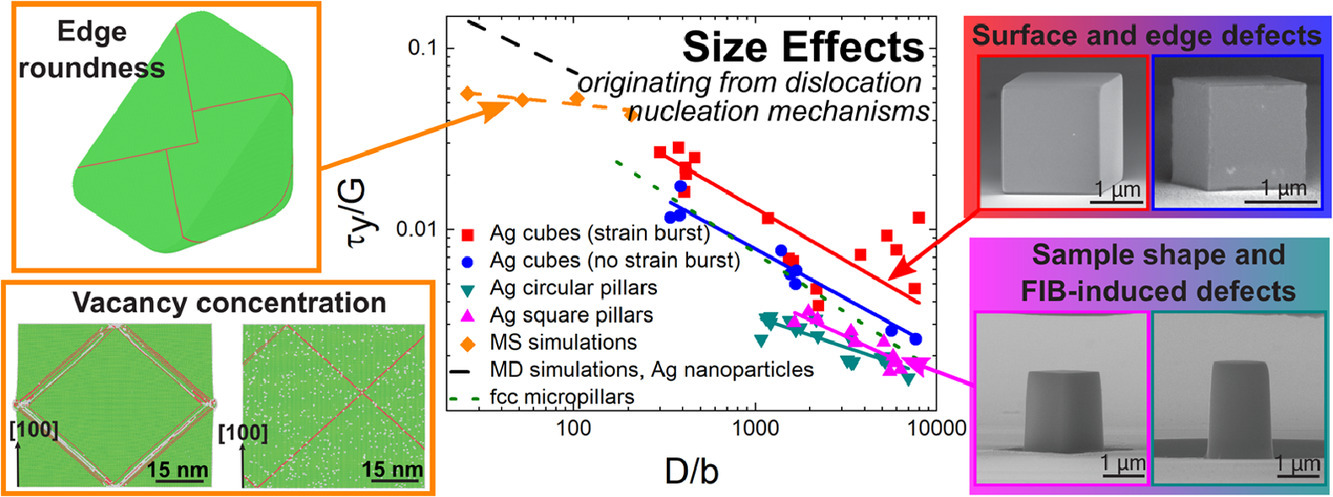
ACTA
Vol. 214,1 Aug. 2021, 117021
5. Representative volume elements for plasticity and creep measured from high-resolution microscale strain fields
基于微觀應(yīng)變場的高分辨表征測量材料塑性和蠕變的代表體積元
R.B. Vieira, H. Sehitoglu, J. Lambros?
J. Lambros:lambros@illinois.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117021
摘要
均勻化方法被廣泛應(yīng)用于放大顯微尺度的數(shù)值結(jié)果,以預(yù)測材料的宏觀性能。均勻化通常是基于代表體積元(RVE)進(jìn)行的,因此,準(zhǔn)確測量RVE尺寸和闡明RVE尺寸的影響因素是材料建模成功的關(guān)鍵。本研究中,我們通過不同參數(shù)條件下的塑性和蠕變實(shí)驗(yàn)對奧氏體不銹鋼的RVE尺寸進(jìn)行了實(shí)驗(yàn)測定。我們通過高分辨率數(shù)字圖像關(guān)聯(lián)(DIC)方法,對材料在微觀尺度上的殘余應(yīng)變不均勻性進(jìn)行了識別。此外,結(jié)合背散電子電子衍射(EBSD)獲取的材料的表面組織信息,可以進(jìn)一步對晶界附近的局域應(yīng)變進(jìn)行區(qū)分,從而對引起應(yīng)變積累的變形機(jī)制進(jìn)行定量分析。最后,我們通過對比不同加載參數(shù)下的RVE尺寸,以及局部正應(yīng)變和剪應(yīng)變的相對比例,研究了晶界滑移與應(yīng)變不均勻性之間的關(guān)系。高溫下,晶界滑移是材料的主要變形機(jī)制,此時RVE尺寸約為平均晶粒尺寸的4-6倍,明顯小于不明顯發(fā)生滑移的樣品(約為平均晶粒尺寸的10倍)。
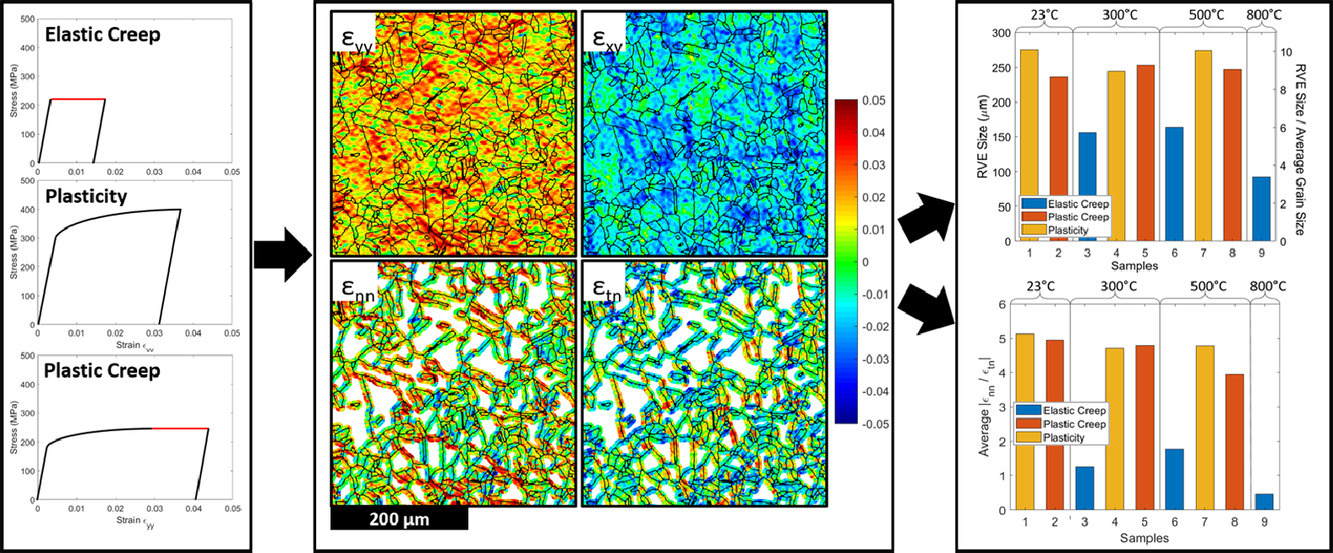
ACTA
Vol. 214,1 Aug. 2021, 117015
6. Role of the local stress systems on microstructural inhomogeneity during semisolid injection
鑄造過程中局部應(yīng)力對微觀組織不均勻性的影響研究
S. Bhagavath, Z. Gong, T. Wigger, S. Shah, B. Ghaffari, M. Li, S. Marathe, P.D. Lee?, S. Karagadde?
P.D. Lee:peter.lee@ucl.ac.uk
S. Karagadde:s.karagadde@iitb.ac.in
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117015
摘要
高壓金屬鑄造是一個冷卻速率和壓強(qiáng)變化很大的動態(tài)過程,這導(dǎo)致在鑄造過程中同一件鑄件的不同部分往往具有不同的固相狀態(tài)和形變特征。工藝參數(shù)及參數(shù)間復(fù)雜的相互作用共同決定了凝固組織中的缺陷。本研究中,我們通過快速同步X射線成像技術(shù)對鋁合金高壓壓鑄過程中,研究了固態(tài)體積分?jǐn)?shù)、加載狀態(tài)和熔體流動對局部組織不均勻性的影響。雖然已有文獻(xiàn)中報(bào)導(dǎo)的原位變形速率可達(dá)10 μm/s,但我們對更快填充和凝固條件下(~100 μm/s)的過程進(jìn)行了研究。結(jié)果表明,當(dāng)固態(tài)體積分?jǐn)?shù)較低時,熔體的變形具有以下兩種典型特征:(1)中間晶粒尺寸較大,近器壁晶粒尺寸較小,(2)由于Cu在液相中的富集導(dǎo)致在固液界面附近發(fā)生重熔。我們對固態(tài)體積分?jǐn)?shù)較大的樣品進(jìn)行了非原位掃描和數(shù)字圖像分析,揭示了基于局部應(yīng)力狀態(tài)、微觀組織和補(bǔ)縮的孔隙形成機(jī)制。我們發(fā)現(xiàn)熔體可以分為具有以下四種不同特征的區(qū)域:(1)塞流區(qū) (2)致密漿料區(qū) (3)剪切區(qū) (4)塊體區(qū)。以上研究對于壓鑄過程中不同區(qū)域缺陷形成的數(shù)值模擬具有指導(dǎo)意義。
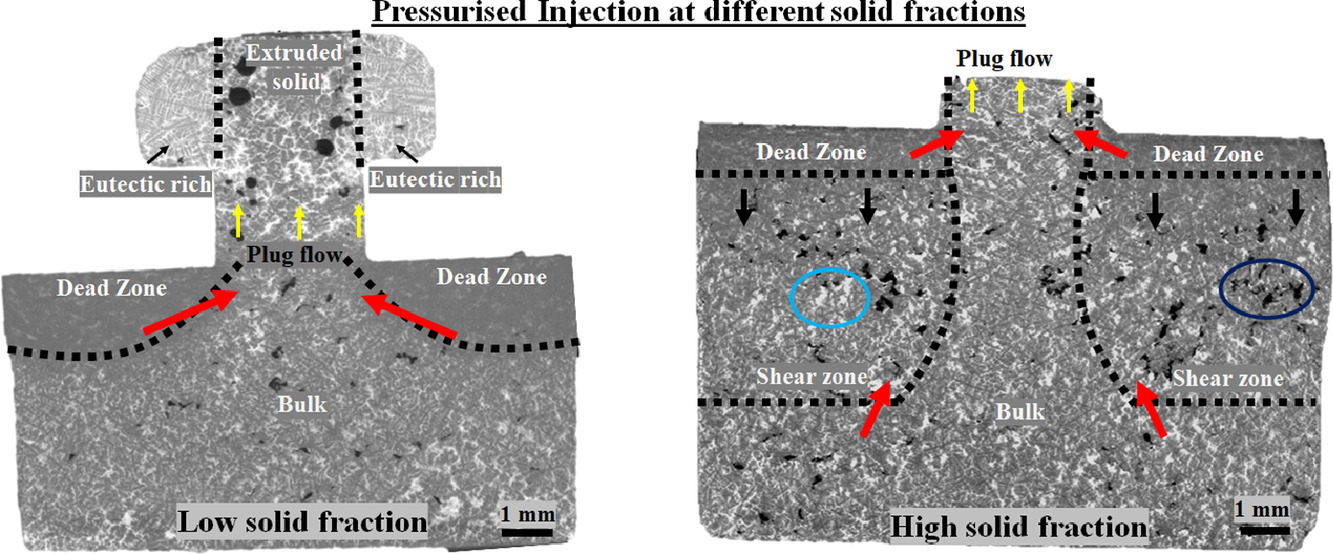
ACTA
Vol. 214,1 Aug. 2021, 116990
7. Segmentation of experimental datasets via convolutional neural networks trained on phase field simulations
利用相場模擬訓(xùn)練的卷積神經(jīng)網(wǎng)絡(luò)實(shí)現(xiàn)對實(shí)驗(yàn)數(shù)據(jù)集的圖像分割
Jiwon Yeom, Tiberiu Stan, Seungbum Hong?, Peter W. Voorhees
S. Hong:seungbum@kaist.ac.kr
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116990
摘要
對大型圖像數(shù)據(jù)集的快速分析能力對于先進(jìn)材料的表征和設(shè)計(jì)至關(guān)重要,而圖像分割是分析過程中最主要和耗時的步驟。卷積神經(jīng)網(wǎng)絡(luò)(CNNs)是一種很有前景的分割方法。然而這一方法的主要難點(diǎn)在于前期需要人工地對數(shù)據(jù)集進(jìn)行分類和標(biāo)記,從而實(shí)現(xiàn)對CNN算法的訓(xùn)練過程。本研究中,我們發(fā)現(xiàn)僅使用簡單的相場模擬對CNN算法進(jìn)行訓(xùn)練,就可能實(shí)現(xiàn)對于實(shí)驗(yàn)數(shù)據(jù)集的圖像分割。我們以Al-Zn合金原位凝固的實(shí)驗(yàn)圖像為例,對相場模擬進(jìn)行了參數(shù)化。以下訓(xùn)練能夠幫助CNN算法有效地捕獲圖像中最重要的組織特征:(1)識別粒子和背景的彌散邊緣 (2)噪聲的優(yōu)化 (3)去除圖像邊緣的粒子 (4) 枝晶上假象的識別。經(jīng)過相場模擬圖像訓(xùn)練的CNN算法對實(shí)驗(yàn)圖像的分割準(zhǔn)確率為99.3%,與直接在實(shí)驗(yàn)數(shù)據(jù)上訓(xùn)練的準(zhǔn)確率相當(dāng)。這種利用計(jì)算機(jī)生成圖像訓(xùn)練算法的方法能夠極快地快速新材料的設(shè)計(jì)研發(fā)。
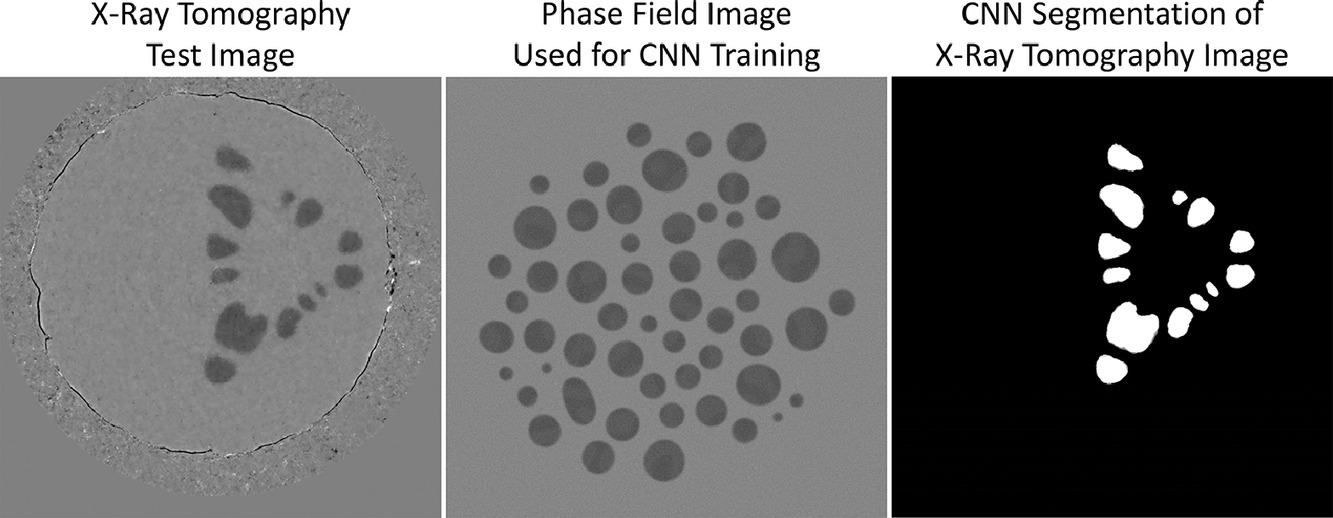
ACTA
Vol. 214,1 Aug. 2021, 117006
8. Studying the micromechanical behaviors of a polycrystalline metal by artificial neural networks
多晶金屬微觀力學(xué)行為的人工神經(jīng)網(wǎng)絡(luò)研究
Wei Dai, Huamiao Wang?, Qiang Guan, Dayong Li, Yinghong Peng, Carlos N. Tomé
H. Wang:wanghm02@sjtu.edu.cn(上海交通大學(xué))
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117006
摘要
盡管基于物理的晶體塑性模型能夠準(zhǔn)確預(yù)測復(fù)雜載荷下的材料力學(xué)響應(yīng),但其較高的計(jì)算成本極大地限制了工程應(yīng)用。另一方面,機(jī)器學(xué)習(xí)技術(shù)目前已被廣泛用于數(shù)據(jù)的分析預(yù)測,且比傳統(tǒng)技術(shù)在計(jì)算效率方面更具優(yōu)勢。本研究中,我們在OFHC銅中根據(jù)物理粘塑性自洽(VPSC)模型得到的數(shù)據(jù)庫基礎(chǔ)上,開發(fā)了人工神經(jīng)網(wǎng)絡(luò)(ANN)模型,并對模型進(jìn)行了訓(xùn)練。結(jié)果表明,ANN模型能夠成功地預(yù)測具有任意織構(gòu)的多晶銅在不同加載路徑下的微觀力學(xué)行為,甚至其泛化能力超出了數(shù)據(jù)集的邊界。ANN模型的精度沒有顯著降低,但計(jì)算效率大幅提升。因此,基于物理模型的人工神經(jīng)網(wǎng)絡(luò)在工程上具有極大的應(yīng)用前景。
ACTA
Vol. 214,1 Aug. 2021, 116986
9. Tailoring the metastable reversed austenite from metastable Mn-rich carbides
通過富錳碳化物調(diào)控亞穩(wěn)逆相變奧氏體
Yuantao Xu, Wei Li?, Hao Du, Huisheng Jiao, Binggang Liu, Yun Wu, Wei Ding, Yi Luo, Yihong Nie, Na Min, Wenqing Liu, Xuejun Jin?
W. Li:weilee@sjtu.edu.cn(上海交通大學(xué))
X. Jin:jin@sjtu.edu.cn(上海交通大學(xué))
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116986
摘要
我們設(shè)計(jì)了兩步回火-配粉工藝,用于調(diào)控冷軋中錳鋼中的碳、錳等奧氏體穩(wěn)定元素。材料經(jīng)450℃回火0.5h和1h后,三維原子探針表征表明,存在大量的亞穩(wěn)態(tài)富錳M12C析出和NiAl納米析出,且大量的碳在NiAl析出附近的界面和位錯上偏聚。M12C碳化物與位錯/界面之間的競爭抑制了亞穩(wěn)態(tài)M12C向更穩(wěn)定碳化物的轉(zhuǎn)變。在隨后630℃,0.5h的配分過程中,亞穩(wěn)M12C溶解,在M12C上形核的細(xì)小奧氏體中呈現(xiàn)出明顯的Mn梯度。亞穩(wěn)態(tài)奧氏體繼承了M12C中的大量錳和碳(Mn: 18.1 at.%, C: 1.56 at.%),且分布彌散(9.8 μm−2)和尺寸細(xì)小(50-200 nm)。由于這些奧氏體兼具硬質(zhì)和可相變的特點(diǎn),因此同時為材料提供了Orowan強(qiáng)化和形變誘導(dǎo)馬氏體相變(TRIP)強(qiáng)化,力學(xué)性能可達(dá)屈服強(qiáng)度~1350 MPa,總延伸率~30%。綜上所述,我們提出了一種有創(chuàng)新性的高強(qiáng)度鋼設(shè)計(jì)策略,使得亞穩(wěn)奧氏體除了TRIP效應(yīng)外,還能夠通過第二相強(qiáng)化材料。
ACTA
Vol. 214,1 Aug. 2021, 117019
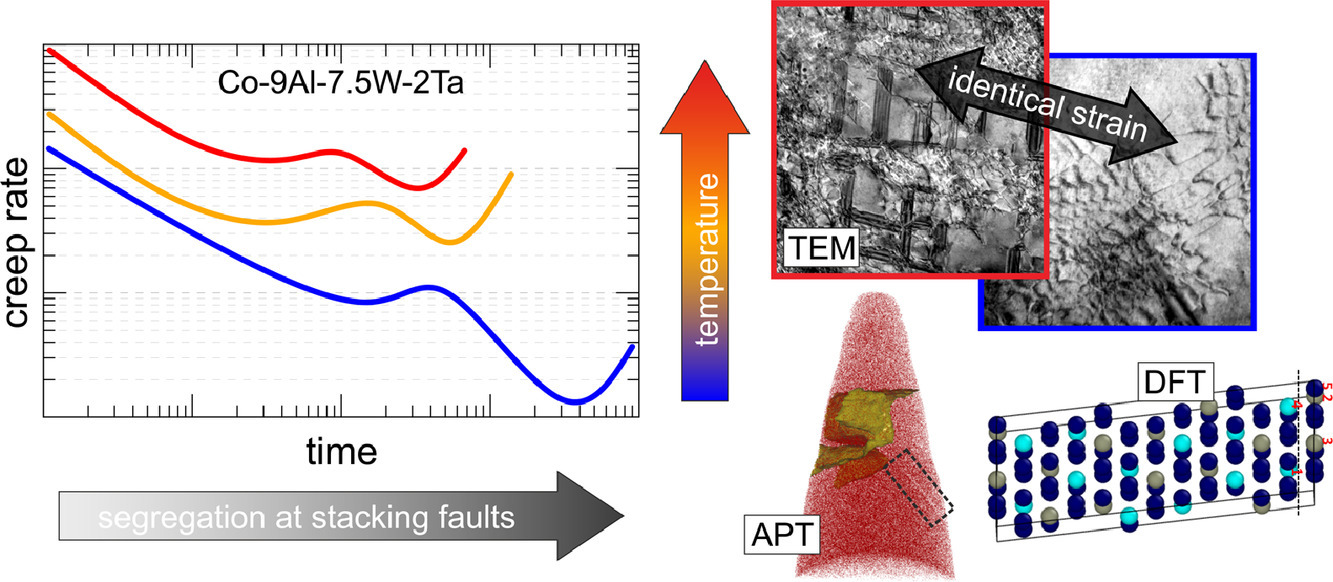
10. Understanding creep of a single-crystalline Co-Al-W-Ta superalloy by studying the deformation mechanism, segregation tendency and stacking fault energy
基于變形機(jī)制、合金元素偏聚和層錯能研究單晶Co-Al-W-Ta高溫合金的蠕變性能
N. Volz?, F. Xue, C.H. Zenk, A. Bezold, S. Gabel, A.P.A. Subramanyam, R. Drautz, T. Hammerschmidt, S.K. Makineni, B. Gault, M. Göken, S. Neumeier
N. Volz:nicklas.volz@fau.de
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117019
摘要
我們對Co-9Al-7.5W-2Ta單晶鈷基高溫合金在950、975和1000℃下的壓縮蠕變性能進(jìn)行了系統(tǒng),揭示了溫度和Al、W和Ta等元素?cái)U(kuò)散速度對變形機(jī)制的影響。在所有的溫度條件下,均能觀測到兩個蠕變率最小值,因此這種現(xiàn)象的變形機(jī)制應(yīng)當(dāng)是相似的。原子探針分析表明,蠕變過程中,γ′相中形成的層錯處存在溶質(zhì)元素偏析。密度泛函理論計(jì)算表明,W和Ta有向?qū)渝e偏聚的趨勢,且能顯著降低層錯能。高溫下元素?cái)U(kuò)散加快,因此偏聚也加快。這使得合金的軟化顯著加快,因?yàn)槠勰軌蛟谌渥冊缙诖龠M(jìn)分位錯切過γ′析出。透射電子顯微鏡表征證實(shí)了上述機(jī)制。因此,高溫下析出體積分?jǐn)?shù)的減小和擴(kuò)散對分位錯剪切γ′相的促進(jìn)作用共同導(dǎo)致了材料蠕變性能的劣化。以上研究對高溫合金設(shè)計(jì)具有指導(dǎo)意義。